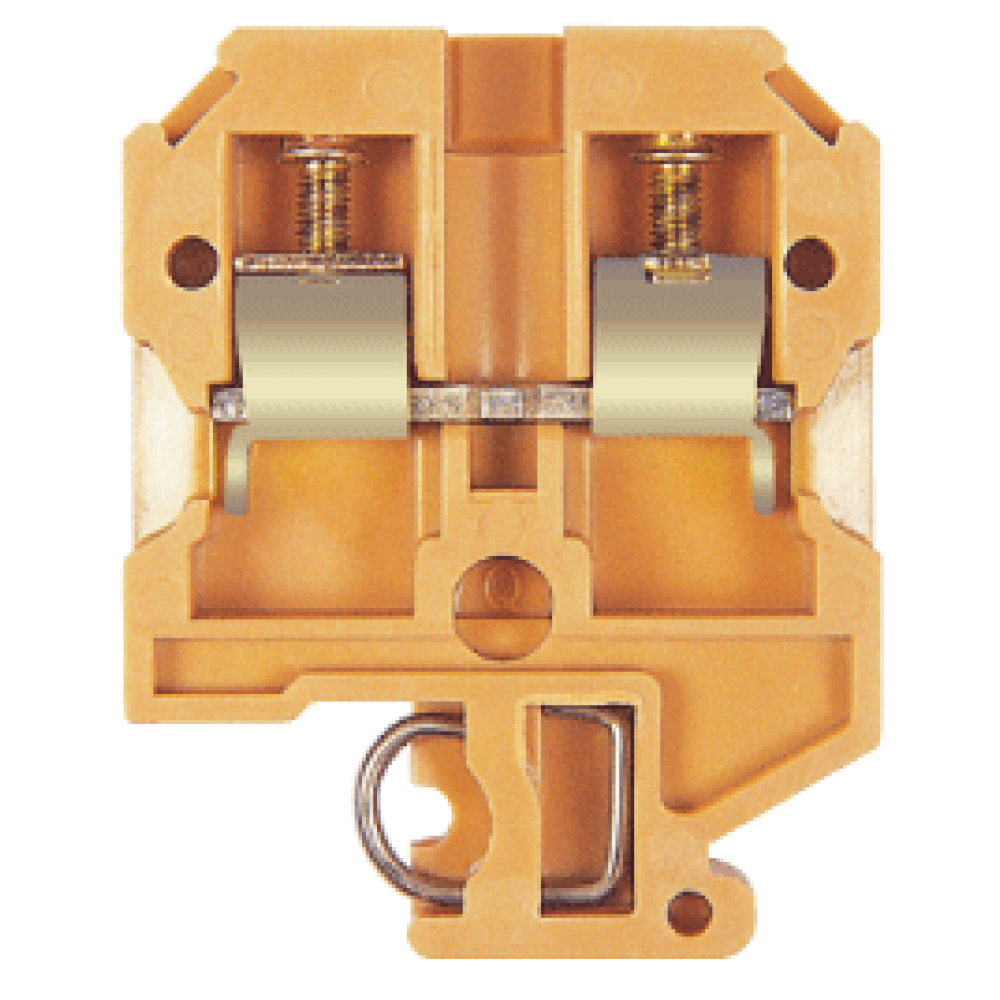
The global terminal block market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for efficient electrical connectivity solutions across industrial automation, energy, and transportation sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global terminal block market size was valued at USD 4.1 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of modular and pluggable terminal blocks in manufacturing and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies. Additionally, advancements in PCB and rail-mounted terminal technologies are enhancing performance and reliability, further propelling market expansion. As industries prioritize safety, scalability, and space efficiency in electrical systems, the role of leading manufacturers becomes increasingly pivotal. In this evolving landscape, the following ten companies stand out for their innovation, global reach, and comprehensive product offerings in the terminal block sector.
Top 10 Terminal Block Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Elmex
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1963
Website: elmex.net
Key Highlights: Elmex is a pioneer in electrical wire termination technology since 1963. We design, manufacture & supply terminal blocks, current transformers, contro……
#2 Rail / Chassis Mount Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1995
Website: wago.com
Key Highlights: Terminal blocks for industry and buildings: the largest selection of terminal blocks for DIN-rails✓ Maintenance-free✓ Push-in technology….
#3 Terminal blocks Klippon® Connect for top hat rails
Domain Est. 1996
Website: weidmuller.com
Key Highlights: Our pluggable terminal blocks can be quickly assembled and are completely factory tested. They allow the connection of up to 4 plugs. Go to product catalog To ……
#4 Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1998
Website: marshelectronics.com
Key Highlights: Marsh Electronics offers a wide selection of wire-to-wire and wire-to-board terminal blocks and strips to meet your power management application and ……
#5 China Electrical Terminal Blocks Connector Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: nbdibo.com
Key Highlights: Dorabo Electric is a professional manufacturer of terminals. It is a large-scale enterprise with technical strength and rapid development….
#6 ENTRELEC Connectors & Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: TE Connectivity manufacture a broad portfolio of M8 & M12 connectors and Din rail terminal blocks….
#7 BlockMaster Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1996
Website: blockmaster.com
Key Highlights: BlockMaster’s HP Series tab style terminal blocks are suitable for todays requirements in appliances, HVAC equipment, panels and similar products….
#8 Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1996
Website: marathonsp.com
Key Highlights: Browse our range of Terminal Blocks: Barrier, Sectional, Deadfront, Motor, Feed Thru Stud, and Military-spec options for various power and voltage needs….
#9 Terminal Block Connectors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: curtisind.com
Key Highlights: We offer standard and custom terminal blocks, or screw terminals. Our team of engineers design and manufacture any terminal blocks to exact specifications….
#10 Terminal Blocks
Domain Est. 1999
Website: automationdirect.com
Key Highlights: Terminal blocks provide easy connection of panel-mounted electronic components to device power and field wiring. A wide variety of modular terminal blocks ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Terminal Block

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Terminal Blocks
The terminal block market in 2026 is poised for robust growth and transformation, driven by evolving industrial automation, energy demands, and technological innovation. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Accelerated Demand from Industrial Automation & Industry 4.0:
As global adoption of smart factories and Industry 4.0 intensifies, the need for reliable, high-performance terminal blocks capable of handling complex data and power signals continues to surge. Terminal blocks with integrated diagnostics, sensor connectivity, and compatibility with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems are becoming standard, enhancing predictive maintenance and system uptime.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicle (EV) Infrastructure:
The expansion of solar, wind, and energy storage systems drives demand for high-voltage, high-current terminal blocks with superior thermal management and safety features. Similarly, the rapid deployment of EV charging stations—especially high-power DC fast chargers—requires durable, compact terminal blocks designed for harsh environments and frequent use.
3. Miniaturization and Space Optimization:
With increasing demand for compact control panels and equipment, terminal block manufacturers are prioritizing space-saving designs. Slim-profile, high-density terminal blocks with enhanced current-carrying capacity per unit volume are gaining traction, particularly in automation, robotics, and transportation sectors.
4. Rising Emphasis on Sustainability and Material Innovation:
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are prompting a shift toward eco-friendly materials, such as halogen-free, flame-retardant thermoplastics. Recyclability, reduced carbon footprint in production, and compliance with RoHS and REACH standards are becoming key differentiators.
5. Digitalization and Smart Terminal Blocks:
Integration of digital features—such as plug-and-play configurations, RFID tagging for asset tracking, and real-time monitoring via embedded electronics—is transforming traditional terminal blocks into intelligent components. This trend supports faster commissioning, improved traceability, and enhanced troubleshooting.
6. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience:
Asia-Pacific remains the largest and fastest-growing market due to industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia. However, nearshoring and supply chain diversification efforts in North America and Europe are creating opportunities for local manufacturing and strategic partnerships to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks.
7. Focus on Safety and Regulatory Compliance:
Stricter global safety standards (e.g., UL, IEC, CE) are driving innovation in insulation, creepage/clearance distances, and arc-fault protection. Products with enhanced safety certifications are increasingly required across industries like rail, energy, and process automation.
In summary, the 2026 terminal block market is characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability imperatives, and strong tailwinds from electrification and digital transformation. Manufacturers that innovate in connectivity, efficiency, and reliability will be best positioned to capture emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Terminal Blocks (Quality, IP)
Sourcing terminal blocks involves more than just matching electrical specifications—overlooking critical quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Price Over Quality
Choosing the lowest-cost terminal blocks often results in substandard materials, inconsistent manufacturing, and poor long-term reliability. Cheap terminals may use inferior copper alloys or plastics that degrade under heat or vibration, leading to increased resistance, overheating, or mechanical failure.
2. Assuming IP Rating Applies to the Entire Assembly
A terminal block may be rated IP67, but this rating typically applies only when properly installed with compatible end covers, sealing gaskets, and mating connectors. Failing to use all required components voids the IP protection, leaving the system vulnerable to dust and moisture ingress.
3. Misunderstanding IP Rating Requirements for the Environment
Selecting terminal blocks with insufficient IP protection (e.g., using IP20 in outdoor or washdown environments) exposes connections to contaminants. Conversely, over-specifying (e.g., IP69K where IP54 suffices) increases cost unnecessarily. Always match the IP rating to the actual operating environment.
4. Overlooking Certification and Compliance
Using non-certified terminal blocks (e.g., lacking UL, VDE, or IEC approvals) can lead to regulatory issues, void equipment warranties, or fail safety inspections. Ensure components meet regional and industry-specific standards for fire resistance, tracking index (CTI), and voltage/current ratings.
5. Ignoring Long-Term Availability and Supplier Reliability
Sourcing from obscure suppliers or using obsolete parts risks supply chain disruptions. Lack of continuity can halt production or complicate maintenance. Choose reputable suppliers with documented product lifecycle support.
6. Neglecting Mechanical Durability and Vibration Resistance
In industrial or transportation applications, terminal blocks must withstand mechanical stress. Poor clamping mechanisms or brittle housings can lead to loose connections and intermittent faults. Verify suitability for expected vibration and thermal cycling.
7. Inadequate Consideration of Installation Practices
Even high-quality, high-IP-rated terminal blocks fail if installed incorrectly—such as improper torque on screws, incomplete wire insertion, or mismatched wire gauges. Provide clear installation guidelines and training to ensure performance matches specifications.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures reliable, safe, and compliant electrical connections throughout the product lifecycle.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Terminal Blocks
Proper logistics and compliance management are essential when handling terminal blocks to ensure safety, reliability, and adherence to international standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the transportation, storage, import/export, and regulatory compliance of terminal blocks.
Transportation & Packaging
Terminal blocks must be packaged securely to prevent damage during transit. Use manufacturer-recommended packaging that provides protection against moisture, vibration, and physical impact. Avoid stacking heavy items on top of terminal block packages. When shipping internationally, ensure packages are labeled with appropriate handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Crush”). Use climate-controlled transport when moving through extreme temperature or high-humidity environments.
Storage Conditions
Store terminal blocks in a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environment. Recommended storage conditions are typically between 5°C and 40°C with relative humidity below 75%. Keep products in original packaging until ready for use to protect against dust, moisture, and contamination. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, corrosive gases, or conductive particles. Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices to minimize aging-related degradation.
Import/Export Regulations
Verify customs requirements based on the destination country. Terminal blocks may fall under HS Code 8536.90 (other electrical apparatus for switching or protecting electrical circuits). Ensure accurate product classification, documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin), and compliance with local electrical safety regulations. Be aware of REACH, RoHS, and other chemical substance restrictions that may affect cross-border shipments.
Regulatory Compliance
Terminal blocks must comply with relevant international and regional standards, including but not limited to:
- IEC 60947-7-1 / IEC 60998: Safety and performance standards for terminal blocks
- UL 1059 (North America): Standard for terminal blocks
- RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical equipment
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals
- CE Marking: Required for sale within the European Economic Area
- UKCA Marking: Required for sale in the United Kingdom
Ensure all terminal blocks are certified by accredited bodies (e.g., TÜV, UL, CSA) and that certification documentation is available upon request.
Labeling & Traceability
Each terminal block or packaging unit should include clear labeling with part number, manufacturer name, ratings (voltage, current, temperature), and compliance markings (e.g., CE, UL). Batch or lot numbers must be traceable to support quality control and recalls if necessary. Labeling must be durable and legible throughout the product’s lifecycle.
Handling & Worker Safety
Train personnel on proper handling procedures to prevent damage to terminal blocks and ensure workplace safety. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling large or sharp-edged components. Follow electrostatic discharge (ESD) precautions when dealing with sensitive versions, especially in control or signal applications.
End-of-Life & Environmental Compliance
Dispose of defective or obsolete terminal blocks in accordance with local environmental regulations. Many components are recyclable (e.g., copper, brass, thermoplastic housings). Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to ensure responsible disposal.
Conclusion for Sourcing Terminal Blocks:
Sourcing terminal blocks requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, quality standards, supplier reliability, and cost-efficiency. It is essential to select terminal blocks that meet the electrical, mechanical, and environmental requirements of the intended application—such as current and voltage ratings, temperature range, insulation material, and mounting type. Prioritizing reputable manufacturers and certified products ensures long-term performance, safety, and compliance with international standards (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS).
Additionally, building strong relationships with reliable suppliers, considering lead times, and assessing total cost of ownership—rather than just unit price—contribute to a resilient and efficient supply chain. By aligning sourcing decisions with engineering needs and operational goals, organizations can achieve enhanced system reliability, reduce maintenance costs, and support scalability in electrical and industrial applications.