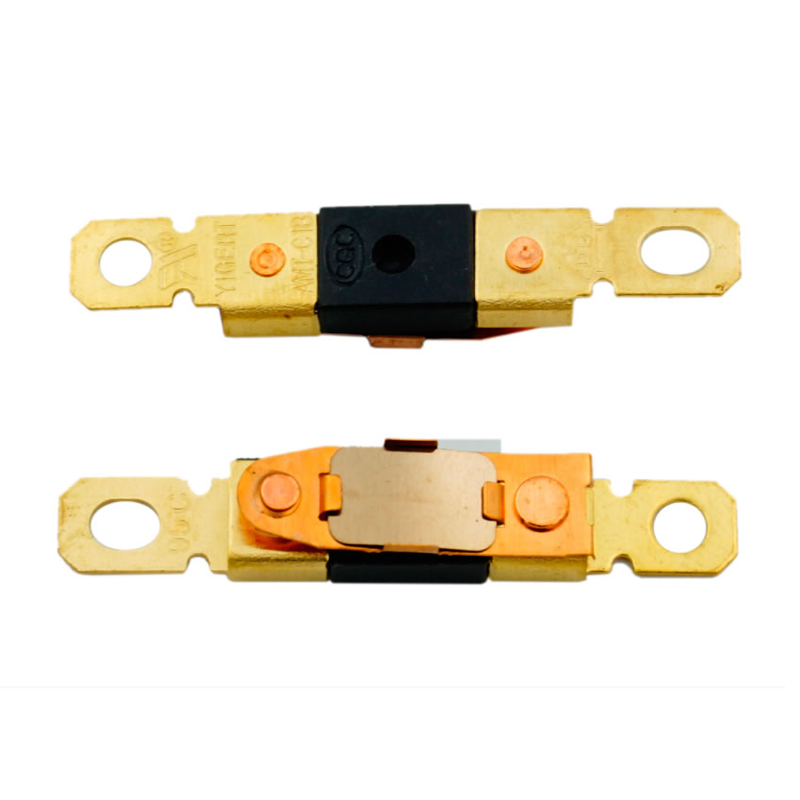
The global temporary fuse market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand from automotive, industrial, and electronics sectors for reliable circuit protection solutions. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global fuse market—encompassing temporary and resettable varieties—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and smart infrastructure. Temporary fuses, which offer quick, safe circuit interruption for testing and maintenance, are gaining traction due to their role in minimizing downtime and enhancing operational safety. Grand View Research further supports this trend, noting that the rise in industrial automation and demand for modular electrical protection components is accelerating innovation among manufacturers. As the need for precision and reliability intensifies, the top nine temporary fuse manufacturers have emerged as leaders through advanced product design, global distribution networks, and compliance with international safety standards. These players are not only shaping industry benchmarks but are also strategically positioned to capitalize on the expanding protection device landscape.
Top 9 Temp Fuse Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PPTC Resettable Fuse
Domain Est. 2000 | Founded: 1999
Website: fuzetec.com
Key Highlights: Established in 1999, Fuzetec Technology is a leading manufacturer of circuit protection components, offering innovative and reliable solutions for the ……
#2 Circuit Protection, Fuses, Power Control & Sensing Solutions
Domain Est. 1996
Website: littelfuse.com
Key Highlights: Littelfuse is a global manufacturer of leading technologies in circuit protection, power control & sensing. Our products are found in automotive ……
#3 Fuses and fuse holders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: Bussmann series fuses play a major role in industrial or commercial facilities by providing reliable, maximum protection to power systems….
#4 Thermal Fuse
Domain Est. 1995
Website: rotork.com
Key Highlights: Midland-ACS 316L Stainless Steel thermal fuses for fire release. Available in a range of temperature settings….
#5 Fuse Tech
Domain Est. 1998
Website: fusetech.com
Key Highlights: Fuse Tech is driven to be your long-term solution for ceramic welding, professional furnace maintenance, service and repair….
#6 Thermal Fuse Series
Domain Est. 2005
Website: betterfuse.com
Key Highlights: Rated current: 10A,15A. Action Temperature:73℃~240℃. Rated Voltage:250Vac. No.BTA. Plastic shell thermal fuse. Details · Download. Rated Current:…
#7 Fuses
Domain Est. 2006
Website: us.mersen.com
Key Highlights: Mersen develops customized solutions and delivers key products to its clients in order to meet the new technological challenges shaping tomorrow’s world….
#8 SETfuse
Domain Est. 2007
Website: setfuse.com
Key Highlights: SETfuse designs, manufactures, and markets industry-leading circuit control and safety protection components, providing comprehensive circuit safety solutions….
#9 Products
Domain Est. 2007
Website: setsafe.com
Key Highlights: SETsafe | SETfuse Designs, Manufactures and Markets industry-leading Circuit Control and Safety Protection Components, Providing Comprehensive Circuit Safety ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Temp Fuse

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Temp Fuse
As we approach 2026, the market for temporary electrical fuses—commonly referred to as “Temp Fuses”—is expected to undergo significant transformation driven by advancements in technology, evolving safety regulations, and growing demand across industrial, automotive, and residential sectors. Temp Fuses, used primarily for diagnostic and short-term circuit protection applications, are seeing increased innovation due to the broader electrification of systems and the need for rapid, safe troubleshooting methods.
-
Growth in Automotive and EV Diagnostics
The automotive industry, particularly electric vehicles (EVs), is a major driver of Temp Fuse adoption. With increasingly complex electrical architectures in EVs, technicians rely on Temp Fuses for safe circuit testing and fault isolation. As global EV production continues to rise—projected to exceed 40 million units annually by 2026—the demand for reliable, reusable diagnostic tools like Temp Fuses is expected to grow significantly. OEMs and aftermarket service providers are investing in smart Temp Fuse solutions integrated with diagnostic software platforms. -
Smart and IoT-Enabled Temp Fuses
A key trend emerging by 2026 is the integration of digital and IoT capabilities into Temp Fuse systems. Smart Temp Fuses equipped with sensors and wireless communication (e.g., Bluetooth or NFC) enable real-time current monitoring, overload alerts, and data logging. These features improve safety and efficiency in industrial maintenance and building management systems. Companies are developing cloud-connected Temp Fuse solutions that feed diagnostic data into predictive maintenance platforms, reducing downtime and preventing electrical failures. -
Focus on Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory bodies such as UL, IEC, and OSHA are introducing stricter standards for temporary electrical devices. By 2026, Temp Fuses are expected to comply with enhanced safety protocols, including tamper-proof designs, thermal cutoffs, and clear visual indicators for fault conditions. Markets in North America and Europe are leading this shift, pushing manufacturers to redesign products for higher reliability and reduced risk of misuse. -
Expansion in Renewable Energy and Microgrid Applications
With the global push toward renewable energy, Temp Fuses are increasingly used in solar inverters, battery storage systems, and microgrids during commissioning and maintenance. Their role in safely isolating circuits without disrupting entire systems makes them essential in field service operations. The decentralized energy market is expected to boost demand, especially in emerging economies adopting off-grid solutions. -
Sustainability and Reusability
Environmental concerns are influencing product design. By 2026, leading Temp Fuse manufacturers are shifting toward reusable, modular designs made from recyclable materials. Single-use fuses are being phased out in favor of durable, resettable versions that reduce electronic waste and operational costs—especially in industrial settings where frequent testing occurs. -
Market Consolidation and Innovation
The Temp Fuse market is witnessing increased competition and consolidation, with major electrical component suppliers acquiring niche diagnostic tool developers. Innovation is focused on miniaturization, compatibility with multiple fuse types (e.g., blade, cartridge, bolt-down), and integration with handheld multimeters or mobile apps.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the Temp Fuse market will transition from a simple diagnostic tool to an intelligent, connected component within broader electrical safety and maintenance ecosystems. Growth will be fueled by electrification trends, digitalization, and stricter safety standards, positioning Temp Fuses as essential tools in modern electrical systems across automotive, industrial, and energy sectors.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Temp Fuses (Quality, IP)
Sourcing temporary fuses—especially for critical applications in electronics, automotive, or industrial systems—can present significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these pitfalls helps mitigate risks and ensures reliable, compliant components.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Temp fuses sourced from low-cost or unverified suppliers often lack adherence to international quality standards (e.g., IEC, UL, AEC-Q200). This can result in inconsistent performance, premature failure, or non-compliance with safety regulations, especially under thermal or electrical stress.
Lack of Traceability and Testing Documentation
Many suppliers, particularly in the gray market, fail to provide full traceability (lot numbers, production dates) or independent test reports (e.g., thermal cycling, current interruption tests). Without this data, verifying reliability or conducting root-cause analysis during field failures becomes nearly impossible.
Counterfeit or Substandard Components
Temp fuses are susceptible to counterfeiting, including remarked fuses or those using inferior materials (e.g., subpar fusible links or casing). These components may appear authentic but fail under operational conditions, leading to system downtime or safety hazards.
Inadequate Environmental and Lifecycle Testing
Some suppliers do not perform or disclose results from environmental stress tests (humidity, vibration, temperature extremes). This increases the risk of field failures in harsh operating environments, undermining product durability and customer trust.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unlicensed or Cloned Designs
A significant risk when sourcing from certain regions is the use of temp fuse designs that infringe on patented technologies. Using such components can expose the buyer to legal liability, product recalls, or shipment seizures, especially in regulated markets.
Lack of IP Indemnification
Many suppliers, especially smaller or offshore manufacturers, do not offer IP indemnification clauses in contracts. If a third party claims patent infringement, the buyer may bear full legal and financial responsibility without recourse.
Reverse-Engineered Specifications
Some temp fuses are reverse-engineered from leading brands without proper licensing. While these may meet basic electrical specs, they often lack the nuanced design features (e.g., precise time-current curves, fail-safe mechanisms) protected by IP, leading to performance gaps and legal exposure.
Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Designs
When working with contract manufacturers on custom temp fuses, unclear agreements on IP ownership can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim rights to design modifications or reuse proprietary designs for competing customers, eroding competitive advantage.
Mitigation Strategies
- Qualify suppliers rigorously using audits, sample testing, and certification checks (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949).
- Demand full documentation, including test reports, material disclosures, and traceability data.
- Use authorized distributors or direct OEM channels to avoid counterfeit risks.
- Include strong IP clauses in procurement contracts, specifying indemnification and ownership of custom designs.
- Conduct patent landscape reviews before adopting new temp fuse designs, especially for high-volume or regulated applications.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures not only technical reliability but also legal and commercial safety in the supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Temp Fuse
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for handling, transporting, and managing Temp Fuse, a temporary electrical fuse solution. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
Product Overview
Temp Fuse is a temporary fuse device designed for short-term electrical circuit protection during maintenance, testing, or troubleshooting. It is not intended for permanent installation and must be removed and replaced with the correct permanent fuse upon completion of work.
Regulatory Compliance
Temp Fuse must be used in accordance with applicable national and international regulations, including but not limited to:
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910 (Occupational Safety and Health Standards)
– NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code)
– IEC 60269 (Low-voltage fuses)
– RoHS and REACH (for material content and environmental compliance)
Users must ensure that the use of Temp Fuse does not violate local electrical codes or safety regulations. Documentation proving compliance with these standards is available upon request.
Handling and Storage
- Store Temp Fuse in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (15°C to 30°C).
- Avoid exposure to moisture, direct sunlight, and corrosive substances.
- Keep in original packaging until ready for use to prevent damage or contamination.
- Handle with clean, dry hands or use appropriate gloves to avoid introducing contaminants.
Transportation Requirements
- Ship Temp Fuse in approved, non-conductive packaging to prevent short circuits.
- Label packages with: “Electrical Device – Handle with Care” and “Do Not Drop.”
- Ensure compliance with IATA/IMDG regulations if shipping internationally, especially for air or sea freight.
- Include safety data sheets (SDS) and compliance documentation with each shipment.
Installation and Usage
- Only qualified electricians or authorized personnel may install or use Temp Fuse.
- Verify the correct voltage and current rating before installation.
- Use only for temporary applications (maximum 72 hours unless otherwise specified and supervised).
- Clearly label the installed Temp Fuse with date, time, and responsible technician.
- Never bypass or override safety interlocks when using Temp Fuse.
Inspection and Maintenance
- Inspect each unit prior to use for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear.
- Do not use if any physical defects are observed.
- After use, clean and inspect the device before storage.
- Maintain a log of usage, inspections, and disposal.
Disposal and End-of-Life
- Temp Fuse is not a permanent component and must be removed after use.
- Dispose of used units in accordance with local e-waste and hazardous material regulations.
- Do not discard in regular trash.
- Recycle components where possible through certified electronic waste recyclers.
Training and Documentation
- All personnel using Temp Fuse must complete approved safety and operational training.
- Maintain training records for audit purposes.
- Keep logs of all Temp Fuse deployments, including purpose, duration, and technician details.
- Documentation must be retained for a minimum of three years.
Incident Reporting
- Report any malfunction, misuse, or safety incident involving Temp Fuse immediately to the supervisor and safety officer.
- Complete an incident report form detailing the event, contributing factors, and corrective actions.
- Investigate and address root causes to prevent recurrence.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the safe, compliant, and effective use of Temp Fuse within their operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing Temporary Fuses:
In conclusion, sourcing temporary fuses requires a careful balance between safety, compliance, availability, and cost-effectiveness. While temporary fuses may be necessary in emergency repair situations or during equipment troubleshooting, they should only be used as a short-term solution in accordance with relevant electrical standards and safety regulations. It is essential to source such components from reputable suppliers that provide products meeting recognized industry standards (e.g., UL, IEC) to ensure reliability and minimize risks such as fire, equipment damage, or personal injury. Additionally, proper documentation and risk assessment should accompany any temporary fuse application, with a clear plan for replacing it with a permanent, appropriately rated fuse as soon as possible. Ultimately, while sourcing options exist, prioritizing safety and regulatory compliance is paramount in the selection and use of temporary fuses.