The global welding equipment market, driven by rising demand in construction, automotive, and heavy manufacturing sectors, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, according to Mordor Intelligence. Within this expanding landscape, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding remains a preferred method for precision and high-quality welds—especially in aerospace, automotive restoration, and custom fabrication. As demand for operator safety and efficiency increases, so does the need for advanced protective gear, particularly auto-darkening TIG welding helmets. Technological advancements such as adjustable shading, improved response times (as fast as 0.1 milliseconds), and ergonomic designs are shaping buyer preferences. With the personal protective equipment (PPE) segment gaining traction within the welding industry, key manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to enhance user experience and compliance with international safety standards. In this dynamic environment, eight manufacturers have consistently risen to the forefront through innovation, reliability, and strong market presence—setting the benchmark in TIG welding helmet performance.
Top 8 Tig Welding Helmet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 HobartWelders
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hobartwelders.com
Key Highlights: Hobart Welders is a leading welding manufacturer in the U.S. Browse a variety of welders, welding equipment, gear and projects to find the best match for ……
#2 3M Welding Helmets
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: The 3M Speedglas G5-01 Heavy-Duty Welding Helmet offers integrated respiratory protection and is quickly adjustable for both welding and grinding….
#3 Digital Elite™, Forged in Freedom™, ClearLight 4x
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millerwelds.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.7 (699) · Free deliveryAutomatically sets the helmet sensitivity by sensing your welding environment. Ideal for weld operators who frequently adjust their settings for…
#4 Welding Helmets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: Lone Star Welding Helmet K4134-1 Lone star welding helmet is a solar-powered, auto-darkening hood for safety and protection….
#5 John Tillman Co.
Domain Est. 1999
Website: jtillman.com
Key Highlights: MENU. PRODUCTS · NEW PRODUCTS · Essentials · Gloves · Impact Resistant · Stick · MIG · TIG · Drivers · Mechanics-TrueFit® · Seamless Knit · Cut Resistant ……
#6 LaserWELD™ LASER/MIG/TIG Welding Helmet with ADF and WIN …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: kenteklaserstore.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryLaserWELD™ LASER/MIG/TIG Welding Helmet with ADF and WIN-C900F. $1,250.00. Ships in 3 weeks. P/N. WLD-CFPRO. Qty. Add to Cart Add to Quote….
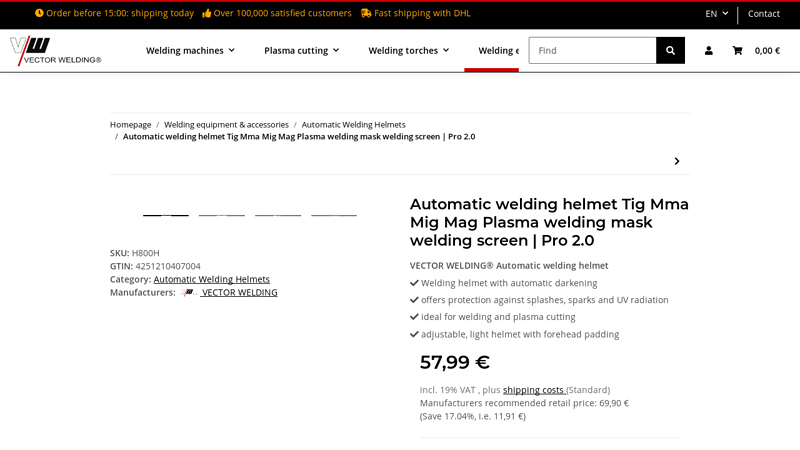
#7 Automatic welding helmet Tig Mma Mig Mag Plasma welding mask …
Domain Est. 2015
Website: vector-welding.com
Key Highlights: Automatic welding helmets for protection during welding and plasma cutting. Automatic darkening at arc start. ✓ high quality, low prices ✓ 100% safety….
#8 ANDELI Welder: ANDELI
Domain Est. 2020
Website: andelimall.com
Key Highlights: ANDELI: Your one-stop shop for welding machines, safety helmets & replacement parts. High-performance tools for metal fabrication, car repair & DIY projects ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tig Welding Helmet

2026 Market Trends for TIG Welding Helmets
Advancements in Auto-Darkening Technology
By 2026, TIG welding helmets are expected to feature next-generation auto-darkening filters with faster reaction times (under 0.1 milliseconds) and wider dynamic range (shade 5 to 13+). Enhanced sensors will better distinguish between TIG arc initiation and background light, reducing false triggers. Integration with artificial intelligence will allow helmets to automatically adjust sensitivity and delay settings based on welding parameters and user behavior, improving precision and reducing eye strain during intricate TIG applications.
Increased Integration of Connectivity and Smart Features
Smart welding helmets will gain momentum, with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity enabling integration with mobile apps and workshop management systems. Users will be able to monitor welding time, arc-on duration, and helmet usage analytics for training and productivity tracking. Some high-end models may offer voice control, heads-up display (HUD) notifications, and over-the-air (OTA) firmware updates, improving usability and maintenance efficiency.
Focus on Ergonomics and User Comfort
As welders demand longer wearability, manufacturers will prioritize lightweight materials such as advanced composites and magnesium alloys. Improved weight distribution, adjustable headgear with enhanced padding, and better ventilation systems will reduce fatigue during extended TIG welding sessions. Helmets will be designed with low center of gravity to minimize neck strain, especially important for precision TIG work in overhead or tight positions.
Expansion of Solar-Powered and Energy-Efficient Designs
Sustainability and reliability will drive the adoption of hybrid power systems combining solar cells with long-life lithium batteries. By 2026, most premium TIG helmets will operate primarily on solar energy with battery backup, eliminating the need for frequent battery replacements. Energy-efficient LCD filters and low-power sensor technologies will extend operational life, appealing to industrial users focused on cost savings and environmental impact.
Rising Demand in Aerospace and Precision Manufacturing
The TIG welding helmet market will benefit from growth in high-precision industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. These sectors require superior weld quality, driving demand for helmets with high optical clarity (Shade 10+ in light state), minimal image distortion, and excellent peripheral vision. Specialized helmets with enhanced UV/IR protection and compliance with stringent safety standards like ANSI Z87.1 and EN 379 will be increasingly sought after.
Growth in Emerging Markets and DIY Segments
Expanding industrialization in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa will increase demand for affordable yet reliable TIG helmets. At the same time, the rise of skilled hobbyists and makerspaces will boost the mid-range consumer segment. Manufacturers will introduce cost-effective models with core auto-darkening features, targeting both professional and enthusiast users, further diversifying the product landscape by 2026.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing TIG Welding Helmets (Quality & IP)
Sourcing TIG welding helmets, especially from international suppliers, can lead to significant issues if quality control and intellectual property (IP) concerns are not carefully managed. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Optical Quality and Inconsistent Shade Performance
Many low-cost helmets on the market use substandard auto-darkening filters (ADFs) that fail to meet industry standards (e.g., ANSI Z87.1 or EN 379). This results in inconsistent shade transitions, slow reaction times, or inadequate UV/IR protection—posing serious safety risks to welders. Sourcing from suppliers without verified certifications increases the likelihood of receiving counterfeit or non-compliant optics.
Non-Compliance with Safety and Regulatory Standards
A major pitfall is importing helmets that do not meet the safety requirements of the target market. Some suppliers provide falsified test reports or claim compliance without actual certification. This exposes buyers to legal liability, product recalls, and rejected shipments at customs—especially in regions like the U.S., EU, or Australia, where regulatory enforcement is strict.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Sourcing from manufacturers that copy branded helmet designs (e.g., replicating the look or functionality of知名品牌 like Lincoln Electric or Miller) risks IP violations. Even if the supplier claims the design is “generic,” using patented shapes, user interfaces, or electronic features can lead to cease-and-desist orders, customs seizures, or lawsuits—particularly when importing into IP-enforcement-heavy jurisdictions.
Inadequate Build Quality and Ergonomics
Low-cost helmets often use brittle plastics, poor headgear mechanisms, or uncomfortable padding, leading to premature breakage and user dissatisfaction. Thin or poorly sealed housings may allow light leakage, compromising welder safety. These quality issues increase long-term costs due to higher replacement rates and reduced productivity.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate key specs—such as switching speed (e.g., claiming 1/25,000 sec when actual is slower), viewing area size, or battery life. Without independent testing or reliable third-party verification, buyers may receive helmets that underperform in real-world TIG applications, where precision and clarity are critical.
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts
Many generic suppliers do not offer warranties, technical support, or replacement parts (like lenses or headgear components). This creates operational downtime and additional costs for end users, undermining customer trust and brand reputation for the buyer or distributor.
Supply Chain and Consistency Risks
Sourcing from low-tier manufacturers can lead to batch-to-batch inconsistencies in materials, electronics, and assembly. A helmet that passes initial inspection may degrade in later shipments, making it difficult to maintain quality standards across inventory.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence: verify certifications, perform sample testing, audit suppliers, and consult legal experts on IP compliance—especially when branding or private-labeling. Partnering with reputable manufacturers and using third-party inspection services can help ensure both quality and legal safety in your sourcing strategy.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for TIG Welding Helmet
Product Classification and HS Code
TIG welding helmets typically fall under the category of personal protective equipment (PPE) for industrial use. The Harmonized System (HS) code may vary by country, but common classifications include:
– HS 6307.90: Other made-up articles, including protective garments and accessories (commonly used for welding helmets in many regions).
– HS 9025.19 or 9031.80: For helmets with electronic components (e.g., auto-darkening filters), depending on technical specifications.
Consult local customs authorities for precise classification, as misclassification can lead to delays or penalties.
Import Regulations and Documentation
Ensure compliance with destination country requirements:
– Commercial Invoice: Must include product description, value, quantity, HS code, country of origin, and supplier/buyer details.
– Packing List: Itemizes contents per package, weight, dimensions, and markings.
– Certificate of Origin: Required by some countries to determine tariff eligibility (e.g., under free trade agreements).
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB): Essential for freight tracking and customs clearance.
– Safety and Compliance Certifications: Include documentation proving conformity with local PPE standards (see Compliance section below).
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
- Packaging: Use durable materials to prevent damage during transit. Individual units should be protected with cushioning to safeguard lenses and electronic components.
- Labeling: Each unit and shipping container must display:
- Product name and model number
- Manufacturer information
- Safety warnings (e.g., “Protective Equipment – Not for Medical Use”)
- Compliance marks (e.g., CE, ANSI)
- Country of origin
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) per ISO 780 standards
Compliance with Safety Standards
TIG welding helmets must meet regional safety certifications:
– United States: ANSI Z87.1 (Occupational and Educational Eye and Face Protection)
– European Union: CE marking under the PPE Regulation (EU) 2016/425, often requiring Notified Body involvement for Category III PPE
– Canada: Complies with CSA Z94.3 (Eye and Face Protectors)
– Australia/New Zealand: AS/NZS 1337.1 (Eye and Face Protection – Filters for Welding)
Ensure all helmets have visible certification marks and technical documentation available upon request.
Shipping and Transportation
- Choose carriers experienced in handling industrial safety equipment.
- Declare all shipments accurately to avoid customs inspections or seizures.
- For air freight, confirm that lithium batteries (if used in auto-darkening helmets) comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (typically classified as UN3481, PI 966 Section IB).
- Use temperature-controlled transport if specified by the manufacturer, especially for electronic components.
Import Duties and Taxes
- Calculate applicable duties based on the HS code and trade agreements.
- Include VAT, GST, or other local taxes in landed cost calculations.
- Leverage preferential tariffs if the product qualifies under agreements like USMCA, CETA, or RCEP (requires valid Certificate of Origin).
Post-Import Compliance and Recordkeeping
- Maintain records of all compliance documentation, test reports, and certifications for a minimum of 10 years (as required under EU PPE Regulation).
- Monitor for product recalls or updates to safety standards.
- Ensure end-users receive instruction manuals in the local language, covering safe use, maintenance, and limitations.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Comply with local e-waste regulations for helmets with electronic parts (e.g., WEEE Directive in the EU).
- Provide guidance on proper disposal or recycling of helmets, lenses, and batteries.
- Avoid shipping to countries with strict environmental import restrictions without proper certification.
By adhering to this guide, importers and distributors can ensure smooth logistics operations and full regulatory compliance for TIG welding helmets across global markets.
In conclusion, sourcing a TIG welding helmet requires careful consideration of key factors such as auto-darkening feature quality, shade range, response time, optical clarity, comfort, durability, and compatibility with TIG welding applications. It is essential to balance performance and cost while prioritizing safety and user comfort. Opting for helmets from reputable manufacturers with strong safety certifications (such as ANSI and CE) ensures reliable protection and long-term value. Additionally, considering user reviews, warranty options, and availability of replacement parts can further enhance satisfaction. Whether sourcing for individual use or bulk procurement, investing in a high-quality TIG-specific welding helmet not only improves welding precision and efficiency but also safeguards the welder’s health, making it a crucial component of any professional welding setup.