The global titanium filter market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-performance filtration solutions across industries such as aerospace, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. According to Grand View Research, the global titanium market size was valued at USD 7.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2024 to 2030, with titanium-based components—especially filtration systems—playing a significant role in this growth. The material’s exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, and durability in extreme environments make it ideal for critical filtration applications. As industries prioritize efficiency, sustainability, and long-term cost savings, the adoption of titanium filters continues to rise. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as leaders, combining advanced engineering, rigorous quality standards, and scalable production capabilities. Based on technological innovation, market presence, and performance metrics, the following eight companies represent the forefront of titanium filter manufacturing worldwide.
Top 8 Titanium Filter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
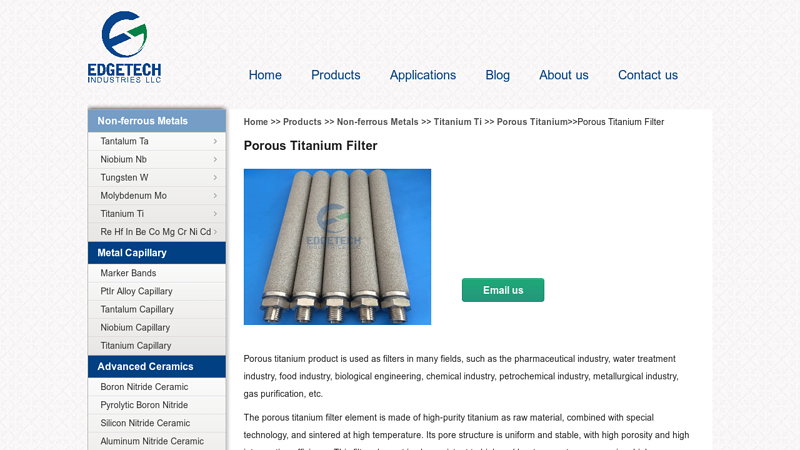
#1 Porous Titanium Filter
Domain Est. 2015
Website: edge-techind.com
Key Highlights: The porous titanium filter element is made of high-purity titanium as raw material, combined with special technology, and sintered at high temperature….
#2 Titanium Filter
Domain Est. 2018
Website: lyfilter.com
Key Highlights: Lvyuan titanium filter housings manufacturer for sea water desalination….
#3 Titanium Filter Manufacturers and Suppliers
Domain Est. 2021
Website: micron-filter.com
Key Highlights: Porous titanium filters are made of ultrapure titanium using special process through sintering. Their porous structure is uniform and stable….
#4 Titanium Dioxide
Domain Est. 2004
Website: clear-edge.com
Key Highlights: Clear Edge offers advanced filter cloth solutions for a variety of pigment applications, including dewatering high solids titanium dioxide (TiO2) slurries….
#5 Titanium Satellite
Domain Est. 2013
Website: titaniumsatellite.com
Key Highlights: Innovation Quality Value. Titanium Satellite is a design, development and retail distribution company with over 35 years of industry experience….
#6 Filson Sintered Titanium
Domain Est. 2016
Website: filsonfilters.com
Key Highlights: Filson excels at manufacturing kinds of sintered titanium filters which are used pure titanium powder with a purity of over 99.4%. Besides, Filson standard ……
#7 Titanium filter element
Domain Est. 2016
Website: giant-metals.com
Key Highlights: Titanium filter element ( including tube and plate type ) is made of high purity titanium powder. · – The pore diameter is uniform, the hole shape is stable and ……
#8 Sintered Titanium Filter
Domain Est. 2020
Website: sinteredfilter.net
Key Highlights: 20 years of experience focusing on the sintered bronze filter, sintered stainless steel filter and sintered plastic filter, more than 10,000+ developed models ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Titanium Filter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Titanium Filters
As we approach 2026, the global market for titanium filters is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand from high-performance industries, and growing emphasis on sustainability. Here’s an analysis of the key trends expected to shape the titanium filter market in 2026:
1. Strong Demand from Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense sectors will remain primary drivers of titanium filter adoption. Titanium’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it ideal for critical filtration applications in jet engines, auxiliary power units (APUs), and hydraulic systems. With the projected recovery and expansion of global air travel and continued military modernization programs (especially in the U.S., China, and Europe), demand for high-reliability titanium filters is expected to rise steadily through 2026.
2. Growth in the Chemical and Petrochemical Industries
Titanium filters are increasingly preferred in aggressive chemical processing environments due to their outstanding resistance to acids, chlorides, and high temperatures. As chemical manufacturers prioritize operational safety, longer equipment lifecycles, and reduced maintenance downtime, the shift from stainless steel to titanium-based filtration systems will accelerate. This trend is particularly evident in chlorine production, desalination plants, and offshore oil & gas platforms.
3. Rise of Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
By 2026, additive manufacturing (AM) will play a transformative role in titanium filter production. 3D printing enables the creation of complex, customized filter geometries—such as graded porosity structures and optimized flow paths—that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional sintering methods. This innovation will enhance filtration efficiency, reduce pressure drops, and support lightweighting in end applications. Major aerospace and medical firms are expected to adopt AM-produced titanium filters at scale, driving innovation and reducing production lead times.
4. Expansion in Medical and Biotech Applications
The medical device sector will see growing use of titanium filters, especially in implantable devices, surgical tools, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Titanium’s biocompatibility, sterilizability, and corrosion resistance make it suitable for sterile filtration in vaccine production and cell therapy processes. Regulatory approvals for advanced titanium-based filtration systems in GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) environments are expected to increase, supporting market expansion in life sciences.
5. Sustainability and Lifecycle Cost Advantages
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals will further boost the appeal of titanium filters. Despite higher initial costs, their extended service life, minimal maintenance, and recyclability offer superior total cost of ownership compared to alternatives. Industries facing stringent emissions standards (e.g., power generation, marine) will increasingly adopt titanium filters in gas and liquid purification systems to meet compliance targets and reduce environmental impact.
6. Regional Market Developments
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): China, Japan, and India will lead regional growth, driven by expanding aerospace manufacturing, chemical production, and government investments in clean energy infrastructure.
- North America & Europe: Mature markets will focus on technological innovation and retrofitting existing systems with high-efficiency titanium filters, supported by strong R&D ecosystems and regulatory frameworks.
7. Supply Chain and Material Challenges
While demand grows, the market may face constraints due to the high cost and energy-intensive processing of titanium. Efforts to improve titanium powder recycling, develop alternative alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V with enhanced filtration properties), and secure supply chains will be critical to sustaining growth into 2026 and beyond.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the titanium filter market will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and increased adoption across high-value industries. Advances in manufacturing technology, coupled with performance and sustainability benefits, will solidify titanium’s position as a premium filtration material. Companies investing in R&D, strategic partnerships, and sustainable production methods will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Titanium Filters (Quality & Intellectual Property)
Sourcing titanium filters—commonly used in aerospace, medical, chemical processing, and high-performance filtration applications—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly failures, compliance issues, or legal disputes. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Compromised Material Quality and Certification
One of the most frequent issues is receiving substandard titanium that does not meet required specifications (e.g., ASTM B348, AMS 4928). Pitfalls include:
- Lack of Mill Test Certificates (MTCs): Suppliers may provide filters without proper traceability or certified material test reports, making it difficult to verify alloy composition, mechanical properties, or corrosion resistance.
- Use of Recycled or Downgraded Titanium: Some suppliers blend lower-grade or recycled titanium to cut costs, which can compromise filter strength, porosity consistency, and longevity.
- Inconsistent Porosity and Pore Size: Poor manufacturing control leads to non-uniform pore distribution, reducing filtration efficiency and potentially causing premature failure.
Best Practice: Always require full material traceability, third-party lab testing, and compliance with relevant industry standards.
2. Inadequate Manufacturing Process Controls
The fabrication method (e.g., sintering, electron beam welding, additive manufacturing) significantly impacts filter performance. Common issues include:
- Poor Sintering Techniques: Inconsistent temperature or pressure during sintering can create weak spots or uneven pore structures.
- Welding Defects: Improper welding (e.g., porosity, cracking) in assembled filter elements can lead to leaks or structural failure under pressure.
- Surface Contamination: Residual oils, oxides, or foreign particles introduced during manufacturing can degrade biocompatibility or chemical resistance.
Best Practice: Audit supplier facilities or require process validation data (e.g., SEM imaging, pressure decay tests) to ensure consistent production quality.
3. Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Titanium filter designs often involve proprietary engineering—especially in aerospace, medical devices, or custom filtration systems. Pitfalls include:
- Unlicensed Replication: Suppliers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, may copy patented designs or reverse-engineer OEM filters without authorization.
- Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts: Failure to include clear IP ownership, confidentiality, and non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) can result in design theft or unauthorized resale.
- Gray Market Goods: Purchasing from unauthorized distributors may result in counterfeit or diverted genuine products, voiding warranties and risking IP litigation.
Best Practice: Conduct due diligence on supplier legitimacy, secure IP rights in contracts, and work with trusted partners who respect design patents and trade secrets.
4. Misaligned Specifications and Application Requirements
Sourcing filters based solely on price or generic specs can lead to mismatched performance. Pitfalls include:
- Incorrect Grade Selection: Using Ti-6Al-4V instead of commercially pure titanium (Grades 1–4) in corrosive environments may lead to galvanic or stress corrosion issues.
- Overlooking Environmental Factors: Filters may fail if not rated for temperature, pressure cycles, or chemical exposure specific to the application.
- Insufficient Testing Data: Suppliers may provide theoretical performance data instead of real-world validation under operational conditions.
Best Practice: Define detailed technical requirements upfront and require performance testing under simulated use conditions.
5. Supply Chain Transparency and Counterfeit Risk
The titanium supply chain can be complex and opaque, increasing the risk of counterfeit or non-conforming materials.
- Unverified Sub-Tier Suppliers: Raw material sources may be hidden, making it hard to confirm titanium origin or processing history.
- Fake Certifications: Some suppliers provide forged MTCs or false compliance claims.
- Geopolitical and Regulatory Risks: Sourcing from regions with sanctions or unreliable quality oversight increases exposure to compliance violations.
Best Practice: Implement supply chain mapping, use accredited certification bodies (e.g., NADCAP), and conduct on-site audits when feasible.
Conclusion: To mitigate risks when sourcing titanium filters, prioritize suppliers with verifiable quality systems (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100), enforce strong IP protections, and demand full transparency from raw material to finished product. Investing in due diligence upfront prevents costly failures, legal exposure, and operational downtime.
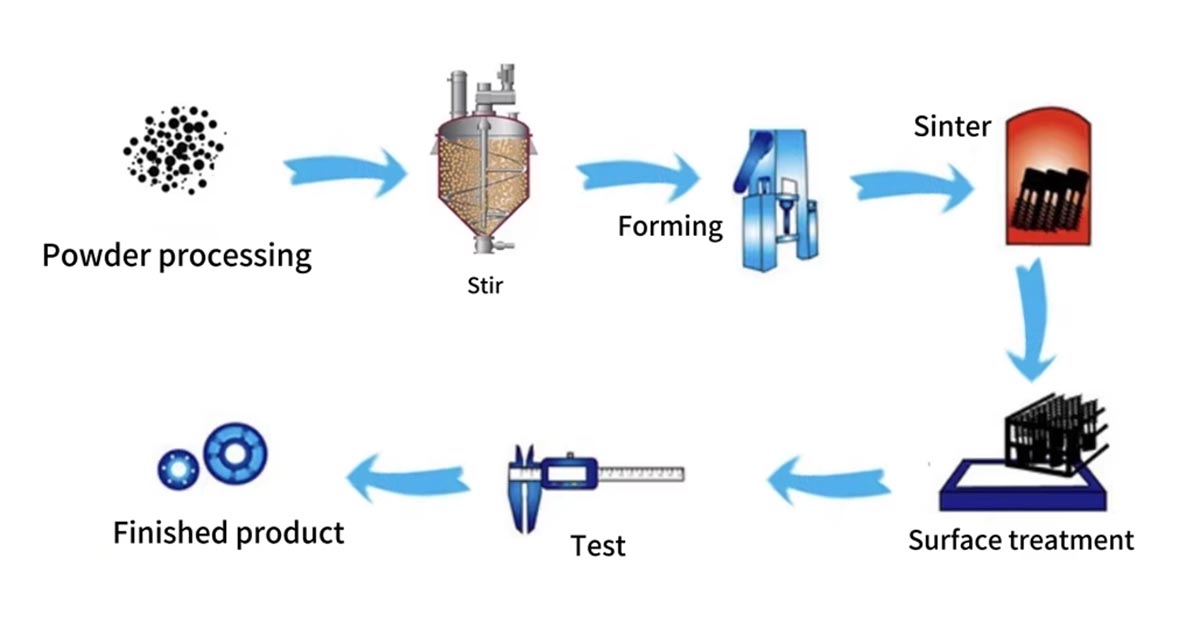
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Titanium Filter
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling, transportation, and use of titanium filters. Adherence to these guidelines ensures operational integrity, regulatory compliance, and product longevity.
Regulatory Compliance
Titanium filters, particularly those used in high-purity or critical applications (e.g., pharmaceutical, aerospace, semiconductor), are subject to various international and industry-specific regulations. Key compliance areas include:
- Material Certification: Ensure all titanium filters come with certified material test reports (CMTRs) confirming compliance with ASTM B265 (Standard Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Strip, Sheet, and Plate) or equivalent standards.
- REACH and RoHS Compliance: Verify that the titanium and any associated components (e.g., coatings, binders) comply with EU regulations regarding restricted substances.
- FDA Compliance (if applicable): For filters used in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical processing, confirm compliance with FDA 21 CFR for materials in contact with consumables.
- Export Controls: Titanium, especially in certain forms or purities, may be subject to export regulations (e.g., ITAR, EAR). Confirm licensing requirements when shipping internationally.
Transportation & Handling
Proper handling and transportation are critical to prevent contamination and physical damage:
- Packaging: Titanium filters must be packaged in clean, anti-static, and moisture-resistant materials. Use sealed plastic bags with desiccants for moisture-sensitive applications.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with contents, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Protect from Moisture”), and relevant hazard symbols if applicable.
- Shipping Environment: Avoid exposure to corrosive atmospheres, extreme temperatures, or high humidity during transit. Use climate-controlled shipping when necessary.
- Handling Precautions: Use clean gloves to prevent oil and salt contamination from skin contact. Avoid contact with carbon steel tools to prevent iron contamination and pitting corrosion.
Storage Requirements
- Environment: Store in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (15–25°C, <50% RH recommended).
- Separation: Keep titanium filters isolated from dissimilar metals (especially carbon steel, copper) to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Shelf Life: While titanium itself does not degrade, protective packaging and filter integrity should be inspected periodically. Follow manufacturer recommendations for maximum storage duration.
Installation & Operational Compliance
- Pre-Installation Cleaning: Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning procedures (e.g., ultrasonic cleaning in solvent or deionized water) to remove handling residues.
- Compatibility Verification: Ensure compatibility with process fluids, temperatures, and pressures. Titanium is highly corrosion-resistant but can react with strong acids (e.g., hydrofluoric, sulfuric at high concentrations).
- Documentation: Maintain records of installation, maintenance, and performance testing to support audit and quality assurance requirements.
Maintenance & Disposal
- Cleaning Procedures: Use only approved cleaning agents (avoid chlorides and fluorides). Validate cleaning methods to ensure no degradation of filter integrity.
- Inspection Regimen: Implement routine inspections for clogging, erosion, or structural damage. Use non-destructive testing (e.g., pressure decay, visual inspection under magnification) as needed.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Spent titanium filters are generally non-hazardous and recyclable. Recycle through certified metal reclamation facilities to support sustainability and comply with waste regulations (e.g., WEEE, local hazardous waste rules if contaminated).
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain comprehensive documentation throughout the product lifecycle, including:
- Batch numbers and serial numbers
- Certificates of Conformance (CoC) and Material Test Reports (MTR)
- Shipping and handling logs
- Installation, maintenance, and inspection records
- Disposal or recycling certificates
Proper traceability supports quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) and regulatory audits.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the reliable performance of titanium filters while meeting all applicable legal, safety, and environmental standards.
In conclusion, sourcing titanium filters requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Titanium is an ideal material for filtration applications due to its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength-to-density ratio, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. When sourcing, it is essential to evaluate suppliers based on material quality, manufacturing standards (such as ASTM or ISO certifications), customization capabilities, and traceability.
Additionally, understanding the specific application—whether in aerospace, medical, chemical processing, or water treatment—will guide the selection of pore size, micron rating, filter configuration, and surface finish. While titanium filters may have a higher initial cost compared to other materials, their durability and low maintenance needs offer long-term savings and operational efficiency.
Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers, conducting rigorous quality testing, and considering total cost of ownership rather than upfront price will lead to a successful sourcing strategy. Ultimately, investing in high-quality titanium filters enhances system performance, extends service life, and supports safety and sustainability goals across critical industries.