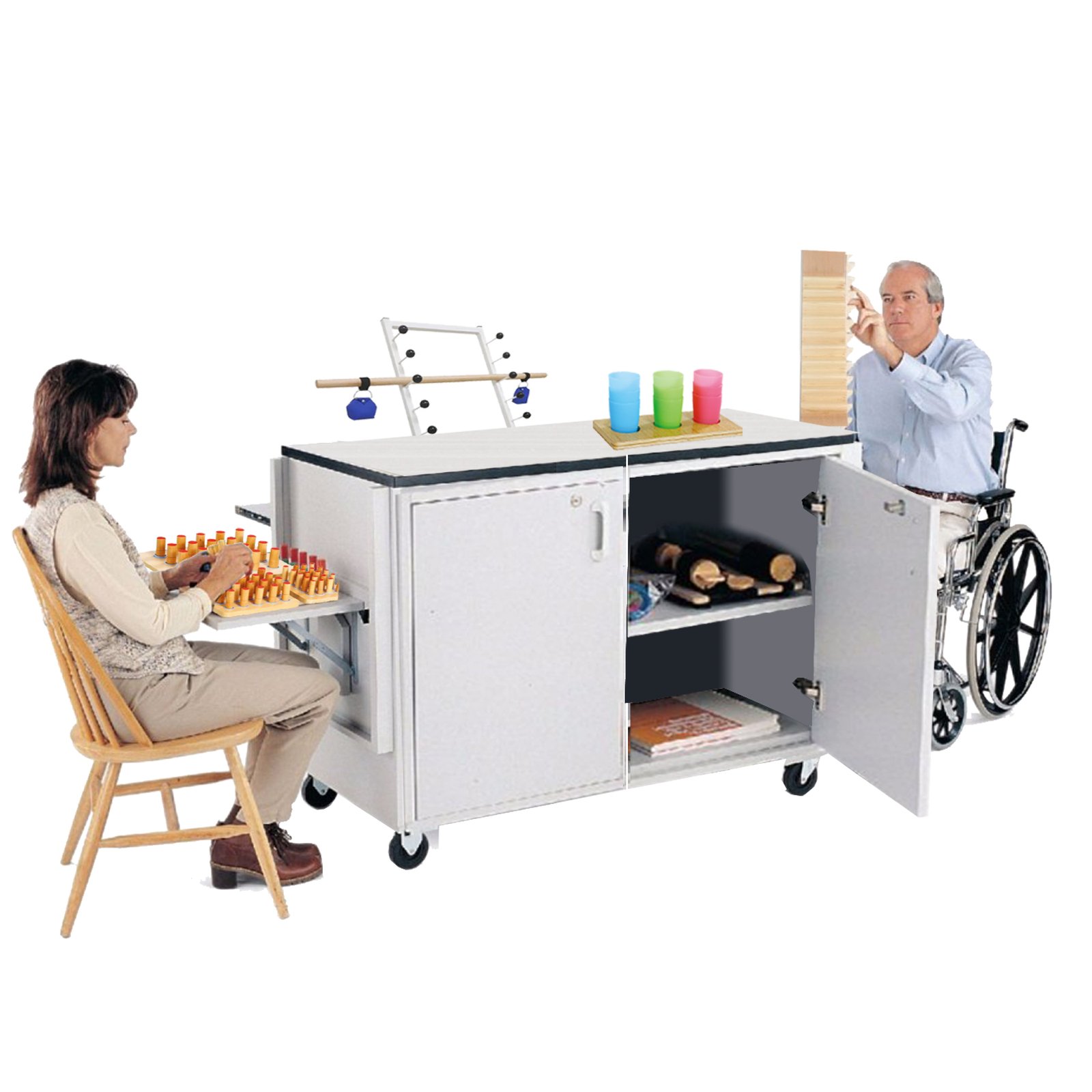
The global occupational therapy equipment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by an aging population, rising prevalence of chronic conditions, and increased focus on rehabilitation services. According to Grand View Research, the global rehabilitation equipment market was valued at USD 2.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of approximately 6.5% over the forecast period 2024–2029, underscoring the escalating demand for advanced therapeutic devices. This growth is further amplified by technological advancements in assistive and adaptive equipment, increased healthcare spending, and supportive government initiatives. As demand for occupational therapy solutions rises across hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and home care settings, manufacturers are innovating to meet diverse clinical needs. Below, we spotlight the top 10 occupational therapy equipment manufacturers leading the industry through innovation, product quality, and global reach.
Top 10 Therapy Equipment Occupational Therapy Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Rifton
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rifton.com
Key Highlights: Leading manufacturer of complex rehab technology in the USA. Find durable adaptive equipment and innovative assistive technology at Rifton Equipment….
#2 OPTP
Domain Est. 1995
Website: optp.com
Key Highlights: KNOWLEDGE FOR HEALTH. OPTP® is a leading provider of innovative physical therapy, fitness and wellness products developed by renowned experts….
#3 Southpaw Enterprises
Domain Est. 1995
Website: southpaw.com
Key Highlights: Southpaw continues to work closely with therapists and specialists from all over the country to provide you with the best Sensory Integration and Multi-Sensory ……
#4 Bailey Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: baileymfg.com
Key Highlights: Bailey Manufacturing makes physical therapy, occupational therapy and sports medicine products in the size and color that fits your need….
#5 North Coast Medical
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ncmedical.com
Key Highlights: North Coast Medical is a global Occupational, Physical and Hand rehabilitation distributor specializing in supplying the most commonly requested brands and ……
#6 Therapy & Rehabilitation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: medline.com
Key Highlights: We have all Cognitive Therapy, Dining Aids, Evaluation Supplies, Exercise & Mobility, Foot Stools, Grooming & Dressing Aids, Hearing Assistance, Heel & Elbow ……
#7 Rehabmart.com
Domain Est. 1999
Website: rehabmart.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryRehabmart.com is an Online discount medical equipment and supply company that is owned and operated by occupational and physical therapists….
#8 Sammons Preston
Domain Est. 2002
Website: performancehealth.com
Key Highlights: Dedicated to offering innovative aids to daily living, and products for exercise therapy, bathing and toileting, fall prevention and positioning, mobility and ……
#9
Domain Est. 2008 | Founded: 1974
Website: fab-ent.com
Key Highlights: Since 1974. Fabrication Enterprises Inc (FEI) has manufactured and distributed PT, OT. and Chiropractic products being used through-out the world today….
#10
Domain Est. 2010
Website: btetechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Evidence-based rehabilitation equipment developed for Occupational Therapists, Physical Therapists, Athletic Trainers, Chiropractors, and other Physiotherapy ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Therapy Equipment Occupational Therapy

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Occupational Therapy Equipment
The global occupational therapy equipment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by demographic shifts, technological advancements, and increased healthcare awareness. Several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape in the coming years.
-
Aging Population and Rising Chronic Diseases
The growing elderly population worldwide—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia—is a primary driver of demand for occupational therapy (OT) equipment. Age-related conditions such as arthritis, stroke, Alzheimer’s, and mobility impairments necessitate greater use of assistive devices, adaptive tools, and rehabilitation equipment. By 2026, this demographic trend is expected to sustain market growth, especially in home healthcare settings. -
Expansion of Home-Based and Telehealth Services
The shift toward decentralized care models, accelerated by the pandemic, continues to influence OT equipment demand. By 2026, there will be increased adoption of portable, user-friendly devices designed for home use, such as grab bars, reachers, dressing aids, and digital therapy platforms. Integration with telehealth platforms allows clinicians to remotely monitor patient progress and recommend equipment adjustments, further driving innovation in smart OT tools. -
Technological Integration and Smart Devices
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), wearable sensors, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into OT equipment is a major trend. Smart rehabilitation devices—such as sensor-embedded gloves for hand therapy or balance trainers with real-time feedback—are expected to gain traction by 2026. These technologies enhance therapeutic outcomes, improve patient engagement, and provide data-driven insights for personalized care plans. -
Personalization and Customization
There is a growing emphasis on patient-specific solutions in occupational therapy. Equipment manufacturers are increasingly offering customizable and modular products, including adaptive seating systems, orthotics, and ergonomic tools tailored to individual physical and cognitive needs. This trend aligns with the broader healthcare movement toward precision medicine and patient-centered care. -
Growth in Pediatric and Mental Health Applications
Occupational therapy equipment for children with developmental disorders (e.g., autism, ADHD) and those requiring sensory integration therapy is expected to expand significantly by 2026. Additionally, rising awareness of mental health issues is leading to increased use of OT tools in psychiatric and behavioral health settings, including sensory rooms and stress-reduction equipment. -
Regulatory Support and Reimbursement Improvements
Government initiatives and insurance reforms in countries like the U.S., Germany, and Japan are improving access to occupational therapy services and equipment. By 2026, clearer reimbursement pathways for adaptive and assistive devices are likely to encourage greater market penetration and investment in innovative OT solutions. -
Sustainability and Ergonomic Design
Environmental concerns are influencing product development, with manufacturers adopting sustainable materials and energy-efficient production methods. Simultaneously, ergonomic design principles are being prioritized to ensure long-term usability and comfort, especially for caregivers and patients with prolonged equipment use.
In conclusion, the 2026 occupational therapy equipment market will be defined by innovation, personalization, and accessibility. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, clinicians, and policymakers—must align efforts to meet evolving patient needs and leverage technology for improved therapeutic outcomes.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Occupational Therapy Equipment (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing occupational therapy (OT) equipment involves more than just finding the lowest price. Missteps in evaluating quality and overlooking intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to significant risks, including compromised patient safety, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Regulatory Compliance and Certification
One of the most critical quality pitfalls is assuming that all available equipment meets necessary medical or safety standards. Occupational therapy tools—especially those used for mobility, sensory integration, or assistive technology—may be classified as medical devices in many regions. Sourcing products without proper certifications (such as FDA 510(k) clearance in the U.S., CE marking in the EU, or ISO 13485 for manufacturing quality management) can result in legal penalties and unsafe products in clinical settings.
Prioritizing Cost Over Durability and Functionality
Budget constraints often lead purchasers to select cheaper alternatives, but low-cost equipment may be made from substandard materials or lack ergonomic design. Poorly constructed items may break under regular use, posing injury risks to patients and therapists. Additionally, non-functional or poorly designed tools can hinder therapy outcomes, undermining the effectiveness of treatment plans.
Ignoring Evidence-Based Design and Clinical Validation
High-quality OT equipment should be developed with input from occupational therapists and grounded in evidence-based practice. Sourcing products without clinical validation or user testing may result in tools that look promising but fail to deliver therapeutic benefits. Always verify whether the equipment has been tested in real-world clinical environments and whether peer-reviewed research supports its use.
Failing to Verify Manufacturer Authenticity and Reputation
Counterfeit or imitation therapy products are increasingly common, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. These products may mimic reputable brands but lack the same quality controls, materials, or safety features. Always vet suppliers thoroughly—check for verifiable business credentials, customer reviews, and direct communication with the manufacturer. A red flag is when a supplier cannot provide detailed product documentation or traceability.
Neglecting Intellectual Property Rights
Using or distributing OT equipment that infringes on patents, trademarks, or copyrights exposes organizations to legal action. Some manufacturers develop proprietary designs for splints, adaptive tools, or sensory equipment protected by IP laws. Sourcing knock-offs or unlicensed copies—even unintentionally—can lead to cease-and-desist orders, financial penalties, or forced product recalls. Always confirm that the equipment does not violate existing patents and that branding/logos are authorized for use.
Assuming One-Size-Fits-All Across Regions
Equipment approved or commonly used in one country may not meet local regulations or cultural needs in another. Sourcing without considering regional differences in healthcare standards, patient demographics, or therapy approaches can result in unusable or inappropriate products. For example, an adaptive seating system designed for adult use in the U.S. might not accommodate pediatric patients common in another market.
Skipping Pilot Testing and User Feedback
Jumping straight into bulk procurement without testing a sample can be a costly mistake. Always request prototypes or trial units and involve occupational therapists and end-users in the evaluation process. Their feedback on usability, safety, and therapeutic value is crucial to ensuring the equipment meets practical needs.
By being vigilant about quality benchmarks and intellectual property considerations, healthcare providers and procurement teams can source occupational therapy equipment that is safe, effective, legally compliant, and truly supportive of patient outcomes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Occupational Therapy Equipment
Equipment Procurement and Sourcing
When acquiring occupational therapy (OT) equipment, it is essential to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and therapeutic requirements. Procurement should prioritize equipment that meets FDA classifications (Class I, II, or III) as appropriate. Suppliers must provide documentation such as 510(k) clearances, CE marking (for international use), or ISO 13485 certification. Establish vendor agreements outlining delivery timelines, warranty terms, and return policies. Consider ergonomic design, adjustability, and accessibility to ensure equipment supports diverse patient needs.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
All therapy equipment must comply with applicable regulations including the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820), HIPAA (if equipment collects patient data), and ADA accessibility standards. Maintain detailed records for each device, including model number, serial number, purchase date, service history, and compliance certifications. Ensure that software-based tools (e.g., digital assessment platforms) are updated and secured in accordance with cybersecurity best practices. Regular audits should verify adherence to regulatory requirements.
Transportation and Delivery Management
Coordinate equipment deliveries to minimize disruptions in clinical operations. Use insured and trackable shipping methods, particularly for high-value or specialized devices. Upon delivery, inspect all items for damage and verify contents against packing lists. Require signature upon receipt and document delivery conditions. For equipment requiring assembly, ensure trained personnel are available and follow manufacturer instructions precisely to maintain warranty validity and safety standards.
Installation, Calibration, and Commissioning
Before clinical use, all equipment must be properly installed and calibrated according to manufacturer guidelines. This includes mechanical adjustments, software setup, and network integration (if applicable). Document the calibration process and retain records for audits. For devices such as sensory integration tools or motor assessment systems, perform initial performance checks to confirm accuracy and functionality. Only certified staff should commission complex equipment.
Maintenance and Servicing Protocols
Implement a preventive maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations and usage frequency. Maintenance logs should track inspections, repairs, part replacements, and technician certifications. Establish procedures for responding to equipment malfunctions, including temporary replacement strategies to maintain continuity of care. Keep spare parts and service manuals on-site or readily accessible. Contract with authorized service providers to ensure repairs meet regulatory and safety standards.
User Training and Competency
All occupational therapists and support staff must receive training on the safe and effective use of therapy equipment. Training should cover operational procedures, safety precautions, cleaning protocols, and emergency shutdown processes. Maintain training records and require competency assessments for high-risk or complex devices. Provide updated training when new equipment is introduced or existing equipment is modified.
Infection Control and Sanitization
OT equipment, especially shared or patient-contact items (e.g., splints, adaptive tools, therapy balls), must be cleaned and disinfected according to CDC guidelines and manufacturer instructions. Use EPA-registered disinfectants appropriate for each material type. Establish a cleaning schedule and assign responsibility to specific staff members. Document sanitization activities, particularly for clinics with high patient turnover or immunocompromised populations.
Equipment Lifecycle and Disposal
Monitor equipment lifespan and plan for timely replacement of outdated or non-compliant devices. Decommission equipment that no longer meets safety or performance standards. Follow proper disposal protocols in accordance with environmental regulations (e.g., e-waste for electronic devices) and data protection laws (for devices storing patient information). For donated or resold equipment, ensure data is securely wiped and functionality is verified.
Risk Management and Incident Reporting
Establish a system for reporting equipment-related incidents, such as malfunctions, injuries, or near misses. Investigate all reports promptly and document findings. Report adverse events to the FDA via the MAUDE database when required. Use incident data to improve procurement decisions, training programs, and maintenance schedules. Conduct periodic risk assessments to identify potential hazards associated with equipment use.
Audit Preparedness and Record Retention
Maintain an organized compliance file for each piece of equipment, including purchase records, service logs, training documentation, and inspection reports. Retain records per regulatory requirements—typically 5–7 years, or longer for implantable or high-risk devices. Prepare for internal and external audits by conducting regular self-assessments and updating policies to reflect current standards and best practices in occupational therapy equipment management.
Conclusion: Sourcing Occupational Therapy Equipment
In conclusion, sourcing occupational therapy equipment requires a thoughtful and strategic approach that balances clinical effectiveness, client needs, safety standards, and budget considerations. The selection and acquisition of appropriate tools and devices are critical to supporting clients’ independence, enhancing therapeutic outcomes, and facilitating meaningful participation in daily activities. It is essential to collaborate with reputable suppliers, assess product quality and evidence-based design, and stay informed about technological advancements and ergonomic innovations in the field.
Furthermore, involving occupational therapists in the procurement process ensures that equipment aligns with therapeutic goals and accommodates diverse client populations, including pediatric, geriatric, and neurorehabilitation cases. Considering factors such as durability, accessibility, and ease of use ultimately contributes to long-term cost-efficiency and client satisfaction.
By adopting a comprehensive and client-centered strategy in sourcing occupational therapy equipment, healthcare providers and institutions can create enabling environments that promote recovery, independence, and improved quality of life for individuals across the lifespan.