The global thread cutting screw market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the fasteners market — a category in which thread cutting screws play a critical role — is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by advancements in metalworking technologies, increasing infrastructure investments, and the growing need for high-strength, durable fastening solutions. As industries prioritize precision and reliability, thread cutting screws, known for their ability to create internal threads in pre-drilled holes without prior tapping, have become indispensable. With the Asia Pacific region leading in both production and consumption, and North America witnessing strong demand due to automotive and aerospace applications, competition among manufacturers has intensified. In this evolving landscape, a select group of companies stand out for their innovation, product quality, and global reach—setting the benchmark in the thread cutting screw industry.
Top 10 Thread Cutting Screw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Metal Thread Forming Screw Manufacturers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: shakeproof.com
Key Highlights: As a leader among thread forming screw manufacturers, we offer the following types of screws: Plastite; Taptite; Torx; Torx Plus; ACR II; Quadrex; MAThread; PSD ……
#2 Custom Screw Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2003
Website: kdfasteners.com
Key Highlights: KD Fasteners carries a variety of standard screw types and also offers custom screw solutions to satisfy any application. Visit KD Fasteners today to learn ……
#3 Thread cutting screw
Domain Est. 2007
Website: katsuhana.com.tw
Key Highlights: Katsuhana Fasteners Corp, Taiwan professional screw manufacturer, provides High Stable Quality of Drywall Screw, SDS screw, Painted Screw, Tapping Screw, ……
#4 BDN Fasteners: Asia’s Leading Self
Domain Est. 2015
Website: bdnfasteners.com
Key Highlights: OUR PRODUCT. BDN Fasteners offer a full range of self-drilling and self-tapping screws that drill, tap threads, and fasten in one swift process….
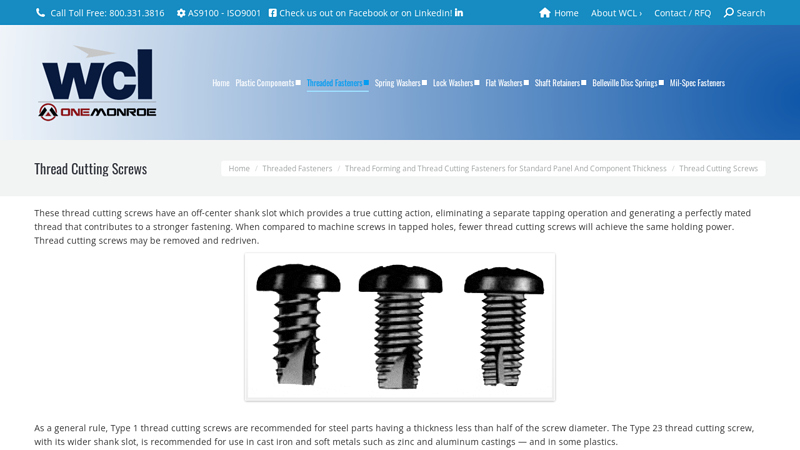
#5 Thread Cutting Screws
Domain Est. 1997
Website: wclco.com
Key Highlights: WCL provides thread cutting screws in diameters ranging from a number 4 through a 3/8′′ and in lengths from 1/4′′ through 2′′. All conventional head styles and ……
#6 Slotted Thread Cutting Screws
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metricmcc.com
Key Highlights: Metric MMC supplies slotted thread cutting screws in various sizes. Shop metric slotted thread cutting screws and take advantage of volume discounts today….
#7 Thread Cutting Screws
Domain Est. 1999
Website: associatedfasteners.com
Key Highlights: A thread-cutting screw, also known as a thread-forming screw, is a type of fastener designed to create its own internal threads in a pre-drilled hole….
#8 Thread Cutting Screw Supplier
Domain Est. 2002
Website: apf.com
Key Highlights: Our thread-cutting screws are available in flat-head, pan-head, and hex-washer-head configurations, in a variety of materials and coatings….
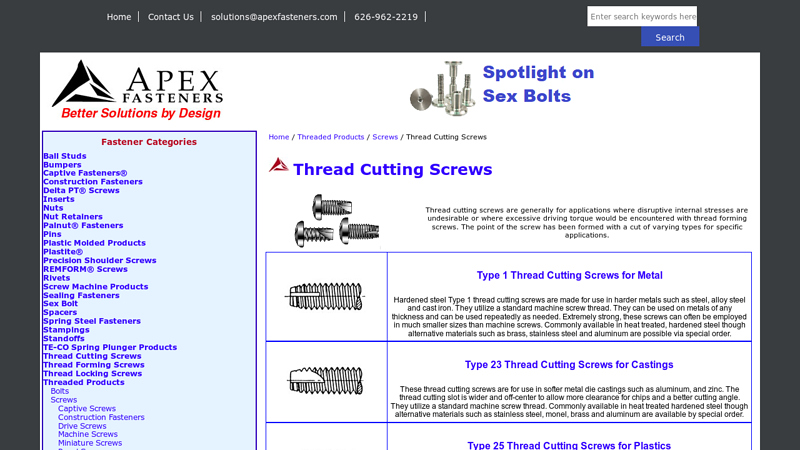
#9 Thread Cutting Screws
Domain Est. 2002
Website: apexfasteners.com
Key Highlights: Type 1 thread cutting screws are made for use in harder metals such as steel, alloy steel and cast iron. They utilize a standard machine screw thread….
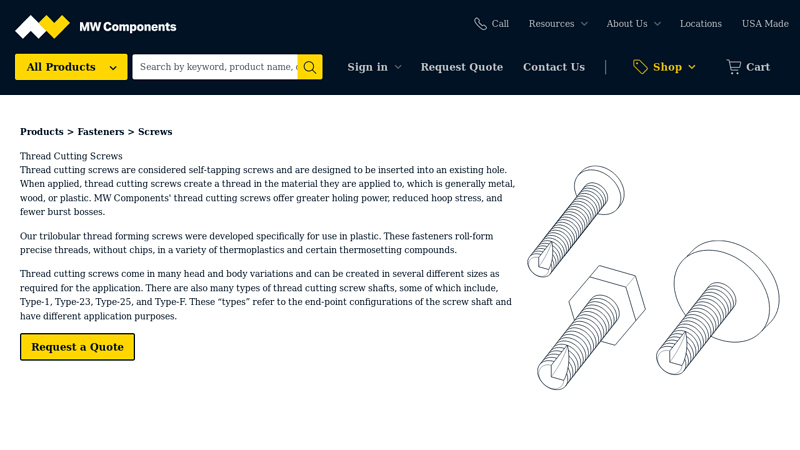
#10 Thread Cutting Screws
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: Order standard or custom thread cutting or thread forming screws through MW Components. These screws cut threads into wood, plastic, and metal materials….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Thread Cutting Screw
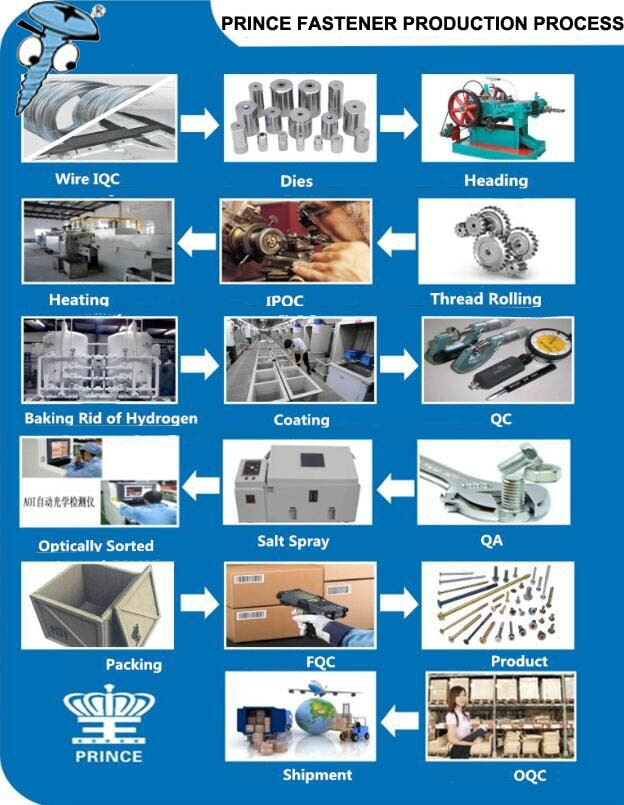
H2: Projected Market Trends for Thread Cutting Screws in 2026
The global thread cutting screw market is anticipated to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, increasing demand across key end-use industries, and a shift toward high-performance fastening solutions. Several macroeconomic and sector-specific trends are expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
-
Rising Demand from Automotive and Construction Sectors
The automotive industry continues to adopt lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel, which require specialized fasteners like thread cutting screws for secure joint integrity. As electric vehicle (EV) production scales globally, the need for precision-engineered fasteners in battery enclosures and motor assemblies will further boost demand. Similarly, in the construction sector, urbanization and infrastructure development—particularly in emerging economies—will sustain the need for durable and corrosion-resistant thread cutting screws. -
Technological Advancements and Material Innovation
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in coatings and alloy compositions to enhance screw performance under extreme conditions. Innovations such as self-tapping thread cutting screws with improved thread-forming geometry reduce installation time and increase joint reliability. By 2026, expect wider adoption of screws made from stainless steel, titanium, and composite materials, especially in aerospace, medical devices, and renewable energy applications. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is projected to remain the largest and fastest-growing market for thread cutting screws, led by industrial expansion in China, India, and Southeast Asia. North America and Europe will see moderate growth, supported by automation in manufacturing and strict regulatory standards requiring high-quality fasteners. Localized production and supply chain resilience will become critical, reducing dependence on single-source suppliers. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production processes and recyclable materials. By 2026, companies that integrate sustainable practices—such as energy-efficient cold forging and reduced waste generation—will gain competitive advantage. End-of-life recyclability of fasteners will also influence procurement decisions in green building and automotive design. -
Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT-enabled quality control and predictive maintenance in screw production lines, will enhance precision and reduce costs. Customization through digital design tools will allow manufacturers to meet specific client requirements more efficiently, particularly in high-mix, low-volume applications.
In summary, the 2026 thread cutting screw market will be shaped by innovation, sustainability, and regional industrial growth. Companies that adapt to evolving material demands, embrace digital transformation, and align with global sustainability goals are likely to lead the market in the next few years.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Thread Cutting Screws (Quality, IP)
When sourcing thread cutting screws, especially for industrial or high-precision applications, several common pitfalls can compromise product quality, performance, and compliance—particularly concerning quality standards and IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. Being aware of these issues helps ensure reliable sourcing outcomes.
1. Assuming All Screws Meet Specified Quality Standards
A frequent error is assuming that all thread cutting screws meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ASTM) based on supplier claims alone. In reality, many manufacturers—especially low-cost overseas suppliers—may provide substandard materials or inconsistent heat treatment, leading to brittle or weak screws prone to stripping or breakage.
Mitigation:
– Request material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH, ISO 898-1 for mechanical properties).
– Conduct independent quality audits or third-party testing.
– Verify thread accuracy and tensile strength through sample testing before full procurement.
2. Overlooking Material Compatibility and Corrosion Resistance
Thread cutting screws are often used in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or outdoor conditions. Sourcing screws without proper material selection (e.g., using standard steel instead of stainless steel or zinc-coated variants) can lead to premature corrosion—even if an IP rating is claimed.
Mitigation:
– Match screw material to environmental requirements (e.g., A2/A4 stainless steel for corrosive environments).
– Ensure any plating or coating meets durability standards (e.g., salt spray test results).
– Confirm that coatings do not interfere with thread cutting function or IP seal integrity.
3. Misunderstanding the Role of Screws in IP Rating Compliance
A critical misconception is that using screws labeled as “IP-rated” automatically ensures the entire assembly meets a specific Ingress Protection level. In truth, the screw alone does not define IP performance—it depends on the full enclosure design, gasket integrity, and proper installation.
Mitigation:
– Recognize that IP ratings apply to complete enclosures, not individual fasteners.
– Ensure screws are designed to maintain enclosure compression (e.g., proper drive type, head geometry).
– Work with enclosure manufacturers to validate that the screw choice supports the system-level IP rating.
4. Inconsistent Thread Cutting Performance Due to Poor Manufacturing
Poorly manufactured thread cutting screws may have inconsistent flute geometry, incorrect thread profiles, or inadequate hardness, leading to incomplete thread formation, excessive torque, or damage to the base material.
Mitigation:
– Source from suppliers with proven manufacturing controls and tooling precision.
– Inspect flute design and cutting edge sharpness.
– Test screws on actual base materials during prototyping.
5. Lack of Traceability and Supplier Qualification
Sourcing from unqualified or unknown suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant products. Without proper traceability (e.g., lot numbers, material test reports), it becomes difficult to address quality issues or recalls.
Mitigation:
– Qualify suppliers through audits, certifications (ISO 9001), and performance history.
– Require full documentation with every shipment.
– Establish long-term partnerships with reliable, transparent suppliers.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common pitfalls requires due diligence in supplier selection, clear understanding of technical requirements, and verification through testing and documentation. Ensuring quality and supporting IP compliance is not just about the screw itself—but how it integrates into the broader system.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Thread Cutting Screws
Overview
Thread cutting screws are specialized fasteners designed to cut threads into pre-drilled holes in materials such as metal, plastic, or composites. Due to their mechanical function and global usage, they are subject to various logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements across international markets. This guide outlines key logistics practices and compliance standards applicable to the distribution and use of thread cutting screws.
Classification & HS Code
Thread cutting screws are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) Code 7318.15 – “Screws and bolts, whether or not with their nuts or washers, of iron or steel, threaded, self-tapping.”
– Accurate HS code classification is essential for customs declaration, duty assessment, and trade compliance.
– Variants made from non-ferrous materials (e.g., stainless steel, brass) may fall under different subheadings (e.g., 7318.16 for stainless steel), requiring careful material-based classification.
– Always verify with local customs authorities or use a certified customs broker for precise coding.
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
- Packaging: Screws should be packed to prevent corrosion, damage, and contamination during transit. Common packaging includes:
- Plastic or paper bags inside rigid cardboard or plastic containers
- Anti-corrosion coatings (e.g., zinc plating) or vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) for metal screws
- Palletized shipments secured with stretch wrap for bulk transport
- Labeling: Must include:
- Product description (e.g., “Thread Cutting Screw, M4 x 20mm, Zinc Plated”)
- Quantity per package
- Manufacturer or supplier name and contact information
- Batch/lot number for traceability
- Country of origin
- Compliance markings (e.g., RoHS, REACH, if applicable)
Transportation & Handling
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, and land freight. For air freight, ensure packaging meets IATA standards for weight and security.
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent rust and degradation. Avoid exposure to moisture and corrosive chemicals.
- Handling: Use appropriate material handling equipment (e.g., forklifts, hand trucks) to prevent damage to packaged goods and ensure worker safety.
Regulatory Compliance
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances – EU): Applies to electrical and electronic equipment. If screws are used in such applications, they must comply with limits on lead, cadmium, mercury, and other substances.
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals – EU): Requires declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC). Suppliers must provide safety data sheets (SDS) if requested.
- Conflict Minerals (U.S. Dodd-Frank Act): If screws contain tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold (common in plating), suppliers may need to disclose sourcing from conflict-affected areas.
- Marking & Certification: Products sold in the EU may require CE marking if part of a construction or machinery assembly. While screws alone may not require CE, compliance with EN standards (e.g., EN ISO 1479 for thread cutting screws) is recommended.
Import/Export Documentation
Ensure all shipments include:
– Commercial invoice (with accurate product description, value, and HS code)
– Packing list
– Bill of lading or air waybill
– Certificate of Origin (may be required for duty preferences under free trade agreements)
– Export license (if required by export control regulations, e.g., for strategic materials)
Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
- Promote recyclability: Steel screws are highly recyclable; communicate this in product literature.
- Minimize packaging waste through efficient design and use of recyclable materials.
- Comply with local waste disposal regulations for industrial fasteners.
Quality Standards & Traceability
- Adhere to international standards such as ISO 1479 (Mechanical properties and dimensions of thread cutting screws).
- Implement batch traceability systems to support recalls or quality investigations.
- Provide test reports or certifications (e.g., tensile strength, torque performance) upon request.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and compliance with international regulations are critical for the successful global distribution of thread cutting screws. By adhering to classification rules, packaging standards, and environmental regulations, suppliers can ensure product integrity, regulatory approval, and customer satisfaction across markets. Regular audits and staying updated on regulatory changes are recommended to maintain compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Thread Cutting Screws:
In conclusion, sourcing thread cutting screws requires careful consideration of material compatibility, application requirements, quality standards, and supplier reliability. These screws offer a strong, permanent fastening solution by forming their own internal threads during installation, eliminating the need for pre-tapped holes. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to prioritize consistent product quality, adherence to industry standards (such as ISO or ASTM), and the ability to deliver in required volumes and timelines.
Additionally, evaluating factors such as thread design, drive type, coating, and corrosion resistance ensures optimal performance in specific environments. Partnering with reputable suppliers who offer technical support and have a proven track record can significantly reduce supply chain risks and enhance product reliability. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach to thread cutting screws contributes to improved assembly efficiency, reduced manufacturing costs, and enhanced overall product durability.