The global laser cutting market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision manufacturing across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 9.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.4% through 2028, fueled by advancements in automation and increasing adoption of fiber laser technology. A key differentiator among manufacturers in this competitive landscape is the ability to achieve tight tolerances—often within ±0.1 mm—required for mission-critical components. As precision becomes a decisive factor in production quality, companies specializing in toleranz laserschneiden (precision laser cutting) are gaining strategic importance. Based on production capabilities, technological innovation, and industry reputation, the following five manufacturers stand out as leaders in delivering high-tolerance laser cutting solutions worldwide.
Top 5 Toleranz Laserschneiden Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Standard Tolerances in Manufacturing
Website: xometry.pro
Key Highlights: This article will explore the key tolerance standards used in subtractive manufacturing, specifically ISO 2768, ISO 286 and GD&T….
#2 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#3 ISO Fits and Tolerances according to DIN ISO 286
Website: trelleborg.com
Key Highlights: Our Fits & Tolerances Calculator allows you to easily determine type of fits using the tolerances according to DIN ISO 286….
#4 Understanding Surface Quality Specifications
Website: edmundoptics.com
Key Highlights: Precision laser applications typically require a scratch-dig of 20-10, whereas the most demanding laser applications, such as intra-cavity laser optics, usually ……
#5 CNC Machining Center EVOLUTION 7405 4mat
Website: m.holzherusa.com
Key Highlights: Unique in its class, the EVOLUTION 7405 4mat offers absolutely precise edge routing on all four workpiece edges and thus complete formatting for panel material….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Toleranz Laserschneiden
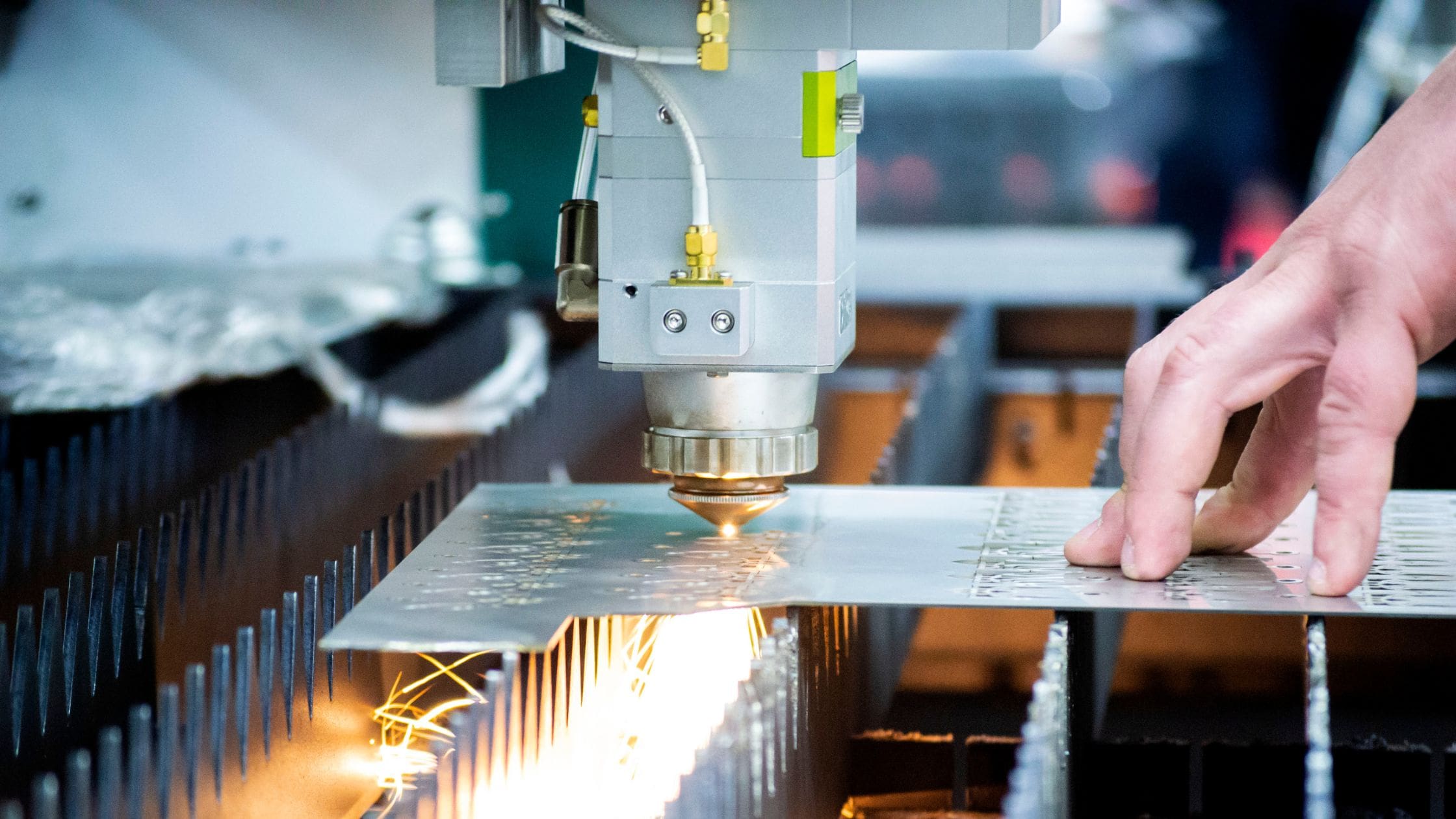

H2: Market Trends in Tolerance Laser Cutting (2026 Outlook)
As we approach 2026, the precision manufacturing sector—specifically tolerance laser cutting—continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in technology, rising demand for miniaturization, and the need for tighter tolerances across key industries. Tolerance laser cutting, which refers to the high-precision cutting of materials with minimal dimensional deviation, is becoming increasingly critical in aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing. Below are the key market trends shaping the landscape for tolerance laser cutting in 2026:
-
Tighter Tolerance Requirements Across Industries
By 2026, industry standards are demanding tighter tolerances—often in the ±5 to ±10 micron range—especially in high-performance sectors. Aerospace components, surgical instruments, and semiconductor manufacturing tools require near-perfect edge quality and dimensional accuracy, pushing laser cutting systems to achieve unprecedented precision. Fiber and ultrafast (picosecond/femtosecond) lasers are at the forefront, enabling clean, burr-free cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. -
Growth in Ultrafast and Fiber Laser Adoption
Ultrafast lasers are gaining traction due to their ability to ablate material with minimal thermal distortion, essential for micro-cutting and heat-sensitive materials. Fiber lasers, meanwhile, dominate in high-speed, high-precision industrial applications due to improved beam quality and energy efficiency. In 2026, the adoption of hybrid systems—combining fiber and ultrafast technologies—is expected to rise, offering manufacturers flexibility across material types and thicknesses. -
Automation and Integration with Industry 4.0
Laser cutting systems are increasingly integrated into smart factories, with real-time monitoring, AI-driven process optimization, and predictive maintenance. In 2026, CNC laser platforms equipped with IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms will autonomously adjust cutting parameters to maintain tolerance consistency, reducing scrap rates and improving throughput. Closed-loop feedback systems ensure real-time correction, vital for high-mix, low-volume production environments. -
Expansion in Electric Vehicle and Renewable Energy Sectors
The EV boom continues to fuel demand for precision-cut battery foils, stator laminations, and power electronics. In 2026, manufacturers are relying on laser cutting to achieve the micron-level tolerances required for efficient battery stacking and electric motor performance. Similarly, photovoltaic cell production benefits from precise edge isolation and patterning enabled by high-tolerance laser systems. -
Material Innovation and Multi-Material Processing
As advanced composites, thin metal foils, ceramics, and flexible hybrid electronics enter mainstream production, laser systems must adapt. In 2026, multi-wavelength and adaptive optics systems allow a single platform to cut diverse materials while maintaining tight tolerances. This versatility is crucial for industries like medical device manufacturing, where biocompatible alloys and polymers are often processed in the same facility. -
Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Geopolitical factors and supply chain resilience have led to regionalization of high-precision manufacturing. In 2026, North America and Europe are investing heavily in domestic tolerance laser cutting capabilities, reducing reliance on offshore production. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific remains a hub for volume manufacturing, with China and South Korea advancing in high-precision laser technology R&D. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing laser manufacturers to develop more energy-efficient systems. By 2026, next-generation lasers with higher wall-plug efficiency and recyclable component designs are becoming standard. Additionally, reduced material waste through precision cutting supports circular economy initiatives.
Conclusion:
In 2026, tolerance laser cutting is no longer just a manufacturing capability—it is a strategic enabler of innovation across high-tech industries. The convergence of tighter tolerances, intelligent automation, and sustainable production practices is redefining market expectations. Companies that invest in advanced laser technologies, digital integration, and workforce upskilling will lead the competitive landscape, meeting the evolving demands of a precision-driven global economy.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Toleranz Laserschneiden – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing laser cutting services with tight tolerances (Toleranz Laserschneiden), businesses often face critical challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to production delays, increased costs, or legal complications. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two areas:
H2: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Tolerance Adherence
A major risk is selecting suppliers who claim to meet tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.1 mm) but lack the equipment calibration, process control, or quality assurance protocols to do so consistently. Variability between batches can compromise part functionality, especially in precision industries like medical devices or aerospace. -
Lack of Process Documentation and Traceability
Many suppliers fail to provide detailed process documentation, such as laser power settings, cutting speeds, or material batch tracking. Without this, reproducing results or troubleshooting defects becomes difficult. -
Inadequate Material Handling and Post-Processing
Poor handling of materials before or after cutting—such as improper cleaning, deburring, or storage—can introduce distortions or surface defects that affect dimensional accuracy, invalidating tight-tolerance specifications. -
Insufficient Quality Control Measures
Suppliers may rely on spot checks rather than statistical process control (SPC) or automated inspection (e.g., CMM or optical scanning). This increases the risk of undetected deviations in high-precision components.
H2: Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
-
Unprotected Design Files and CAD Data
Sharing detailed CAD models or technical drawings with suppliers without proper non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or data protection clauses exposes companies to IP theft or unauthorized replication, especially when sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement. -
Lack of Clear Ownership Clauses in Contracts
Ambiguity in contracts about who owns the tooling, programs (e.g., CNC/laser paths), or modified designs can lead to disputes. Some suppliers may reuse or resell designs if terms are not explicitly defined. -
Third-Party Subcontracting Without Consent
A supplier might subcontract the laser cutting work to a secondary vendor without informing the client. This not only reduces control over quality but also increases the risk of IP exposure across multiple, unvetted parties. -
Insecure Data Transfer and Storage
Sending design files via unencrypted channels or allowing suppliers to store data on unsecured servers heightens the risk of data breaches or industrial espionage.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, businesses should conduct thorough supplier audits, enforce strict quality protocols (e.g., ISO 9001 certification), implement robust IP protection strategies (NDAs, encrypted data sharing, and clear contractual terms), and maintain direct oversight of the manufacturing process. Proactive management of both quality and IP aspects is essential for successful sourcing of Toleranz Laserschneiden services.
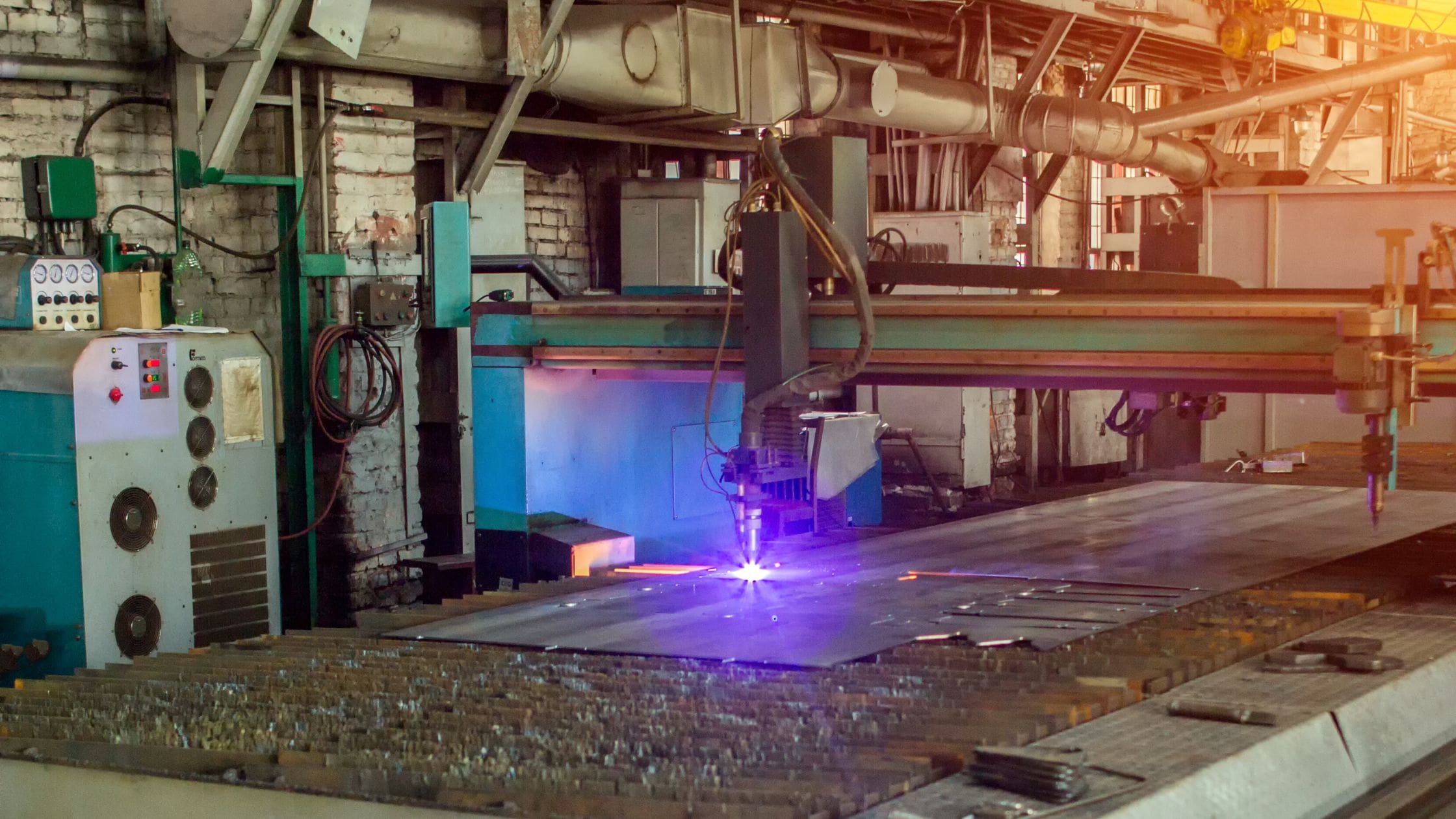

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Toleranz Laserschneiden
This guide outlines the logistical and compliance considerations for manufacturing components using laser cutting with specified dimensional tolerances (“Toleranz”). Adherence to these guidelines ensures product quality, regulatory compliance, and efficient supply chain operations.
Order Processing & Documentation
All laser cutting orders must include clearly defined technical drawings with explicit tolerance specifications (e.g., ISO 2768-m, DIN 18201, or project-specific tolerances). Purchase orders and work instructions must reference applicable standards and inspection requirements. Documentation must be maintained for a minimum of 10 years in accordance with ISO 9001:2015 and relevant industry regulations.
Material Handling & Traceability
Raw materials used in laser cutting must be accompanied by material certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2) verifying chemical composition and mechanical properties. Materials shall be stored in a controlled environment to prevent corrosion or deformation. Full traceability—from raw material batch to finished part—must be ensured through barcoding or digital tracking systems, particularly for regulated industries such as medical devices or aerospace.
Production Tolerances & Process Validation
Laser cutting processes must be validated to consistently achieve specified tolerances. Standard geometric tolerances for laser-cut sheet metal typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm, depending on material thickness and machine capability. Critical dimensions must be verified during first article inspection (FAI) using calibrated measurement equipment (e.g., CMM, optical comparators). Process parameters (laser power, speed, assist gas) must be documented and controlled per internal work instructions.
Quality Control & Inspection
Finished parts must undergo dimensional inspection per the approved inspection plan. Non-conforming parts must be quarantined and documented using a non-conformance report (NCR) system. Regular internal audits and capability studies (e.g., Cpk analysis) must be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with tolerance requirements and process stability.
Packaging & Shipping
Cut parts must be packaged to prevent damage, contamination, or deformation during transit. Protective measures (VCI paper, edge protectors, custom fixtures) should be used based on part geometry and material. Shipping documentation must include packing lists, certificates of conformance (CoC), and any required export documentation for international shipments.
Regulatory Compliance
Laser cutting operations must comply with local and international regulations, including:
– Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (EU)
– OSHA standards for laser safety (29 CFR 1910.97, U.S.)
– REACH and RoHS directives for material restrictions
– GDPR for handling customer data
Environmental compliance includes proper disposal of metal waste and fume extraction system maintenance in line with EPA or equivalent standards.
Supplier & Subcontractor Management
If laser cutting is subcontracted, suppliers must be qualified and audited for compliance with this guide. Agreements must specify adherence to defined tolerances, quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949), and data security requirements. Performance is monitored through KPIs such as on-time delivery and defect rate.
Continuous Improvement
Feedback from logistics, quality, and customer complaints must be analyzed regularly. Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are to be implemented through a structured continuous improvement process (e.g., PDCA, Six Sigma) to enhance tolerance consistency and supply chain efficiency.
Conclusion for Sourcing Toleranz Laserschneiden (Laser Cutting Tolerances):
When sourcing laser cutting services, understanding and specifying dimensional tolerances is crucial to ensure the quality, functionality, and interchangeability of the final parts. Laser cutting offers high precision, but actual tolerances depend on various factors including material type and thickness, laser technology (CO₂, fiber, etc.), machine calibration, and the complexity of the geometry.
Typical laser cutting tolerances range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for thin sheets (up to 3 mm), while thicker materials may require looser tolerances (±0.3 mm or more). Critical applications may demand tighter controls, which can increase costs due to additional process validation or secondary finishing.
To ensure reliable sourcing:
– Clearly define tolerance requirements in technical drawings.
– Collaborate with experienced suppliers who maintain well-calibrated equipment and quality control processes (e.g., ISO-certified workshops).
– Consider design for manufacturing (DFM) principles to avoid unnecessarily tight tolerances that drive up costs.
– Perform prototyping and first-article inspections to verify dimensional accuracy before full production.
In conclusion, while laser cutting provides excellent precision, successful sourcing depends on a balanced approach between technical requirements, material limitations, and cost-efficiency. Establishing clear communication and quality standards with suppliers ensures consistent, high-quality results.