The global tofu coagulant market has seen steady expansion in recent years, driven by rising plant-based diets and increasing demand for soy-based protein alternatives. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global tofu market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, with coagulants like nigari playing a critical role in maintaining product texture and quality. Nigari, a natural coagulant derived from seawater, is particularly favored for its clean label appeal and minimal processing. As demand escalates, especially in Asia-Pacific and North America, manufacturers are scaling production and innovating formulations to meet food safety and sustainability standards. This growing market momentum underscores the importance of reliable, high-purity nigari suppliers. Below is a data-informed overview of the top nine nigari manufacturers shaping the tofu coagulant landscape.
Top 9 Tofu Coagulant Nigari Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
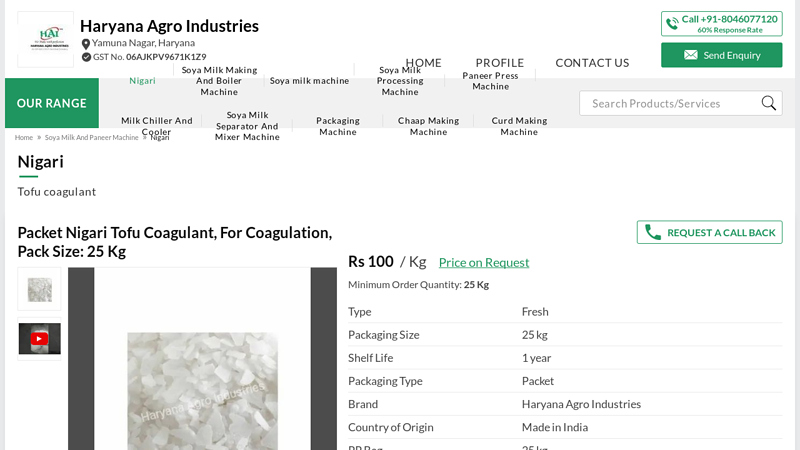
#1 Packet Nigari Tofu Coagulant, For Coagulation, Pack Size
Domain Est. 2017
Website: haryanaagroindustries.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of Nigari – Packet Nigari Tofu Coagulant, For Coagulation, Pack Size: 25 Kg offered by Haryana Agro Industries, Yamuna Nagar, Haryana….
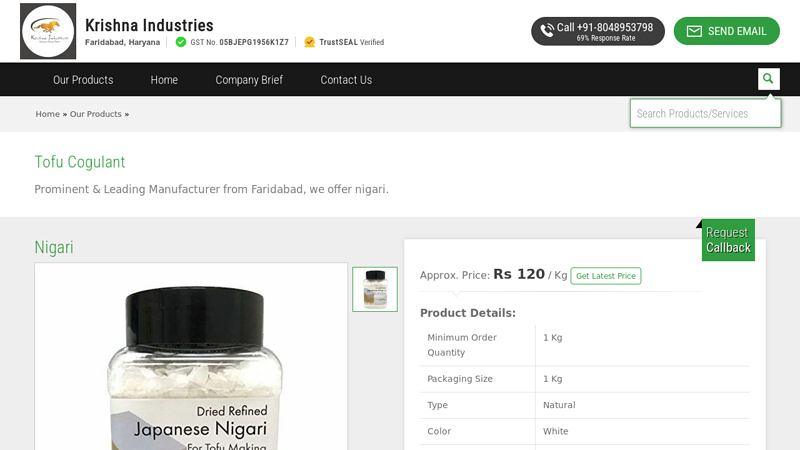
#2 Tofu Cogulant
Domain Est. 2018
Website: shrikrishnaindustry.com
Key Highlights: We are able to provide an excellent quality range of Japanese Nigari Tofu Coagulant. This is an excellent magnesium source. It recharges the ageing human body….
#3 Magnesium Chloride / Nigari Flakes, Food Grade
Domain Est. 2011
#4 BANRAI Coagulant for DIY Tofu “JUN
Domain Est. 2011
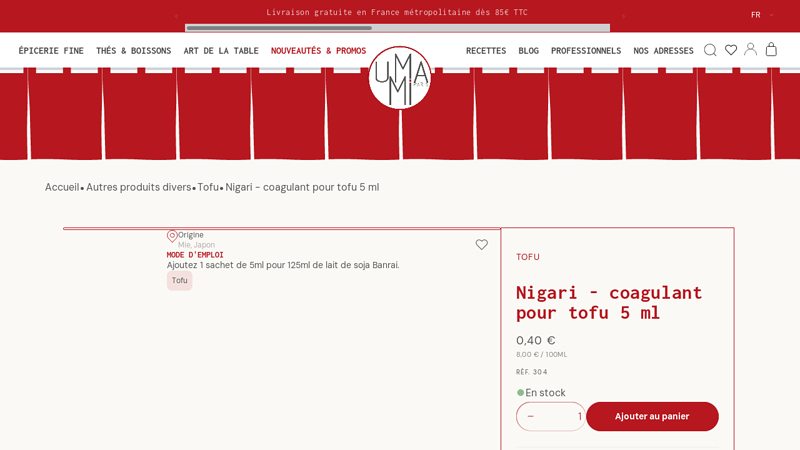
#5 Nigari – Tofu Coagulant 5 ml
Domain Est. 2013
#6 Nigari
Domain Est. 2014
Website: sanlinxusa.com
Key Highlights: In stock 2–5 day deliveryNatural ocean nigari (magnesium chloride) is often praised for making the best-tasting tofu. Ours comes in a hefty 8 ounce, zip-sealed package – enough to …
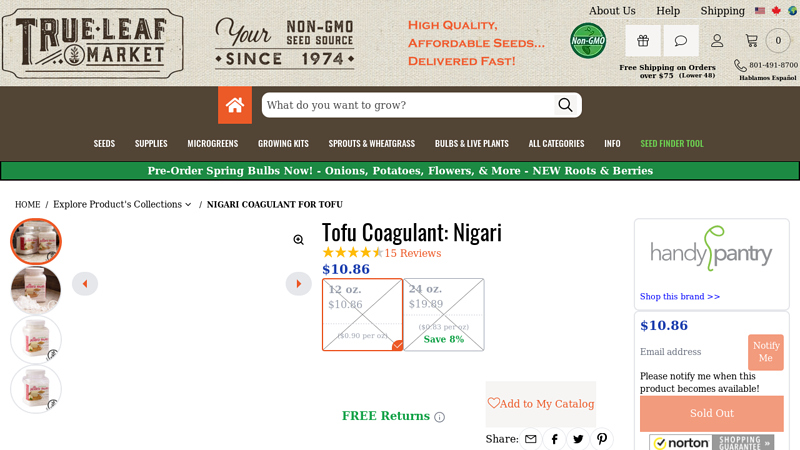
#7 Tofu Coagulant: Nigari
Domain Est. 2015
#8 Tofu Coagulant, Nigari, Bittern, Magnesium Salt
Domain Est. 2020
#9 Natural liquid Nigari
Website: sahu.vn
Key Highlights: The main chemical formula of Natural Liquid Nigari is MgCl(OH)x, giving it a bitter and astringent taste. It serves as a natural coagulant for making tofu….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tofu Coagulant Nigari

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tofu Coagulant Nigari
The global market for tofu coagulant nigari is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by rising health consciousness, plant-based diet adoption, and increased demand for clean-label food ingredients. Nigari, a natural coagulant derived from seawater and rich in magnesium chloride, continues to gain preference over synthetic alternatives due to its minimal processing and traditional appeal.
Key Market Drivers:
-
Expansion of Plant-Based Food Industry:
The surge in veganism and flexitarian diets is fueling tofu consumption worldwide. As a critical ingredient in premium tofu production, nigari benefits directly from this trend. By 2026, the global plant-based food market is projected to exceed $100 billion, with Asia-Pacific and North America leading in tofu demand. -
Clean-Label and Organic Food Movement:
Consumers are increasingly favoring natural and minimally processed food additives. Nigari’s status as a traditional, non-GMO, and chemical-free coagulant aligns with clean-label demands, particularly in Europe and North America. This is encouraging tofu manufacturers to switch from glucono delta-lactone (GDL) or calcium sulfate to nigari in premium product lines. -
Regional Production and Supply Chain Refinement:
Japan remains a dominant producer and exporter of high-purity nigari, but emerging suppliers in China, South Korea, and Southeast Asia are enhancing production capacity and quality control. By 2026, localized sourcing and improved logistics are expected to reduce costs and increase availability in developing markets. -
Innovation in Formulations and Applications:
Manufacturers are developing standardized liquid and powdered nigari formulations to improve consistency in tofu texture and yield. Research into optimized magnesium chloride ratios and hybrid coagulant blends may expand nigari’s use beyond traditional tofu into functional dairy alternatives and fermented soy products. -
Sustainability and Seawater Resource Management:
As environmental scrutiny increases, sustainable harvesting of seawater for nigari production is becoming a competitive differentiator. Companies investing in eco-friendly evaporation and purification technologies are likely to gain market share, particularly among ESG-conscious buyers.
Market Challenges:
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in seawater mineral content and energy costs for evaporation can impact nigari pricing.
- Competition from Alternative Coagulants: While natural, nigari may face competition from innovative plant-derived coagulants and fermentation-based solutions entering the market.
Outlook:
By 2026, the global tofu coagulant nigari market is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2%, reaching an estimated value of USD 180–200 million. Asia-Pacific will remain the largest consumer, with Japan, China, and South Korea driving demand, while North America and Western Europe exhibit the fastest growth due to expanding plant-based food sectors.
In summary, nigari’s alignment with health, sustainability, and authenticity trends positions it favorably in the evolving tofu and alternative protein landscape, ensuring its relevance and growth through 2026 and beyond.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Tofu Coagulant Nigari (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality Nigari, the traditional coagulant used in tofu production, requires careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to inconsistent tofu output, regulatory issues, or even legal disputes. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Product Quality and Purity
One of the most frequent challenges in sourcing Nigari is ensuring consistent quality and purity. Nigari is primarily composed of magnesium chloride extracted from seawater, but its composition can vary significantly.
- Inconsistent Mineral Profile: Low-grade or improperly processed Nigari may contain variable levels of magnesium chloride, along with excessive amounts of sodium chloride, sulfates, or other trace minerals. This inconsistency affects tofu texture, yield, and flavor, leading to batch-to-batch variability.
- Contaminants: Sourcing from unverified suppliers may result in Nigari contaminated with heavy metals (e.g., lead, arsenic) or pollutants, especially if harvested from polluted waters. This poses health risks and may violate food safety regulations (e.g., FDA, EU standards).
- Adulteration: Some suppliers may dilute Nigari with salt or other fillers to reduce costs. Without proper testing (e.g., HPLC, ICP-MS), such adulteration is difficult to detect, compromising tofu quality.
Best Practice: Require third-party lab certifications (e.g., Certificate of Analysis) verifying magnesium chloride content, absence of contaminants, and compliance with food-grade standards (e.g., FCC, JECFA). Conduct regular supplier audits and batch testing.
Misrepresentation and Labeling Issues
The term “Nigari” is often used loosely, leading to confusion and potential mislabeling.
- Synthetic vs. Natural Nigari: Some products labeled as Nigari are actually re-crystallized magnesium chloride derived from mineral sources rather than evaporated seawater. While functionally similar, purists and certain markets may consider this inauthentic, impacting brand reputation.
- Grade and Form Confusion: Nigari is available in liquid, flake, and powder forms, each with different concentrations and handling requirements. Mislabeling or unclear specifications can result in incorrect usage and suboptimal coagulation.
Best Practice: Clearly define sourcing specifications, including origin (natural seawater), form, concentration (e.g., 95% MgCl₂), and processing method. Verify labeling claims with documentation.
Intellectual Property and Brand Authenticity Risks
While Nigari itself is a generic substance, branding and proprietary blends can involve intellectual property considerations.
- Trademark Infringement: Some companies trademark specific Nigari-based formulations or brand names (e.g., “Nigari Gold,” “Organic Nigari Plus”). Sourcing a product with a similar name or packaging may lead to IP disputes.
- Trade Secret Exposure: If sourcing custom-formulated Nigari blends, ensure supplier agreements include confidentiality clauses to protect your tofu-making process and unique recipes.
- Geographical Indications (GIs): Although rare, certain regions may associate Nigari with specific traditional methods (e.g., Japanese artisanal production). Misrepresenting origin could lead to consumer backlash or legal challenges under fair trade laws.
Best Practice: Conduct due diligence on supplier branding and product names. Use legal agreements to safeguard proprietary information and avoid mimicking established brands.
Supply Chain and Sustainability Concerns
- Unreliable Sourcing: Nigari production depends on seawater availability and evaporation processes. Suppliers in regions prone to climate variability or regulatory changes may face supply disruptions.
- Lack of Traceability: Without transparent supply chains, it’s difficult to verify sustainable harvesting practices or ethical labor standards, which are increasingly important to consumers.
Best Practice: Partner with suppliers who offer traceability, sustainable certifications (e.g., organic, eco-harvested), and long-term supply agreements.
By addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, tofu producers can ensure a reliable, safe, and authentic coagulant supply, supporting consistent product quality and brand integrity.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tofu Coagulant Nigari
Overview
Nigari, a natural coagulant derived from seawater and primarily composed of magnesium chloride, is widely used in the production of tofu. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure the safety, quality, and regulatory adherence of Nigari throughout the supply chain. This guide outlines key considerations for the transportation, storage, labeling, and regulatory compliance of Nigari used in food manufacturing.
Regulatory Compliance
Food Safety Standards
Nigari must comply with food safety regulations in the destination market. In the United States, it is regulated by the FDA under the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and must meet specifications in the Food Chemicals Codex (FCC). In the European Union, it falls under Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives and must be approved for use as a coagulant (E511 – magnesium chloride).
Labeling Requirements
Proper labeling is mandatory and must include:
– Product name (“Nigari” or “Magnesium Chloride Solution”)
– Ingredient list
– Net weight or volume
– Name and address of manufacturer/distributor
– Batch number and date marking (use-by or best-before)
– Storage instructions
– Allergen information (if applicable)
– Country of origin
– Regulatory compliance statements (e.g., “Food Grade,” “For Food Use Only”)
Import & Export Documentation
For international trade, ensure the following documents are prepared:
– Certificate of Analysis (CoA) confirming purity and compliance with food-grade standards
– Certificate of Origin
– Commercial Invoice and Packing List
– FDA Prior Notice (for U.S. imports)
– EU Health Certificate (if required)
– Sanitary or Phytosanitary certificates as applicable
Storage & Handling
Storage Conditions
- Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
- Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures
- Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination
- Ideal storage temperature: 15–25°C (59–77°F)
- Protect from freezing, especially for liquid nigari formulations
Shelf Life
- Solid (flaked or powdered) Nigari: Typically 24–36 months when stored properly
- Liquid Nigari: Approximately 12–18 months
- Always observe manufacturer’s expiration date and conduct periodic quality checks
Handling Precautions
- Use clean, food-grade utensils and containers
- Avoid cross-contamination with non-food substances
- Personnel should follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and wear appropriate protective gear when handling bulk quantities
Transportation & Logistics
Packaging Standards
- Use food-grade packaging materials compliant with FDA 21 CFR or EU Regulation 10/2011 on plastic materials
- Common packaging: sealed plastic bags (for flakes/powder), HDPE bottles or drums (for liquid)
- Ensure packaging is leak-proof and resistant to moisture and physical damage
Transport Conditions
- Transport in clean, dry, and odor-free vehicles
- Protect from rain, direct sunlight, and temperature extremes
- For international shipments, comply with International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code if applicable (note: food-grade Nigari is generally non-hazardous but verify classification)
- Maintain segregation from hazardous or contaminating materials
Cold Chain Considerations
- Not typically required for Nigari, but avoid prolonged exposure to high temperatures (>40°C) which may affect stability
- Monitor conditions during long-haul or tropical region shipments
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Supplier Verification
- Source Nigari only from certified suppliers with HACCP, GMP, or ISO 22000 certification
- Conduct regular audits and request updated CoAs with each shipment
Incoming Inspection
- Verify packaging integrity upon receipt
- Check batch numbers, expiration dates, and labeling accuracy
- Perform sensory and basic quality checks (color, odor, texture)
- Retain samples for traceability (minimum 6–12 months)
Traceability System
- Implement a full lot-tracking system from supplier to final product
- Maintain records of receipt, storage, usage, and disposal
- Comply with recall readiness requirements under FSMA or equivalent
Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- Dispose of expired or contaminated Nigari in accordance with local waste regulations
- Do not pour large quantities of liquid Nigari down drains; consult local environmental guidelines
- Packaging should be recycled where possible, following local recycling protocols
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of Nigari ensures the safety and quality of tofu production while meeting global regulatory standards. By adhering to storage, transportation, labeling, and documentation best practices, food manufacturers can maintain supply chain integrity and consumer trust. Regular training and audits are recommended to ensure ongoing compliance.
In conclusion, sourcing tofu coagulant nigari requires careful consideration of purity, origin, form (liquid or powder), and supplier reliability. Nigari, traditionally derived from seawater and rich in magnesium chloride, plays a crucial role in determining the texture and quality of tofu. To ensure consistent results and food safety, it is essential to obtain nigari from reputable suppliers who provide transparent sourcing and quality testing. Whether for commercial production or artisanal tofu making, selecting high-quality, food-grade nigari contributes significantly to producing flavorful, firm, and nutritious tofu. Additionally, understanding regional variations and regulatory standards can further guide effective sourcing decisions in different markets.