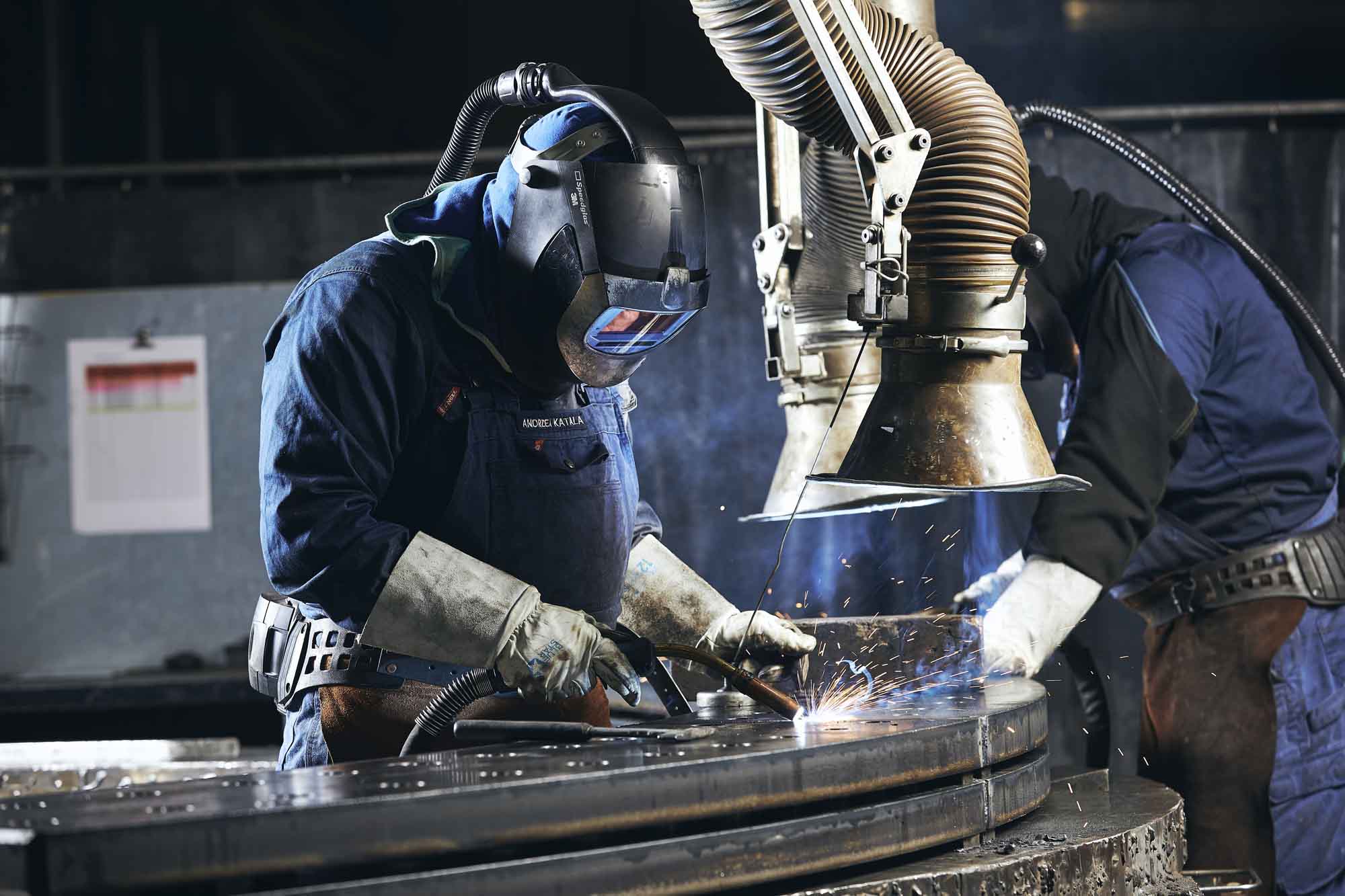
The global stainless steel welding market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand across industries such as construction, automotive, energy, and food processing. According to Mordor Intelligence, the stainless steel market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, with welding applications forming a critical segment due to the material’s corrosion resistance and durability. This growth is further supported by rising infrastructure investments and stringent regulatory standards favoring long-lasting, low-maintenance materials. As demand for high-quality stainless steel welding solutions intensifies, manufacturers are scaling innovation in precision, automation, and weld integrity. Below, we highlight the top 10 manufacturers excelling in svejsning af rustfrit stål (welding of stainless steel), selected based on production capacity, technological advancement, global footprint, and industry reputation.
Top 10 Svejsning Af Rustfrit Stål Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Svejsning i Rustfrit Stål
Website: as-vst.dk
Key Highlights: AS-VST tilbyder højkvalitets svejsning i rustfrit stål og andre reparationsløsninger der lever op til dine industrielle krav. Læs mere her….
#2 Svejsning i rustfrit stål
Website: brimas.dk
Key Highlights: Der er udviklet følgende tilsatsmaterialer til svejsning af duplex rustfri stål: Beklædte elektroder; TIG-tråde; MIG/MAG; Tråde og pulver til pulversvejsning….
#3 Svejsning
Website: aleks-steen.dk
Key Highlights: Er I på udkig efter professionel svejsning i rustfrit stål? . Vi tilbyder specialiserede svejsetjenester, der sikrer kvalitet i rustfristålkonstruktioner….
#4 Svejsning
Website: nmf.dk
Key Highlights: Vi udfører TIG-svejsning i rustfri stål og aluminium. Denne type svejsning leverer vi oftest til industrier hvor kravet til finish er højt. TIG (tungsten ……
#5 Svejsning i rustfrit stål: Bearbejdning af metal
Website: metals.it
Key Highlights: Svejsecyklussen styres med pulserende TIG- og digitalt MIG-udstyr på robotøer for at opnå den højeste kvalitet, selv ved tynde tykkelser….
#6 Svejsning i Hadsten nær Randers
Website: hadstenmaskinfabrik.dk
Key Highlights: Hos Hadsten Maskinfabrik A/S tilbyder vi professionel svejsning, af høj præcision og kvalitet af enhver emnetype. Vi svejser både i rustfrit/syrefast stål, ……
#7 Andersen Steel Company
Website: andersenssteel.dk
Key Highlights: Vi udfører TIG- og CO₂-svejsning i rustfri stål med høj præcision. Med mange års erfaring leverer vi holdbare løsninger tilpasset dit behov – uanset opgavens ……
#8 Svejsning
Website: ferrum-group.dk
Key Highlights: Ferrum-group har specialiseret sig i svejsning og bearbejdning af rustfri stål, aluminium og jern. Vores kerne kompetence er fremstilling af rør, ……
#9 Grinding, Polishing & Service for the Chemical Industry
Website: magrinding.com
Key Highlights: Svejsning af Rustfrit Stål til Kemisk Industri. Sikring af Tætte Svejsninger til Kemisk Forarbejdningsudstyr. I kemisk industri udsættes rustfrit ståludstyr ……
#10 Svejsning
Website: abj.dk
Key Highlights: Helt grundlæggende kan man dog sige, at svejsning er at forene to eller flere emner, til en ubrudt enhed. Når man svejser, opvarmer man kontaktfladerne på disse ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Svejsning Af Rustfrit Stål

H2: Market Trends for Svejsning Af Rustfrit Stål (Stainless Steel Welding) in 2026
The market for svejsning af rustfrit stål (welding of stainless steel) is projected to experience steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by industrial modernization, sustainability demands, and technological advancements across key sectors such as construction, renewable energy, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. This analysis outlines the primary trends expected to shape the stainless steel welding landscape in 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Green Energy and Infrastructure
The global push toward carbon neutrality is accelerating investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including hydrogen production facilities, offshore wind turbines, and biogas plants—all of which rely heavily on corrosion-resistant stainless steel components. As a result, demand for high-quality stainless steel welding services is increasing, particularly in Northern Europe, where stringent environmental standards favor durable, low-maintenance materials.
2. Advancements in Automated and Robotic Welding
By 2026, automation is becoming standard in high-precision stainless steel welding applications. Robotics and AI-driven welding systems are enhancing consistency, reducing human error, and improving productivity—especially in repetitive industrial tasks. In Denmark and other Nordic countries, companies are increasingly adopting collaborative robots (cobots) for TIG and MIG welding of stainless steel, ensuring cleaner welds with minimal post-processing.
3. Focus on Sustainability and Circular Economy
Sustainability is a driving force in material selection and fabrication methods. The recyclability of stainless steel aligns with circular economy principles, boosting its preference over carbon steel in many applications. Furthermore, welding techniques that reduce energy consumption and fume emissions—such as pulsed arc welding and hybrid laser processes—are gaining traction, supported by tightening EU environmental regulations.
4. Skilled Labor Shortage and Upskilling Initiatives
Despite technological progress, there remains a shortage of certified stainless steel welders, especially those proficient in advanced techniques like orbital welding and handling duplex/super-austenitic grades. In response, industry stakeholders and vocational institutions in Scandinavia are expanding training programs focused on modern welding technologies, digital diagnostics, and quality control (e.g., ISO 15614 and ASME IX compliance).
5. Growth in Hygienic and High-Purity Applications
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food & beverage, and semiconductor manufacturing require ultra-clean welds to meet hygiene standards (e.g., 3-A, EHEDG). By 2026, the demand for orbital welding and automated tube welding systems is expected to grow significantly, driven by the need for seamless, passivated joints that resist microbial growth and contamination.
6. Regional Market Dynamics in Scandinavia
In Denmark and neighboring countries, public infrastructure projects, offshore energy developments, and shipbuilding are key end markets for stainless steel welding. Local fabrication companies are increasingly investing in digital welding management systems (e.g., cloud-based monitoring of weld parameters) to ensure traceability and compliance, particularly for large-scale projects.
Conclusion
By 2026, svejsning af rustfrit stål will be characterized by a blend of technological innovation, regulatory compliance, and sector-specific demand. Companies that invest in automation, workforce development, and sustainable practices will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this resilient and evolving market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Svejsning Af Rustfrit Stål (Welding of Stainless Steel) – Quality and Intellectual Property Issues

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Svejsning Af Rustfrit Stål (Welding of Stainless Steel)
Material Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage of stainless steel materials are critical to maintain material integrity and prevent contamination. Always store stainless steel in a dry, clean environment, separated from carbon steel or other metals to avoid cross-contamination. Use non-metallic supports such as plastic or wood to prevent galvanic corrosion. Handle materials with clean gloves and tools dedicated solely to stainless steel to prevent iron contamination, which can compromise corrosion resistance.
Transportation Requirements
During transportation, stainless steel components and raw materials must be protected from physical damage and environmental exposure. Use moisture-resistant coverings and secure loads to prevent movement. Avoid direct contact with carbon steel transport surfaces—use separators such as rubber or plastic sheets. Ensure vehicles and containers are clean and free from residues that may introduce contaminants. For international shipments, comply with IATA, IMDG, or ADR regulations if applicable, particularly when transporting accompanying consumables like shielding gases.
Welding Process Compliance
All welding operations for stainless steel must adhere to relevant standards such as ISO 15614 (welding procedure qualification), ISO 9606 (welder approval), and EN 1090 for structural components. Use approved welding procedures (WPS) specific to the stainless steel grade (e.g., 304, 316, duplex). Ensure proper selection of filler materials, shielding gases (e.g., argon or argon-helium mixtures), and welding techniques (TIG, MIG, etc.) to maintain corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Regulations
Welding stainless steel produces hazardous fumes containing chromium and nickel compounds, some of which may be carcinogenic (e.g., hexavalent chromium). Ensure compliance with OSHA (or local equivalents such as Arbejdstilsynet in Denmark) regulations by using local exhaust ventilation (LEV) systems and providing appropriate respiratory protection. Conduct regular air quality monitoring. Dispose of welding residues, grinding dust, and contaminated consumables according to regional hazardous waste regulations (e.g., EU Waste Framework Directive).
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Maintain comprehensive documentation for full traceability and compliance. This includes material test certificates (MTCs), welding procedure specifications (WPS), welder qualifications, inspection reports (visual, NDT), and heat treatment records (if applicable). For regulated industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, or offshore, additional certifications like ASME BPE or NORSOK may apply. Implement a documented quality management system compliant with ISO 9022 or ISO 3834.
Import/Export and Trade Compliance
When moving stainless steel weldments across borders, ensure compliance with customs regulations, including correct HS codes (e.g., 7225.99 for welded stainless steel structures). Adhere to REACH and RoHS directives in the EU, which regulate chemical substances used in production. For exports, verify destination-specific standards and certification requirements. Maintain accurate records of origin, material declarations, and conformity assessments to facilitate customs clearance.
Konklusion på sourcing af svejsning af rustfrit stål
Sourcing af svejsning af rustfrit stål kræver en omhyggelig vurdering af både tekniske kompetencer, kvalitetsstandarder og leveringssikkerhed hos leverandørerne. Rustfrit stål stiller særlige krav til svejseprocesser, herunder korrekt valg af svejseteknik (fx TIG- eller MIG-svejsning), brug af passende tilføjsmaterialer og efterlevelse af strenge kvalitetskrav, især i brancher som fødevare, farmaceut og offshore, hvor korrosionsbestandighed og rent svejsning er afgørende.
Ved sourcing bør der lægges vægt på leverandørers certificeringer (fx EN 1090, ISO 3834, eller AD 2000), dokumentation af proceskontrol og evne til at levere konsekvent høj kvalitet. Lokal sourcing kan tilbyde fordele i form af kortere leveringstider, nemmere samarbejde og inspektion, mens international sourcing måske giver omkostningsfordele – men ofte på bekostning af fleksibilitet og kvalitetsstyring.
Konkluderende bør beslutningen om sourcing baseres på en afvejning mellem kvalitet, pris, leveringstid og langsigtede samarbejdsmuligheder. En strategisk tilgang med god leverandørvalg og kvalitetssikring er afgørende for at sikre holdbarhed, pålidelighed og konkurrencedygtighed i produktionen af konstruktioner i rustfrit stål.