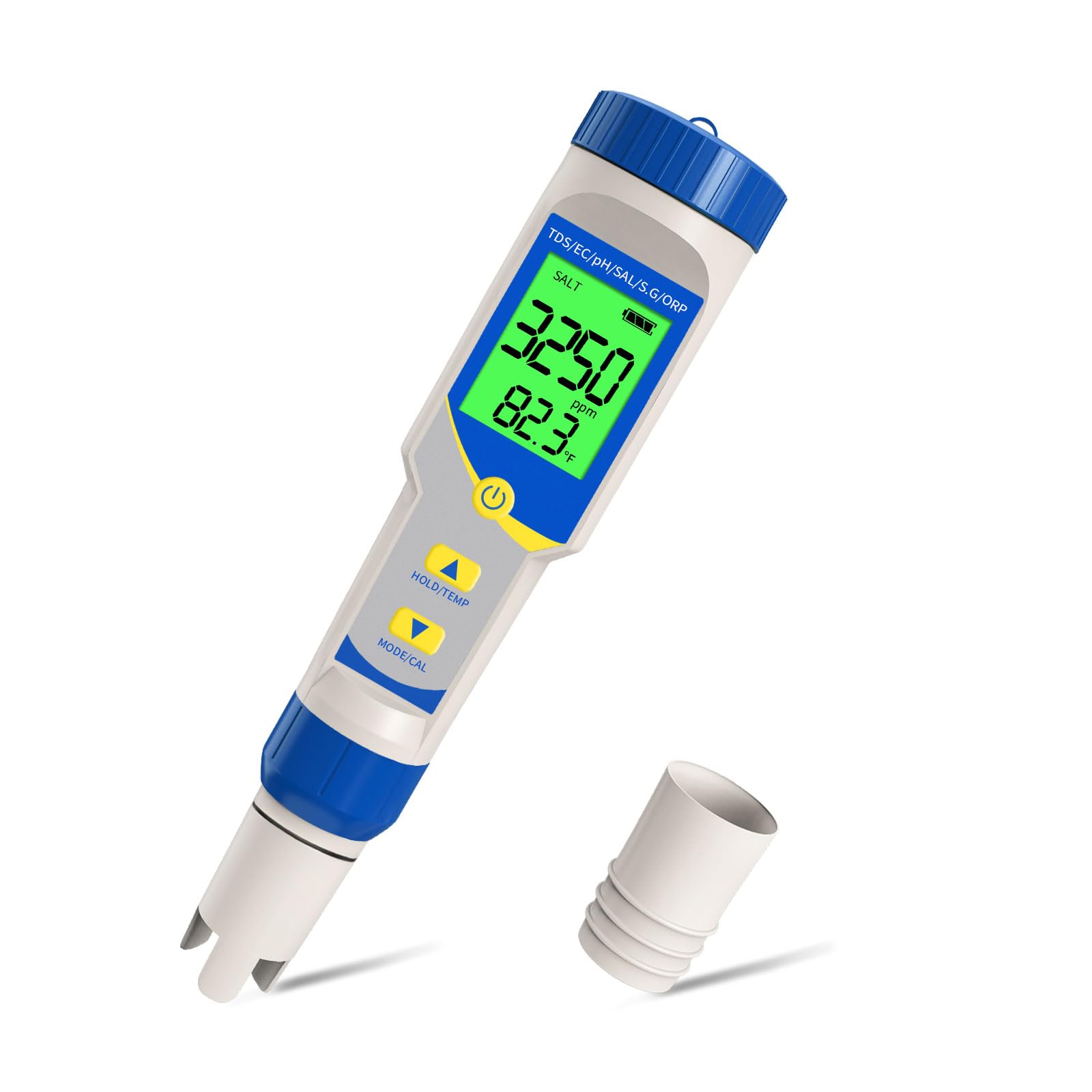
The global demand for accurate and reliable water quality monitoring solutions has surged in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of hygiene standards and the growing popularity of private and commercial swimming pools. According to Grand View Research, the global water quality monitoring market was valued at USD 6.02 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. A key segment within this landscape is salinity testing, especially as saltwater pools—which offer a gentler, lower-maintenance alternative to chlorine systems—gain traction among homeowners and facilities managers alike. Mordor Intelligence projects the pool & spa equipment market to grow at a CAGR of over 5.5% through 2028, further underscoring the rising need for precision salinity testers. As a result, manufacturers specializing in pool salinity measurement devices are experiencing heightened demand, innovation, and competition. Below are the top 9 swimming pool salinity tester manufacturers leading this evolving market with advanced, data-accurate solutions.
Top 9 Swimming Pool Salinity Tester Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hach
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hach.com
Key Highlights: At Hach, our products are meant to make water analysis better, faster, and more informative with our knowledgeable experts and easy to use products….
#2 How To Test Saltwater Pools
Domain Est. 1995
Website: palintest.com
Key Highlights: It is recommended to test salinity in the pool weekly. If the salt concentration is too high, it can cause damage to the cell and other pool hardware….
#3 Pocket Testers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lamotte.com
Key Highlights: Pocket Testers · Dissolved Oxygen – TRACER PockeTester™ · ORP / pH TRACER PockeTester™ Kit · ORP TRACER PockeTester™ · pH / Total Chlorine TRACER PockeTester™ Kit….
#4 Rapid Test Strips and Digital Salt Tester
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pentair.com
Key Highlights: Our rapid test strips and digital salt testers are engineered and manufactured to the highest standards of precision and quality to minimize installation ……
#5 Parameters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hannainst.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200 · 30-day returnsProduct · Meters. Portable meters; Benchtop meters; Photometers; Refractometers · Testers · Process controllers · Titrators. Potentiometric…
#6 NSF Product and Service Listings
Domain Est. 1996
Website: info.nsf.org
Key Highlights: NSF Product and Service Listings ; Pool eXact® EZ Photometer[1] [2], Free Chlorine, 0.0 ppm – 12 ppm, L1, Pool ; Spa eXact® EZ Photometer[1] [2], pH, 6 – 8.4, L2 ……
#7 Water Testing for Pools with a Salt Chlorinator
Domain Est. 1998
Website: taylortechnologies.com
Key Highlights: Salt chlorine generators are popular among pool owners because of the convenience of not having to transport, store, and handle chlorine….
#8 PoolPro
Domain Est. 2003
Website: myronlproducts.com
Key Highlights: Pool and Spa Water Quality Testing. The fastest, most accurate, reliable, easy-to-use handheld water quality analysis tool for any pool or spa….
#9 Salt Water Swimming Pool pH Meter Kit PCE
Domain Est. 2010
Website: pce-instruments.com
Key Highlights: The pool pH meter is the ideal measuring instrument for every swimming pool owner who values optimal water quality….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Swimming Pool Salinity Tester

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Swimming Pool Salinity Testers
The global market for swimming pool salinity testers is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, growing consumer awareness, and the rising popularity of saltwater pools. This analysis explores key trends shaping the industry landscape in the year 2026.
-
Increased Adoption of Smart and Digital Testers
By 2026, digital and smart salinity testers are expected to dominate the market. Consumers are increasingly favoring handheld digital devices and IoT-enabled testers that offer real-time monitoring, wireless connectivity (via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi), and integration with mobile applications. These smart testers allow pool owners to track salinity levels remotely, receive maintenance alerts, and access historical data for better pool management. -
Rising Popularity of Saltwater Pools
The shift from traditional chlorine pools to saltwater pools continues to accelerate. Saltwater pools are perceived as more comfortable, eco-friendly, and easier to maintain. This shift directly fuels demand for accurate, user-friendly salinity testers, as proper salinity balance is critical for the effective operation of salt chlorination systems. -
Focus on Accuracy and Calibration Features
Manufacturers are prioritizing precision and long-term reliability. In 2026, leading salinity testers will feature advanced calibration options, temperature compensation, and self-diagnostic functions to ensure consistent accuracy. Products with auto-calibration and digital diagnostics are gaining consumer trust and market share. -
Growth in Residential and Commercial Segments
Both residential and commercial sectors are expanding their use of salinity testers. In residential markets, DIY pool maintenance is on the rise, prompting demand for affordable, easy-to-use testers. Meanwhile, commercial facilities—such as hotels, resorts, and aquatic centers—are investing in professional-grade equipment to meet health regulations and ensure guest safety. -
Sustainability and Eco-Conscious Design
Environmental concerns are influencing product development. By 2026, many salinity testers are expected to be built with recyclable materials, energy-efficient components, and longer-lasting sensors to reduce electronic waste. Companies are also emphasizing sustainable packaging and energy-saving features. -
Regional Market Expansion
While North America and Europe remain key markets due to high pool ownership rates, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth. Countries like China, India, and Australia are witnessing increased construction of residential and public pools, driving demand for pool maintenance tools, including salinity testers. -
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established brands and new entrants investing in R&D. Key players are focusing on product differentiation through features such as multi-parameter testing (measuring pH, chlorine, and salinity in one device), intuitive user interfaces, and compatibility with smart home ecosystems. -
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Stricter water quality regulations in several countries are pushing pool operators to adopt certified testing equipment. In 2026, compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, NSF) will be a critical factor in product acceptance, especially in commercial and public pool applications.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the swimming pool salinity tester market will be characterized by technological sophistication, consumer-centric design, and strong growth fueled by the global rise in saltwater pool adoption. Manufacturers that innovate in digital integration, accuracy, and sustainability will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Swimming Pool Salinity Testers (Quality and IP Rating)
When sourcing swimming pool salinity testers, businesses and pool maintenance professionals must navigate several critical challenges—particularly concerning product quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these factors can lead to inaccurate readings, equipment failure, and increased long-term costs. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
1. Prioritizing Low Cost Over Long-Term Accuracy
One of the most frequent mistakes is choosing the cheapest available salinity tester without evaluating build quality or calibration stability. Low-cost models often use inferior electrode materials or lack proper shielding, leading to:
- Drifting calibration over time
- Inconsistent readings due to temperature fluctuations
- Shorter lifespan requiring frequent replacements
Result: Higher total cost of ownership and unreliable pool water management.
2. Ignoring IP Rating Requirements for Wet Environments
Many buyers overlook the importance of Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, assuming all testers are waterproof. However, poolside environments expose equipment to splashes, humidity, and occasional submersion.
- Common Mistake: Selecting devices with low IP ratings (e.g., IP65) for handheld use near water, where IP67 or IP68 is more appropriate.
- Risk: Water ingress can damage internal electronics, leading to premature failure or safety hazards.
Best Practice: Always verify the IP rating matches the intended use—IP67 (immersion up to 1 meter for 30 minutes) is typically recommended for handheld testers used poolside.
3. Assuming All Testers Are Calibrated Out-of-Box
Some suppliers provide testers without proper factory calibration or documentation. Relying on unverified calibration can result in:
- Misdiagnosis of salt levels
- Over- or under-chlorination in saltwater pools
- Damage to salt chlorinators due to incorrect salinity
Solution: Source from suppliers who provide NIST-traceable calibration certificates and offer recalibration services.
4. Overlooking Electrode Quality and Maintenance Needs
The electrode is the core component of any salinity tester. Poor-quality electrodes:
- Degrade faster in chlorinated water
- Require frequent cleaning or replacement
- Are not replaceable in some low-end models
Pitfall: Choosing testers with non-replaceable or proprietary electrodes increases downtime and cost.
Recommendation: Opt for devices with durable, replaceable electrodes made from corrosion-resistant materials like titanium or gold-plated sensors.
5. Failing to Verify Compliance and Certifications
Not all salinity testers meet international safety or performance standards. Avoid sourcing from manufacturers that cannot provide:
- CE, RoHS, or UKCA compliance
- IP certification test reports
- ISO 9001 manufacturing standards
Consequence: Non-compliant devices may fail safety inspections or void warranties.
6. Underestimating Environmental Impact on Performance
Temperature swings, UV exposure, and chemical fumes near pools can affect digital testers. Devices without proper environmental hardening may:
- Suffer screen fading or casing brittleness
- Deliver inaccurate readings in extreme heat or cold
Tip: Choose models with UV-resistant housings and wide operating temperature ranges (e.g., 0°C to 50°C).
By recognizing and avoiding these common pitfalls—especially those related to quality assurance and appropriate IP ratings—buyers can ensure reliable, safe, and cost-effective salinity testing for swimming pools. Always partner with reputable suppliers who provide transparent specifications, testing data, and post-purchase support.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Swimming Pool Salinity Tester
This guide outlines the key logistics considerations and regulatory compliance requirements for the distribution, import, and sale of Swimming Pool Salinity Testers across major markets. Adherence to these guidelines ensures smooth operations and legal market access.
H2: Regulatory Compliance Requirements
1. Electrical Safety (Applicable to Digital Testers)
* United States (US): Must comply with UL 61010-1 (Standard for Safety Requirements for Electrical Equipment for Measurement, Control, and Laboratory Use) or equivalent. FCC Part 15 Class B certification is required for any device emitting radio frequency energy (e.g., Bluetooth-enabled testers).
* European Union (EU): Requires CE marking under the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU). Compliance with EN 61010-1 is standard. RoHS (2011/65/EU) and REACH regulations apply to substance restrictions.
* United Kingdom (UK): Requires UKCA marking (replacing CE for GB market) under the UKCA equivalent regulations of LVD and EMC. RoHS (UK) and REACH (UK) apply.
* Canada: Requires certification to CSA C22.2 No. 61010-1 or UL/CSA 61010-1 standard, typically by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) like CSA Group or UL.
* Australia/New Zealand: Requires compliance with AS/NZS 61010.1 and EMC standards. SAA approval (or RCM mark) is mandatory.
* International: IEC 61010-1 is the foundational international safety standard often referenced.
2. Product Labeling & Packaging
* Mandatory Information: Include product name, model number, manufacturer/importer name and address, applicable safety marks (CE, UKCA, FCC, RCM, etc.), voltage rating, battery type (if applicable), and country of origin.
* Language: Labels and instructions must be in the official language(s) of the destination country (e.g., English for US/CA/UK/AU/NZ, French for FR/CA, German for DE, etc.).
* Warnings: Include clear safety warnings (e.g., “Do not disassemble,” “Keep away from children,” “Dispose of batteries properly”).
* Instructions for Use (IFU): Must be comprehensive, accurate, and in the local language, covering operation, calibration, maintenance, battery replacement, and disposal.
3. Chemical Safety (Applicable to Test Strips/Reagents)
* GHS/CLP: If the tester includes chemical reagents (strips, liquid drops), they may be classified as hazardous. Compliance with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) for classification, labeling, and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) is crucial. In the EU, this is enforced via the CLP Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008.
* Transport Regulations: Chemical components are subject to transport regulations (e.g., ADR for road in Europe, IATA/IMDG for air/sea) based on their classification. Proper UN numbers, hazard class, packing group, and labeling are required.
* REACH/RoHS: Ensure all chemical components comply with substance restrictions (SVHCs under REACH, restricted substances under RoHS).
4. Environmental & Waste Compliance
* WEEE (EU/UK): If the digital tester contains electrical/electronic components, it falls under WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) regulations. Producers must register, report sales, and finance the collection and recycling of end-of-life products.
* Battery Regulations: Batteries (especially button cells) are subject to specific disposal and recycling rules (e.g., EU Battery Directive, US state laws like CA). Labeling with the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol is often required.
* General Waste: Packaging must comply with local waste regulations (e.g., recyclability, material restrictions).
5. Data Privacy (Smart Testers)
* If the tester connects to an app and collects user data (e.g., pool readings, location), compliance with data protection laws is essential:
* GDPR (EU/UK): Requires lawful basis for processing, user consent, data minimization, and security.
* CCPA/CPRA (California, USA): Grants consumers rights over their personal data.
* Other Jurisdictions: Similar laws exist in Canada (PIPEDA), Australia (Privacy Act), Brazil (LGPD), etc.
H2: Logistics & Supply Chain Considerations
1. Import/Export Documentation
* Commercial Invoice: Detailed description of goods, value, currency, Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP), buyer/seller details.
* Packing List: Itemizes contents per package, weights, dimensions.
* Bill of Lading (Sea) / Air Waybill (Air): Contract of carriage and receipt.
* Certificate of Origin: May be required for tariff determination or trade agreements.
* Compliance Certificates: Copies of test reports, safety certifications (UL, CE, etc.), SDS (for chemicals).
* Import Licenses/Permits: Required in some countries (less common for testers, but verify).
2. Classification & Tariffs
* HS Code (Harmonized System): Accurately classify the product for customs. Likely codes include:
* 9027.20 (Instruments/apparatus for measuring or checking pH, acidity/alkalinity)
* 9027.80 (Other instruments/apparatus for physical/chemical analysis)
* Note: Classification depends on primary function and design. Chemical strips might fall under 3822 (chemical reagents). Confirm with a customs broker.
* Duties & Taxes: Research applicable import duties, VAT (EU/UK), GST (AU/NZ/CA), and sales tax (US states). Tariff rates vary significantly by country and HS code.
3. Transportation & Handling
* Mode Selection: Balance cost, speed, and reliability (Air freight for speed, Ocean freight for volume/cost).
* Packaging: Robust packaging to prevent damage during transit. Protect electronics from moisture and shock. Clearly mark fragile items. Ensure chemical components are securely contained and meet transport hazard requirements.
* Temperature Control: Avoid extreme temperatures during storage and transit, especially for electronic components and chemical reagents.
* Battery Transport: Lithium batteries (common in digital testers) have strict IATA/IMDG regulations for air/sea freight (e.g., State of Charge limits, packaging, labeling, documentation). Non-lithium batteries are less restricted but still require care.
4. Warehousing & Distribution
* Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment away from direct sunlight and chemicals.
* Inventory Management: Implement systems to track stock, manage expiration dates (critical for test strips/reagents), and prevent obsolescence.
* Last-Mile Delivery: Partner with reliable carriers experienced in handling consumer electronics and potentially hazardous goods (if applicable). Ensure final packaging protects the product.
5. After-Sales & Returns
* Warranty: Clearly define warranty terms (duration, coverage, process) in local language.
* Returns Process: Establish a clear returns policy (RMA process) compliant with local consumer protection laws (e.g., EU 14-day right of withdrawal).
* End-of-Life Management: Plan for take-back and recycling, especially if subject to WEEE. Provide clear disposal instructions to consumers.
Critical Action Steps:
1. Identify Target Markets: Determine specific countries for launch.
2. Engage Experts: Consult with regulatory specialists (for compliance) and freight forwarders/customs brokers (for logistics).
3. Obtain Certifications: Secure all necessary safety, EMC, and chemical compliance certifications before shipment.
4. Verify HS Code & Duties: Confirm classification and calculate landed costs.
5. Develop Compliant Packaging & Documentation: Ensure labels, manuals, and shipping docs meet all requirements.
6. Implement Quality Control: Ensure consistent product quality and batch traceability.
7. Monitor Regulatory Changes: Stay updated on evolving regulations (e.g., new RoHS substances, updated WEEE categories).
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations are complex and subject to change. Always consult with qualified legal, regulatory, and logistics professionals for advice specific to your product and target markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Swimming Pool Salinity Tester:
After evaluating various options, it is clear that sourcing a reliable and accurate swimming pool salinity tester is essential for maintaining optimal water quality and ensuring the longevity of pool equipment. Digital salinity testers offer superior precision, ease of use, and consistent results compared to traditional test strips. When sourcing, key considerations include accuracy, calibration options, durability, ease of maintenance, and cost-effectiveness.
Based on performance and value, it is recommended to source digital handheld salinity testers from reputable suppliers with proven track records in pool maintenance equipment. Models featuring automatic temperature compensation (ATC), waterproof design, and simple calibration procedures provide the best balance of functionality and reliability. Additionally, choosing suppliers that offer technical support and warranties enhances long-term satisfaction.
In conclusion, investing in a high-quality salinity tester not only improves pool water management but also reduces operational inefficiencies and maintenance costs. Prioritizing accuracy, durability, and supplier credibility will ensure a successful sourcing decision for both residential and commercial pool applications.