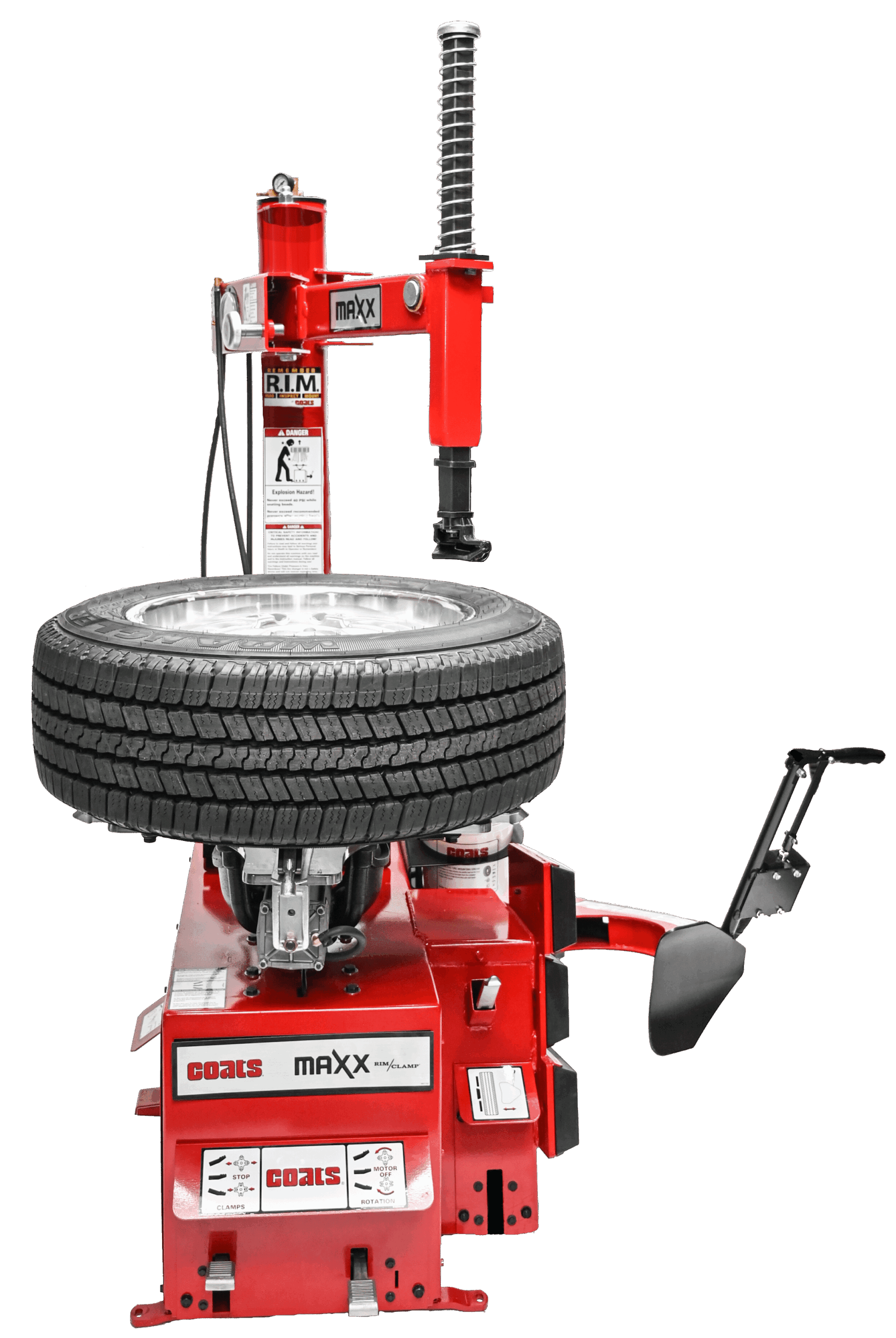
The global tire changer market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising vehicle ownership, increased demand for automotive maintenance equipment, and the expansion of tire service centers worldwide. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global automotive tire market size was valued at USD 139.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory directly fuels demand for advanced tire servicing tools, including automated and semi-automated tire changers. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects strong expansion in the automotive aftermarket segment, noting that increasing vehicle fleet sizes and the need for efficient maintenance solutions are key drivers for equipment adoption. As repair shops and service centers seek faster, safer, and more reliable tire-changing solutions, manufacturers are investing in innovation, automation, and ergonomic design. In this evolving landscape, a handful of companies have emerged as leaders, setting industry benchmarks for performance, durability, and technological integration. Here’s a look at the top 8 tire changer manufacturers shaping the future of automotive service equipment.
Top 8 Tire Changer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tire Changers & Tire Mounters by Ranger Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bendpak.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryOur state-of-the-art tire changer design offers cutting-edge technology and advanced features to make this one of the most profitable pieces of wheel service ……
#2 Corghi Usa Inc.
Domain Est. 2009
Website: corghiusa.us
Key Highlights: All Tire Changers, Balancers, Alignment, and HD equipment are IN STOCK! From entry level, to basic, to fully automatic, to diagnostic! NO NEED TO WAIT 60-120 ……
#3 Hunter Tire Changers
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hunter.com
Key Highlights: Whether you’re looking for a table-top, center-clamp, or fully-automatic tire changer, Hunter offers powerful tire changers to meet any need….
#4 Automotive Equipment
Domain Est. 1996
Website: johnbean.com
Key Highlights: John Bean® is an industry leader in automotive equipment. Browse our line of modern Tire Changers, Auto Lifts, Wheel Balancers and more….
#5 Tire Changers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: eagleequip.com
Key Highlights: Tire Changer Model ETC-590. $6,856.92. Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page. Tire Changer Model ……
#6 Tire Machines
Domain Est. 2016
Website: hofmann-equipment.com
Key Highlights: At Hofmann we offer premiere wheel service equipment including our line of innovative tire machines with tilt tower, leverless, swing arm, or heavy-duty ……
#7 Coats Company
Domain Est. 2022
Website: coatscompany.com
Key Highlights: Coats Company offers premium tire changers, wheel balancers, and auto lifts, all American-made for precision, durability, and efficiency in professional ……
#8 M&B Engineering
Website: mbengineering.info
Key Highlights: A wide range of our tire changers and wheel balancers for cars. A big thank you to everyone who visited our stand! See you at the next event!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tire Changer

H2 2026 Market Trends for Tire Changers
The tire changer market in the second half of 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving vehicle designs, and shifting service demands. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Rise of EV-Specific Tire Changers:
With electric vehicle (EV) adoption accelerating globally, tire changers are being redesigned to handle the unique challenges posed by EVs—higher vehicle weights, larger wheels, and low-profile tires prone to bead damage. By H2 2026, expect widespread availability of tire changers with enhanced clamping force, soft-jaw technologies, and intelligent torque control to prevent rim damage on expensive alloy wheels common in EVs.
2. Integration of Smart Technology and IoT:
Tire changers are becoming smarter, with built-in sensors, wireless connectivity, and integration into shop management systems. In H2 2026, leading models will offer real-time diagnostics, automatic calibration, usage analytics, and remote monitoring. This enables predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves technician efficiency—key for high-volume service centers.
3. Emphasis on Technician Safety and Ergonomics:
As labor shortages persist, retaining skilled technicians becomes critical. Tire changers in 2026 will increasingly feature ergonomic designs—lower operating heights, reduced physical strain, and automated functions (e.g., automatic bead breaking and mounting). Safety interlocks and AI-assisted alignment systems will minimize the risk of injury, appealing to safety-conscious fleets and independent shops alike.
4. Growth in Mobile and Compact Solutions:
The demand for mobile tire service continues to rise, fueled by convenience-driven consumers and fleet maintenance needs. By H2 2026, expect innovation in portable, lightweight tire changers with high performance, powered by efficient electric motors and battery systems. These units will support both passenger vehicles and light commercial EVs.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency:
Environmental regulations and operational cost concerns are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient tire changers. Airless and low-energy hydraulic systems, along with recyclable components, will become more common. Service centers aiming for green certifications will prioritize eco-friendly equipment, influencing procurement decisions.
6. Consolidation and Aftermarket Service Expansion:
The market may see consolidation among equipment manufacturers, with larger players acquiring niche innovators. Simultaneously, the aftermarket service segment—refurbished units, upgrades, and parts—will grow as cost-conscious operators seek value. OEMs will expand service networks to support longer equipment lifecycles.
Conclusion:
In H2 2026, the tire changer market will be defined by intelligence, specialization, and adaptability. Equipment must align with the EV revolution, support technician well-being, and integrate seamlessly into digital shop ecosystems. Success will favor manufacturers that innovate beyond mechanics to deliver connected, safe, and future-ready solutions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tire Changers: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Poor Build Quality and Durability
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing tire changers—especially from low-cost manufacturers—is substandard build quality. Components such as bead loosening arms, turntables, and clamps may use inferior metals or poor welding techniques, leading to premature wear, mechanical failure, or safety hazards. Buyers may discover that the machine cannot handle heavy-duty or commercial use, resulting in downtime and increased maintenance costs.
Inaccurate or Inconsistent Performance
Low-quality tire changers often suffer from inconsistent performance, such as difficulty mounting or dismounting tires, especially on modern alloys or low-profile tires. Poorly calibrated heads or misaligned arms can damage rims, leading to customer complaints and liability risks. This inconsistency stems from inadequate R&D and lack of rigorous quality control during manufacturing.
Lack of Safety Features
Many budget tire changers omit essential safety mechanisms like automatic pressure release, secure locking systems, or protective guards. This increases the risk of workplace injuries and may result in non-compliance with OSHA or other regional safety standards. Sourcing machines without proper safety certifications can expose businesses to legal and financial liabilities.
Misrepresentation of Specifications and Capabilities
Suppliers, particularly on online B2B platforms, may exaggerate a tire changer’s capabilities—such as maximum wheel diameter, compatibility with run-flat tires, or ease of use. This misrepresentation can lead to purchasing equipment that fails to meet operational needs, especially in professional automotive or fleet service environments.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from certain regions increases the risk of purchasing tire changers that copy patented designs, control systems, or branding from established brands (e.g., Hofmann, Corghi, Rotary). Using such equipment may expose the buyer to legal challenges, especially if the machines are imported into markets with strong IP enforcement. Additionally, counterfeit or cloned models often lack technical support and spare parts availability.
Inadequate Technical Support and Spare Parts Availability
Off-brand or IP-infringing tire changers frequently come with limited or non-existent after-sales support. Spare parts may be difficult to obtain, and technical documentation may be incomplete or poorly translated. This leads to extended downtime and higher long-term ownership costs.
Non-Compliance with Regional Standards
Tire changers sourced internationally may not meet local electrical, mechanical, or safety standards (e.g., CE, UL, CSA). Importing or operating non-compliant equipment can result in fines, equipment seizure, or voided insurance coverage. Always verify certifications relevant to your target market before procurement.
Hidden Costs from Poor Ergonomics and Training Needs
Low-cost models may lack ergonomic design, increasing operator fatigue and training time. This reduces productivity and can lead to higher labor costs over time. Additionally, unclear instructions or poor user interfaces can necessitate additional training investments not factored into the initial purchase price.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tire Changer Equipment
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations when shipping, handling, importing, or operating tire changer equipment globally. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and smooth operations.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all tire changers meet relevant safety and environmental standards before shipment or use. Key regulations include:
- CE Marking (Europe): Tire changers must comply with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU), and Electromagnetic Compatibility (2014/30/EU). Documentation such as the Declaration of Conformity and technical file must be available.
- UL/CSA Certification (North America): Equipment must be certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL or CSA to meet OSHA and local electrical and mechanical safety standards.
- EPA & CARB Regulations (USA): If the tire changer includes air compressors or pneumatic systems, verify compliance with emissions and noise standards, especially in California (CARB).
- RoHS & REACH (EU): Confirm that materials used in manufacturing comply with restrictions on hazardous substances (RoHS) and chemical registration (REACH).
- Local Market Approvals: Check country-specific requirements for electrical voltage (e.g., 110V vs. 230V), plug types, and labeling (e.g., language, safety warnings).
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling minimize damage during transit and ensure worker safety.
- Secure Packaging: Use robust wooden crates or heavy-duty cardboard with internal bracing to secure moving parts. Anchor the machine to prevent shifting.
- Protect Sensitive Components: Cover control panels, jaws, and turntables with protective caps or foam. Remove or secure hydraulic/pneumatic lines if applicable.
- Lifting Points: Use manufacturer-designated lifting points only. Never lift by arms, hoses, or electrical components.
- Forklift & Pallet Use: Ensure equipment is palletized correctly with adequate weight distribution. Verify load capacity of pallets and forklifts.
- Hazard Labels: Affix labels for “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” as needed.
Shipping and Transportation
Follow best practices for domestic and international shipping.
- Freight Classification: Classify correctly under the National Motor Freight Classification (NMFC) or Harmonized System (HS Code – typically 8462.39 for machine tools). Provide accurate dimensions, weight, and freight class.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificates of compliance. For international shipments, complete export declarations and customs forms.
- Mode of Transport: Use flatbed trucks for oversized units. For air freight, verify weight and size restrictions. Sea freight requires waterproof packaging and moisture protection (e.g., desiccants).
- Insurance: Declare full value and secure cargo insurance covering damage, theft, and delays.
Import and Customs Clearance
Prepare for customs inspections and duties.
- Duty Rates: Research applicable tariffs based on HS code and country of origin. Leverage free trade agreements if eligible (e.g., USMCA, EU agreements).
- Import Licenses: Verify if import permits or registrations are required (e.g., in India, China, or Brazil).
- Customs Broker: Engage a licensed customs broker to manage declarations, duties, and compliance with local import laws.
- Product Testing: Some countries may require on-site testing or certification by local authorities (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC Mark in South Korea).
Installation and Operational Compliance
Ensure safe and compliant use upon delivery.
- Site Assessment: Verify floor load capacity, power supply compatibility (voltage, phase, frequency), and adequate ventilation.
- Training: Provide operator training per manufacturer guidelines and OSHA (or local equivalent) safety standards.
- Maintenance Logs: Maintain service records to comply with warranty terms and safety inspections.
- Waste Management: Follow local laws for disposal of worn components (e.g., rubber, metal scraps) and used lubricants.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Noise Levels: Confirm equipment meets local noise ordinances (e.g., <85 dB(A) in workplaces).
- Waste Handling: Implement procedures for responsible disposal of packaging materials and end-of-life equipment.
- Emergency Procedures: Equip work areas with emergency stop protocols and first-aid access.
By following this guide, businesses can ensure efficient logistics and full compliance when deploying tire changer equipment worldwide. Always consult local regulations and the equipment manufacturer for model-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Tire Changer
Sourcing the right tire changer is a critical decision that impacts workshop efficiency, service quality, and long-term operational costs. After evaluating various options based on features, durability, ease of use, safety mechanisms, brand reputation, and total cost of ownership, it is evident that selecting a tire changer should align closely with the specific needs of the facility—whether it serves passenger vehicles, heavy-duty trucks, or high-performance automobiles.
Investing in a reliable, well-reviewed model from a reputable manufacturer ensures consistent performance, minimizes downtime, and enhances technician safety. Additionally, considering after-sales support, warranty, and availability of spare parts is essential for sustained operations. While initial cost is a factor, prioritizing quality and compatibility over price alone leads to better value in the long run.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach—guided by thorough assessment, user feedback, and future scalability—will enable automotive service providers to procure a tire changer that boosts productivity, ensures customer satisfaction, and supports business growth.