The global temperature control unit (TCU) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision thermal management across industries such as pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, plastics, and semiconductor manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial process cooling equipment market—encompassing TCUs—was valued at USD 21.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts a CAGR of over 5.8% for the temperature control equipment market through 2028, citing rising automation and stringent process requirements in manufacturing as key drivers. With growing emphasis on energy efficiency, process stability, and compliance with regulatory standards, companies are increasingly investing in advanced TCUs capable of maintaining tight temperature tolerances. As competition intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as industry leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and global reach to meet evolving thermal control demands. Here are the top 10 temperature control unit manufacturers shaping the future of industrial temperature management.
Top 10 Temperature Control Unit Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SELCO Products
Domain Est. 1996
Website: selcoproducts.com
Key Highlights: Temperature controller manufacturer Selco Products offers a range of customizable temperature controller products. Learn more!…
#2 Athena Controls
Domain Est. 1996
Website: athenacontrols.com
Key Highlights: Athena Controls offers precision temperature controllers, power controls and sensors ideal for a variety of industrial equipment. Get a free quote!…
#3 Industrial Temperature Control Equipment
Domain Est. 1997
Website: deltatsys.com
Key Highlights: Delta T Systems manufactures industrial temperature control equipment, including chillers, central chillers, and more for various industries and commercial ……
#4 Temperature control and cooling technology for labs and industry
Website: lauda.de
Key Highlights: We are LAUDA – the world leader in precise temperatures. Our Constant temperature equipment and systems are at the heart of important applications….
#5 Temperature Controllers
Domain Est. 1993
Website: eurotherm.com
Key Highlights: Temperature Controllers. High accuracy Eurotherm temperature controllers improve process efficiency, product quality and minimise waste….
#6 HUBER
Domain Est. 1996
Website: huber-online.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the leading suppliers of high-precision temperature control solutions for research and industry. We offer dynamic temperature control systems….
#7 TECSYSTEM
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tecsystem.it
Key Highlights: For over 40 years, we have been designing and manufacturing a range of electronic and electromechanical equipment for temperature control of transformers, ……
#8 Temperature Controllers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: automation.omron.com
Key Highlights: Keep your operations at the precise temperature necessary to ensure quality and maximize production with Omron’s PID process controllers….
#9 HUBER
Domain Est. 2004
Website: huber-usa.com
Key Highlights: We are one of the leading suppliers of high-precision temperature control solutions for research and industry. We offer dynamic temperature control systems….
#10 Temperature Controllers & Process Controllers
Domain Est. 2009
Website: west-cs.com
Key Highlights: Temperature Control experts combining the strengths of CAL, Partlow, PMA & West for high performance process and PID temperature controllers….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Temperature Control Unit

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Temperature Control Units
The global Temperature Control Unit (TCU) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, expanding industrial automation, and growing demand across pharmaceutical, chemical, plastics, and semiconductor sectors. Key trends shaping the market landscape include:
-
Increased Demand from High-Tech Manufacturing
The rise of precision manufacturing in semiconductors and advanced materials is fueling demand for high-accuracy TCUs. As semiconductor fabrication processes require stringent thermal management—especially in lithography and wafer processing—the need for ultra-stable, rapidly responsive temperature control systems is accelerating. This trend is particularly pronounced in Asia-Pacific regions like Taiwan, South Korea, and China, where semiconductor investments are surging. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and IoT
By 2026, smart TCUs equipped with IoT connectivity and predictive analytics are expected to dominate new installations. These units enable real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and integration with centralized process control systems. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting digital twins and cloud-based platforms to optimize thermal processes, reduce downtime, and improve energy efficiency. -
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Focus
With global emphasis on decarbonization and sustainable manufacturing, energy-efficient TCUs are becoming a competitive differentiator. Innovations such as regenerative cooling, variable-speed compressors, and heat recovery systems are being incorporated into next-generation units. Regulatory pressures and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are pushing industries to retrofit older systems with greener alternatives. -
Growth in the Pharmaceutical and Biotech Sectors
The pharmaceutical industry’s expansion—especially in biologics and mRNA vaccine production—requires precise temperature control during fermentation, purification, and storage. Single-use bioreactor systems, which rely heavily on external TCUs, are gaining traction, driving modular and compact TCU designs tailored for cleanroom environments. -
Regional Market Expansion and Localization
While North America and Europe maintain strong market shares due to advanced industrial infrastructure, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026. Local manufacturing hubs in India, Vietnam, and Southeast Asia are investing in process automation, creating new opportunities for TCU suppliers. Additionally, geopolitical trends are encouraging supply chain localization, prompting global vendors to establish regional production and service centers. -
Advancements in Control Algorithms and AI
AI-driven adaptive control systems are being integrated into TCUs to improve response times and stability under dynamic process conditions. Machine learning models analyze historical data to predict thermal loads and preemptively adjust parameters, enhancing process consistency and reducing energy consumption. -
Rise of Modular and Compact Designs
As production facilities face space constraints and demand flexibility, modular TCUs with plug-and-play capabilities are gaining popularity. These units support quick deployment, scalability, and easier maintenance—ideal for pilot plants and contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs).
In summary, the 2026 TCU market will be characterized by digitalization, sustainability, and precision, with innovation focused on intelligence, efficiency, and adaptability. Companies that invest in smart, scalable, and eco-friendly temperature control solutions are best positioned to capture emerging opportunities across high-growth industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Temperature Control Units (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Temperature Control Units (TCUs) involves significant risks if not managed carefully, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failure to address these pitfalls can lead to operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage.
Inadequate Quality Assurance and Verification
Many organizations face quality issues when sourcing TCUs, especially from low-cost or unfamiliar suppliers. Common problems include inconsistent temperature regulation, poor durability, use of substandard materials, and non-compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, CE, UL). Overlooking rigorous supplier vetting, factory audits, and third-party testing increases the risk of receiving malfunctioning or unreliable units that disrupt production processes and increase total cost of ownership.
Insufficient Intellectual Property Protection
When custom TCUs are developed or modified to meet specific operational needs, strong IP safeguards are essential. Key pitfalls include unclear ownership agreements, lack of confidentiality clauses in contracts, and failure to register design patents or technical specifications. Without proper IP protection, companies risk reverse engineering by suppliers, unauthorized replication of designs, and loss of competitive advantage—particularly when sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement.
Overlooking Compliance and Certification Requirements
TCUs used in regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food processing, semiconductors) must meet strict regulatory standards. Sourcing units without verified certifications (such as ATEX for hazardous environments or 21 CFR Part 11 for data integrity) can result in non-compliance, failed audits, and costly production halts. Buyers often assume compliance based on supplier claims without independent verification, leading to significant downstream risks.
Poor Supplier Transparency and Traceability
A lack of transparency in the supply chain—such as undisclosed subcontractors or untraceable component sources—can compromise both quality and IP security. Without clear documentation of materials, manufacturing processes, and software/firmware origins, companies face challenges in root-cause analysis during failures and increased exposure to counterfeit parts or embedded malware in smart TCUs.
Inadequate Contractual Safeguards
Weak contracts that omit detailed quality specifications, performance benchmarks, warranty terms, and IP clauses leave buyers vulnerable. Ambiguities in service-level agreements (SLAs), post-sale support, and software licensing can lead to disputes, especially when firmware updates or remote monitoring features are involved. Ensuring legally binding agreements with clear accountability is crucial to mitigate both quality and IP risks.
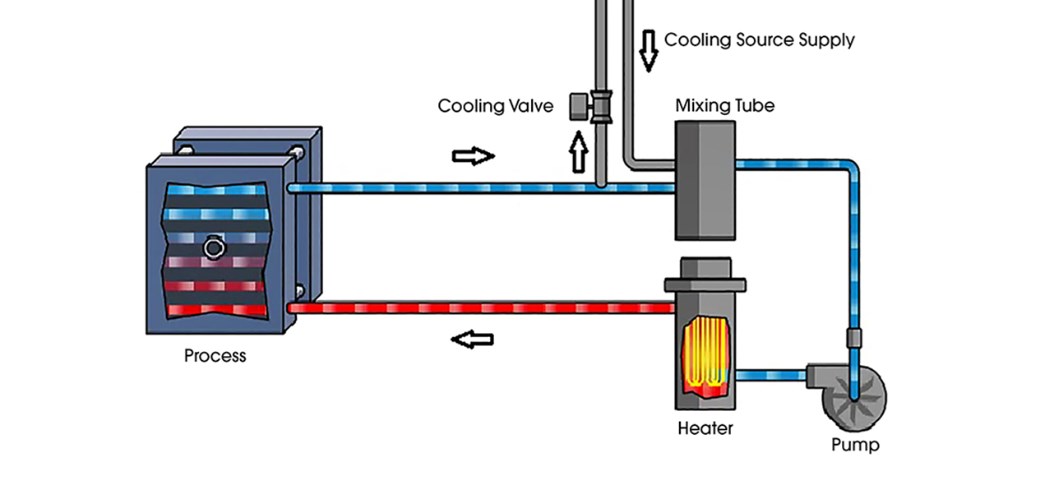
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Temperature Control Units (TCUs)
Overview and Purpose
This guide provides comprehensive instructions for the proper handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory compliance of Temperature Control Units (TCUs). TCUs are critical in maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals, biologics, and perishable goods. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product safety, efficacy, and compliance with international and local regulations.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
TCU operations must comply with relevant regulations and standards, including but not limited to:
– Good Distribution Practice (GDP) – EU and WHO guidelines for pharmaceutical distribution.
– FDA 21 CFR Part 211 – Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) for finished pharmaceuticals.
– ICH Q1A–Q1F – Stability testing guidelines.
– ATP Agreement – For international transport of perishable foodstuffs (if applicable).
– ISO 13485 – Quality management for medical devices (if TCUs are used in medical contexts).
Ensure all equipment and procedures meet these standards through regular audits and documentation.
Equipment Qualification and Validation
All TCUs must undergo qualification and periodic requalification, including:
– Design Qualification (DQ) – Confirming the TCU design meets user requirements.
– Installation Qualification (IQ) – Verifying correct installation and setup.
– Operational Qualification (OQ) – Demonstrating the unit operates as intended across its range.
– Performance Qualification (PQ) – Validating performance under real-world conditions (e.g., door openings, ambient temperature fluctuations).
Validation reports must be maintained and reviewed annually or after significant modifications.
Temperature Monitoring and Data Logging
- TCUs must be equipped with calibrated temperature monitoring devices capable of continuous logging.
- Data loggers should record at intervals no greater than 5 minutes and include timestamps, temperature readings, alarms, and user access.
- Monitoring systems must have real-time alerting capabilities for excursions (e.g., SMS/email notifications).
- Data must be stored securely for a minimum of 5 years and be accessible for regulatory audits.
Cold Chain Transportation Requirements
- Use only pre-qualified TCUs (refrigerated trucks, cold boxes, or active shippers) that maintain the required temperature range (e.g., 2–8°C, -20°C, or -70°C).
- Conduct pre-trip inspections to ensure equipment is clean, powered, and functioning.
- Perform pre-cooling of the unit to target temperature before loading.
- Minimize door openings; use air curtains or dock shelters during loading/unloading.
- Use secondary packaging with phase change materials (PCMs) or gel packs where appropriate.
Storage Conditions and Facility Management
- Store TCUs in dedicated, climate-controlled areas away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Maintain segregation of products by temperature zone (e.g., refrigerated vs. frozen).
- Conduct routine temperature mapping of storage areas annually or after layout changes.
- Implement preventive maintenance schedules for all TCUs, including cleaning, defrosting, and sensor calibration.
Handling and Operational Procedures
- Train personnel on SOPs for TCU operation, including emergency response for temperature excursions.
- Use closed-door policies and restrict unauthorized access.
- Label all units clearly with temperature range, validation status, and calibration due dates.
- Document all handling activities (e.g., loading, maintenance, incidents) in a logbook or digital system.
Temperature Excursion Management
- Define acceptable excursion limits based on product stability data and regulatory guidance.
- Implement an immediate response protocol for excursions:
- Isolate affected products.
- Notify quality assurance and regulatory teams.
- Conduct a risk assessment to determine product impact.
- Document root cause and corrective actions.
- Report critical excursions to regulatory authorities as required.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain complete records for:
– Equipment qualification and validation reports.
– Temperature logs and calibration certificates.
– Maintenance and repair histories.
– Training records for personnel.
– Excursion investigations and resolutions.
All documents must be legible, time-stamped, and stored securely (electronically or physically) with controlled access.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
- Conduct internal audits at least annually to verify compliance.
- Schedule external audits by regulatory bodies or third parties as needed.
- Use audit findings to drive corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs).
- Review and update this guide annually or in response to regulatory changes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance management of Temperature Control Units is essential to ensure product quality and regulatory adherence. By following this guide, organizations can mitigate risks, maintain cold chain integrity, and support patient safety and product efficacy.
Conclusion for Sourcing Temperature Control Units
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, cost structures, and long-term reliability, sourcing temperature control units (TCUs) should be approached with a strategic focus on quality, energy efficiency, and supplier support. The selected units must meet precise operational requirements such as temperature range, accuracy, fluid compatibility, and integration capabilities with existing systems.
Supplier selection should prioritize those with proven industry experience, robust after-sales service, and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE). While initial cost is a consideration, total cost of ownership—including energy consumption, maintenance, and downtime—should guide the decision-making process.
In conclusion, sourcing the right temperature control units involves balancing performance, reliability, and lifecycle costs. Partnering with reputable suppliers and investing in high-quality, energy-efficient models will ensure improved process stability, reduced operational risks, and long-term cost savings across production or laboratory environments.