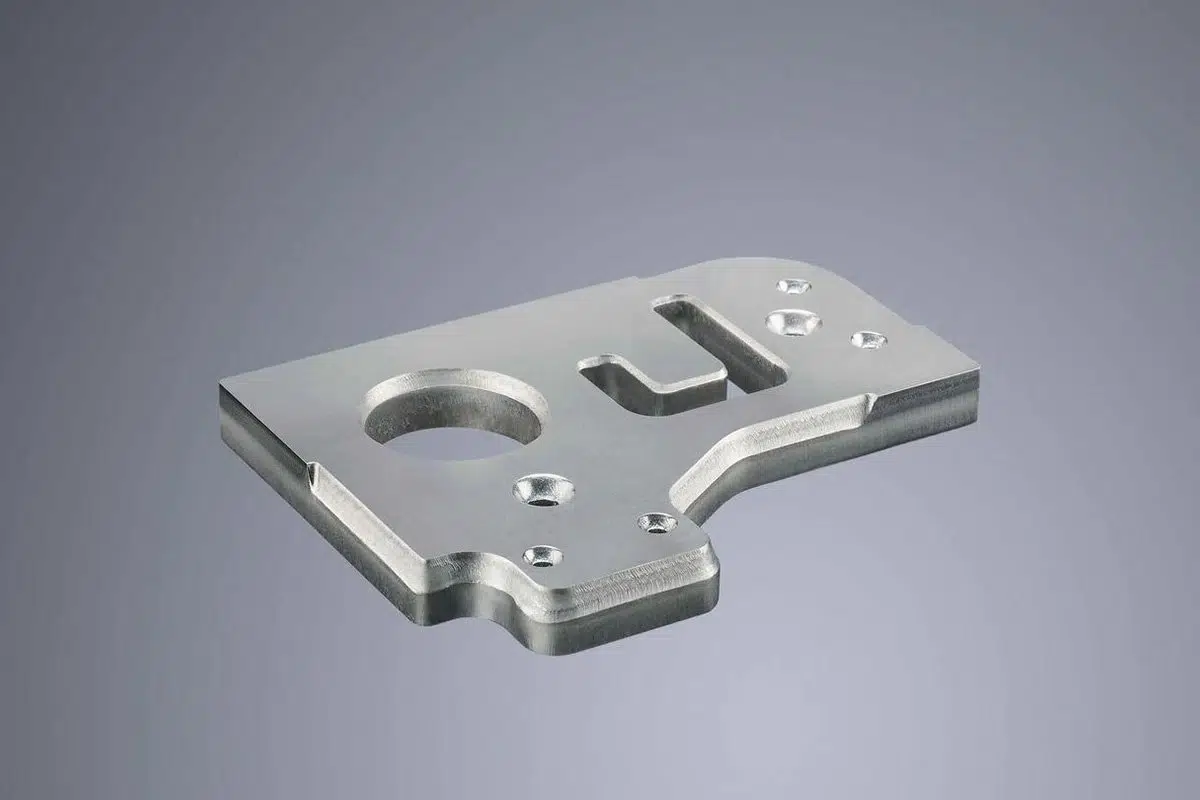
The global laser cutting machine market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision fabrication across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to register a CAGR of over 7.2% through 2029. This expansion reflects manufacturers’ growing reliance on advanced laser technologies capable of delivering tighter tolerances, faster processing speeds, and improved energy efficiency. As precision becomes a critical differentiator in metal and non-metal fabrication, the tolerance capability—often within ±0.1 mm or better—has emerged as a key performance metric. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers have consistently demonstrated superior control over dimensional accuracy and process repeatability. The following explores the top eight laser cutting machine manufacturers recognized for their exceptional tolerance performance, technological innovation, and industry footprint.
Top 8 Tolerance Of Laser Cutting Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
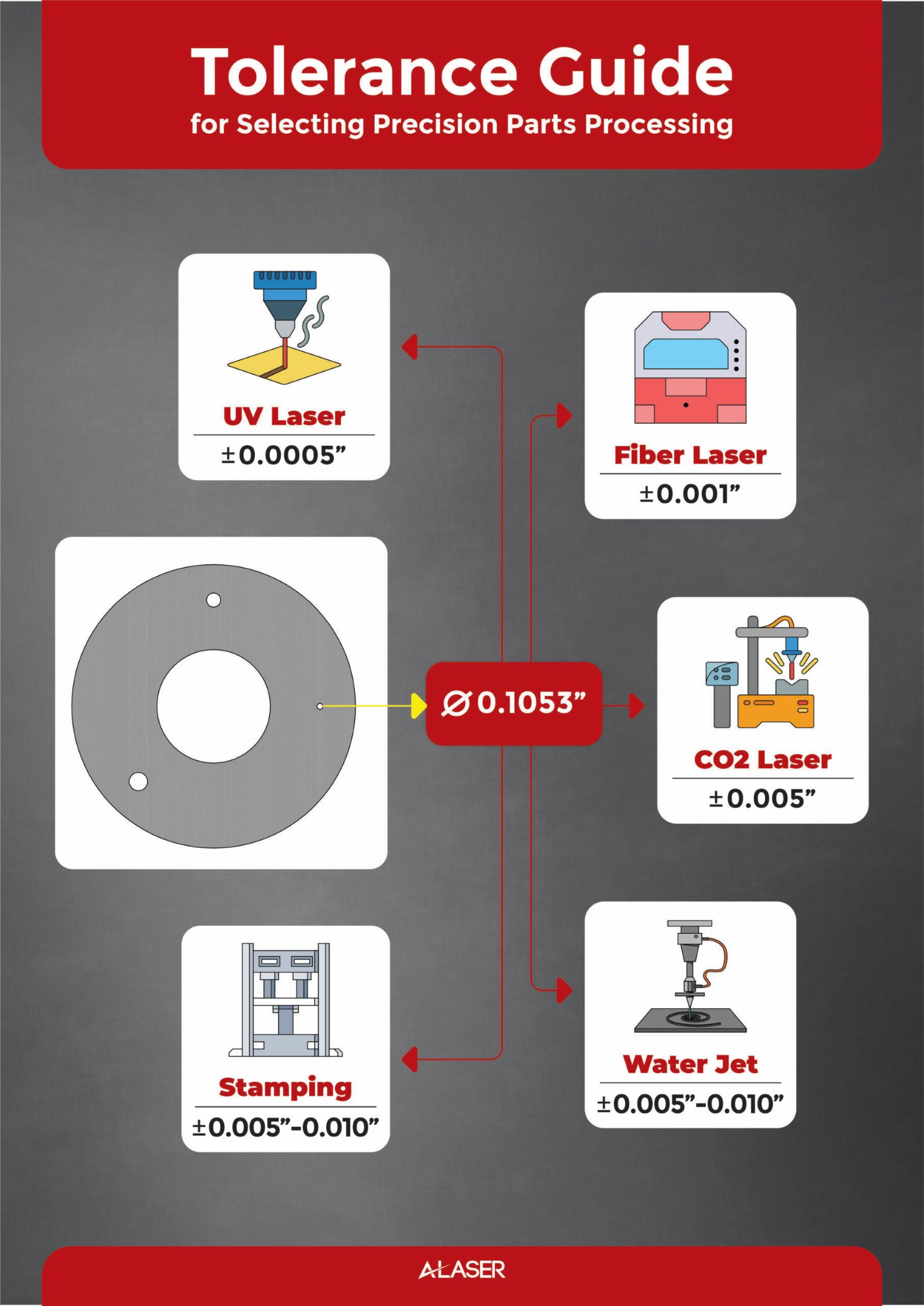
#1 Laser Cutting Tolerances
Website: a-laser.com
Key Highlights: In the laser precision cutting world, tight tolerance is defined as the acceptable amount of variation when a part is being processed….
#2 What is the tolerance of laser cut parts?
Website: fabworks.com
Key Highlights: The tolerance of laser cut parts typically ranges from +/- 0.002 inches to +/- 0.05 inches, depending on various factors such as part size and feature ……
#3 Laser tolerances
Website: hypertherm.com
Key Highlights: There is less variability in the process. Generally, a laser can hold cut part dimensional tolerances of under 0.01″ (0.25 mm)….
#4 How Accurate is Laser Cutting
Website: accurl.com
Key Highlights: Cutting tolerances are typically within ±0.005 inches, ensuring high precision in manufacturing applications. How Accurate is Laser Cutting?…
#5 Metal Profile Cutting Tolerances
Website: protocase.com
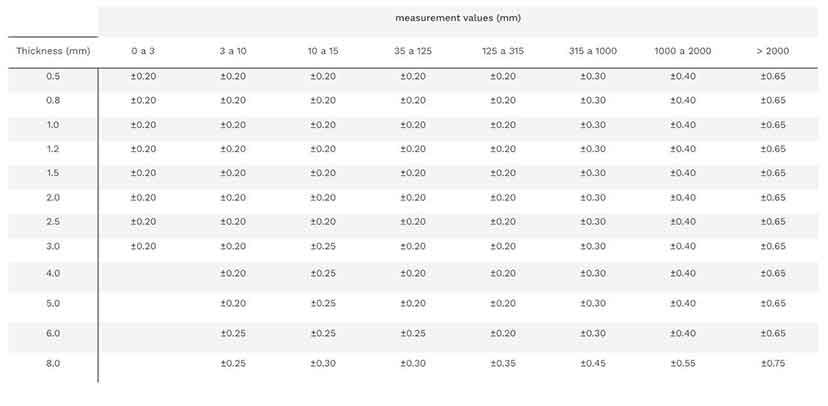
Key Highlights: Profile Cutting Tolerances ; Laser, ± 0.005″ | 0.13mm ; Extruded Chopsaw Extrusions 48″ (1219.2mm) or Shorter, +0.010″, -0.000″ | +0.25mm, -0.00mm ; Extruded ……
#6 Standard Tolerances in Manufacturing
Website: xometry.pro
Key Highlights: This article will explore the key tolerance standards used in subtractive manufacturing, specifically ISO 2768, ISO 286 and GD&T….
#7 Tolerances and accuracy in laser cutting
Website: teprosa.de
Key Highlights: All cutting parts are manufactured according to the standard DIN ISO 2768-1 m (general tolerances) for the geometric dimension, unless otherwise agreed with ……
#8 Laser Cutting Metal Parts Design Guide
Website: laserboost.com
Key Highlights: 0.3 mm ~ 8 mm. Cutting Thickness Ranges. * Check here for manufacturing tolerances….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tolerance Of Laser Cutting
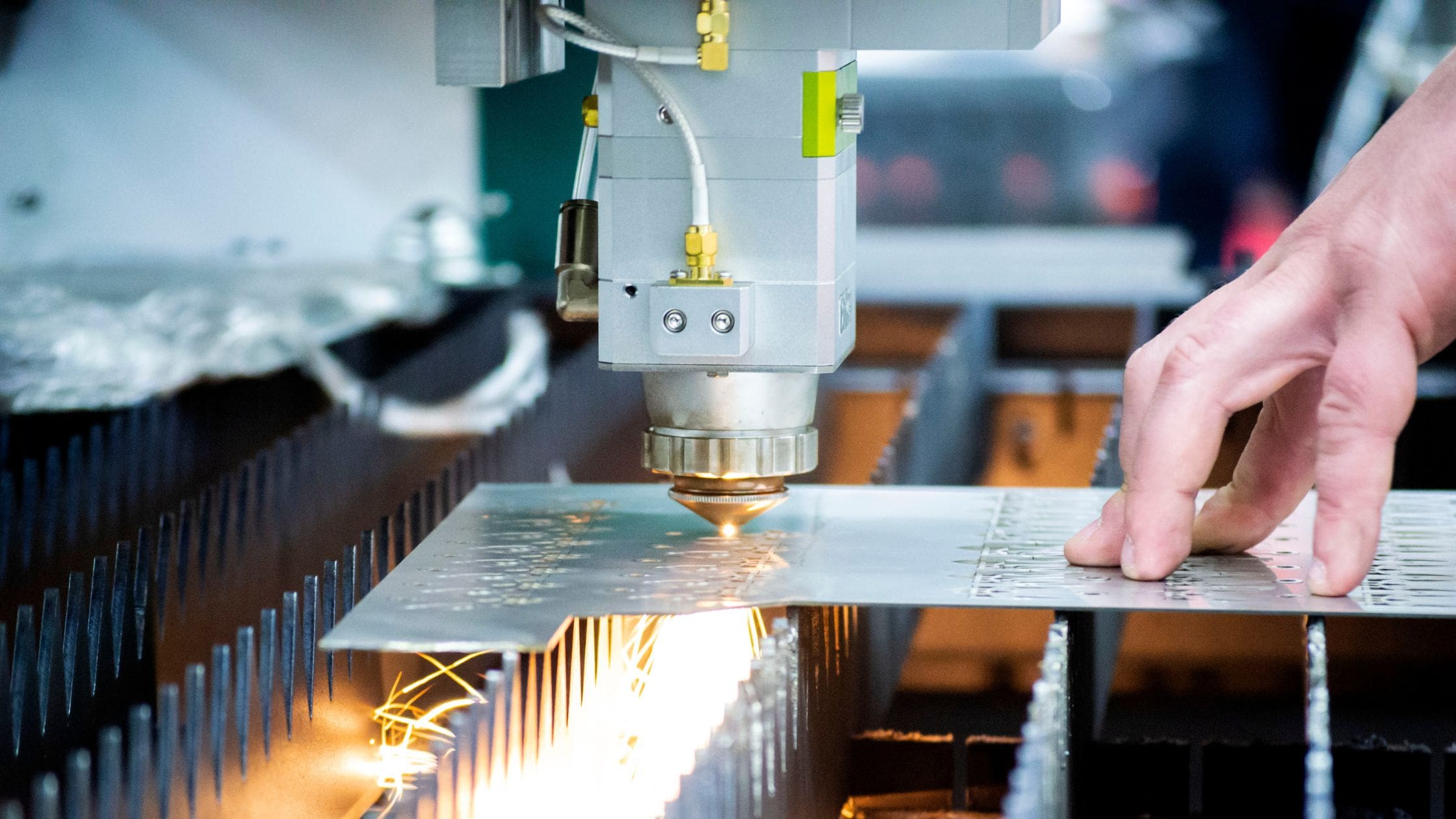

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tolerance in Laser Cutting
As the manufacturing and industrial sectors continue to embrace advanced automation and precision engineering, the demand for tighter and more consistent tolerances in laser cutting is expected to rise significantly by 2026. The tolerance of laser cutting—referring to the allowable deviation in dimensions during the cutting process—is a critical performance metric influencing product quality, fit, and functionality across industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and electronics.
Several key trends are shaping the evolution of laser cutting tolerances in the lead-up to 2026:
-
Advancements in Laser Technology
Fiber and ultrafast (e.g., picosecond and femtosecond) lasers are becoming more prevalent, enabling micron-level precision. These technologies deliver improved beam quality and thermal control, reducing heat-affected zones and material deformation. As a result, achievable tolerances are tightening, with many high-end systems now consistently achieving ±0.05 mm or better. -
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Predictive maintenance and real-time process optimization powered by artificial intelligence are enhancing repeatability and accuracy. AI-driven feedback systems can dynamically adjust laser parameters (power, speed, focus) during operation to compensate for material variations or environmental fluctuations, ensuring that specified tolerances are maintained across high-volume production runs. -
Growth in High-Precision Industries
Sectors like medical device manufacturing and semiconductor packaging require extremely tight tolerances (often ±0.01 mm or less). This demand is driving innovation in laser cutting systems tailored for micro-machining applications, with increased adoption of hybrid systems combining laser cutting with other precision technologies. -
Material Diversity and Complexity
As manufacturers work with advanced materials—including high-strength alloys, composites, and ceramics—laser cutting systems must adapt to maintain tolerances across varying thermal conductivities and reflectivity. Process-specific calibration and multi-axis beam control are becoming standard to ensure dimensional consistency. -
Standardization and Quality Certification
Industry 4.0 initiatives are promoting tighter integration between design (CAD), manufacturing execution systems (MES), and quality control (CMM, vision systems). By 2026, traceability and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO 2768, ASME Y14.5) will be increasingly enforced, making tolerance documentation and validation a core component of procurement and quality assurance. -
Global Competition and Cost Pressures
While demand for tighter tolerances grows, cost-efficiency remains a driver. Innovations in diode lasers and automation (e.g., robotic loading, automated nozzle changers) are helping mid-tier manufacturers achieve tighter tolerances without proportional increases in operational costs.
In summary, the 2026 market for laser cutting tolerance is defined by a convergence of technological innovation, industry-specific demands, and digital integration. As precision becomes a competitive differentiator, manufacturers investing in high-tolerance laser systems and process control will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities across advanced manufacturing sectors.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Laser Cutting (Tolerance, Quality, IP)
When sourcing laser cutting services, overlooking key factors related to tolerance, quality, and intellectual property (IP) can lead to costly delays, rework, or legal issues. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
Unclear or Unrealistic Tolerance Expectations
Many buyers specify tight tolerances without considering material type, thickness, or laser capabilities. Assuming standard tolerances (±0.1 mm) apply universally can result in rejected parts. Always consult with the supplier early to align on achievable tolerances based on your material and design.
Inadequate Quality Control Specifications
Failing to define acceptance criteria—such as surface finish, burr limits, or kerf width—can lead to inconsistent output. Some suppliers may meet dimensional tolerances but deliver parts with excessive dross or heat-affected zones. Require documented quality checks and request sample parts before full production.
Overlooking Machine Capability and Maintenance
Not all laser cutters are equal. Older or poorly maintained machines may struggle with precision, especially on thicker materials. Avoid assuming all vendors deliver the same quality. Ask about machine types (fiber vs. CO₂), age, calibration schedules, and process validation records.
Ignoring Material-Specific Challenges
Different metals (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum, mild steel) react uniquely to laser cutting. Aluminum, for example, reflects laser light and requires specialized settings. Sourcing without accounting for material behavior can compromise edge quality and dimensional accuracy.
Poor Communication of Design Intent
Sending incomplete or ambiguous CAD files—without notes on critical features or tolerance zones—increases the risk of misinterpretation. Use detailed drawings with Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) where necessary and confirm understanding with the supplier.
Neglecting Intellectual Property Protection
Sharing design files without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) or IP clauses exposes your innovations. Some offshore suppliers may lack strict IP safeguards. Always formalize IP ownership in contracts and limit access to sensitive design data.
Focusing Only on Price, Not Process Capability
Choosing a supplier solely on cost can backfire if they lack the technology or expertise to meet your requirements. A slightly higher price from a qualified vendor often saves money long-term by reducing scrap and rework.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Failing to require certifications, material test reports, or process documentation makes it difficult to resolve quality disputes. Ensure your contract includes provisions for traceability and record retention.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, clear communication, and a partnership approach with your laser cutting supplier.
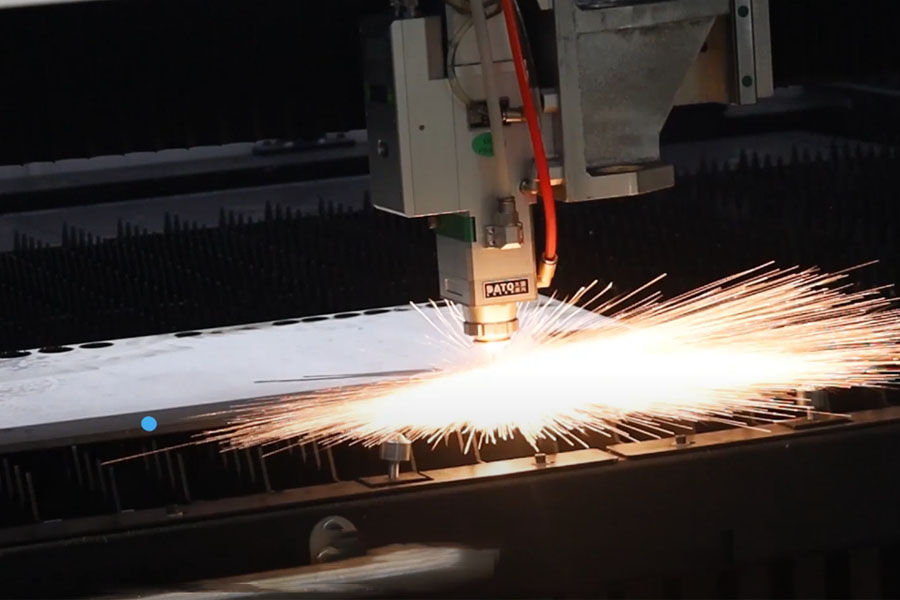

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tolerance of Laser Cutting
Understanding and managing laser cutting tolerances is critical for ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and smooth logistics operations. This guide outlines key considerations for maintaining tolerance accuracy throughout the supply chain and meeting industry standards.
Understanding Laser Cutting Tolerances
Laser cutting tolerances refer to the permissible deviation from specified dimensions in a cut part. These tolerances are influenced by material type, thickness, laser power, cutting speed, and machine calibration. Typical tolerance ranges are:
– Standard Tolerance: ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for thin materials (up to 6 mm)
– Precision Tolerance: ±0.05 mm or tighter, achievable with high-end systems and optimized parameters
Consistent tolerance control ensures parts fit correctly in assemblies and meet functional requirements.
Material Selection and Handling
Material properties significantly affect cutting precision. Key logistics considerations include:
– Material Consistency: Source materials from certified suppliers to minimize variations in thickness and composition
– Storage Conditions: Store metals and composites in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent warping or moisture absorption
– Handling Procedures: Use non-marring tools and fixtures during transport to avoid surface damage that could affect cutting accuracy
Ensure material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) are maintained for traceability and compliance.
Machine Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration of laser cutting equipment is essential for sustained tolerance performance:
– Perform daily or weekly alignment checks using calibration tools
– Schedule preventative maintenance to clean optics, check nozzle condition, and verify beam focus
– Maintain a documented maintenance log for audit purposes
Use standardized calibration procedures aligned with ISO 9001 or similar quality management systems.
Quality Control and Inspection Protocols
Implement rigorous inspection processes to verify tolerance compliance:
– Use Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM), optical comparators, or laser scanners for dimensional checks
– Conduct first-article inspections (FAI) for new production runs
– Apply statistical process control (SPC) to monitor tolerance trends over time
Retain inspection records for traceability and regulatory audits.
Documentation and Regulatory Compliance
Maintain comprehensive documentation to support compliance:
– Engineering Drawings: Clearly specify tolerances using ISO 2768 or ASME Y14.5 standards
– Process Control Plans: Document cutting parameters, inspection frequency, and acceptance criteria
– Compliance Certifications: Adhere to industry-specific regulations (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100 for aerospace, ISO 13485 for medical devices)
Ensure all documentation is version-controlled and accessible during audits.
Supply Chain and Logistics Coordination
Coordinate tolerance requirements across the supply chain:
– Communicate tolerance expectations clearly with subcontractors and vendors
– Include tolerance clauses in procurement contracts
– Verify incoming parts with receiving inspections when outsourcing cutting operations
Use digital platforms for real-time tracking of quality data and non-conformance reports.
Continuous Improvement and Corrective Actions
Establish a feedback loop to improve tolerance performance:
– Analyze root causes of out-of-tolerance parts using tools like 5 Whys or fishbone diagrams
– Implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) promptly
– Train operators on best practices and new technologies (e.g., adaptive control systems)
Regular internal audits help ensure sustained compliance and process optimization.
By integrating precise tolerance management into logistics and compliance frameworks, organizations can enhance product quality, reduce waste, and meet regulatory demands effectively.
Conclusion on Sourcing Tolerance in Laser Cutting:
Achieving tight and consistent tolerances in laser cutting requires careful consideration during the sourcing process. Variability in material type, thickness, machine capability, and supplier expertise significantly influences final part accuracy. To ensure quality and dimensional reliability, it is essential to partner with experienced and well-equipped laser cutting vendors who maintain calibrated machinery, adhere to strict quality control procedures, and provide clear documentation of achievable tolerances.
Standard laser cutting tolerances typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.2 mm for most sheet materials, but tighter tolerances may be attainable with high-precision equipment and optimized processes. When sourcing, clearly define required tolerances in technical drawings, consider material behavior during cutting (such as thermal distortion), and allow for post-processing if needed. Proactive communication, sample testing, and supplier audits help mitigate risks and ensure that the chosen provider can consistently meet the required specifications.
In summary, successful sourcing of laser cutting services hinges on aligning design requirements with supplier capabilities, emphasizing precision, repeatability, and quality assurance to achieve optimal results in production.