The global tissue paper market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising hygiene awareness, urbanization, and increasing demand across household, commercial, and healthcare sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global tissue paper market size was valued at USD 79.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. A key differentiator in this competitive landscape is branded and printed tissue paper, which appeals to consumer preferences for aesthetics and premium branding. Printed tissue products—ranging from embossed designs to custom logos—are gaining traction among retailers and private-label brands seeking to enhance perceived value and brand recognition. This growing demand has propelled the emergence of specialized tissue paper printing manufacturers capable of high-quality, efficient, and scalable print solutions. Based on production capacity, technological innovation, geographic reach, and client portfolio, the following eight manufacturers stand out as leaders in the tissue paper printing space.
Top 8 Tissue Paper Printing Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Central National Gottesman Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: cng-inc.com
Key Highlights: At CNG, our brands and companies sell, market and distribute paper for printing, packaging for shipping, tissue for cleaning, and a range of office supplies….
#2 First Quality
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1989
Website: firstquality.com
Key Highlights: A leading manufacturer of everyday essentials for personal and household care, we’re a family-owned business founded in 1989….
#3 International Paper
Domain Est. 1997
Website: internationalpaper.com
Key Highlights: We transform renewable resources into innovative and sustainable packaging solutions, corrugated cardboard boxes, pulp and paper products, ……
#4 Seaman Paper
Domain Est. 1999
Website: seamanpaper.com
Key Highlights: Seaman Paper provides eco-friendly commercial tissue paper customized packaging alternatives to single-use plastic packaging for businesses….
#5 Custom Tissue Papers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: fastprinting.com
Key Highlights: 7-day returnsFast Printing USA offers a wide range of high quality Tissue Paper Printing Services and more⭐️ Customise your design today….
#6 Nine Dragons Paper (Holdings) Limited
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ndpaper.com
Key Highlights: Overview · Products · Containerboard Products · Printing and Writing Paper · Specialty Paper · High Performance Corrugated Cardboard Products ……
#7 Clearwater Paper Corporation
Domain Est. 2008
Website: clearwaterpaper.com
Key Highlights: We are a premier independent supplier of paperboard packaging products to North American converters. Our team produces high-quality paperboard….
#8 Twin Rivers Paper Company Specialty and Consumer Packaging
Domain Est. 2010
Website: twinriverspaper.com
Key Highlights: Our broad range of highly functional coated and uncoated papers are designed for packaging applications that require oil and grease resistance….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tissue Paper Printing

2026 Market Trends in Tissue Paper Printing: Key Developments and Projections
The tissue paper printing market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increasing environmental awareness. As sustainability, customization, and digital integration gain prominence, manufacturers and brands must adapt to remain competitive. Below are the key trends expected to shape the tissue paper printing landscape in 2026.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Printing Practices
Environmental concerns will continue to dominate the tissue paper industry in 2026. Consumers and regulatory bodies are demanding greener production methods, pushing manufacturers toward sustainable inks, biodegradable dyes, and renewable energy-powered printing processes. Water-based and soy-based inks are expected to replace solvent-based alternatives, reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Additionally, demand for FSC-certified and recycled tissue substrates will grow, with printed designs increasingly used to highlight a brand’s eco-commitment.
Digital Printing for Customization and Short Runs
Digital printing technology will play a pivotal role in 2026 by enabling high-quality, on-demand customization with minimal waste. Unlike traditional flexographic printing, digital methods allow for variable data printing, vibrant color reproduction, and rapid design changes—ideal for limited editions, seasonal campaigns, and personalized packaging. This flexibility supports direct-to-consumer (DTC) models and private-label growth, especially in the premium and luxury tissue segments.
Smart Packaging and QR Code Integration
Tissue paper printing will increasingly incorporate smart features such as QR codes, NFC tags, and scannable designs. By 2026, printed tissues may serve as interactive touchpoints, linking consumers to brand stories, sustainability certifications, or digital promotions. This trend aligns with the broader movement toward connected packaging and enhances traceability across supply chains, particularly for eco-conscious buyers.
Premiumization and Aesthetic Innovation
Consumers are willing to pay more for aesthetically pleasing and premium tissue products, especially in hospitality, retail, and gift packaging. In 2026, expect intricate patterns, metallic finishes, embossing, and multi-color prints to become more common. Brands will use sophisticated printing techniques to convey luxury, with an emphasis on minimalist design, artisanal motifs, and culturally inspired artwork to differentiate products in crowded markets.
Regional Market Growth and Localization
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will drive volume growth, while North America and Europe focus on innovation and sustainability. Localization of designs—featuring regional art, languages, and cultural themes—will be critical for brand resonance. Printing technologies will adapt to support regional preferences, with localized production facilities reducing lead times and carbon footprints.
Regulatory and Compliance Pressures
By 2026, stricter global regulations on packaging waste, ink safety, and carbon emissions will influence tissue printing practices. Compliance with EU Green Deal standards, FDA food-contact regulations, and extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes will require printed tissue producers to adopt transparent sourcing and safer chemical formulations. This will accelerate the shift toward non-toxic, compostable printing solutions.
In conclusion, the 2026 tissue paper printing market will be defined by sustainability, digital agility, and enhanced consumer engagement. Companies that invest in eco-conscious printing technologies, embrace customization, and integrate smart features will be best positioned to lead in an increasingly competitive and responsible marketplace.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Tissue Paper Printing: Quality and Intellectual Property Issues
Sourcing tissue paper printing, especially for branded packaging, promotional use, or private-label products, involves several risks that, if overlooked, can lead to reputational damage, legal issues, and financial losses. Two critical areas where companies often encounter problems are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) violations. Understanding these pitfalls helps buyers make informed decisions and implement effective risk mitigation strategies.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Print Registration and Color Accuracy
One of the most frequent quality issues in tissue paper printing is misalignment of printed patterns (poor registration) and color variation between batches. This often occurs due to low-grade printing equipment, uncalibrated machinery, or lack of quality control processes at the supplier’s facility. Buyers may receive samples with vibrant, precise prints, only to get bulk orders with blurred images or off-tone colors.
Tip: Request production samples from the actual batch and insist on standardized color matching (e.g., Pantone references) with proper tolerances defined.
Poor Ink Adhesion and Rub-Off
Low-quality inks or improper drying processes can result in ink that rubs off easily, especially when the tissue paper is folded or used. This not only affects the visual appeal but can also raise hygiene concerns, particularly in food-related packaging.
Tip: Conduct rub tests (e.g., finger-rub or machine-based abrasion tests) during quality inspections to verify ink durability.
Substandard Base Tissue Quality
The foundation of printed tissue paper is the base sheet, which can vary significantly in thickness (grammage), softness, strength, and absorbency. Some suppliers may substitute lower-grade tissue to cut costs, leading to tearing, pilling, or poor print performance.
Tip: Specify technical requirements (e.g., GSM, tensile strength) and conduct physical testing on received goods.
Lack of Environmental and Safety Compliance
Printed tissue paper used in food packaging or consumer goods must comply with food-safe ink standards (e.g., FDA, EU Framework Regulation). Some suppliers may use non-compliant inks containing heavy metals or volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Tip: Require third-party test reports (e.g., SGS, Intertek) confirming compliance with relevant safety standards.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Branded Designs or Copyrighted Artwork
Suppliers in certain regions may reproduce well-known patterns, logos, or copyrighted designs without proper licensing. When buyers unknowingly source such tissue paper, they risk legal action for trademark or copyright infringement, even if they were unaware of the violation.
Tip: Only work with suppliers who can provide proof of IP clearance for any pre-existing designs and sign IP indemnity clauses in contracts.
Reverse Engineering and Design Theft
Sharing custom design files with overseas suppliers can expose a buyer’s unique artwork to theft. Unscrupulous manufacturers may sell the designs to competitors or produce unauthorized copies for third parties.
Tip: Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), watermark design proofs, and limit the distribution of high-resolution files.
Lack of Trademark Protection in Sourcing Countries
Even if a design is trademarked in the buyer’s home country, it may not be protected in the manufacturing country. This allows local suppliers to legally replicate and export printed tissue bearing those designs.
Tip: Register trademarks and designs in key manufacturing and export jurisdictions to strengthen legal recourse.
Inadequate Contractual Safeguards
Many sourcing agreements fail to clearly define ownership of custom designs, permitted usage rights, and penalties for IP misuse. This ambiguity can lead to disputes or misuse of intellectual property after production.
Tip: Include explicit IP clauses in contracts specifying design ownership, permitted use, and audit rights.
Conclusion
Avoiding pitfalls in tissue paper printing sourcing requires due diligence in both quality assurance and legal protection. Conducting thorough supplier audits, enforcing strict quality control protocols, and securing IP rights through contracts and registrations are essential steps. Proactive risk management not only ensures product integrity but also protects brand reputation and legal standing in global markets.
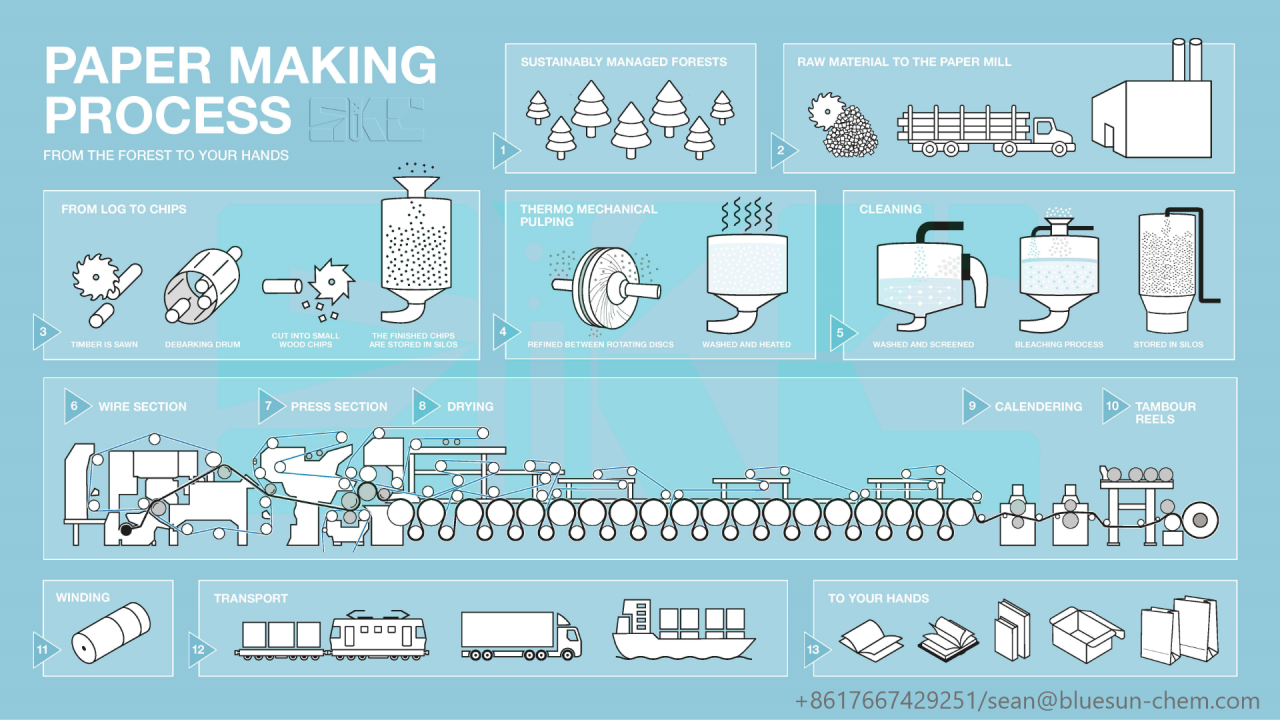
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tissue Paper Printing
This guide outlines essential logistics considerations and compliance requirements for businesses involved in the printing of tissue paper products, including packaging, decorative tissues, and specialty printed tissues.
Regulatory Compliance
Food Contact Compliance
When tissue paper is intended for direct or indirect food contact (e.g., sandwich wraps, bakery liners, or food packaging), compliance with food safety regulations is mandatory. In the U.S., this falls under FDA 21 CFR regulations, particularly for indirect food additives. In the EU, compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and specific measures like Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 for plastic materials (if coated or laminated) or Commission Regulation (EU) No 2020/1245 for paper and board must be ensured. Manufacturers must use inks, coatings, and adhesives that are food-safe and migration-tested.
Chemical Restrictions (REACH, RoHS, Prop 65)
Ensure all inks, dyes, and processing chemicals comply with international chemical regulations:
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Confirm that substances used (e.g., solvents, pigments) are registered and not on the SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) list.
– RoHS (EU & others): Restriction of Hazardous Substances. While primarily for electronics, some printed tissues used in electronic packaging may need to comply.
– California Proposition 65: Products sold in California must not contain listed carcinogens or reproductive toxins above safe harbor levels. Labeling may be required if applicable.
Labeling & Claims Compliance
Environmental claims such as “biodegradable,” “compostable,” or “recyclable” must be substantiated and follow guidelines from authorities like the FTC (Green Guides) in the U.S. or the EU’s Green Claims Directive. Misleading claims can result in penalties. Proper labeling of recycled content (e.g., percentage) should meet ISO 14021 standards.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
FSC/PEFC Certification
To demonstrate responsible sourcing of paper fiber, tissue paper should ideally be certified under Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC) standards. Chain-of-custody certification is required to make certified claims on printed tissue products.
Recyclability & Compostability Standards
Printed tissue must not hinder recyclability or compostability. Inks and coatings should be water-based or approved for composting under standards such as:
– EN 13432 (EU): For industrial compostability.
– ASTM D6400 (U.S.): Standard specification for compostable plastics.
Avoid heavy metal-based pigments and non-degradable laminates.
Waste & Emissions Control
Printing facilities must comply with local environmental regulations regarding VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions, wastewater discharge, and solid waste disposal. Use of low-VOC or VOC-free inks and proper solvent recovery systems are recommended.
Logistics & Supply Chain Management
Ink & Material Sourcing
Source inks and additives from suppliers providing full compliance documentation (e.g., Safety Data Sheets, Statements of Compliance). Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certifications. Maintain traceability for raw materials throughout the supply chain.
Storage & Handling
Store tissue paper in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent moisture absorption and maintain print quality. Roll packaging should protect against dust and physical damage. Printed tissues must be stored separately from non-compliant materials to avoid contamination.
Transportation & Packaging
Use protective packaging (e.g., stretch-wrapped pallets, moisture barriers) during transit. Ensure compliance with regulations for international shipping, including:
– ISPM 15: For wooden pallets in international trade.
– IMDG Code / IATA Regulations: If transporting hazardous inks (e.g., solvent-based).
Proper labeling of packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”) is essential.
Inventory Management
Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) practices to prevent aging of tissue rolls and inks. Monitor shelf life of printed products, especially those with food contact or compostability claims, which may degrade over time.
Quality Assurance & Testing
Batch Testing & Documentation
Conduct regular batch testing for:
– Migration of substances (for food contact applications)
– Color fastness and print durability
– Microbial contamination (if applicable)
Maintain a Quality Management System (QMS) aligned with ISO 9001 standards.
Third-Party Certification
Engage accredited laboratories for compliance testing. Obtain certifications such as:
– EU Hygienic Compliance Certificates
– FDA Letter of Guarantee
– OK Compost or Seedling Logo (for compostable claims)
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the logistics and compliance landscape in tissue paper printing requires attention to regulatory details, sustainable practices, and robust supply chain management. Proactive compliance not only mitigates legal risk but also enhances brand reputation and market access globally. Regular audits, staff training, and supplier collaboration are key to maintaining standards.
In conclusion, sourcing printed tissue paper requires a careful balance of quality, cost, sustainability, and supplier reliability. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who can deliver consistent print quality, color accuracy, and material durability while adhering to environmental standards and ethical production practices. Evaluating factors such as customization options, minimum order quantities, lead times, and compliance with industry regulations will ensure a smooth and efficient supply chain. By prioritizing both performance and sustainability, businesses can source printed tissue paper that not only enhances product presentation but also aligns with brand values and customer expectations. Ultimately, a well-considered sourcing strategy contributes to enhanced customer satisfaction and long-term business success.