The global adhesive tapes market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as packaging, automotive, healthcare, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 63.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% from 2024 to 2030. Key factors fueling this expansion include increasing e-commerce activity, which boosts packaging tape consumption, and advancements in adhesive technologies that enhance performance and sustainability. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued momentum, citing Asia-Pacific as the fastest-growing regional market due to rapid industrialization and urbanization. As demand intensifies, innovation and reliability have become critical differentiators among manufacturers. In this competitive landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as leaders, consistently delivering high-performance tape adhesive solutions and shaping the future of the industry.
Top 10 Tape Adhesive Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Adhesives Research
Domain Est. 1996
Website: adhesivesresearch.com
Key Highlights: Adhesives Research is your expert developer and manufacturer of high-performance adhesive tapes, specialty films, coatings, laminates, release liners and drug ……
#2 Shurtape®
Domain Est. 1996
Website: shurtape.com
Key Highlights: Shurtape Industrial is your trusted supplier of HVAC tape, heavy-duty duct tape, packaging tape and more. · Electrical Tapes · HVAC Tapes · Packaging Tapes….
#3 Worldwide Leading Adhesive Tape Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tesa.com
Key Highlights: tesa North America is a leading manufacturer of adhesive tape solutions. We support industry partners in optimizing their processes & improving their ……
#4 Shurtape Technologies, LLC
Domain Est. 2015
Website: shurtapetech.com
Key Highlights: Shurtape Technologies, LLC, is a leading manufacturer and marketer of adhesive tape and consumer home and office products….
#5 3M Tapes
Domain Est. 1988
Website: 3m.com
Key Highlights: 3M Tapes: Anti-slip & Grip Tapes, Anti-slip & Grip Tapes, Barricade & Warning Tapes, Barricade & Warning Tapes, Bonding, Mounting & Transfer Tapes….
#6 Avery Dennison
Domain Est. 1993
Website: tapes.averydennison.com
Key Highlights: Bringing decades of experience in adhesives, we collaborate with you – the customer – to identify tape solutions for your application….
#7 Adchem
Domain Est. 1997
Website: adchem.com
Key Highlights: We are a company of over 100 including Ph.D’s, chemists, engineers, and executives dedicated to Adhesive Tape Engineering and creating the perfect product….
#8 Tapes, labels and self
Domain Est. 2000
Website: next.henkel-adhesives.com
Key Highlights: Henkel boasts an expansive portfolio of adhesive tapes characterized by exceptional adhesion, temperature, and chemical resistance….
#9
Domain Est. 2003
Website: atp-ag.com
Key Highlights: ATP specializes in the development and manufacture of customized adhesive tape solutions, such as non-woven adhesive tapes, transfer adhesive tapes and ……
#10 Custom Adhesive Products
Domain Est. 2008
Website: captape.com
Key Highlights: CAP is a leading provider of advanced pressure-sensitive tapes, offering innovative adhesive solutions to a wide range of industries….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tape Adhesive

H2: Market Trends Shaping the Tape Adhesive Industry in 2026
By 2026, the global tape adhesive market is poised for significant transformation, driven by evolving end-user demands, technological advancements, and a heightened focus on sustainability. Key trends shaping this landscape include:
1. Accelerated Shift Towards Sustainable & Bio-Based Solutions (H3)
Environmental regulations and consumer pressure are pushing manufacturers to prioritize eco-friendly alternatives. Expect substantial growth in:
* Bio-based adhesives: Derived from renewable resources (e.g., starch, cellulose, soy) replacing petroleum-based polymers.
* Water-based & solvent-free formulations: Reducing VOC emissions and improving workplace safety.
* Recyclability & Compostability: Development of tapes compatible with recycling streams (e.g., paper tapes) or certified compostable options, particularly for packaging.
* Circular Economy Models: Increased focus on take-back schemes and design for recyclability.
2. Dominance of Performance-Driven Applications (H3)
Demand will surge in high-growth sectors requiring specialized tape properties:
* Electric Vehicles (EVs) & Electronics: Advanced tapes for battery bonding (thermal management, structural integrity), component fixation in compact devices, and EMI shielding. Conductive and thermally conductive adhesives are critical.
* Renewable Energy: High-performance tapes for solar panel assembly (backsheet bonding) and wind turbine blade construction (lightweight, durable bonding).
* Advanced Packaging: Growth in e-commerce fuels demand for high-strength, tamper-evident, and easily recyclable tapes. Smart tapes with RFID or tracking capabilities may emerge.
3. Technological Innovation in Formulation & Substrates (H3)
Advancements will focus on:
* Enhanced Performance: Tapes with superior temperature resistance, UV stability, chemical resistance, and long-term durability.
* Multi-Functionality: Integration of properties like adhesion + insulation, adhesion + damping, or adhesion + antimicrobial features.
* Novel Substrates: Increased use of lightweight, high-strength materials (e.g., advanced polyesters, non-wovens) and functional coatings.
* Digital Integration: Potential for “smart” tapes with sensors or data-logging capabilities for industrial applications.
4. Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization (H3)
Post-pandemic and geopolitical factors drive strategies to mitigate risk:
* Nearshoring/Reshoring: Companies diversify manufacturing locations closer to key markets (e.g., North America, Europe) to reduce dependency on single regions.
* Vertical Integration: Larger players may acquire raw material suppliers (e.g., polymer producers) for greater control and stability.
* Inventory Optimization: Adoption of advanced analytics for better demand forecasting and stock management.
5. Consolidation & Strategic Partnerships (H3)
The competitive landscape will see:
* M&A Activity: Larger players acquiring niche technology leaders (especially in sustainable or high-performance tapes) to expand portfolios.
* Collaborations: Partnerships between adhesive producers, substrate manufacturers, and end-users (e.g., OEMs) to co-develop tailored solutions.
* Focus on Value-Added Services: Suppliers offering technical support, application engineering, and sustainability consulting alongside products.
In summary, the 2026 tape adhesive market will be defined by a powerful convergence of sustainability imperatives, technological innovation driven by high-performance applications (especially EVs and electronics), and strategic adaptations to supply chain and competitive pressures. Companies investing in R&D for eco-friendly, advanced-performance solutions and building resilient, collaborative business models are best positioned for success.
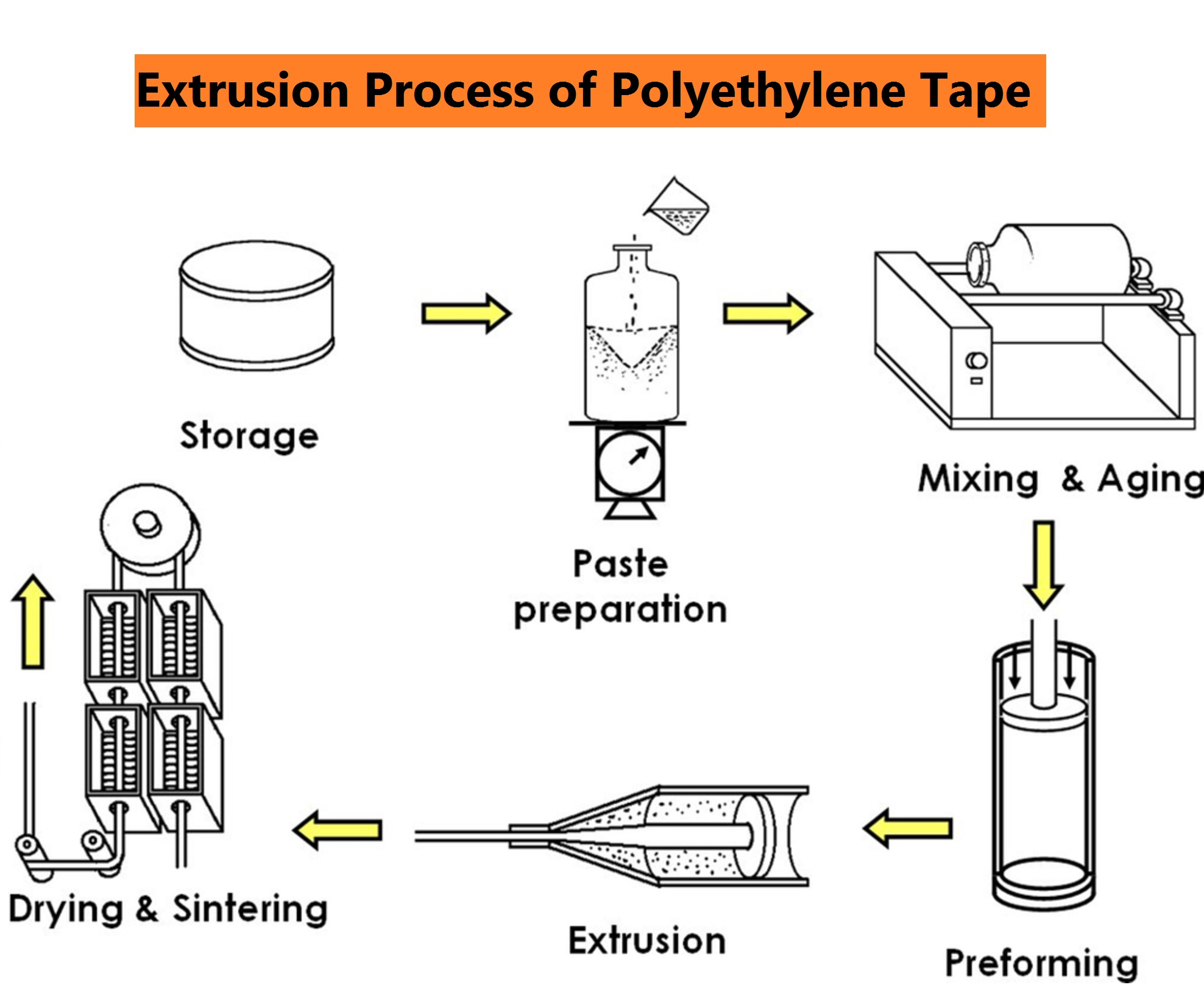
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Tape Adhesive: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing tape adhesive can be deceptively complex, with significant risks related to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to product failures, legal disputes, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Adhesive Performance
One of the most frequent issues is variability in adhesive properties such as tack, peel strength, shear resistance, and temperature tolerance. Sourcing from suppliers without stringent quality control or inadequate testing protocols can result in batch-to-batch inconsistencies, causing failures in end-use applications.
Substandard Raw Materials
Suppliers may cut costs by using inferior or non-specified raw materials (e.g., lower-grade polymers or adhesives), which compromise performance and longevity. Without proper material traceability and certification, buyers risk receiving products that do not meet technical specifications.
Lack of Environmental and Durability Testing
Tape adhesives are often exposed to extreme conditions such as UV light, moisture, or temperature fluctuations. Sourcing without verified test data (e.g., ASTM or ISO standards) for aging, weathering, or chemical resistance can lead to premature adhesive failure in real-world environments.
Insufficient Documentation and Certifications
Missing or falsified certificates of conformance (CoC), material safety data sheets (MSDS), or regulatory compliance documents (e.g., RoHS, REACH) can hinder traceability and compliance, especially in regulated industries like medical devices or automotive.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of Proprietary Formulations
Many high-performance adhesives are protected by patents or trade secrets. Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate branded adhesive chemistries (e.g., mimicking 3M or Tesa products) without licensing exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims, even if unintentional.
Reverse-Engineered Adhesives
Suppliers may offer “compatible” or “equivalent” tapes that are reverse-engineered from branded products. While marketed as cost-effective alternatives, these often violate IP rights and may lack reliability or long-term performance data.
Ambiguous Supplier Agreements
Contracts that fail to explicitly address IP ownership, indemnification clauses, or liability for infringement leave buyers vulnerable. Without clear terms, the buyer may be held responsible for third-party IP claims arising from the adhesive used.
Lack of IP Due Diligence
Failing to investigate a supplier’s IP portfolio, patent licenses, or history of litigation can result in sourcing from vendors with questionable practices. This is particularly risky when sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough supplier audits and request independent test reports.
– Require material declarations and compliance certifications.
– Perform side-by-side performance testing against benchmarks.
– Include IP warranty and indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Work with legal counsel to assess potential IP risks, especially with “generic” or “compatible” tapes.
Proactive due diligence in both quality assurance and IP compliance is essential to ensure reliable, lawful, and high-performing tape adhesive sourcing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tape Adhesive
Overview
Tape adhesives are widely used across industries for packaging, assembly, sealing, and protection. Due to their chemical composition and physical form, they are subject to specific logistics and regulatory requirements during storage, transportation, handling, and disposal. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure safe, compliant, and efficient management of tape adhesive products.
Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Tape adhesives may contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs), flammable solvents, or other regulated substances, depending on formulation (e.g., acrylic, rubber-based, silicone). Proper classification under international and national regulations is essential:
– GHS (Globally Harmonized System): Ensure Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are up to date and include hazard classification, pictograms, and precautionary statements.
– UN/DOT Regulations: If classified as hazardous (e.g., flammable adhesives), tape adhesives must be labeled and packaged according to UN 1993 (Flammable Liquids, N.O.S.) or other applicable codes.
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm compliance with substance restrictions and registration requirements for chemical components.
– TSCA (USA): Verify all chemical substances are pre-manufactured notified or exempt under the Toxic Substances Control Act.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents leaks, contamination, and exposure during transit:
– Use sealed, durable containers resistant to punctures and pressure changes.
– Label all packages with:
– Product identifier
– GHS hazard pictograms (if applicable)
– Handling and storage instructions
– Manufacturer or supplier contact information
– For hazardous tape adhesives, include proper shipping names, UN numbers, and hazard class labels as per IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or 49 CFR (road/rail).
Storage Conditions
To maintain product integrity and safety:
– Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources (typically below 30°C or 86°F).
– Keep away from incompatible materials (e.g., oxidizers, strong acids/bases).
– Maintain upright positioning to prevent adhesive seepage.
– Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to avoid product degradation.
Transportation Guidelines
Transport methods must align with adhesive classification:
– Non-hazardous tapes: Standard freight procedures apply; ensure packages are secured to prevent shifting.
– Hazardous tapes: Follow carrier-specific dangerous goods regulations:
– Use UN-certified packaging
– Complete shipping documentation (e.g., Dangerous Goods Declaration)
– Train personnel in hazardous materials handling (e.g., IATA, IMDG, or 49 CFR certification)
– Avoid extreme temperatures during transit to prevent adhesive performance issues.
Handling and Worker Safety
Ensure personnel are trained and protected:
– Provide appropriate PPE (gloves, safety glasses, respiratory protection if vapor exposure is possible).
– Use in well-ventilated areas; consider local exhaust ventilation for large-scale operations.
– Follow SDS instructions for spill response and first aid.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
Dispose of waste tape adhesives and packaging responsibly:
– Classified waste must be handled per RCRA (USA), Waste Framework Directive (EU), or local regulations.
– Empty containers may still contain residual adhesive; clean or dispose of as hazardous waste if required.
– Partner with certified waste management providers for recycling or disposal.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain compliance through proper documentation:
– Up-to-date Safety Data Sheets (SDS) accessible to all handlers
– Shipping manifests and dangerous goods declarations (if applicable)
– Training records for personnel handling hazardous materials
– Inventory logs and audit trails for traceability
Conclusion
Compliance in the logistics of tape adhesives ensures operational safety, environmental protection, and legal adherence. By understanding classification, proper handling, and regulatory requirements, companies can mitigate risks and optimize supply chain performance. Always consult local regulations and update procedures as standards evolve.
Conclusion for Sourcing Tape Adhesive:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, material specifications, cost considerations, and performance requirements, it is evident that sourcing tape adhesive requires a strategic balance between quality, reliability, and cost-efficiency. The selected supplier should demonstrate consistent product performance across key parameters such as adhesion strength, temperature resistance, durability, and suitability for the intended application—whether industrial, medical, packaging, or electronic.
Additionally, factors such as supply chain stability, lead times, technical support, and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, RoHS, REACH) are critical to ensuring long-term success. A reliable supplier partnership not only minimizes operational risks but also supports innovation and scalability.
In conclusion, the optimal sourcing strategy involves selecting a qualified supplier offering high-performance tape adhesive solutions backed by stringent quality control, prompt service, and a track record of reliability. Continuous performance monitoring and periodic reviews will further ensure that the chosen adhesive solution continues to meet evolving project and production needs.