The global market for industrial fastening solutions has seen steady expansion, driven by rising demand across automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global fasteners market was valued at approximately USD 111.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% through 2029. Tension pins, a critical category within precision fasteners, are gaining traction due to their reliability in high-vibration environments and ease of installation. As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and mechanical integrity, the need for high-quality tension pins has intensified. This growing demand has elevated the prominence of specialized manufacturers who combine engineering precision with scalable production. Based on market presence, product innovation, global reach, and industry certifications, the following eight companies have emerged as leading tension pin manufacturers shaping the future of industrial assembly.
Top 8 Tension Pin Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SPIROL
Domain Est. 1996
Website: spirol.com
Key Highlights: We are the leading global manufacturer of engineered fasteners, shims, installation machines, and parts feeding equipment producing over two billion components ……
#2 Tension Pin Manufacturer Supplier Exporter
Domain Est. 2006 | Founded: 1988
Website: karmasteels.com
Key Highlights: Karma Steels is the leading manufacturer supplier and exporter of forged tension pin, spring pin, coiled Pin, dowel pin in india since 1988….
#3 Roll Pins
Domain Est. 1996
Website: olander.com
Key Highlights: Shop roll pins from Olander, your trusted go-to experts for quality hardware. Browse spring pins, tension pins, and much more from our large inventory today ……
#4 Spring Pins
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lawsonproducts.com
Key Highlights: 90-day returnsLawson spring pins offer flexibility and secure fastening for mechanical jobs. Designed for strength and reliability in tough applications—shop ……
#5 Roll Pins: 20 X 80 SPRING TENSION PIN
Domain Est. 2012
Website: keysandpins.com
Key Highlights: Size Range: Various sizes ensure compatibility with different applications. Material Options: Choose from carbon steel, stainless steel, or other suitable ……
#6 Vogelsang Fastener Solutions
Domain Est. 2013
Website: vogelsangfastener.com
Key Highlights: The slotted tension pin (Rollpin) is a multi-purpose, non-threaded, versatile, and economic fastener. Material, hardness, and design provide a stronger joint ……
#7 Spring Pins
Domain Est. 2015
Website: rcfastener.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsOrder spring pins (roll pins) in steel or stainless steel with plain or black oxide finishes. Available in inch and metric sizes with fast shipping and …
#8 Slotted Spring Pins & Roll Pins
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mwcomponents.com
Key Highlights: Slotted spring pins and roll pins for sale. We offer stock and custom sizes and materials. See our full product offering online and request a quote….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tension Pin

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tension Pins
The global tension pin market is poised for steady growth in 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, rising automation across key industries, and increasing demand for precision fastening solutions. Tension pins—also known as roll pins or spring pins—are widely used in automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and electronics sectors due to their high shear strength, ease of installation, and ability to withstand dynamic loads.
-
Growing Demand in Automotive and EV Manufacturing
The automotive sector remains the largest consumer of tension pins, with continued expansion in electric vehicle (EV) production expected to significantly influence demand in 2026. As EV manufacturers prioritize lightweight, durable, and efficient components, the use of high-precision tension pins in drivetrains, suspension systems, and battery assemblies is projected to increase. The shift toward modular vehicle platforms will further bolster the need for reliable, interchangeable fasteners like tension pins. -
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Robotics
The rise of smart factories and industrial automation is fueling demand for reliable mechanical components. Tension pins are increasingly used in robotic joints, conveyor systems, and precision gearboxes. In 2026, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies will require components that ensure long-term durability and minimal maintenance—attributes inherent to high-quality tension pins. -
Material Innovation and Customization
Market players are expected to focus on material innovation, including the use of corrosion-resistant stainless steel, high-strength alloys, and composite materials. Custom-designed tension pins tailored to specific applications—such as high-temperature or high-vibration environments—will gain traction, particularly in aerospace and defense sectors. -
Regional Market Shifts
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to dominate the tension pin market in 2026, led by manufacturing hubs in China, India, and Southeast Asia. Increasing investments in infrastructure, automotive production, and electronics manufacturing in these regions will drive demand. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will see growth driven by aerospace modernization and sustainable manufacturing practices. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Optimization
Environmental regulations and sustainability goals will influence production methods. Manufacturers are likely to adopt greener production processes and recyclable materials. Additionally, supply chain resilience will remain a priority, with companies investing in localized production and digital inventory systems to reduce lead times and mitigate disruptions. -
Competitive Landscape and M&A Activity
The tension pin market is moderately consolidated, with key players such as SPIROL, PennEngineering, and Rotor Clip expected to expand through product innovation and strategic acquisitions. Smaller niche manufacturers may focus on specialized applications, fostering competition based on precision engineering and technical support.
In summary, the 2026 tension pin market will be shaped by technological advancements, evolving end-user demands, and regional industrial growth. Companies that prioritize innovation, sustainability, and application-specific solutions are likely to gain a competitive edge in this expanding market.
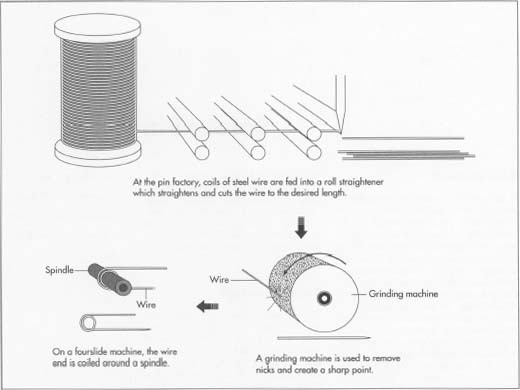
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Tension Pins: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing tension pins—commonly used in machinery, automotive, and industrial applications—can present several challenges, particularly concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these issues can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to watch for in both areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
Suppliers may use substandard or non-compliant materials (e.g., incorrect stainless steel grades or low-tensile alloys) to cut costs. This compromises the pin’s strength, corrosion resistance, and fatigue life. Always verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) and conduct third-party testing if necessary.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy
Tension pins require tight tolerances to ensure proper fit and function. Inconsistent machining can lead to assembly issues or premature failure. Request first-article inspections and use geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) in specifications.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Coating
Improper surface treatments (e.g., plating, passivation) can reduce performance or accelerate wear. Ensure that finish requirements are clearly defined and validated through sample testing.
Lack of Quality Control Processes
Suppliers without ISO 9001 or similar quality management systems may lack consistent inspection and traceability procedures. Audit potential suppliers to confirm their QC capabilities.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Reverse Engineering
Some suppliers, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement, may reverse-engineer patented tension pin designs. This exposes your company to legal liability and risks infringement lawsuits from original patent holders.
Design Theft and Replication
Sharing detailed technical drawings with unveted suppliers increases the risk of your proprietary designs being copied and sold to competitors. Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and limit design access to only essential components.
Infringement of Patented Features
Tension pins may incorporate patented geometries, retention mechanisms, or assembly methods. Sourcing generic versions without freedom-to-operate analysis can result in IP violations. Conduct patent landscape reviews before finalizing designs.
Weak Contractual Protections
Failure to include IP ownership clauses in supplier agreements may result in disputes over who owns tooling, design modifications, or custom iterations. Clearly define IP rights in procurement contracts.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough supplier due diligence, require quality certifications, perform regular audits, and involve legal counsel in IP risk assessment. Using trusted manufacturing partners and investing in proper documentation can safeguard both product integrity and intellectual property.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tension Pin
Overview of Tension Pin
Tension pins are mechanical fasteners used to secure components under high-stress conditions, commonly found in industrial, automotive, aerospace, and construction applications. Due to their critical function, proper logistics handling and compliance with regulatory standards are essential to ensure safety, performance, and legal adherence.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Tension pins must comply with relevant international, national, and industry-specific standards. Key regulations include:
– ISO Standards: ISO 8748 (for taper pins) and ISO 2338 (for parallel pins) may apply depending on design.
– ASTM/ASME Standards: For material strength and testing, such as ASTM A307 or ASME B18.8.1.
– REACH & RoHS Compliance: Required for pins exported to the EU, ensuring restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) are within permissible limits.
– ITAR/EAR Regulations: If tension pins are used in defense or aerospace applications, export controls under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) may apply.
Manufacturers and distributors must maintain documentation, including material test reports (MTRs), certificates of compliance (CoC), and traceability records.
Packaging & Handling Procedures
Proper packaging ensures tension pins arrive undamaged and corrosion-free:
– Use anti-corrosion materials such as VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper or desiccants for metal components.
– Secure pins in rigid containers or trays to prevent movement during transit.
– Label packages with product identification, lot numbers, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Keep Dry”).
– Avoid exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and contaminants during storage and transport.
Transportation & Shipping Guidelines
Follow these best practices for domestic and international shipping:
– Classify tension pins correctly under the Harmonized System (HS) Code (e.g., 7318.19 for non-threaded steel pins).
– Declare accurate weight, dimensions, and material composition for customs clearance.
– Use freight carriers experienced in handling industrial components; consider insured and trackable shipping options.
– For air freight, comply with IATA regulations; for sea freight, adhere to IMDG Code if hazardous materials (e.g., coatings) are present.
Import & Export Documentation
Ensure all shipments include:
– Commercial invoice with detailed description, unit price, and total value.
– Packing list specifying quantities, weights, and packaging types.
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB).
– Certificate of Origin, especially for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements.
– Export license, if required by destination country or controlled under dual-use regulations.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
Implement a traceability system to track tension pins from raw material to final delivery:
– Assign batch/lot numbers to enable recalls if non-conformances arise.
– Conduct periodic audits and inspections per ISO 9001 standards.
– Retain compliance documentation for a minimum of 5–10 years, depending on industry requirements.
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Recycle packaging materials where possible and comply with local waste disposal regulations.
- Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if pins have surface treatments (e.g., zinc plating, oil coatings).
- Train personnel in safe handling to prevent injury from sharp edges or heavy loads.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for tension pins reduces risk, ensures product integrity, and supports smooth international trade. Adherence to technical standards, accurate documentation, and secure handling practices are essential for all stakeholders in the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing Tension Pins
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, cost considerations, quality standards, and lead times, an optimal sourcing strategy for tension pins has been established. The selected supplier offers a competitive balance of quality, reliability, and cost-efficiency, meeting the required mechanical and dimensional specifications. Material traceability, compliance with industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO), and consistent production capabilities were key deciding factors.
Additionally, the supplier demonstrates strong logistical support and responsive customer service, ensuring on-time delivery and minimal supply chain disruption. This sourcing decision supports operational efficiency, product reliability, and long-term cost savings. Continuous performance monitoring and periodic reviews will be implemented to maintain quality and explore further optimization opportunities.
In conclusion, the chosen sourcing solution for tension pins aligns with both technical requirements and strategic procurement objectives, contributing to enhanced manufacturing consistency and overall product performance.