The global battery manufacturing industry is experiencing unprecedented expansion, driven by rising demand for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage, and portable electronics. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global battery market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.7% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated value of USD 188.6 billion by 2028. This rapid growth, coupled with advancements in lithium-ion and solid-state battery technologies, has placed immense pressure on manufacturers to improve production efficiency, ensure product reliability, and maintain stringent safety standards—all of which hinge on the performance of terminal connections in battery cells.
Terminals, the critical interface for electrical current flow, play a vital role in determining battery efficiency, thermal management, and longevity. With increasing automation in gigafactories and tighter tolerances required for next-gen batteries, selecting the right terminal technology has become a key operational imperative. From stamped copper terminals with anti-corrosion coatings to advanced laser-welded designs, innovation in terminal engineering is keeping pace with market demands. As competition intensifies and production scales, battery manufacturers are prioritizing terminals that offer high conductivity, robust mechanical strength, and compatibility with high-speed assembly lines. The following list highlights the top 10 terminal solutions shaping the future of battery manufacturing, based on technical performance, industry adoption, and alignment with evolving safety and scalability standards.
Top 10 Terminal For Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 A.C. Terminals
Domain Est. 2000 | Founded: 1973
Website: acterminals.com
Key Highlights: A.C. Terminals has been a leading battery terminal manufacturer since 1973. We make and supply terminals and accessories to businesses across the US….
#2 Terminal Technologies
Domain Est. 2000
Website: terminaltechnology.com
Key Highlights: We are India’s leading manufacturers and suppliers of terminal, connector solutions, serving the Auto, Appliances, Electronics, and Electrical industries ……
#3 Keystone Electronics Corp.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: keyelco.com
Key Highlights: Electronic Components & Hardware · Battery Clips Contacts Holders · Fuse Clips Holders · Terminals Test Points · Spacers Standoffs · Panel Hardware · Pins Plugs Jacks ……
#4 Stamped Battery Terminals
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Eaton’s stamped battery terminals deliver robust electrical connections, perfect for power distribution and battery management applications….
#5 QuickCable
Domain Est. 1996
Website: quickcable.com
Key Highlights: QuickCable is your source for the widest selection of battery terminals and lugs. We manufacture our products using die-cast copper or premium copper tubing to ……
#6 Automotive Battery Terminals
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mta.it
Key Highlights: MTA produces different kinds of battery terminals: Strip, double ring, quick lock battery terminals; Go/No-go battery terminals; Intelligent battery ……
#7 Terminal Supply Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: terminalsupplyco.com
Key Highlights: Our electrical line includes Molex heat shrink terminals and Bussmann fuses and circuit breakers. We carry a wide inventory of Cole Hersee switches and ……
#8 Wire, Cable, Terminals, & More Battery Accessories
Domain Est. 2002
Website: eastpennmanufacturing.com
Key Highlights: Explore battery accessories from Deka & East Penn Manufacturing. Find wires, cables, terminals, clamps, & custom solutions fast with our application guide….
#9 Terminals
Domain Est. 2009 | Founded: 2005
Website: 4xspower.com
Key Highlights: 3-day delivery 30-day returnsXS Power Batteries was established in 2005 on the east coast of the US with a passion for powering the impossible….
#10 Terminal Manufacturing
Domain Est. 2024
Website: kingterminals.com
Key Highlights: Solutions for sensitive and critical electrical connection terminals have been specifically developed by us. Our comprehensive product range includes connection ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Terminal For Battery

H2: Market Trends for Battery Terminals in 2026
As the global shift toward electrification accelerates, the battery terminal market is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in energy storage, electric vehicles (EVs), renewable integration, and industrial automation, demand for high-performance, durable, and efficient battery terminals is expected to grow substantially. Below is an in-depth analysis of key market trends shaping the battery terminal industry in 2026:
1. Surge in Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
The automotive sector remains the largest driver of battery terminal demand. With EV sales projected to exceed 40 million units annually by 2026 (according to BloombergNEF), manufacturers are increasingly investing in high-capacity lithium-ion and solid-state batteries. This growth necessitates advanced battery terminals capable of handling higher currents, improved thermal management, and enhanced conductivity.
- Trend: Rising demand for copper and aluminum terminals with anti-corrosion coatings.
- Innovation: Integration of smart terminals with embedded sensors for real-time monitoring of voltage, temperature, and connection integrity.
2. Expansion of Renewable Energy Storage Systems
As solar and wind power penetration increases globally, utility-scale and residential energy storage systems (ESS) are becoming essential for grid stability. These systems rely heavily on large-format batteries requiring robust terminal connectors.
- Trend: Growth in demand for modular, scalable terminal solutions compatible with lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and sodium-ion batteries.
- Regional Focus: Asia-Pacific and North America lead in ESS deployment, boosting regional terminal manufacturing.
3. Material Innovation and Sustainability
Environmental regulations and supply chain concerns are pushing manufacturers to explore alternative materials and sustainable production methods.
- Trend: Increased R&D in copper-alloy composites and recycled copper terminals to reduce reliance on virgin materials.
- Sustainability: Emphasis on lead-free, RoHS-compliant terminals and eco-friendly plating processes (e.g., tin-silver coatings over cadmium).
4. Miniaturization and High-Density Packaging
In consumer electronics and portable medical devices, the trend toward smaller, more powerful batteries demands compact, high-efficiency terminals.
- Trend: Development of micro-terminals with enhanced current-carrying capacity and resistance to thermal cycling.
- Technology: Use of precision stamping and surface-mount technologies (SMT) for integration into compact battery packs.
5. Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Battery terminal production is becoming increasingly automated to meet quality, scalability, and cost-efficiency requirements.
- Trend: Adoption of Industry 4.0 practices, including AI-driven quality control and IoT-enabled production lines.
- Impact: Reduced defect rates and faster time-to-market for customized terminal designs.
6. Geopolitical and Supply Chain Dynamics
Trade policies, raw material availability (especially copper), and regional manufacturing incentives are shaping supply chain strategies.
- Trend: Regionalization of production to mitigate risks—e.g., nearshoring in North America and Europe.
- Opportunity: Growth in local terminal manufacturing hubs in India, Mexico, and Eastern Europe.
7. Standardization and Safety Regulations
As battery applications diversify, standardization of terminal designs and safety protocols is gaining importance.
- Trend: Alignment with IEC, UL, and ISO standards for terminal performance and fire safety.
- Regulatory Push: Stricter requirements for arc resistance, vibration tolerance, and overcurrent protection in EV and ESS applications.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the battery terminal market will be defined by innovation, sustainability, and integration with smart technologies. Key players will need to adapt to evolving material demands, regional regulatory landscapes, and the need for high-reliability components across EVs, energy storage, and industrial sectors. Companies investing in R&D, automation, and circular economy models are likely to lead the market, capitalizing on the electrification megatrend.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Terminals for Batteries (Quality and IP)
When sourcing battery terminals—critical components for electrical connectivity and safety—overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, and legal risks. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Material Quality and Conductivity
One of the most frequent issues is selecting terminals made from substandard materials such as low-grade copper alloys or impure brass. Inferior materials result in higher electrical resistance, leading to overheating, voltage drops, and potential fire hazards. Ensure terminals are made from high-conductivity materials like oxygen-free copper (OFC) or appropriately rated copper alloys, and verify material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH).
Inadequate Plating and Corrosion Resistance
Terminals often require plating (e.g., tin, silver, or nickel) to resist oxidation and improve conductivity. Poor or inconsistent plating thickness—common with low-cost suppliers—can lead to premature corrosion, increased contact resistance, and connection failure, especially in harsh environments. Always specify minimum plating thickness and request salt spray test results to validate durability.
Non-Compliance with IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
Battery terminals used in outdoor, automotive, or industrial applications must meet specific IP ratings (e.g., IP67, IP68) to prevent dust and moisture ingress. A common pitfall is assuming that a terminal housing is sealed based on appearance alone, without verifying actual test certifications. Always request third-party IP test reports and ensure the entire terminal assembly—not just individual parts—meets the required standard.
Lack of Mechanical Durability and Vibration Resistance
In applications like electric vehicles or industrial equipment, terminals must withstand constant vibration and mechanical stress. Poorly designed or manufactured terminals may loosen over time, leading to arcing or disconnection. Avoid terminals without proper strain relief, locking mechanisms, or mechanical retention features. Request proof of vibration and thermal cycling testing.
Inconsistent Dimensional Tolerances
Terminals with poor dimensional control may not fit properly on battery posts or mating connectors, resulting in loose connections or installation difficulties. This is especially problematic when sourcing from suppliers without stringent quality control (QC) processes. Require detailed dimensional drawings and first-article inspections (FAI) to ensure compatibility.
Counterfeit or Substandard Components
Sourcing from unauthorized or unreliable suppliers increases the risk of receiving counterfeit terminals that mimic reputable brands but fail under load. These components often lack proper traceability and certification. Always source through authorized distributors or directly from OEMs, and verify batch traceability and test reports.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Copying or reverse-engineering patented terminal designs—even unintentionally—can expose your company to legal liability. Some terminal designs (e.g., specific locking mechanisms, sealing technologies) are protected by patents. Conduct an IP clearance review before finalizing designs or sourcing from third-party manufacturers, especially in competitive markets like EVs or consumer electronics.
Inadequate Testing and Certification Documentation
Many suppliers provide incomplete or falsified test reports. Relying on self-declared compliance without independent verification can lead to field failures. Require up-to-date certifications from accredited labs (e.g., UL, TÜV, IEC) for electrical, thermal, and environmental performance.
Overlooking Supply Chain Reliability
Even high-quality terminals are of little use if the supplier cannot deliver consistently. Unreliable lead times, lack of scalability, or poor communication can disrupt production. Assess supplier stability, manufacturing capacity, and quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification) before committing.
By addressing these common pitfalls—particularly around material quality, IP compliance, and environmental protection—you can ensure reliable, safe, and legally sound battery terminal sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Terminal for Battery
Overview
This guide provides essential logistics and compliance information for the safe and legal handling, transportation, storage, and disposal of battery terminals—components used in connecting batteries to electrical systems. Battery terminals are often made of conductive metals (such as lead, copper, or brass) and may be coated or plated. While not classified as hazardous on their own, their association with batteries and materials used in manufacturing necessitates adherence to specific regulatory and logistical standards.
Regulatory Classification
Battery terminals are generally not classified as hazardous materials when shipped independently. However, classification depends on composition, coating, and intended use.
– UN/DOT Regulations: Typically not subject to hazardous material (hazmat) shipping requirements under 49 CFR when not attached to batteries.
– IATA/ICAO: Not regulated as dangerous goods under Packing Instructions unless contaminated with electrolyte or shipped with batteries.
– IMDG Code: Similar to air regulations; terminals alone are not considered dangerous goods.
– REACH & RoHS Compliance: Must comply with EU regulations restricting hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical components. Ensure material declarations are available from suppliers.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging ensures physical protection and prevents short circuits or contamination.
– Use non-conductive, anti-static packaging materials (e.g., plastic bags with shielding) to prevent electrical contact.
– Secure terminals in rigid containers to avoid movement during transit.
– Clearly label packages with part number, quantity, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
– If terminals are lead-based, include appropriate environmental hazard labels per local regulations.
Transportation Guidelines
- Domestic (USA): Ship via standard freight; no hazmat endorsement required for standalone terminals. Use common carriers (e.g., FedEx, UPS, freight lines) with tracking.
- International: Declare accurate HS Code (typically 8546.90 – Insulators and parts thereof, or 8536.90 – Electrical apparatus for circuit connection). Confirm import regulations in destination country.
- Air & Sea: No special dangerous goods documentation required unless combined with batteries. Avoid mixed shipments with hazardous battery types unless compliant with IATA/IMDG.
Storage Conditions
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent corrosion.
- Keep away from conductive materials to reduce risk of short circuits.
- Segregate lead-containing terminals from food, pharmaceuticals, and sensitive electronics.
- Follow OSHA and local fire codes for metal component storage.
Handling & Worker Safety
- Use gloves and eye protection when handling sharp or plated terminals.
- Ensure proper ventilation if handling large volumes of lead-coated terminals to minimize dust exposure.
- Follow site-specific safety protocols and provide training on material handling.
Environmental & Disposal Compliance
- Waste Classification: Spent or defective terminals may be classified as electronic waste (e-waste) or scrap metal.
- Recycling: Recycle through certified metal recyclers. Lead-containing terminals must be handled as hazardous waste under EPA regulations (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act – RCRA) if discarded.
- Documentation: Maintain records of waste disposal and recycling certificates (e.g., Certificate of Recycling).
Documentation & Traceability
- Maintain Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS) for all terminal types, especially those with plating or coatings.
- Keep records of compliance certifications (RoHS, REACH, UL).
- Provide packing lists, commercial invoices, and origin certificates for international shipments.
Special Considerations for Battery-Integrated Shipments
If terminals are shipped attached to batteries:
– Full battery transportation regulations apply (e.g., IATA PI 965–970, IMDG 38.3 testing).
– Terminals contribute to the risk of short circuit; insulate all terminals and secure connections.
– Follow manufacturer instructions for packing and labeling.
Conclusion
Battery terminals, while often non-hazardous, require careful logistics planning and compliance with environmental and transportation regulations—especially concerning material composition and end-of-life management. Always verify regulations based on destination, volume, and material content, and partner with certified suppliers and logistics providers to ensure full compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Terminals for Batteries
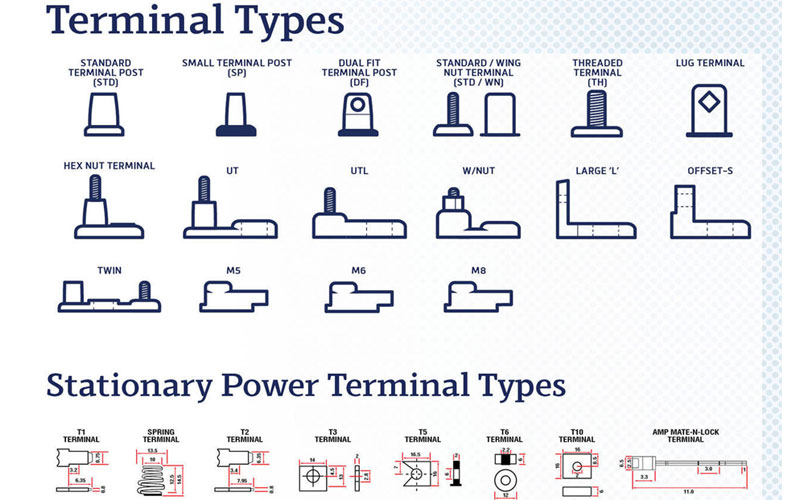
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate terminal for a battery application is a critical decision that directly impacts performance, safety, reliability, and compatibility. Key factors such as conductivity, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and dimensional accuracy must be carefully evaluated when sourcing terminals. Materials like copper, brass, and tin-plated variants are commonly preferred due to their excellent electrical properties and durability.
Additionally, adherence to industry standards (e.g., DIN, ANSI, JIS) and compatibility with specific battery types—such as lead-acid, lithium-ion, or NiMH—are essential to ensure seamless integration and long-term functionality. The choice between threaded studs, quick-disconnect terminals, or blade terminals should align with the application requirements, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers with stringent quality control processes and certifications (such as ISO 9001) further ensures consistency and reliability. In fast-evolving markets like electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and portable electronics, investing in high-quality, properly specified battery terminals supports system efficiency and reduces the risk of failure.
Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach—balancing cost, quality, and technical suitability—will optimize battery performance and support the demands of modern power systems.