The global demand for toroidal coils has seen steady growth, driven by increasing adoption in power electronics, medical devices, renewable energy systems, and industrial automation. According to Grand View Research, the global transformer market—of which toroidal coils are a critical component—was valued at USD 53.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence supports this trajectory, projecting a CAGR of approximately 6.8% for the transformer market through 2028, citing rising investments in energy efficiency and compact power solutions. As industries prioritize space-saving designs, low electromagnetic interference, and high-efficiency performance, toroidal coil manufacturers are gaining strategic importance in the electronics supply chain. Innovation in materials, manufacturing processes, and customization capabilities has become central to competitiveness. The following list highlights the top 10 toroidal coil manufacturers leading this growth, recognized for product quality, technological expertise, global reach, and customer-driven innovation.
Top 10 Toroidal Coil Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Toroids
Domain Est. 2009
Website: amgistoroids.com
Key Highlights: Select from our high-efficiency toroidal transformers and current sensors for industrial and medical applications….
#2 Coilcraft: Magnetic Components Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1995
Website: coilcraft.com
Key Highlights: Coilcraft is a global magnetic components manufacturer specializing in inductors and transformers – proudly serving a number of industries….
#3 Custom Toroid Coils for Aerospace & More
Domain Est. 1996
Website: qualitycoils.com
Key Highlights: We work with copper wire in different wire gauges to create custom toroid coils, transformers and other coils based on your specifications….
#4 Toroidal Coil Suppliers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: electriccoils.net
Key Highlights: Connect with the leading toroidal coil suppliers in the country who can fulfill any sized order and ship their products quickly at affordable prices….
#5 Gowanda Electronics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gowanda.com
Key Highlights: Gowanda Electronics: Precision-engineered electronic components & inductors for demanding applications. Quality solutions for critical designs….
#6 Toroidal Custom Transformers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: toroid.com
Key Highlights: Standard Toroidal Transformers We offer the industry’s largest selection of standard designed toroidal transformers with dual primaries and dual secondaries….
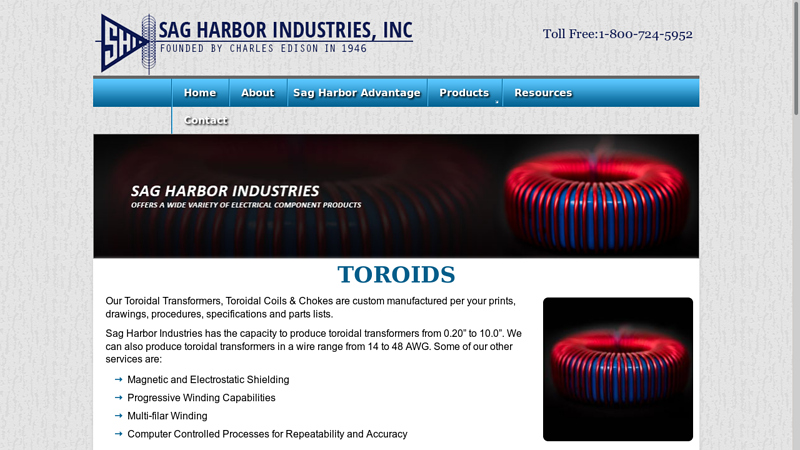
#7 Toroidal Coils
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sagharborind.com
Key Highlights: Sag Harbor Industries manufactures high-quality toroidal transformers with multi-filar windings, available in wire sizes ranging from 14 to 48 AWG….
#8 Toroids
Domain Est. 1999
Website: torelco.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in providing custom toroid and bobbin transformers that are built to the exact specs of drawings provided to us….
#9 Customer
Domain Est. 2010
Website: kukcoils.com
Key Highlights: KUK manufactures customer-specific toroidal core coils with an inner diameter from 3 mm. Toroidal coils are used by our customers for various applications….
#10 Winding Machines
Domain Est. 2014
Website: joviluniversal.com
Key Highlights: Our Toroidal winding machines are easy to operate and handle. They are micro-processor controlled and programmed with runtime software that makes your work ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Toroidal Coil
2026 Market Trends for Toroidal Coil
The toroidal coil market is poised for substantial evolution by 2026, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for energy efficiency, and expanding applications across various industries. This analysis explores key trends shaping the toroidal coil landscape in the coming years.
Rising Demand in Power Electronics and Renewable Energy
A major driver of growth in the toroidal coil market by 2026 is the expanding adoption of power electronics in renewable energy systems such as solar inverters, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions. Toroidal coils are preferred in these applications due to their high efficiency, compact size, and low electromagnetic interference (EMI). As global investments in clean energy infrastructure accelerate, particularly under national decarbonization goals, the need for reliable and efficient magnetic components will surge. This trend is expected to boost toroidal coil demand significantly in power conversion and conditioning equipment.
Growth in Electric Vehicles and Automotive Electronics
The automotive sector, especially electric vehicles (EVs), will play a pivotal role in shaping the 2026 toroidal coil market. Toroidal inductors and transformers are increasingly used in EV onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, and motor control units due to their superior thermal performance and space-saving design. With the global EV market projected to expand rapidly through 2026, supported by government incentives and stricter emission regulations, demand for high-performance toroidal coils will follow suit. Additionally, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and vehicle electrification trends will further stimulate market growth.
Miniaturization and High-Frequency Applications
As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, there is a growing emphasis on component miniaturization and performance at higher frequencies. Toroidal coils offer excellent performance in high-frequency switching power supplies, making them ideal for use in consumer electronics, telecommunications, and industrial automation equipment. By 2026, advancements in core materials—such as nanocrystalline and advanced ferrites—will enable toroidal coils to operate efficiently at higher frequencies with reduced core losses. This innovation will support their integration into next-generation compact and high-efficiency power systems.
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The global push toward Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing is increasing the deployment of automated systems, robotics, and process control equipment—all of which rely on stable and efficient power supplies. Toroidal coils are integral to power supplies, servo drives, and power quality management systems used in industrial settings. Their low EMI and high reliability make them well-suited for noise-sensitive environments. As factories modernize and adopt IoT-enabled systems, the demand for toroidal coils in industrial power solutions is expected to rise steadily by 2026.
Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Shifts
Asia-Pacific, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, will remain a dominant region in both production and consumption of toroidal coils by 2026. The region’s robust electronics manufacturing ecosystem, coupled with strong government support for renewable energy and electric mobility, positions it as a key growth hub. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are witnessing increased localization of supply chains due to geopolitical concerns and sustainability mandates. This shift may lead to higher investments in domestic manufacturing of magnetic components, including toroidal coils, particularly for strategic sectors like defense, aerospace, and healthcare.
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing material choices in the toroidal coil market. By 2026, there will be a greater focus on recyclable core materials, lead-free winding techniques, and energy-efficient production processes. Manufacturers are investing in eco-design principles to reduce the environmental footprint of magnetic components. Additionally, research into alternative core materials—such as amorphous metals and composite alloys—aims to improve performance while reducing reliance on rare-earth elements.
Competitive Landscape and Technological Differentiation
The toroidal coil market is expected to become increasingly competitive by 2026, with key players focusing on product differentiation through customization, improved thermal management, and enhanced reliability. Companies that offer application-specific designs—such as coils tailored for medical devices, aerospace systems, or high-reliability industrial applications—will gain a competitive edge. Strategic partnerships with OEMs and participation in standardization initiatives will also be critical for market leadership.
In conclusion, the 2026 toroidal coil market will be shaped by technological innovation, energy transition efforts, and evolving industrial needs. Stakeholders who align with these trends—particularly in renewable energy, electric mobility, and smart manufacturing—will be well-positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Toroidal Coils (Quality, IP)
Sourcing toroidal coils—especially for demanding applications—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance issues, supply chain disruptions, and legal risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Assurance Processes
Many suppliers, particularly lower-cost manufacturers, may lack robust quality control systems. This can result in inconsistent core material properties, winding imperfections, or poor insulation. Always verify that the supplier adheres to international standards (e.g., ISO 9001) and performs rigorous testing such as hipot (high-potential) testing, inductance tolerance checks, and thermal cycling.
Poor Material Selection and Verification
The performance of a toroidal coil heavily depends on core material (e.g., ferrite, powdered iron, nanocrystalline) and wire insulation class. Some suppliers may substitute lower-grade materials to cut costs without disclosure. Ensure material specifications are clearly documented and validated through third-party testing or material certifications (e.g., UL, RoHS).
Inaccurate or Incomplete Specifications
Ambiguous or incomplete datasheets—such as unspecified tolerances, missing thermal derating curves, or unclear mounting requirements—can lead to integration issues. Always request full performance data, including frequency response, core loss graphs, and mechanical drawings, before finalizing a supplier.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Without proper batch traceability and test reports, diagnosing field failures becomes difficult. Reputable suppliers should provide certificates of conformance (CoC), lot traceability, and detailed test records. This is especially critical in regulated industries like medical or aerospace.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing from regions with weak IP enforcement can expose your design to unauthorized replication. Using custom-wound or proprietary toroidal coils without proper legal safeguards (e.g., NDAs, IP assignment clauses) may result in cloned components entering the market. Always establish clear IP ownership in contracts and consider working with trusted, legally compliant partners.
Overreliance on “Copy Exactly” Without Validation
Mimicking an existing coil design from a competitor or obsolete part without thorough electrical and thermal validation can lead to reliability issues. Even minor deviations in winding technique or core gap can significantly affect performance. Always prototype and test under real operating conditions.
Supply Chain Vulnerability
Toroidal coils, especially custom variants, may have long lead times or depend on single-source components. Failing to assess supplier financial stability, geographic risk, and alternative sourcing options can disrupt production. Diversify suppliers where possible and consider dual-sourcing strategies.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable, high-performance toroidal coils while protecting their intellectual property and supply chain integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Toroidal Coil
Overview
Toroidal coils, widely used in power supplies, transformers, and electronic filtering applications, require careful handling, packaging, and adherence to regulatory standards throughout the logistics chain. This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements to ensure safe, efficient, and lawful transportation and distribution.
Packaging Requirements
Toroidal coils must be protected against mechanical shock, moisture, and electrostatic discharge. Use anti-static bags for sensitive models, and cushion coils within rigid corrugated boxes to prevent deformation of windings. Clearly label packages with “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators. Group coils by size and current rating to prevent internal movement during transit.
Storage Conditions
Store toroidal coils in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–30°C, RH < 60%). Avoid exposure to corrosive gases, dust, and direct sunlight. Keep coils elevated off the floor on pallets to prevent moisture absorption. Rotate stock using the First-In, First-Out (FIFO) method to maintain component integrity.
Transportation Guidelines
Use only certified carriers compliant with ISO and IATA standards for electronic components. For international shipments, ensure compliance with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) agreed upon with the buyer. Avoid extreme temperature fluctuations during air or ground transport—consider climate-controlled vehicles for long-haul or cross-border deliveries.
Regulatory Compliance
Toroidal coils may fall under various regulatory frameworks depending on application and destination. Key compliance areas include:
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) – Ensure lead, mercury, and other restricted substances are below threshold limits in the EU and other adopting regions.
– REACH – Declare Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) in the EU supply chain.
– CE Marking – Required for coils sold in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental standards.
– UL/CSA Certification – Mandatory for coils used in North American electrical systems; verify listing under UL 5085 or CSA C22.2 No. 66.
– IEC Standards – Follow IEC 61558 for safety of power transformers, including toroidal types.
Export Controls
Check if toroidal coils are subject to export regulations such as:
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations, U.S.) – Verify ECCN (Export Control Classification Number); most standard coils are EAR99, but high-frequency or military-grade variants may require licenses.
– Customs Documentation – Prepare accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and a Certificate of Origin. Include technical specifications (inductance, current rating, core material) to facilitate customs clearance.
Labeling and Traceability
Each coil or batch must have a permanent label including:
– Manufacturer name and part number
– Electrical specifications (e.g., 500µH, 10A)
– Date of manufacture and batch/lot code
– Compliance marks (e.g., CE, RoHS)
Maintain traceability records for at least five years to support quality audits or recalls.
Handling and Safety
Train personnel in ESD-safe handling procedures. Use grounded workstations and wrist straps when unpacking or inspecting coils. Avoid dropping or compressing the coil, as this can damage windings or core integrity. For large industrial coils, use mechanical lifting aids to prevent injury.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Dispose of defective or obsolete toroidal coils in accordance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers. Do not incinerate, as components may release harmful fumes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management ensure toroidal coils reach customers in optimal condition while meeting global regulatory demands. Regular audits, staff training, and documentation control are essential for maintaining supply chain integrity and regulatory adherence.
Conclusion for Sourcing Toroidal Coils
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and lead times, sourcing toroidal coils from qualified manufacturers presents a reliable and efficient solution for our application needs. Toroidal coils offer significant advantages, including high inductance with minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI), compact size, and improved energy efficiency—making them ideal for sensitive electronic and power systems.
Based on comparative analysis, partnering with suppliers who demonstrate proven quality assurance (e.g., ISO certification), consistent adherence to custom design requirements, and competitive pricing ensures long-term supply stability and product performance. Additionally, prioritizing suppliers with flexible production capacity and strong technical support will enable scalability and prompt resolution of any design or manufacturing challenges.
In conclusion, proceeding with the selected vendors—balancing cost, quality, and delivery—will support project timelines and performance goals. Continuous monitoring of supply chain performance and maintaining strategic inventory levels will further mitigate risks and ensure uninterrupted production.