The global toroidal magnetic field component market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand in energy, medical imaging, and advanced research applications. According to Grand View Research, the global superconducting magnets market—which includes toroidal systems—was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increased investments in nuclear fusion research, expansion of MRI technology, and advancements in particle accelerators. Toroidal magnetic configurations, known for their efficiency in confining plasma and minimizing magnetic flux leakage, are particularly critical in experimental fusion reactors like ITER and high-performance medical and industrial equipment. As innovation accelerates and global energy demands evolve, manufacturers specializing in precision-engineered toroidal magnetic solutions are well-positioned to lead in this high-tech space. The following list highlights the top 10 manufacturers shaping this dynamic industry.
Top 10 Toroidal Magnetic Field Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Magnetics
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mag-inc.com
Key Highlights: Magnetics® toroids are available in many sizes (outside diameters ranging from 2mm to 140mm) and materials (permeabilities ranging from 750µ to 15,000µ)….
#2 TDK Corporation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tdk.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to TDK corporate website. TDK is the world’s leading electronic components and devices company that has the high magnetics technology….
#3 Toroidal Coil Suppliers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: electriccoils.net
Key Highlights: Toroidal inductors are passive electrical components that store energy in a magnetic field and resist changes in a current as electricity passes through it….
#4 Manufacturing and installation of ITER toroidal field coils
Domain Est. 2022
Website: cnim-groupe.com
Key Highlights: CNIM Industrial Systems has been involved in the manufacturing and installation of these 320 tons magnets through F4E, the EU organisation ……
#5 Magnets
Domain Est. 1997
Website: iter.org
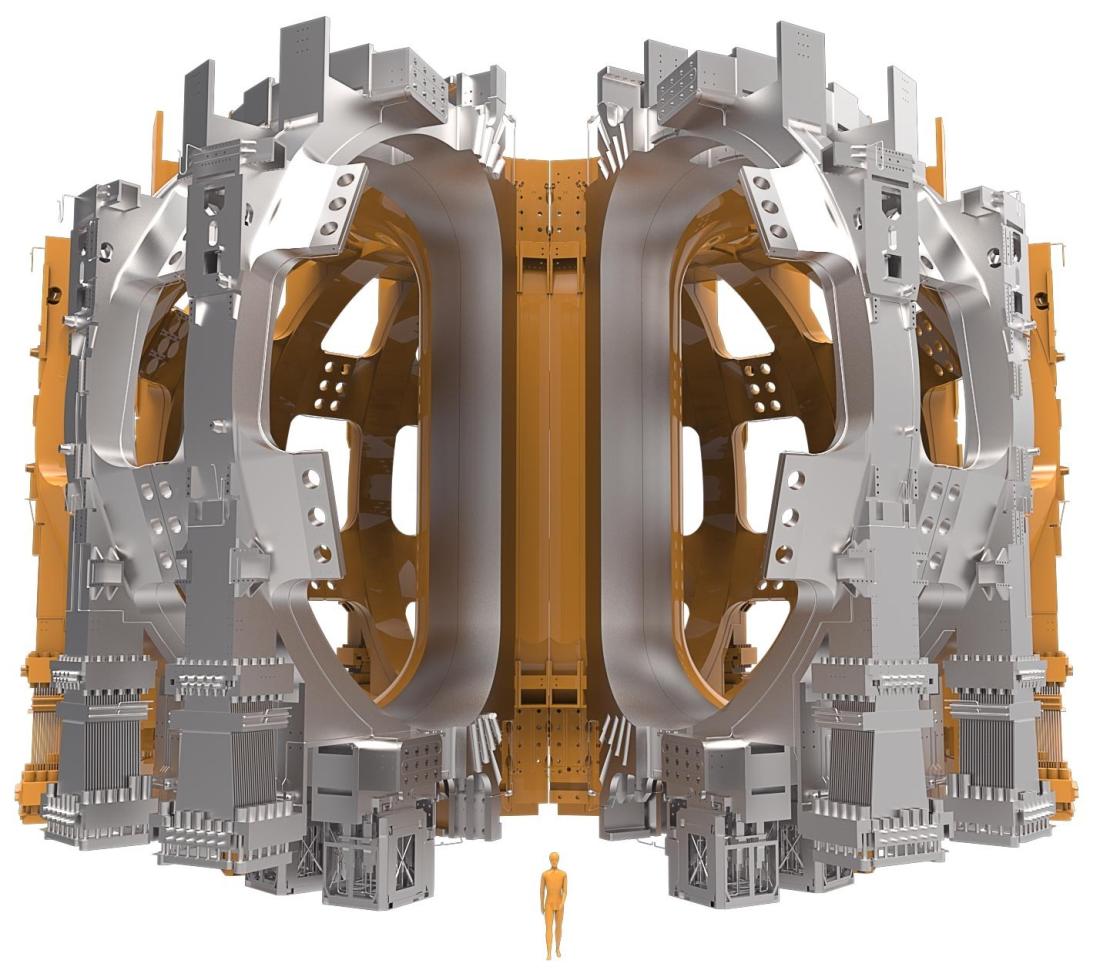
Key Highlights: The toroidal field coils are designed to produce a total magnetic energy of 41 gigajoules and a maximum magnetic field of 11.8 tesla. Weighing 330 tonnes each, ……
#6 SM Magnetics Toroid Design Achieves Self
Domain Est. 2014
Website: smmagnetics.com
Key Highlights: SM Magnetics was engaged to produce a unique toroid magnet with a self-contained and homogenous field….
#7 The contract for the supply of the Toroidal field coils awarded
Domain Est. 2019
Website: dtt-project.it
Key Highlights: The tender for the supply of the 18 modules of the toroidal magnetic field of DTT was launched in December 2020, the starting price of which was set to 35 ……
#8 Superconducting magnets for ITER
Domain Est. 2022
Website: cnim-systemes-industriels.com
Key Highlights: Six PF Coils in total will be positioned outside the toroidal magnetic structure: 2 are manufactured by Chinese and Russian companies, the 4 central magnets, ……
#9 Europe and Japan celebrate completion of ITER Toroidal Field coils
Website: fusionforenergy.europa.eu
Key Highlights: Fusion for Energy and QST Japan produced 19 toroidal field magnets to confine the super-hot plasma in ITER….
#10 Toroidal Inductor Manufacturers Suppliers
Domain Est. 2004
Website: iqsdirectory.com
Key Highlights: IQS Directory implements a thorough list of toroidal inductors manufacturers and suppliers. Utilize our listing to examine and sort top toroidal inductors ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Toroidal Magnetic Field
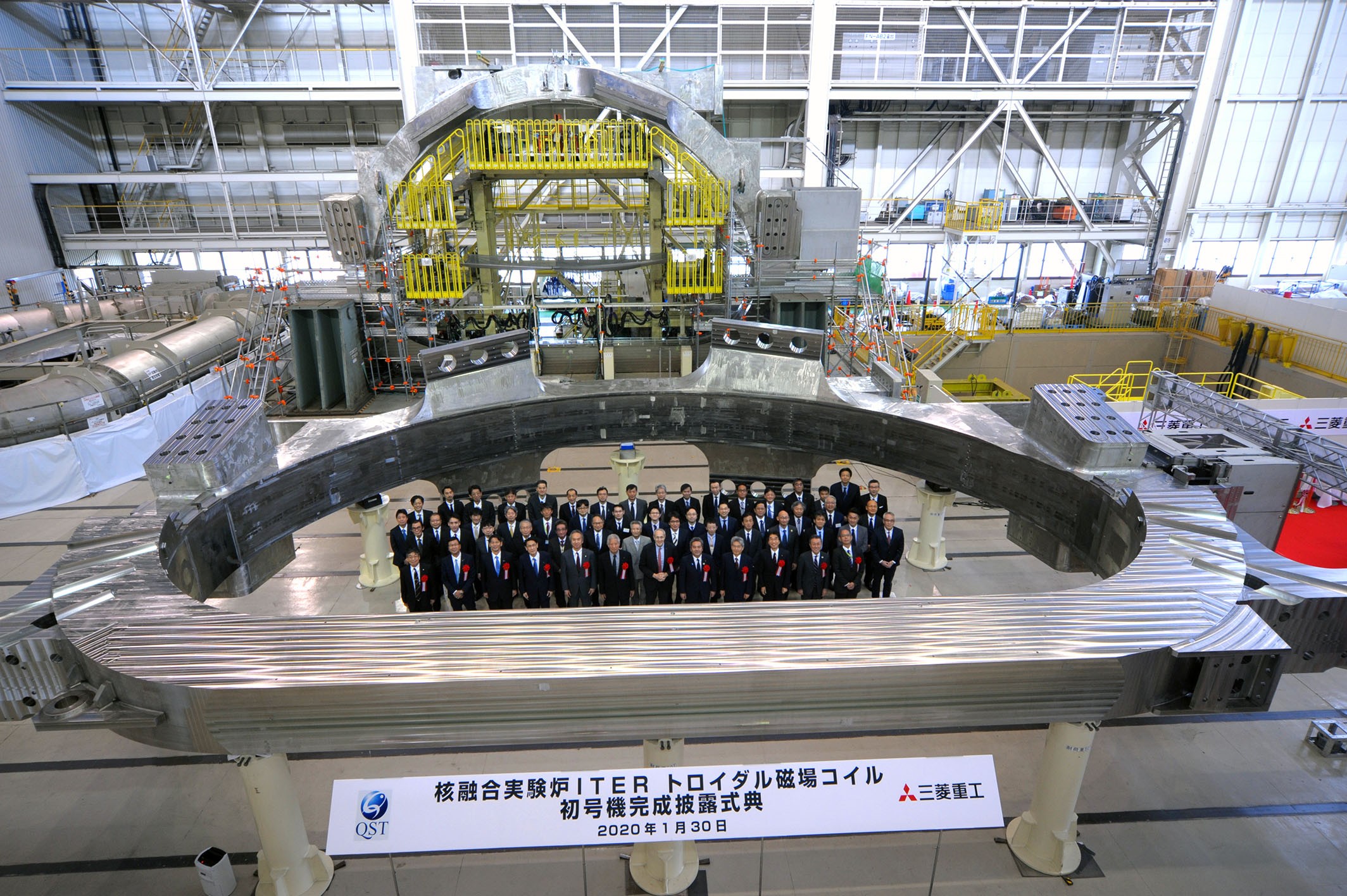

2026 Market Trends for Toroidal Magnetic Field Technology
The market for toroidal magnetic field technology is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven primarily by advancements in nuclear fusion energy, growing demand for high-efficiency power electronics, and emerging applications in scientific research and medical devices. This analysis examines key trends shaping the sector.
Accelerated Fusion Energy Development Driving Demand
The most transformative trend influencing the toroidal magnetic field market by 2026 is the rapid progress in nuclear fusion research, particularly tokamak and stellarator designs. Major projects like ITER, SPARC, and private ventures (e.g., Commonwealth Fusion Systems, Tokamak Energy) are advancing rapidly, with several aiming for net energy gain demonstrations by or shortly after 2026. This has led to increased investment in high-performance superconducting toroidal field (TF) coils. Demand is shifting toward high-temperature superconductors (HTS), such as REBCO tapes, which enable stronger magnetic fields (up to 20 Tesla) in more compact reactor designs. As a result, the market for HTS-based toroidal magnets is expected to grow exponentially, with supply chains expanding to meet fusion’s stringent requirements for reliability, cryogenic performance, and scalability.
Expansion in Power Electronics and Energy Storage
Beyond fusion, toroidal magnetic components—especially inductors and transformers—are seeing increased adoption in high-efficiency power conversion systems. The global push for energy efficiency and electrification is fueling demand for compact, low-loss power supplies in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy inverters, and data centers. Toroidal cores, made from advanced nanocrystalline or ferrite materials, offer superior electromagnetic performance compared to traditional laminated cores. By 2026, the integration of toroidal magnetics in solid-state transformers and next-generation DC-DC converters is expected to rise, driven by miniaturization trends and the need for higher power densities in consumer and industrial electronics.
Growth in Scientific and Medical Applications
Scientific research facilities and advanced medical technologies are expanding the use of toroidal magnetic fields. In particle physics, upgrades to accelerators and detectors require precision magnetic field shaping, where toroidal configurations provide unique advantages in beam control. In medicine, toroidal fields are being explored in novel MRI techniques and targeted cancer therapies using magnetic nanoparticles. While niche, these applications are expected to contribute to market diversification, with specialized manufacturers developing custom low-field and high-homogeneity toroidal systems tailored to biomedical and analytical instrumentation needs.
Supply Chain and Material Innovation
A critical trend by 2026 is the maturation of supply chains for high-performance magnetic materials. The scarcity and cost of rare-earth elements used in permanent magnets and certain superconductors are prompting research into alternatives and recycling methods. Concurrently, additive manufacturing (3D printing) of magnetic components is emerging as a way to produce complex toroidal geometries with reduced material waste. These innovations are expected to lower production costs and increase design flexibility, making toroidal magnetic systems more accessible across industries.
Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are influencing design choices. Energy-efficient toroidal transformers are favored in green building standards and low-carbon product certifications. In fusion, regulatory frameworks for nuclear safety and waste management are shaping magnet design requirements, emphasizing longevity and minimal activation materials. Companies are increasingly adopting lifecycle assessments for magnetic components, aligning with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria that investors and governments prioritize by 2026.
In conclusion, the 2026 toroidal magnetic field market will be defined by fusion energy breakthroughs, rising efficiency demands in power systems, and technological innovation in materials and manufacturing. Stakeholders who invest in HTS technology, sustainable production, and cross-industry applications are likely to lead this dynamic and expanding market.
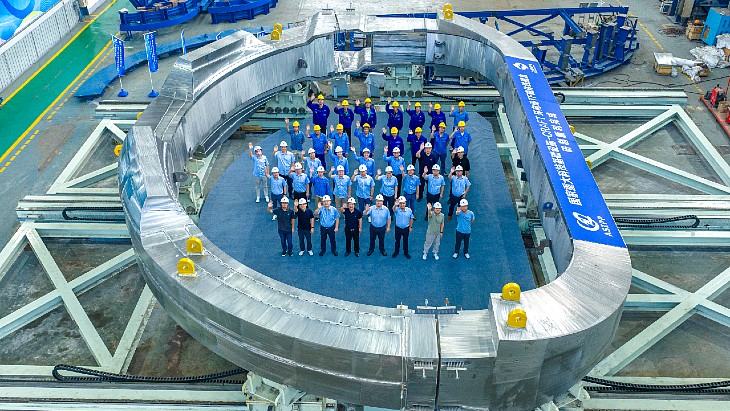

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Toroidal Magnetic Fields (Quality, IP)
Sourcing toroidal magnetic field components or systems—particularly for high-performance applications like fusion reactors, advanced sensors, or specialized research equipment—can present significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to project delays, compromised performance, or legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Verification and Specifications
Many suppliers offer toroidal magnetic field solutions with broad or vague performance claims. Without rigorous quality controls and clear specifications, buyers risk receiving components that fail under operational conditions. Common issues include inconsistent winding uniformity, substandard core materials, or poor thermal management—all of which degrade magnetic field homogeneity and efficiency. Always demand detailed test reports, material certifications, and validation under simulated operating environments.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
High-integrity applications require full traceability of materials and manufacturing processes. A frequent pitfall is sourcing from vendors who do not maintain comprehensive documentation—such as lot numbers, process validation data, or quality inspections. This absence undermines reliability assessments and can violate regulatory or project-specific compliance standards (e.g., in aerospace or nuclear sectors).
IP Infringement and Unprotected Design Sharing
Disclosing sensitive design requirements during the sourcing process can expose your organization to IP risks. Some suppliers may use shared specifications to develop competing products or inadvertently incorporate patented technologies into their offerings. Always establish non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) before technical discussions and verify that the supplier does not infringe on third-party patents—especially in magnet design, winding techniques, or cooling systems.
Ambiguous Ownership of Customized Solutions
When commissioning custom toroidal field components, the ownership of design improvements or tooling can become a legal gray area. Suppliers may claim partial IP rights over enhancements made during development unless explicitly addressed in the contract. Ensure procurement agreements clearly define IP ownership, including rights to modifications, derivative works, and future manufacturing.
Overlooking Export Controls and Compliance
Toroidal magnetic systems—especially those used in fusion or defense-related research—may be subject to export control regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Sourcing from international suppliers without verifying compliance can lead to legal penalties and shipment delays. Confirm that both your organization and the supplier adhere to relevant regulatory frameworks before finalizing agreements.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legally sound procurement of toroidal magnetic field technologies.
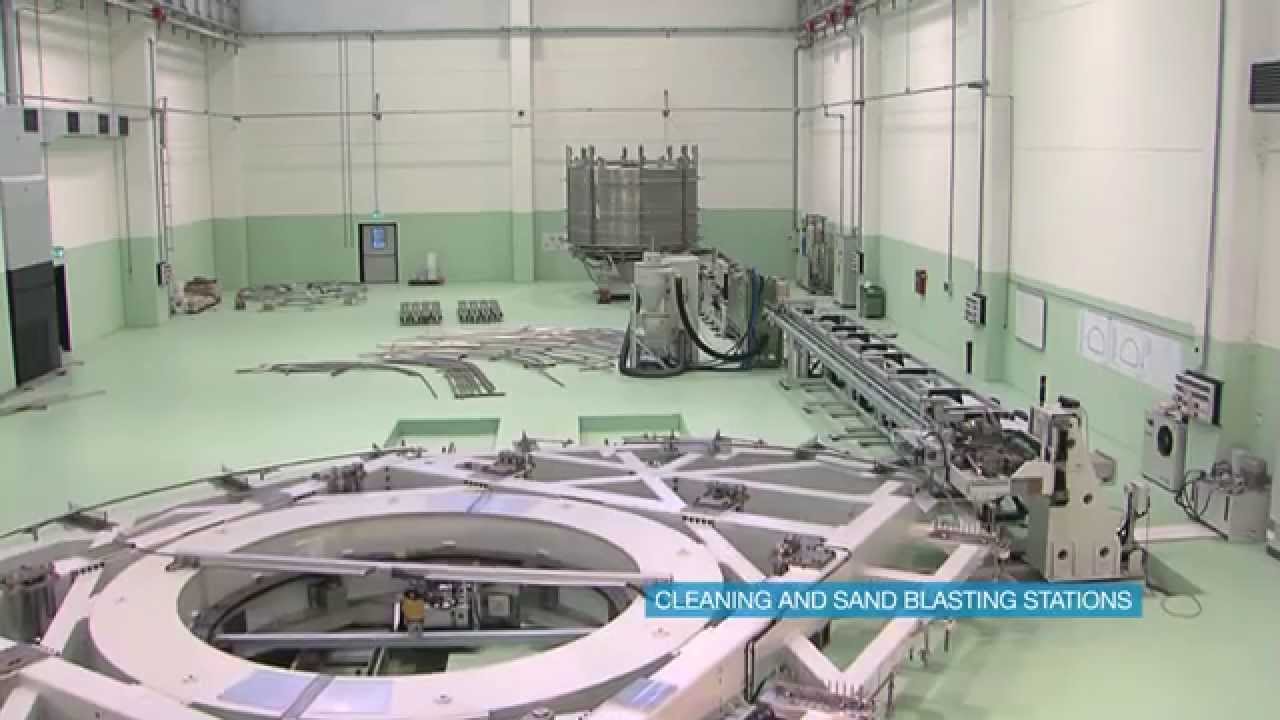

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Toroidal Magnetic Field Devices
Overview
Toroidal Magnetic Field (TMF) devices, commonly used in fusion research, magnetic confinement systems, and advanced industrial applications, require strict logistics planning and regulatory compliance due to their powerful magnetic fields, high energy use, and specialized components. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe and compliant handling, transport, installation, and operation of TMF systems.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
TMF devices must comply with international standards such as:
– IEC 60480: Guidelines for the use and handling of sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) in high-voltage equipment (if applicable).
– IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use.
– ISO 14001: Environmental management systems for minimizing ecological impact during operation and decommissioning.
National and Regional Regulations
- United States: Compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and FDA regulations (if used in medical applications), including electromagnetic field (EMF) exposure limits per IEEE C95.1.
- European Union: Adherence to the EMF Directive 2013/35/EU for worker protection, RoHS for hazardous substance restrictions, and REACH for chemical safety.
- China: GB standards for electromagnetic compatibility (GB/T 18268) and safety of electrical equipment (GB 4793.1).
Radiation and Magnetic Field Safety
- Magnetic fields exceeding 0.5 mT must be assessed for human exposure risks.
- Implement controlled access zones and warning signage per IARC and ICNIRP guidelines.
- Conduct regular EMF monitoring using calibrated gaussmeters.
Transportation and Handling
Packaging and Labeling
- Use non-magnetic, shock-resistant packaging with internal bracing to prevent coil deformation.
- Label packages with:
- “Strong Magnetic Field – Keep Away from Pacemakers and Magnetic Media”
- “Fragile – Handle with Care”
- Proper UN number if transporting energized superconducting components (e.g., UN3171 for battery-powered devices).
Transport Mode Considerations
- Air: Magnetic field strength must be below 0.418 A/m (0.00525 Gauss) at 2.1 meters for air transport (ICAO TI and IATA DGR). Full demagnetization or special permits may be required.
- Sea and Ground: Follow IMDG Code (sea) or ADR/RID (Europe, ground), including secure stowage to prevent shifting.
Pre-shipment Requirements
- Provide a Magnetic Field Measurement Certificate confirming field strength at specified distances.
- Submit a Dangerous Goods Declaration if magnetic field exceeds transport limits.
- De-energize superconducting components and ensure cryogenic systems are fully purged.
Installation and Site Preparation
Facility Requirements
- Ensure structural integrity to support heavy components (toroidal coils may weigh several tons).
- Install magnetic shielding (e.g., mu-metal enclosures) if necessary to protect nearby equipment.
- Provide adequate ventilation, especially if SF₆ or cryogenic coolants are used.
Electrical and Safety Systems
- Install dedicated high-capacity power feeds with surge protection and grounding per IEEE 142.
- Integrate emergency shutdown systems (E-Stop), quench protection for superconductors, and interlocks.
- Equip facilities with fire suppression systems suitable for electrical and cryogenic hazards (e.g., clean agent systems).
Operational Compliance
Personnel Training
- Train operators in:
- Magnetic field hazards and safe distances
- Cryogenic safety (if using liquid helium or nitrogen)
- Emergency response procedures
- Maintain certification records per OSHA 29 CFR 1910 or equivalent.
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Perform regular inspections of coils, insulation, and cooling systems.
- Record magnetic field levels, cryogenic pressures, and electrical parameters.
- Follow a preventive maintenance schedule aligned with ISO 55000 (asset management).
Decommissioning and Disposal
Component Recycling
- Recycle copper and superconducting materials via certified e-waste handlers.
- Recover and reprocess SF₆ gas in accordance with EPA or EU F-Gas regulations.
Environmental Compliance
- Dispose of insulating oils, coolants, and contaminated materials as hazardous waste.
- Document all disposal activities for audit purposes under ISO 14001.
Documentation and Auditing
Required Records
- Risk assessments (including EMF exposure)
- Transport documentation (e.g., magnetic field reports, dangerous goods forms)
- Maintenance logs and inspection records
- Training certifications
Audit Preparedness
- Conduct internal audits annually to verify compliance with all applicable standards.
- Maintain a compliance management system (CMS) for real-time tracking of regulatory changes.
Conclusion
Safe and compliant logistics for Toroidal Magnetic Field devices require a multidisciplinary approach involving engineering, safety, and regulatory expertise. Adherence to international standards, proper handling procedures, and thorough documentation ensures operational safety and legal compliance throughout the device lifecycle.
Conclusion on Sourcing the Toroidal Magnetic Field:
The generation and sustainment of a toroidal magnetic field, particularly in systems such as tokamaks and stellarators used in nuclear fusion research, rely primarily on electromagnetic induction and controlled current drive mechanisms. In tokamaks, the toroidal field is typically produced by external toroidal field coils encircling the plasma vessel, while the poloidal field arises from a current driven within the plasma itself—often via transformer action or auxiliary methods like neutral beam injection and radiofrequency heating. This combination results in a helical total magnetic field essential for confining high-temperature plasma in a toroidal geometry.
Advanced techniques such as non-inductive current drive are critical for achieving steady-state operation, reducing reliance on inductive methods limited by transformer flux constraints. In stellarators, the toroidal magnetic field is similarly generated by external modular coils, but the necessary rotational transform is engineered directly into the coil geometry, eliminating the need for a large plasma current.
Ultimately, the effective sourcing of a toroidal magnetic field is a cornerstone of magnetic confinement fusion, requiring precise engineering, stability control, and integration with auxiliary systems to maintain plasma equilibrium, stability, and confinement. Continued advancements in superconducting magnet technology and plasma current control are vital for realizing practical and sustainable fusion energy.