The global market for natural and herbal healthcare products has experienced robust growth in recent years, driven by rising consumer preference for plant-based remedies and increasing scientific validation of traditional medicine. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global herbal supplements market was valued at approximately USD 120.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.8% through 2029. Within this expanding sector, interest in specialized botanical extracts—such as those derived from the toothache plant (Acmella oleracea)—has gained momentum due to their traditional use in dental pain relief and emerging applications in natural oral care formulations. With growing demand for sustainable, effective, and non-pharmaceutical analgesics, manufacturers capable of standardizing and scaling production of potent Acmella oleracea extracts are positioning themselves at the forefront of the niche nutraceutical and cosmeceutical markets. This report highlights the top seven manufacturers leading innovation and supply in the toothache plant extract space.
Top 7 Toothache Plant Extract Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 China Acmella Flower Extract Suppliers, Manufacturers, Factory
Domain Est. 2016
Website: biowayorganicinc.com
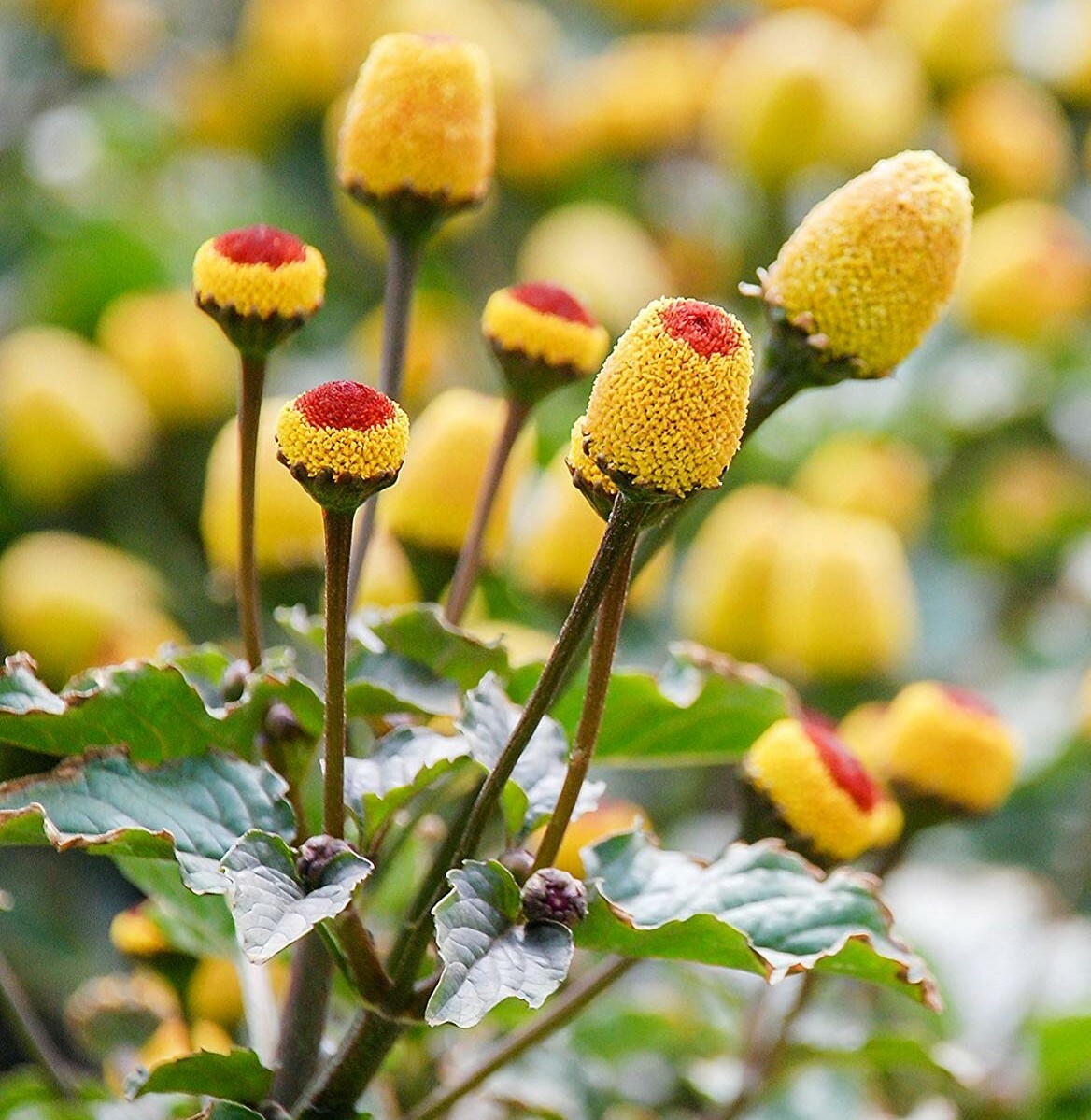
Key Highlights: The plant is traditionally known as the toothache plant and has been coveted for its numbing effect on toothaches, swelling, gum infections, and mouthwashes….
#2 Spilanthes (Acmella oleracea) Tincture, Organic Dried …
Domain Est. 2008
Website: herbalterra.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 (3) As a trusted Florida-based manufacturer, AMPEXT specializes in crafting pure, potent extracts and oils. Whether you’re seeking immune support or natural ….
#3 Spilanthes
Domain Est. 2000
Website: stfrancisherbfarm.com
Key Highlights: In modern herbal medicine, Spilanthes is used to support oral health, enhance immune function, and combat microbial infections. It is also being explored for ……
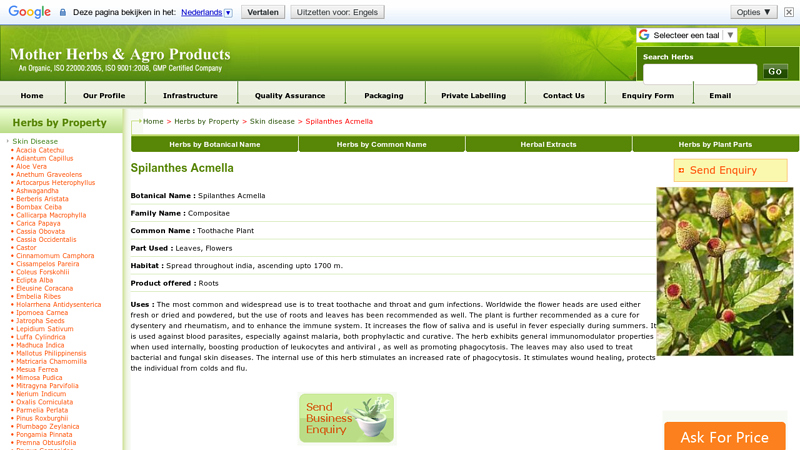
#4 Spilanthes Acmella . Trader
Domain Est. 2003
Website: motherherbs.com
Key Highlights: Botanical Name: Spilanthes Acmella ; Family Name: Compositae ; Common Name: Toothache Plant ; Part Used: Leaves, Flowers ; Product offered: Roots….
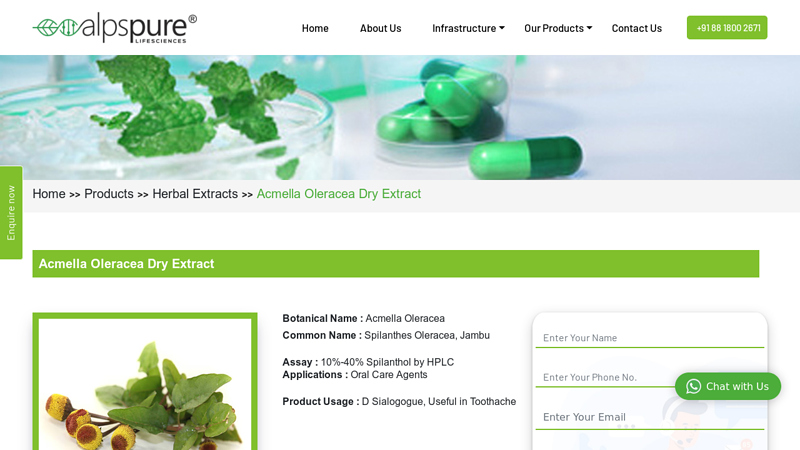
#5 Acmella Oleracea Dry Extract Supplier
Domain Est. 2015
Website: alpspure.in
Key Highlights: Oral health: Spilanthes oleracea extract has a mouth-numbing effect and can help treat toothaches, gum inflammation, and other issues relating to oral health….
#6 Acmella Oleracea Dry Extract
Domain Est. 2016
Website: saherbalbioactives.com
Key Highlights: Popularly, it is known as toothache plant which reduces the pain associated with toothaches and can induce saliva secretion. Various extracts and active ……
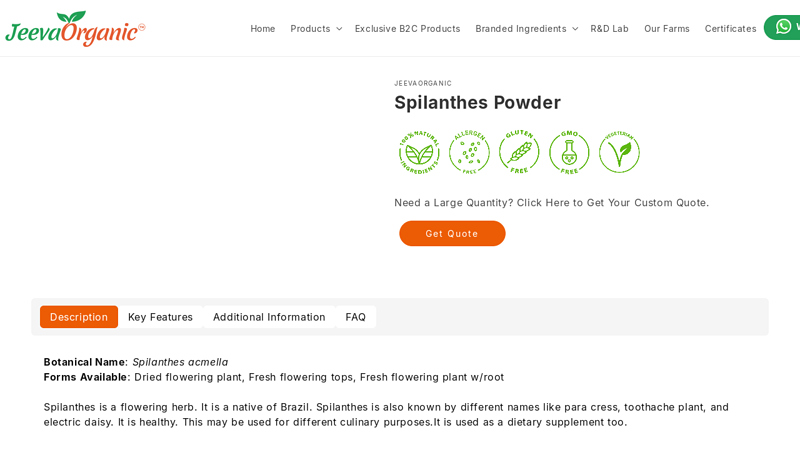
#7 Spilanthes Powder Supplier
Domain Est. 2016
Website: jeevaorganic.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.5 (89) Spilanthes is a flowering herb. It is a native of Brazil. Spilanthes is also known by different names like para cress, toothache plant, and electric daisy….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Toothache Plant Extract
H2: Projected Market Trends for Toothache Plant Extract in 2026
The global market for Toothache Plant Extract (also known as Acmella oleracea or Jambu extract) is poised for significant growth by 2026, driven by rising consumer demand for natural analgesics, increasing interest in herbal dentistry, and expanding applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics. Key market trends shaping the industry include:
-
Growing Demand for Natural Pain Relief Solutions
Consumers are increasingly shifting away from synthetic painkillers due to concerns over side effects and dependency. Toothache Plant Extract, known for its potent natural anesthetic properties attributed to the active compound spilanthol, is gaining traction as a safe and effective alternative for oral pain relief. This trend is expected to accelerate through 2026, particularly in North America and Europe. -
Expansion in Dental and Oral Care Products
By 2026, Toothache Plant Extract is projected to see broader integration into over-the-counter oral care products such as natural toothpastes, mouthwashes, and topical gels. Manufacturers are capitalizing on its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits, promoting its use in holistic and herbal oral hygiene formulations. -
Rise of the Global Herbal and Botanical Supplements Market
The nutraceutical sector is experiencing robust growth, with herbal extracts like Acmella oleracea benefiting from increased health consciousness. The extract is being incorporated into dietary supplements targeting dental health, immune support, and anti-aging, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin American markets. -
Innovation in Cosmetic Applications
Beyond healthcare, the cosmetic industry is exploring Toothache Plant Extract for its muscle-relaxing and skin-firming properties. By 2026, it is expected to feature in anti-wrinkle creams and “non-invasive facelift” serums, leveraging its ability to induce temporary muscle contraction—earning it the nickname “nature’s Botox.” -
Sustainable and Ethical Sourcing Initiatives
As demand increases, supply chain transparency and sustainable cultivation practices are becoming critical. Producers in Brazil, India, and Southeast Asia—the primary regions for Acmella oleracea cultivation—are adopting organic farming and fair-trade certifications to meet the expectations of eco-conscious consumers and regulatory standards. -
Regulatory Support and Standardization Efforts
Regulatory bodies in key markets are beginning to recognize and standardize the use of Toothache Plant Extract in health products. Harmonization of quality control measures and clinical validation of efficacy will likely boost consumer confidence and market penetration by 2026. -
Technological Advancements in Extraction and Formulation
Improved extraction techniques, such as supercritical CO₂ extraction, are enhancing the yield and purity of spilanthol. These innovations are driving cost-efficiency and enabling more stable formulations, supporting scalability and product consistency across industries.
In conclusion, the Toothache Plant Extract market in 2026 will be shaped by a convergence of health trends, technological progress, and sustainable practices. With expanding applications and growing consumer trust in plant-based remedies, the extract is positioned for strong market performance across pharmaceutical, wellness, and beauty sectors globally.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Toothache Plant Extract (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality Toothache Plant Extract (Acmella oleracea), renowned for its spilanthol content and traditional use in oral health and cosmetics, comes with significant challenges related to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to ineffective products, regulatory issues, and legal liabilities.
Inconsistent or Poor Extract Quality
One of the most prevalent issues in sourcing Toothache Plant Extract is the lack of standardized quality, resulting in variable efficacy and potential safety concerns. Key quality pitfalls include:
- Variable Spilanthol Content: The primary bioactive compound, spilanthol (alkylamide), is responsible for the characteristic tingling sensation and analgesic properties. However, spilanthol concentration can vary drastically (e.g., 0.1% to 2%+) based on plant genetics, growing conditions, harvest time, and extraction methods. Sourcing without strict spilanthol specifications (e.g., minimum 0.5% or 1%) risks receiving batches with negligible activity.
- Unreliable Extraction Methods: Low-cost suppliers may use inefficient solvents (e.g., low-proof ethanol, water) or suboptimal processes (temperature, duration), yielding extracts with low spilanthol recovery or high levels of unwanted plant waxes, chlorophyll, or sugars. This affects both potency and formulation stability.
- Adulteration and Dilution: Extracts may be diluted with cheaper carrier oils (e.g., sunflower, soybean) or blended with inactive fillers to reduce costs, significantly lowering the effective concentration of active compounds without proper disclosure.
- Lack of Standardized Testing and Certificates of Analysis (CoA): Reputable suppliers provide detailed CoAs including spilanthol content (via HPLC), solvent residue testing, microbial load, heavy metals, and pesticides. Absence of verifiable CoAs or use of unreliable testing methods makes quality claims untrustworthy.
- Poor Shelf Life and Stability: Spilanthol is sensitive to light, heat, and oxidation. Extracts stored or transported improperly (e.g., without nitrogen flushing, in clear containers, or at high temperatures) degrade rapidly, leading to loss of potency before reaching the end user.
Intellectual Property (IP) and Regulatory Compliance Risks
Sourcing Toothache Plant Extract also involves navigating complex IP landscapes and regulatory requirements, particularly for commercial product development:
- Patent Infringement: Numerous patents exist covering specific extraction methods, standardized formulations, and cosmetic or therapeutic uses of spilanthol-rich Acmella extracts. Sourcing an extract produced using a patented process—or using it in a patented application—without a license can expose the buyer to infringement claims, especially in markets like the US, EU, or Japan.
- Misappropriation of Traditional Knowledge: Acmella oleracea has long been used in traditional medicine (e.g., in South America and parts of Asia). Commercializing extracts based on traditional uses without benefit-sharing or proper attribution can raise ethical concerns and, in some jurisdictions, trigger legal challenges under frameworks like the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-Sharing (ABS).
- Unclear or Incomplete Documentation: Suppliers may not provide adequate documentation regarding the plant’s origin, cultivation practices (organic, wild-harvested), or compliance with biodiversity regulations (e.g., CITES, if applicable). This lack of traceability increases regulatory risk, particularly for products entering strict markets like the EU (REACH, cosmetic regulations) or requiring organic certification.
- Trademark and Labeling Issues: Using proprietary names or claims associated with patented extracts (e.g., “Jambu,” “Spilantol®”) without authorization can lead to trademark violations. Additionally, making unsupported health claims based on the extract’s properties may violate advertising and regulatory standards (e.g., FDA, FTC).
Conclusion: To avoid these pitfalls, buyers must conduct thorough due diligence: demand validated CoAs with spilanthol quantification, audit supplier processes, verify IP freedom-to-operate for intended uses, and ensure full regulatory compliance and traceability. Partnering with transparent, scientifically rigorous suppliers is essential for reliable and legally sound sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Toothache Plant Extract (Spilanthes acmella)
Overview of Toothache Plant Extract
Toothache Plant Extract, derived from Spilanthes acmella (also known as Acmella oleracea), is a botanical extract traditionally used for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. It is commonly used in dietary supplements, oral care products, and natural health formulations. Due to its bioactive compounds—primarily alkylamides such as spilanthol—handling, transporting, and marketing this extract require adherence to specific regulatory and logistical standards globally.
Regulatory Classification and Compliance
Botanical Identity and Nomenclature
Ensure the extract is accurately labeled using the correct botanical name: Spilanthes acmella or Acmella oleracea, with standardized naming per pharmacopeial references (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur.). Misidentification can lead to regulatory rejection.
Regulatory Status by Region
– United States (FDA):
– Regulated as a dietary ingredient under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA).
– Must comply with Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMPs) under 21 CFR Part 111.
– Prior notification may be required if marketed as a New Dietary Ingredient (NDI) via the FDA’s NDI notification program.
– Not approved as a drug; claims must avoid disease treatment language (e.g., “treats toothache”) unless supported by IND/NDAs.
- European Union (EFSA & EMA):
- Regulated under the EU Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 if introduced after 1997. Spilanthes acmella extract is currently authorized as a novel food.
- Must comply with food supplement directives in relevant member states.
-
Labeling must follow EU Regulation 1169/2011 (Food Information to Consumers), including allergen declarations and nutrient content claims.
-
Canada (Health Canada):
- Requires a Natural Health Products (NHP) License under the Natural Health Products Regulations.
- Product License Application (PLA) must include evidence of safety, efficacy, and quality.
-
DIN-HM (Homeopathic Medicine Number) or NPN (Natural Product Number) must be obtained before sale.
-
Australia (TGA):
- Listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) as a complementary medicine.
- Must meet guidelines under the Therapeutic Goods Act 1989.
-
Pre-market assessment required for safety and quality; efficacy claims must be limited to low-risk indications.
-
Other Regions:
- Check local herbal medicine or traditional product regulations in target markets (e.g., China’s NMPA, India’s AYUSH, Brazil’s ANVISA).
Quality and Safety Standards
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
– Manufacturing facilities must be GMP-certified (e.g., ISO 22716 for cosmetics, NSF, or EU GMP for food/pharma).
– Batch records, standard operating procedures (SOPs), and quality control (QC) testing are mandatory.
Testing and Specifications
– Identity Testing: HPLC or TLC to confirm presence of spilanthol and other marker compounds.
– Potency: Standardized to a minimum % of spilanthol (e.g., 0.5–2%).
– Contaminants: Test for heavy metals (lead, arsenic, cadmium, mercury), microbial load (total aerobic count, yeast/mold, pathogens), pesticides, and residual solvents (if solvent extraction used).
– Stability Studies: Required for shelf-life determination (typically 24–36 months under recommended storage).
Excipients and Formulation Compliance
– Any added carriers (e.g., maltodextrin, glycerin) must be food/pharma grade and approved for use in the target market.
– Avoid undeclared allergens or restricted substances.
Labeling and Claims
Mandatory Label Information
– Product name and botanical source (Latin name).
– Extract standardization (e.g., “Standardized to contain 1% spilanthol”).
– Net weight/volume.
– Batch number and expiration date.
– Manufacturer/distributor name and address.
– Storage conditions (typically “Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight”).
– Supplement Facts panel (if applicable in the U.S.).
Marketing and Claims Restrictions
– Avoid unapproved drug claims (e.g., “cures tooth pain”); use structure/function claims like “supports oral health” or “traditionally used for temporary relief of minor mouth discomfort.”
– Claims must be substantiated with scientific literature or traditional use documentation.
– In regions like the EU, claims must align with approved health claim lists (e.g., EFSA Article 13 or 14 claims).
Import/Export and Customs Compliance
HS Code Classification
– Typical HS Code: 1302.19 (Plant extracts, not elsewhere specified) or 3301.90 (Essential oils and resinoids). Final code depends on form (liquid, powder) and intended use. Consult local customs authority.
Import Permits and Phytosanitary Requirements
– Some countries require phytosanitary certificates to prevent introduction of plant pests.
– CITES check: Spilanthes acmella is not CITES-listed, but verify with updated databases.
– Obtain import licenses if required (e.g., for herbal substances in China or India).
Documentation for Shipment
– Commercial invoice (with detailed product description, value, origin).
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from an accredited lab.
– Certificate of Origin.
– Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS) if classified as hazardous (rare for this extract).
– Export declaration and bill of lading/air waybill.
Storage and Transportation
Environmental Conditions
– Store in sealed, light-resistant containers at controlled room temperature (15–25°C).
– Protect from moisture and humidity (relative humidity < 60%).
– Avoid temperature extremes; do not freeze unless specified.
Packaging Requirements
– Use food-grade or pharma-grade packaging (e.g., HDPE bottles, aluminum pouches with moisture barriers).
– Include desiccants if in powder form.
– Ensure tamper-evident seals for consumer products.
Transportation Modes
– Air freight: Preferred for small, high-value shipments; comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (not usually classified as hazardous).
– Sea freight: Cost-effective for bulk; use climate-controlled containers if extended transit times.
– Ground transport: Ensure vehicles are clean, dry, and temperature-stable.
Risk Management and Due Diligence
Supply Chain Verification
– Source raw material from reputable, audited suppliers.
– Request proof of sustainable harvesting practices (e.g., fair wildcrafting, organic certification if claimed).
– Conduct supplier audits and annual quality reviews.
Adverse Event Monitoring
– Establish a pharmacovigilance system to collect and report adverse events, especially if marketed as a health product.
– Report serious events to relevant health authorities within required timelines (e.g., FDA MedWatch, EudraVigilance).
Intellectual Property and Trademarks
– Ensure branding does not infringe on existing trademarks.
– Consider patenting novel extraction methods or formulations where applicable.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the logistics and compliance landscape for Toothache Plant Extract requires a proactive approach to regulatory alignment, quality assurance, and accurate documentation. Stakeholders must remain vigilant about evolving regulations, especially in rapidly changing markets for botanicals and natural health products. Partnering with regulatory consultants and third-party testing labs is recommended to ensure full compliance and market access.
In conclusion, sourcing toothache plant (Acmella oleracea) extract requires careful consideration of quality, sustainability, and authenticity. Identifying reliable suppliers who adhere to good agricultural and collection practices (GACP), provide transparent documentation, and conduct third-party testing for purity and potency is essential. The extraction method—typically using solvents like ethanol or supercritical CO2—also significantly impacts the efficacy of the final product, particularly in preserving bioactive compounds such as spilanthol. Additionally, ethical sourcing and fair trade practices should be prioritized to support local communities and ensure environmental sustainability. By establishing strong supply chain partnerships and verifying product consistency, businesses can ensure a high-quality, effective, and responsibly sourced toothache plant extract suitable for pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, or cosmetic applications.