The global thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) fabric market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as automotive, apparel, healthcare, and consumer electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global TPU market size was valued at USD 2.67 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by TPU’s superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and eco-friendly processing compared to conventional plastics. Additionally, rising environmental concerns are accelerating the shift toward recyclable and non-phthalate materials, further boosting TPU adoption. As innovation in sustainable textiles gains momentum, a select group of manufacturers are leading the way in developing high-performance, application-specific TPU fabrics—setting new benchmarks in quality, durability, and manufacturing scale. The following list highlights the top 10 thermoplastic polyurethane fabric manufacturers shaping this dynamic market landscape.
Top 10 Thermoplastic Polyurethane Fabric Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Thermoplastic Polyurethane
Domain Est. 2012
Website: solutions.covestro.com
Key Highlights: High-performance thermoplastic polyurethane resins and blends with superior properties that meet your specific needs….
#2 Thermoplastic Polyurethane Film
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wimancorp.com
Key Highlights: Wiman Corporation manufactures custom thermoplastic polyurethane film, TPU film & sheets, film laminates, and polymer films for many different industries….
#3 Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Domain Est. 1998
Website: expafol.com
Key Highlights: Expafol has been in the industry for 30 years and is one of Europe’s leading manufacturers of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), along with many other PVC, ……
#4 Polyurethane Film Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americanpolyfilm.com
Key Highlights: American Polyfilm is a family-owned and operated corporation located in Branford, Connecticut, and specializes in Thermoplastic Polyurethane products….
#5 Thermoplastic Polyurethane
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tpu-material.com
Key Highlights: Huafon has specialized in providing polyurethane sole stock solutions, polyurethane product stock solutions and polyester polyol for 26 years….
#6 Waterproof TPU Membrane for Garment Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2018
Website: nanxiongtpu.net
Key Highlights: Jiaxing Nanxiong polymer is specialized in the production of TPU film, which is characterized by water resistance, moisture permeability, mite resistance, ……
#7 Thermoplastic polyurethane fabric Manufacturer & Supplier in China
Domain Est. 2023
Website: tpufabrics.com
Key Highlights: TPU Fabric has its own advantages which make it a popular selection various companies. It is a resistant waterproof Fabric to oil, oil, and chemical compounds….
#8 Bio TPU™
Domain Est. 1993
Website: lubrizol.com
Key Highlights: Bio TPU by Lubrizol is a revolutionary line of bio-based thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) that’s made with renewable-sourced material….
#9 Huntsman Polyurethanes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: huntsman.com
Key Highlights: Huntsman Polyurethanes is a global leader in MDI-based polyurethanes, serving over 3,000 customers in more than 90 countries….
#10 TPU Coated Fabrics
Domain Est. 2000
Website: eastexproducts.com
Key Highlights: TPU fabrics can be RF welded and heat-sealed to create impervious seams which allow for the creation of air and fluid-holding parts and devices….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Thermoplastic Polyurethane Fabric
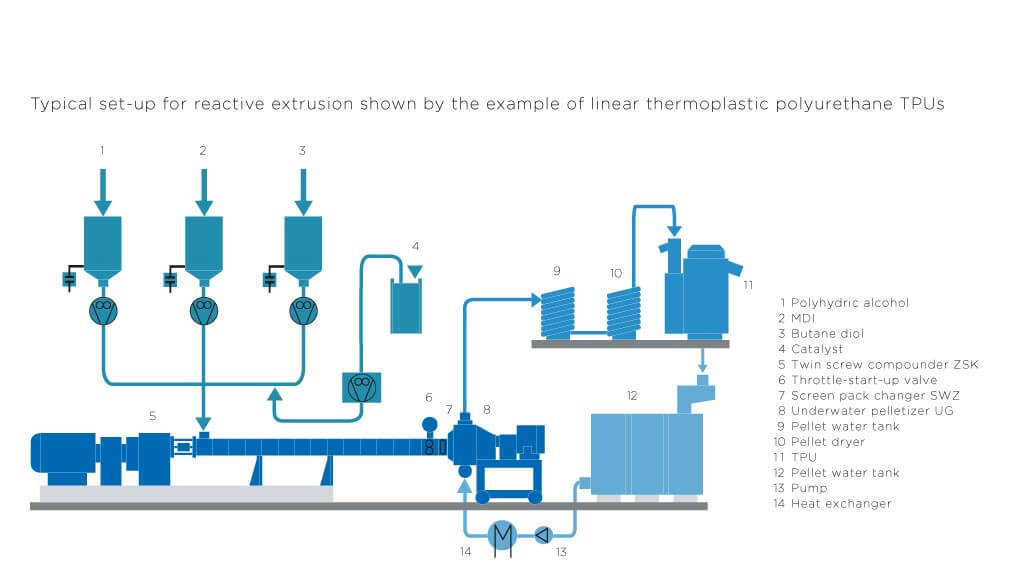
H2: Market Trends for Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Fabric in 2026
The global Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) fabric market is poised for significant transformation and growth by 2026, driven by evolving consumer demands, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. As industries across automotive, apparel, electronics, and healthcare continue to seek high-performance, flexible, and eco-conscious materials, TPU fabric is emerging as a preferred alternative to conventional plastics and rubber-based textiles. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the TPU fabric landscape in 2026:
1. Rising Demand for Sustainable and Recyclable Materials
Environmental regulations and consumer awareness are accelerating the shift toward recyclable and bio-based TPU fabrics. By 2026, manufacturers are increasingly investing in bio-sourced TPU and closed-loop recycling technologies to meet circular economy goals. Brands in the athletic and outdoor apparel sectors—such as Nike, Adidas, and Patagonia—are integrating eco-friendly TPU fabrics into their product lines, boosting market credibility and demand.
2. Expansion in Automotive and Transportation Applications
The automotive industry is a major growth driver, with TPU fabric gaining traction in interior upholstery, airbags, and wire & cable insulation due to its abrasion resistance, flexibility at low temperatures, and compliance with safety standards. As electric vehicle (EV) production increases globally, demand for lightweight, flame-retardant, and durable interior materials like TPU fabric is expected to surge.
3. Growth in Smart Textiles and Wearable Technology
TPU’s excellent elasticity, transparency, and compatibility with conductive inks make it ideal for use in smart textiles and wearable electronics. By 2026, integration of TPU fabrics in fitness trackers, health-monitoring garments, and heated clothing is projected to expand, especially as advancements in printed electronics and flexible sensors continue.
4. Innovation in Coating and Lamination Technologies
Manufacturers are focusing on developing thinner, more breathable, and high-performance TPU-coated fabrics for applications in sportswear, medical textiles, and protective gear. Innovations such as solution-based coating, blow film extrusion, and co-extrusion processes are enabling enhanced barrier properties, improved durability, and reduced environmental impact.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, remains the largest producer and consumer of TPU fabric, fueled by robust textile and manufacturing industries. However, by 2026, North America and Europe are expected to witness accelerated growth due to stricter environmental regulations and a push for localized production to reduce supply chain vulnerabilities exposed during global disruptions.
6. Price Volatility and Raw Material Challenges
Despite growth, the TPU fabric market may face headwinds from fluctuating prices of key raw materials such as polyester/polyether polyols and diisocyanates. Companies are mitigating risks through long-term supplier contracts and R&D into alternative feedstocks, including bio-based monomers.
7. Increased Competition and Product Differentiation
As market attractiveness grows, new entrants and established chemical companies (e.g., Covestro, BASF, Lubrizol) are intensifying competition through product differentiation—offering TPU fabrics with antimicrobial properties, UV resistance, or enhanced softness—tailored to niche applications.
In conclusion, the TPU fabric market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and diversification across high-growth industries. Stakeholders who prioritize eco-design, digital integration, and agile manufacturing are likely to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Fabric – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) fabric presents several challenges, particularly in ensuring consistent quality and avoiding intellectual property (IP) risks. Buyers, manufacturers, and designers must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to performance failures, legal disputes, or reputational damage.
1. Inconsistent Material Quality and Performance
One of the most prevalent issues in sourcing TPU fabric is variability in quality across suppliers. Key performance attributes—such as tensile strength, abrasion resistance, UV stability, and flexibility—can differ significantly due to variations in raw materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards.
- Unverified Specifications: Suppliers may provide misleading or exaggerated technical data sheets. Without independent testing or certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM), performance claims may not reflect real-world behavior.
- Batch-to-Batch Inconsistencies: Especially with lower-tier manufacturers, production processes may lack stringent controls, leading to inconsistent thickness, coating adhesion, or elasticity.
- Substandard Base Fabrics: The performance of TPU-coated fabric depends not only on the TPU layer but also on the underlying textile (e.g., polyester, nylon). Poor-quality base fabrics can compromise durability and drape.
2. Lack of Transparency in Supply Chain
Many TPU fabric suppliers source materials from multiple intermediaries, making it difficult to trace the origin of raw components. This opacity can lead to:
– Use of recycled or off-spec TPU resins that degrade performance.
– Exposure to conflict materials or non-compliant manufacturing practices (e.g., environmental or labor violations).
– Inability to ensure regulatory compliance (e.g., REACH, RoHS).
3. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
TPU fabric technology—particularly high-performance variants with proprietary formulations or lamination techniques—often involves protected IP. Sourcing from unauthorized or unlicensed manufacturers can lead to legal exposure.
- Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products: Some suppliers replicate well-known branded TPU fabrics (e.g., imitation of知名品牌 like Habotex, Ringtex, or Saint-Gobain’s TPU laminates) without proper licensing, infringing on patents or trademarks.
- Patented Manufacturing Processes: Certain TPU application methods (e.g., solution vs. extrusion coating, specific bonding techniques) may be patented. Unlicensed use can result in legal action, especially in export markets with strong IP enforcement.
- Design and Pattern Copying: Custom embossing, textures, or aesthetic features may also be protected, leading to IP conflicts if replicated without permission.
4. Misrepresentation of TPU Content and Type
Suppliers may mislabel or misrepresent the type or percentage of TPU used. For example:
– Blending TPU with cheaper polymers (e.g., PVC or polyethylene) without disclosure.
– Confusing TPU with TPE (thermoplastic elastomer), which has different mechanical and chemical properties.
– Offering “TPU-like” materials that lack the durability and elasticity of genuine TPU.
5. Inadequate Testing and Certification
Many sourced TPU fabrics lack proper third-party validation. Relying solely on supplier assurances without independent testing can result in:
– Failure in end-use applications (e.g., outdoor gear failing in UV exposure, medical fabrics not meeting biocompatibility standards).
– Non-compliance with industry-specific regulations (e.g., food contact, flame retardancy, medical device standards).
Mitigation Strategies
– Conduct factory audits and request material traceability documentation.
– Require sample testing through accredited labs for critical performance metrics.
– Verify IP status of branded fabrics and ensure proper licensing.
– Work with reputable suppliers who provide full transparency and compliance certifications.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that TPU fabric meets performance expectations and legal requirements, protecting both product integrity and brand reputation.
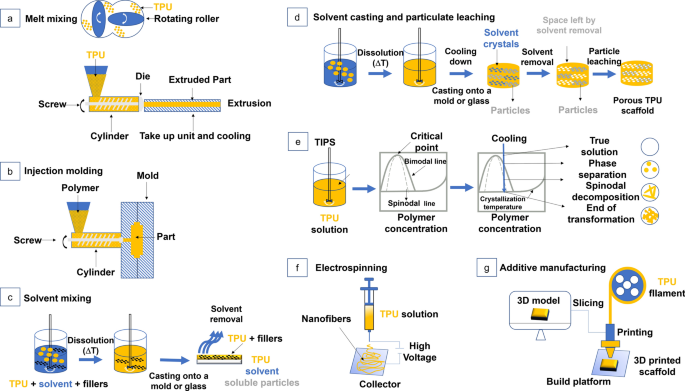
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) Fabric
Overview of TPU Fabric
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) fabric is a versatile, flexible, and durable coated textile widely used in apparel, sports gear, medical devices, and automotive interiors. It combines the elasticity and resilience of rubber with the processability of thermoplastics. Ensuring compliant and efficient logistics is essential for safe handling, transportation, and regulatory adherence.
Classification & Identification
- Chemical Composition: TPU is a polymer formed by reacting diisocyanates with polyols and chain extenders. It is thermoplastic, meaning it can be re-melted and reprocessed.
- HS Code (Harmonized System): Typically classified under 5903.20 (“Textile fabrics impregnated, coated, covered or laminated with plastics, of man-made filaments”). Confirm with local customs for precise coding.
- UN Number: Generally not regulated as hazardous in solid form. However, precursors (e.g., diisocyanates) may be hazardous. Verify based on formulation.
- CAS Number: Varies by manufacturer and formulation; common TPU resins may include CAS 26471-62-5 (generic TPU).
Packaging Requirements
- Roll Protection: TPU fabric is typically supplied in rolls. Use robust cardboard cores, stretch wrap, and outer polyethylene or kraft paper coverings to prevent moisture, dust, and mechanical damage.
- Palletization: Secure rolls on wooden or plastic pallets using straps or shrink film. Avoid overstacking to prevent edge crushing.
- Moisture Control: Include desiccants if shipping to high-humidity regions to prevent hydrolysis (especially in ester-based TPU).
- Labeling: Clearly mark packaging with:
- Product name and grade
- Batch/lot number
- Net weight and dimensions
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Do Not Stack,” “Protect from Sunlight”)
- Manufacturer and contact details
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: Store between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Avoid prolonged exposure above 40°C to prevent softening or deformation.
- Humidity: Maintain relative humidity below 65% to minimize moisture absorption, particularly for hydrolysis-sensitive TPU types.
- Light: Protect from direct sunlight and UV radiation to prevent degradation and discoloration.
- Ventilation: Store in well-ventilated areas away from strong oxidizers, acids, and solvents.
- Shelf Life: Typically 12–24 months when stored properly. Follow manufacturer recommendations.
Transportation Guidelines
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, sea, and air freight in non-hazardous classification.
- Container Conditions: Use dry, clean containers. Avoid condensation during sea freight; consider moisture-absorbing pallets or container desiccants.
- Stacking: Limit stack height to prevent deformation. Use edge protectors if necessary.
- Temperature Control: Avoid extreme temperatures. For sensitive grades, consider climate-controlled transport.
- Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and any requested certificates (e.g., CoA, compliance statements).
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU): Ensure registration of TPU substances under Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. Confirm SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) status; most TPUs are compliant if properly formulated.
- RoHS (EU): Applicable if used in electrical/electronic equipment. TPU fabric typically complies if free of lead, cadmium, mercury, and certain flame retardants.
- REACH SVHC & SCIP: Report if TPU contains SVHCs above 0.1% w/w in articles. Submit to SCIP database if applicable.
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Verify that TPU does not contain listed carcinogens or reproductive toxicants (e.g., certain diisocyanates in residual form).
- TSCA (USA): Confirm TPU polymer is listed on the TSCA Inventory. Most commercial TPUs are compliant.
- REACH & POPs Regulation: Ensure no unintentional presence of persistent organic pollutants (e.g., PFAS, if used as additives).
- Country-Specific Requirements: Check import regulations in destination markets (e.g., China GB standards, Korea K-REACH).
Safety & Handling
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves and safety glasses during handling to avoid skin irritation or eye contact with dust or off-gassing during processing.
- Dust Control: Minimize dust generation during cutting or machining; use local exhaust ventilation.
- Fire Safety: TPU is combustible but typically self-extinguishing. Store away from ignition sources. Use CO₂ or dry chemical extinguishers if fire occurs.
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of waste in accordance with local regulations. TPU is recyclable via reprocessing; incineration should follow environmental standards.
Documentation & Traceability
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA): Provide with each shipment, including physical properties, composition, and compliance status.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Required under GHS (Globally Harmonized System). Ensure SDS reflects the final fabric form, not just raw resin.
- Compliance Declarations: Issue RoHS, REACH, and Prop 65 compliance statements as needed.
- Batch Traceability: Maintain records linking raw materials, production batches, and shipments for recall readiness.
Special Considerations
- Recyclability & Sustainability: Highlight recyclability in marketing and logistics planning. Consider take-back programs for end-of-life TPU products.
- Customs Clearance: Provide accurate product descriptions and technical specifications to avoid delays. Include fabric weight, coating type, and fiber base (e.g., polyester, nylon).
- Cold Chain for Sensitive Grades: Some specialty TPUs (e.g., bio-based or low-temperature flexible) may require temperature-controlled logistics.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management for TPU fabric ensure product integrity, regulatory adherence, and supply chain efficiency. Collaborate closely with suppliers, freight forwarders, and regulatory experts to maintain standards across global operations. Always consult the manufacturer’s technical and safety documentation for product-specific guidance.
In conclusion, sourcing thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) fabric requires careful consideration of quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. TPU fabric offers exceptional performance in terms of flexibility, durability, waterproofing, and breathability, making it ideal for applications in apparel, outdoor gear, medical textiles, and technical fabrics. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to evaluate material specifications, production capabilities, environmental and regulatory compliance (such as REACH, RoHS, and OEKO-TEX), and sustainability practices—especially as demand for eco-friendly materials grows.
Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers, particularly those offering customization, consistent quality control, and transparent supply chains, ensures long-term success. Additionally, staying informed about advancements in TPU technology and alternative sustainable materials can provide a competitive advantage. Ultimately, a strategic and due-diligent approach to sourcing TPU fabric supports product excellence, brand integrity, and market responsiveness.