The Thunderbolt 2 cable market has seen steady demand driven by the increasing need for high-speed data transfer and high-resolution display connectivity in professional audiovisual, creative, and enterprise computing environments. According to Grand View Research, the global Thunderbolt market size was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.4% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by rising adoption of high-performance computing devices and peripherals. As Thunderbolt 2 remains a critical interface for legacy high-end Mac systems and professional workflows requiring reliable bandwidth up to 20 Gbps, manufacturers continue to play a vital role in delivering certified, durable, and high-quality cabling solutions. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 8 Thunderbolt 2 cable manufacturers leading in quality, compliance, and market reach.
Top 8 Thunderbolt 2 Cables Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Thunderbolt™ Technology: A Universe of Possibilities
Domain Est. 1986
Website: intel.com
Key Highlights: With Thunderbolt™ technology, one universal port offers simple, reliable, fast data and video connections to fuel a universe of possibilities….
#2 Thunderbolt™
Domain Est. 1996
Website: belkin.com
Key Highlights: Thunderbolt, developed by Intel, steps up USB port technology by supporting both high‐speed data and video. Harnessing Thunderbolt through a USB-C port ……
#3 StarTech.com 0.5m White Thunderbolt Cable
Domain Est. 2002
Website: gatewayp.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryThis 0.5m (1.64ft) White Thunderbolt cable offers a dependable, high-quality solution for harnessing the speed and power of Thunderbolt technology while ……
#4 Products
Domain Est. 2011
Website: thunderbolttechnology.net
Key Highlights: Thunderbolt is the USB-C that does it all! It’s a single compact port that delivers the fastest, most versatile connection to any dock, display, or data device….
#5 Adaptors for the Thunderbolt or USB
Domain Est. 1987
Website: support.apple.com
Key Highlights: The adapters and cables in this article work with Mac computers with Thunderbolt 5 ports, Thunderbolt 4 ports, Thunderbolt 3 ports or a USB-C port….
#6 Other World Computing Thunderbolt™ Connectivity High …
Domain Est. 1995
Website: owc.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsStarting at $27.99, wide choice of OWC top quality Thunderbolt cables enables maximum flexibility for placement of Thunderbolt devices in home or office….
#7 2m White Thunderbolt Cable
Domain Est. 1998
Website: startech.com
Key Highlights: Out of stock Rating 4.5 28 The TBOLTMM2MW supports both Thunderbolt 1 (10Gbps) and Thunderbolt 2 (20Gbps) devices and can link compatible devices as part of a daisy-chained conne…
#8 Thunderbolt™Cable
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sumitomoelectric.com
Key Highlights: Discover Sumitomo Electric’s Thunderbolt™ cables — engineered for ultra-high-speed data transfer, power delivery, and exceptional durability….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Thunderbolt 2 Cables
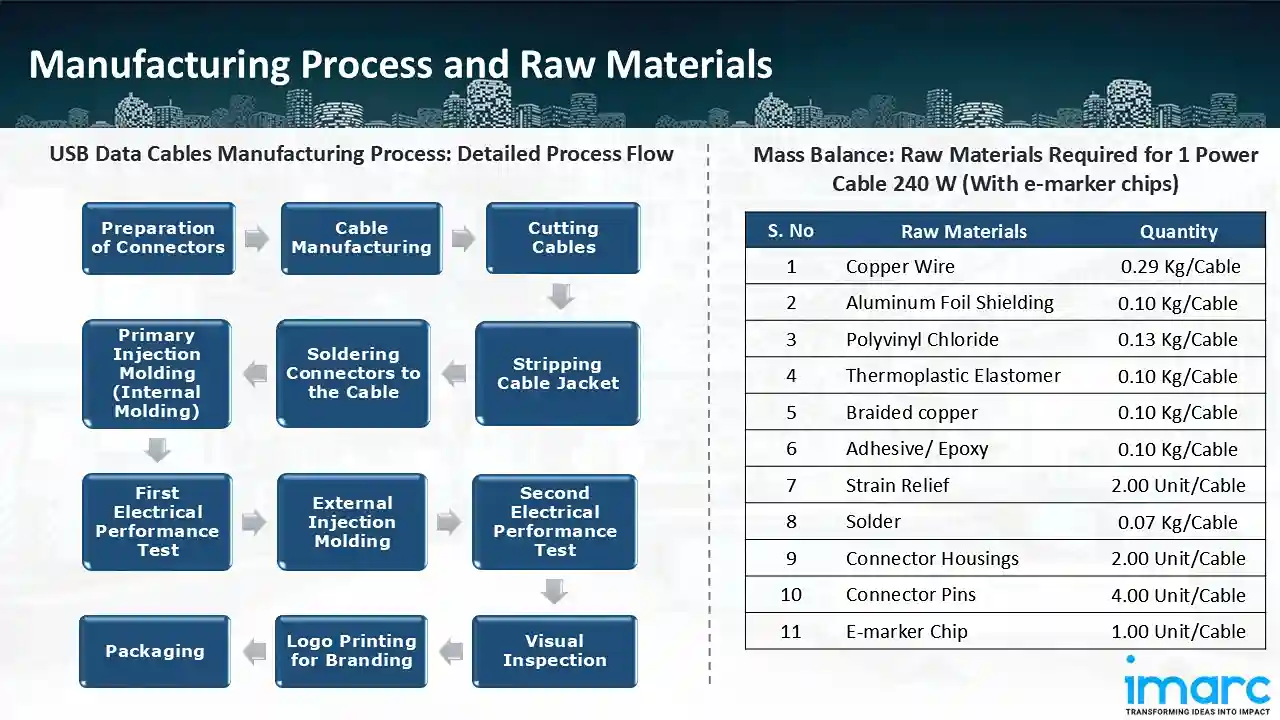
2026 Market Trends for Thunderbolt 2 Cables
As we approach 2026, the market for Thunderbolt 2 cables continues to evolve in response to shifting consumer demands, technological advancements, and the broader ecosystem of high-speed data transfer technologies. Although Thunderbolt 2 has been superseded by newer iterations such as Thunderbolt 3, 4, and the emerging Thunderbolt 5, Thunderbolt 2 cables still maintain a niche presence, primarily due to legacy hardware support and specific industry applications.
Declining Demand Amid Technological Obsolescence
By 2026, Thunderbolt 2 cables are increasingly viewed as legacy products. With the widespread adoption of USB4 and Thunderbolt 3/4—both of which utilize the USB-C connector—consumers and businesses are migrating toward more versatile, higher-bandwidth solutions. Thunderbolt 2, limited to 20 Gbps and reliant on the Mini DisplayPort form factor, no longer meets the performance requirements of modern high-resolution displays, external GPUs, and fast storage devices. As a result, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) have largely discontinued the integration of Thunderbolt 2 ports in new devices, leading to a steady decline in new cable production.
Niche Market Sustained by Legacy Systems
Despite reduced mainstream relevance, Thunderbolt 2 cables retain a foothold in specialized markets. Industries such as media production, audio engineering, and scientific research still operate legacy Mac systems (e.g., MacBook Pro and iMac models from 2013–2015) that rely on Thunderbolt 2 for high-speed connectivity to external RAID arrays, capture cards, and professional peripherals. This sustained demand ensures continued availability of Thunderbolt 2 cables, albeit primarily through third-party suppliers and refurbished equipment markets.
Price Trends and Availability
In 2026, Thunderbolt 2 cables are predominantly sold as refurbished, recycled, or aftermarket products. New production is minimal, with a few manufacturers continuing low-volume production to serve niche needs. Prices have stabilized at moderate levels, with shorter cables (0.5–1 meter) available for $20–$40, while longer or certified premium cables may exceed $60. The secondary market, including platforms like eBay and specialized refurbishers, plays a crucial role in maintaining supply, though buyers face risks related to cable quality and authenticity.
Compatibility and Adapter Use
A notable trend in 2026 is the increased use of adapters to bridge Thunderbolt 2 and newer standards. Users of legacy Thunderbolt 2 devices often rely on Thunderbolt 3-to-2 adapters (e.g., Apple’s discontinued Thunderbolt 3 (USB-C) to Thunderbolt 2 adapter) to maintain connectivity. However, the scarcity of these adapters has driven up prices and created a parallel market for third-party solutions, which may lack full compliance or reliability.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
As part of broader sustainability initiatives, businesses and institutions are extending the lifespan of existing hardware, indirectly supporting continued use of Thunderbolt 2 infrastructure. This trend aligns with the circular economy model, where maintaining legacy systems reduces electronic waste. Consequently, demand for reliable Thunderbolt 2 cables persists in educational institutions, government agencies, and enterprises focused on cost-effective, sustainable IT management.
Conclusion
In summary, the 2026 market for Thunderbolt 2 cables is characterized by diminished but persistent demand, driven by legacy system dependencies and sustainability efforts. While no longer at the forefront of high-speed connectivity, Thunderbolt 2 cables serve as a testament to the long tail of technology lifecycles. Their role is increasingly supportive rather than primary, catering to users who value continuity over cutting-edge performance. As the industry moves toward Thunderbolt 5 and beyond, Thunderbolt 2 will likely transition fully into the realm of historical hardware, preserved through community support and specialized applications.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Thunderbolt 2 Cables: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Poor Build Quality and Reliability
Many low-cost Thunderbolt 2 cables on the market use substandard materials, such as thin shielding, flimsy connectors, and inadequate strain relief. This leads to frequent failures, intermittent connections, and reduced data transfer speeds. Poorly manufactured cables may not support the full 20 Gbps bandwidth or daisy-chaining functionality, undermining the performance advantages of Thunderbolt 2.
Non-Compliant or Counterfeit Components
Some third-party cables falsely claim Thunderbolt 2 certification or use counterfeit controller chips. These cables often lack the required VESA certification and may not include the necessary authentication firmware. As a result, they can cause system instability, fail to work with certain devices, or even damage connected hardware due to improper power delivery or signal integrity.
Intellectual Property and Licensing Violations
Thunderbolt technology is co-developed by Intel and Apple and protected by strict licensing requirements. Unauthorized manufacturers may produce cables without proper licensing, infringing on intellectual property rights. Sourcing such cables exposes businesses to legal risks, including liability for IP infringement and potential supply chain disruptions if enforcement actions are taken.
Lack of Firmware Updates and Support
Genuine Thunderbolt 2 cables benefit from firmware updates and technical support from authorized vendors. Counterfeit or unlicensed cables typically do not receive updates, making them incompatible with newer operating systems or hardware revisions. This lack of support increases long-term maintenance costs and reduces device interoperability.
Inadequate Testing and Certification
Reputable Thunderbolt 2 cables undergo rigorous testing for signal integrity, EMI, and thermal performance. Many budget cables skip these critical tests, leading to compatibility issues—especially in professional environments where reliability is crucial. Always verify VESA certification and purchase from authorized distributors to avoid performance shortfalls.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Thunderbolt 2 Cables
Thunderbolt 2 cables are high-speed data transfer cables developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple, designed to support high-resolution displays and fast peripheral connectivity. Proper logistics handling and compliance with international regulations are essential for the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of these products. This guide outlines key considerations for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers involved in the supply chain of Thunderbolt 2 cables.
Product Classification & HS Code
Thunderbolt 2 cables fall under the category of electrical connection cables for data transmission. The Harmonized System (HS) code generally used for such cables is:
- HS Code: 8544.42 – Electrical conductors, for a voltage not exceeding 80 V, fitted with connectors at both ends.
Note: Specific country variations may apply. Always verify with local customs authorities, as some regions may classify these under data transmission apparatus (e.g., heading 8471 or 8517) depending on intended use.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared and accurate for international shipments:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin (preferably with a signed declaration)
- Product Specification Sheet (including technical details like length, bandwidth, certification marks)
Some countries may require additional documentation such as:
- Import licenses (e.g., in India or Russia)
- Product conformity declarations
- Authorized Representative Letter (for EU compliance)
Regulatory Compliance
European Union (CE Marking & RoHS)
- CE Marking: Required for all electronic products sold in the EU. Thunderbolt 2 cables must comply with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC 2014/30/EU).
- RoHS Compliance (2011/65/EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, mercury). Ensure materials in connectors and insulation meet RoHS limits.
- REACH (EC 1907/2006): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Verify that no substances of very high concern (SVHC) are present above thresholds.
- UKCA Marking: Required for Great Britain (England, Scotland, Wales); Northern Ireland follows EU rules under the Northern Ireland Protocol.
United States (FCC & State Regulations)
- FCC Part 15, Subpart B: Digital devices must not emit harmful radio frequency interference. Thunderbolt 2 cables, especially active ones, may need to comply as incidental radiators.
- California Proposition 65: Requires warning labels if the cable contains chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm (e.g., certain phthalates in PVC insulation).
- State-Level E-Waste Laws: Some states require producer registration and recycling fees (e.g., in California and Washington).
Canada (ISED Certification)
- ISED (Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada): Previously known as Industry Canada (IC). Cables with digital circuitry or connectivity functions may require ICES-003 compliance (EMC standard).
- Ensure labeling includes the IC certification number if applicable.
Other Regions
- China (CCC Mark): Currently, Thunderbolt 2 cables are not typically CCC-certified unless bundled with a power function or integrated device. Confirm based on product configuration.
- Japan (PSE Mark): Non-specific cables may not require PSE, but if the cable incorporates active circuitry, it may fall under Class A or B of the Electrical Appliances and Materials Safety Law.
- South Korea (KC Mark): EMC and safety certification may be required, particularly for active cables.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
- Include compliance marks (e.g., CE, FCC, RoHS) on packaging or product.
- Label with manufacturer/importer name, address, and contact information.
- Provide technical specifications: 20 Gbps bandwidth, compatibility (e.g., Mac computers with Thunderbolt 2, certain Windows systems), and supported devices (e.g., Thunderbolt displays, RAID arrays).
- Use multilingual labeling where required (e.g., French in Canada, German in Austria).
- Avoid misleading claims (e.g., “Thunderbolt 3 compatible” unless verified).
Logistics & Handling
- Temperature & Humidity: Store and transport in dry, temperature-controlled environments (ideally 10°C to 30°C). Avoid condensation.
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Protection: Use anti-static packaging (e.g., pink poly bags) during storage and shipping, especially for bulk handling.
- Physical Protection: Prevent kinking or crushing; use rigid packaging for longer cables (e.g., 2m).
- Shipping Labels: Clearly mark with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “Do Not Bend,” and “Protect from Moisture.”
Warranty & After-Sales Compliance
- Provide a minimum 1-year warranty (aligned with EU consumer law requirements).
- Include a returns and recycling policy compliant with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU.
- Support right-to-repair initiatives where applicable by providing repair information or spare parts.
Conclusion
Thunderbolt 2 cables, while nearing end-of-life in favor of Thunderbolt 3/4 and USB4, still require strict adherence to logistics and compliance standards due to their electronic nature and global distribution. Ensuring proper classification, documentation, and adherence to regional regulations minimizes customs delays, avoids penalties, and supports sustainable and responsible trade practices. Always consult with local regulatory experts and stay informed of evolving standards.
In conclusion, sourcing Thunderbolt 2 cables requires careful consideration of compatibility, quality, and cost. While Thunderbolt 2 technology is now considered legacy—having been superseded by Thunderbolt 3 and 4—there remains a niche demand for these cables, particularly among users of older Mac systems and high-performance peripherals like external storage arrays and high-resolution displays. When sourcing, it is essential to ensure genuine certification to guarantee performance, reliability, and data transfer speeds up to 20 Gbps. Given the decline in new production, buyers often rely on reputable third-party suppliers or the secondary market, where verifying authenticity and inspecting for physical damage are crucial. For long-term sustainability, users should consider upgrading to newer interfaces when feasible, but for existing Thunderbolt 2 ecosystems, investing in well-reviewed, certified cables from trusted brands ensures optimal functionality and protects connected devices.