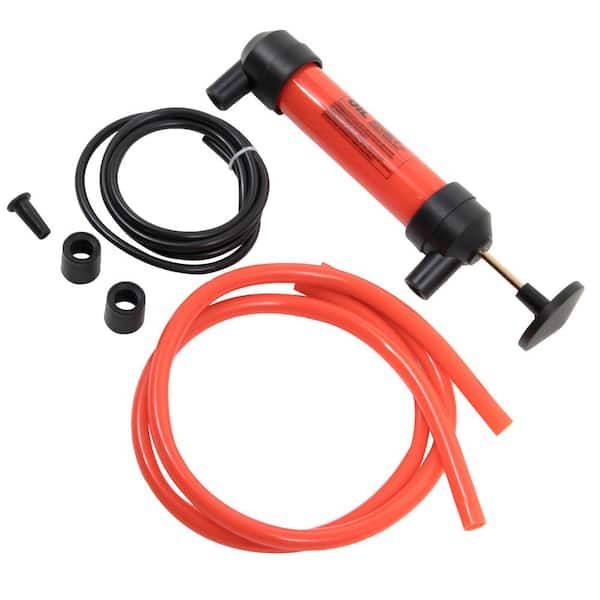
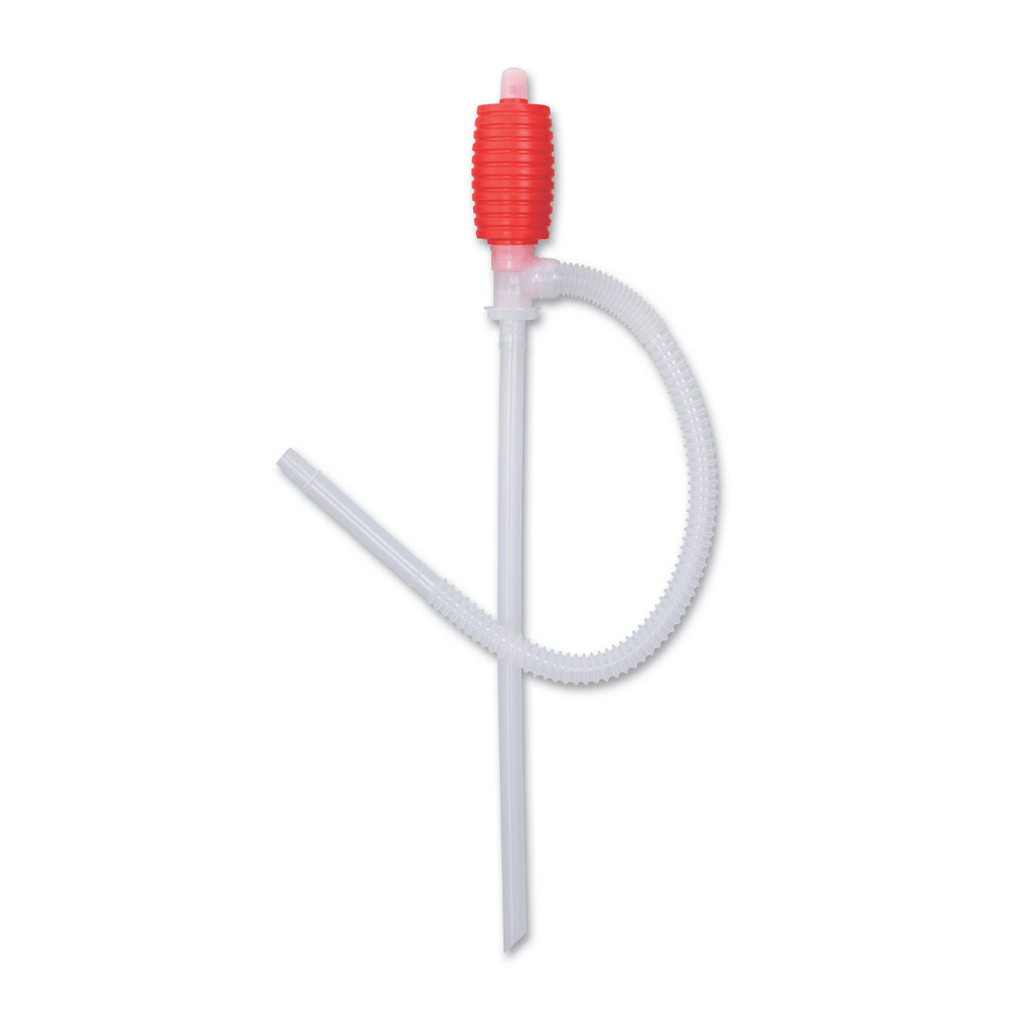
The global syphon pump market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across industrial, agricultural, and wastewater management sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global water pumps market—of which syphon pumps are a key segment—was valued at USD 58.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by rising infrastructure development, stringent environmental regulations, and the need for efficient fluid transfer solutions. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that advancements in energy-efficient pumping technologies and the adoption of automated systems are accelerating market momentum, particularly in emerging economies. As industries prioritize reliability and low-maintenance operations, syphon pumps—known for their simplicity and gravity-driven functionality—are gaining traction in both traditional and niche applications. With demand on the rise, identifying leading manufacturers becomes crucial for stakeholders seeking performance, innovation, and compliance with evolving industry standards.
Top 8 Syphon Pump Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Siphon Pumps
Domain Est. 1998
Website: actionpump.com
Key Highlights: Perfect for safe and efficient fluid transfer in industrial and commercial settings. Shop high-quality siphon pumps today! Polyethylene Siphon Pump 5gpm….
#2 syphon transfer pump
Domain Est. 1999
Website: samoaindustrial.com
Key Highlights: Lever action syphon pump. Design allows transfer by siphoning once the pump has been primed, giving a continuous flow of 8 l/min….
#3 Hand Siphon Pump
Domain Est. 2006
Website: kerosene-wicks.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsThis hand siphon pump safely transfers kerosene fuel via the siphon hose and can be used as a general fluid transfer pump for all your household jobs.Missing: syphon…
#4 Plastic Siphon Pumps, available in 2, 5, and 7 GPM
Domain Est. 2012
Website: grozusa.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.2 (12) The Groz Plastic Siphon Pumps are engineered to seamlessly siphon liquids below the pump’s installation height. This siphon pumps automatically transitio…
#5 Siphon Pumps
Domain Est. 1997
Website: groz-tools.com
Key Highlights: Professional range of equipment for non-commercial transferring and dispensing of fuel. A comprehensive range of highest-quality Diesel, Gasoline and DEF ……
#6 Siphon Pumps
Domain Est. 1999
#7 Siphon King Jr. Mini Pump W/50″ Hose
Domain Est. 2002
Website: kinginnovation.com
Key Highlights: This intake and discharge transfer system can be used to transfer liquids, remove water, chance oil, siphon gas, or inflate small objects….
#8 Hi-Tech Industries 450
Domain Est. 2008
Expert Sourcing Insights for Syphon Pump

H2: Market Trends for Syphon Pump in 2026
As the global industrial and infrastructure sectors continue to evolve, the market for syphon pumps is poised for notable transformation by 2026. Driven by advancements in fluid dynamics, increasing demand for energy-efficient systems, and growing emphasis on sustainable water management, syphon pump technology is expected to play an increasingly strategic role across multiple industries.
-
Rising Demand in Water Management and Irrigation
With climate change intensifying water scarcity in various regions, efficient water transfer solutions are becoming critical. Syphon pumps—valued for their energy-free operation in gravity-driven systems—are gaining traction in agricultural irrigation, particularly in developing economies. By 2026, expanded deployment in large-scale drip and flood irrigation systems is anticipated, especially in arid and semi-arid regions of Africa, South Asia, and the Middle East. -
Integration with Smart Infrastructure
The trend toward smart cities and intelligent water networks is accelerating the integration of syphon systems with IoT-enabled monitoring and control technologies. While traditional syphon pumps operate passively, future systems may incorporate sensors to optimize flow initiation, detect blockages, and manage siphon break mechanisms. This hybrid approach enhances reliability and expands application in urban drainage and stormwater management. -
Growth in Renewable Energy and Green Engineering
Syphon pumps are being re-evaluated in the context of low-carbon infrastructure. Their ability to transfer fluids without external power aligns with sustainability goals, making them attractive in solar-powered irrigation schemes and off-grid rural electrification projects. By 2026, increased funding for green engineering projects is expected to boost adoption, particularly in decentralized water supply systems. -
Technological Innovations and Material Advancements
Ongoing R&D is focused on improving the priming mechanisms and scalability of syphon pumps. Innovations such as self-priming siphon systems, automated air-release valves, and durable composite materials are overcoming historical limitations like dependency on manual priming and susceptibility to clogging. These improvements are broadening the use cases into municipal wastewater transfer and industrial cooling circuits. -
Regional Market Expansion
Asia-Pacific is projected to lead market growth due to expanding agricultural activity and government-led water conservation initiatives. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on retrofitting aging drainage systems with syphon-based solutions to improve flood resilience. Latin America and Sub-Saharan Africa present emerging opportunities due to rising investment in rural water access. -
Competitive Landscape and Industry Collaboration
By 2026, traditional pump manufacturers are expected to collaborate with environmental engineers and agritech startups to develop hybrid syphon systems. This convergence could lead to modular, plug-and-play syphon solutions that reduce installation costs and improve scalability.
In conclusion, the syphon pump market in 2026 will be shaped by sustainability imperatives, technological innovation, and growing global water challenges. While niche compared to powered pumping systems, syphon pumps are emerging as a vital component in energy-efficient and resilient fluid transfer infrastructure.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Syphon Pump (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a syphon pump—especially for industrial, chemical, or precision applications—requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes related to quality and intellectual property (IP). Below are key pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Quality Control and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing syphon pumps is receiving units that do not meet expected durability or performance standards. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard materials (e.g., non-corrosion-resistant plastics or inferior seals), leading to premature failure when handling aggressive fluids or operating under pressure. Always verify material compatibility with your fluid type and operating conditions. Lack of third-party certifications (e.g., ISO 9021, CE, or ATEX for hazardous environments) is a red flag.
Inadequate IP Protection and Design Copying
When sourcing from manufacturers—particularly in regions with lax IP enforcement—there’s a risk that your proprietary syphon pump design could be reverse-engineered and sold to competitors. Ensure robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and work with trusted partners who respect IP rights. Avoid sharing full design specifications until legal protections are in place. Also, verify whether the supplier holds original design rights to avoid unintentional infringement.
Misrepresentation of Performance Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate key performance metrics such as flow rate, suction lift height, or self-priming capability. Without independent test data or performance validation, you may end up with a pump that fails to meet operational requirements. Request real-world test reports or conduct pilot testing before large-scale procurement.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
In regulated industries (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food & beverage), full traceability of components and manufacturing processes is essential. Poor documentation—missing material test reports, calibration records, or batch traceability—can lead to compliance failures during audits. Insist on comprehensive documentation packages from your supplier.
Hidden Costs from Poor Design or Compatibility
Syphon pumps that appear inexpensive upfront may require costly modifications to integrate into existing systems. Watch for mismatched connection types, incorrect voltage, or non-standard mounting configurations. Poor ergonomics or lack of serviceability can also increase long-term maintenance costs.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, prioritize quality over initial cost, and safeguard intellectual property through legal and technical controls. Engaging in site audits, demanding performance validation, and using clear contractual terms can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering these common pitfalls.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Syphon Pump
Overview
This guide outlines the logistics handling, transportation, and regulatory compliance requirements for the Syphon Pump, a fluid transfer device commonly used in industrial, agricultural, and chemical applications. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe shipment, regulatory compliance, and product integrity.
Packaging and Storage
Syphon Pumps must be stored and shipped in protective packaging to prevent damage to the pump housing, seals, and hose connections. Use original manufacturer packaging when available. Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment between 5°C and 40°C (41°F to 104°F). Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, moisture, or corrosive chemicals during storage.
Transportation Requirements
Transport Syphon Pumps via ground or air freight in accordance with IATA, IMDG, or local transport regulations depending on the model and materials. Units containing residual fluids must be properly drained and sealed. Declare contents accurately on shipping documentation. Pumps constructed with non-hazardous materials may be shipped as general freight; confirm material composition with the manufacturer.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all Syphon Pumps comply with relevant regional standards:
– USA: Meets EPA and OSHA guidelines for fluid handling equipment; compliant with 29 CFR 1910.106 for flammable liquid transfer if applicable.
– EU: Conforms to CE marking requirements under Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and REACH regulations for material safety.
– International: Adheres to ISO 8098:2015 standards for safety and performance of hand-operated liquid transfer pumps.
Hazardous Material Considerations
If the Syphon Pump is used with or contains hazardous substances (e.g., fuels, solvents, chemicals), it may be classified as contaminated equipment. Decontaminate thoroughly before servicing or shipping. Follow local waste disposal regulations for cleaning residues. Transport under ADR/RID/IMDG Code if classified as hazardous waste.
Documentation and Labeling
Each unit must be accompanied by:
– Product compliance certificate
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for materials in contact with the pump
– User manual with handling instructions
– Shipping manifest with accurate HS code (e.g., 8413.70 for liquid pumps)
Label packages with:
– Product name and model number
– “Fragile – Handle with Care”
– Directional arrows indicating upright orientation
– Applicable hazard symbols if residual substances are present
Import and Export Controls
Verify export compliance under EAR (Export Administration Regulations) or ITAR if the pump contains controlled components. Importers must ensure conformity with local product safety and environmental laws. Duties and tariffs vary by country—consult Harmonized System (HS) code 8413.70 for classification.
Maintenance and End-of-Life
Perform routine inspections for wear, especially on seals and valves. Dispose of non-functional units in accordance with WEEE directives (EU) or EPA regulations (USA). Recycle metal and plastic components where possible; do not landfill contaminated parts.
Contact and Support
For compliance inquiries or logistics support, contact the manufacturer or authorized distributor with the product’s serial number and region of operation. Updates to regulations or product specifications will be provided through official channels.
Conclusion for Sourcing Syphon Pump
In conclusion, sourcing a syphon pump requires careful consideration of application requirements, material compatibility, flow rate, portability, and durability. Whether intended for industrial, agricultural, automotive, or domestic use, selecting the right syphon pump involves balancing performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating suppliers based on product quality, certifications, after-sales support, and delivery reliability ensures a dependable supply chain. By aligning technical specifications with operational needs and prioritizing reputable suppliers, organizations can secure a syphon pump solution that enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and supports long-term performance goals. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing decision contributes to safer, more sustainable fluid transfer practices across various industries.