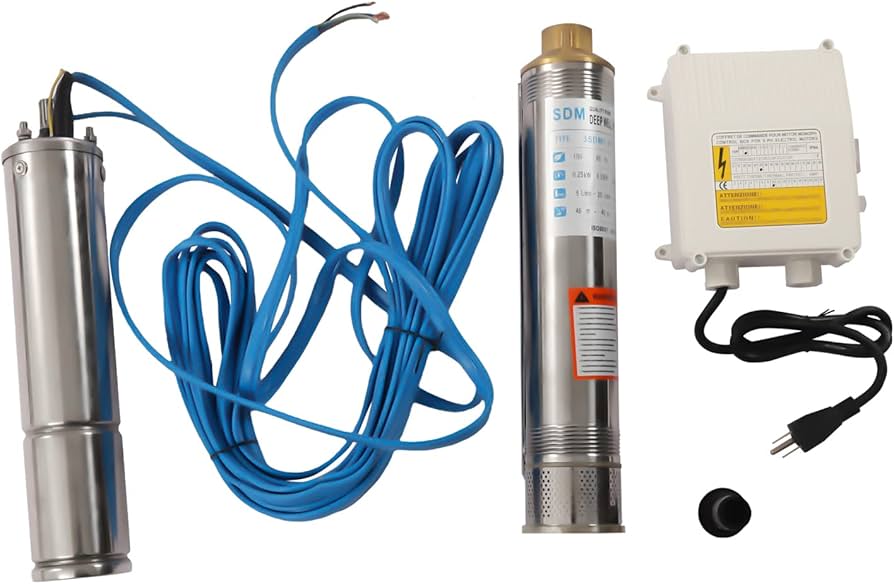
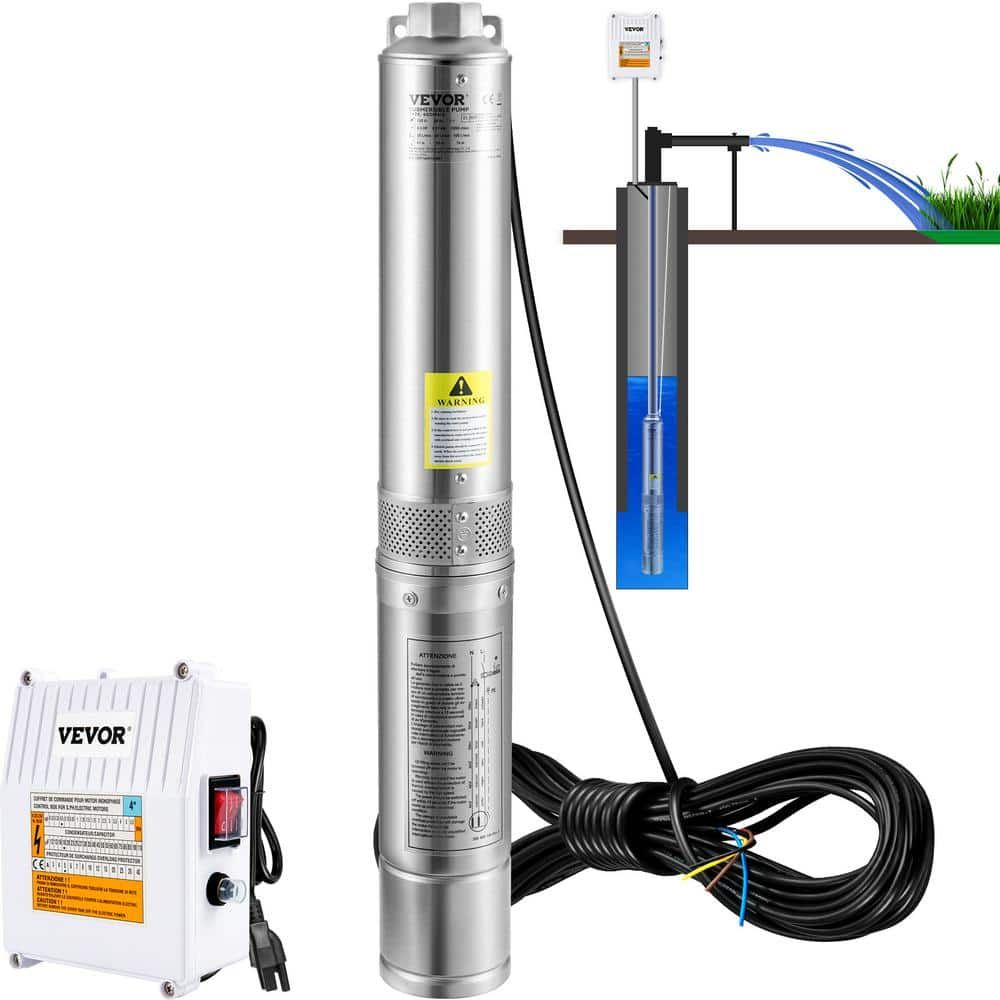
The global submersible pump market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient water extraction solutions in residential, agricultural, and industrial applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 14.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% through 2028. This expansion is fueled by rising groundwater utilization, infrastructure development, and advancements in pump efficiency and durability. As the need for reliable well pumping systems intensifies, especially in regions with limited access to surface water, manufacturers are innovating to meet performance and sustainability benchmarks. Against this backdrop, identifying the leading submersible pump manufacturers becomes critical for end users seeking quality, longevity, and technical excellence. Based on market presence, product innovation, global reach, and customer feedback, the following list highlights the top 10 submersible pump manufacturers for well applications shaping the industry today.
Top 10 Submersible Pump For Well Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Industrial Pumps Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: gouldspumps.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Pumps Manufacturer for a wide range of markets — including chemical, mining, oil & gas, power generation, pulp and paper, and general industry….
#2 Grundfos USA
Domain Est. 1995
Website: grundfos.com
Key Highlights: The full range supplier of pumps and pump solutions. As a renowned pump manufacturer, Grundfos delivers efficient, reliable, and sustainable solutions all ……
#3 Goulds Water Technology
Domain Est. 1995
Website: goulds.com
Key Highlights: Turbine Pumps. Xylem’s Goulds Water Technology is one of the world’s leading brands in residential and commercial water products….
#4
Domain Est. 1998
Website: webtrol.com
Key Highlights: Webtrol is a family owned manufacturer of submersible water well pumps, centrifugal booster pumps, and submersible wastewater pumps for residential, ……
#5 Deep Well Submersible Pumps and Motors
Domain Est. 1997
Website: flowserve.com
Key Highlights: Flowserve’s Deep Well Submersible Pumps and Motors product portfolio is one of the most comprehensive in the flow control industry….
#6 Submersible pumps
Domain Est. 1998
Website: dabpumps.com
Key Highlights: Pulsar Dry by DAB is a 5-inch submersible or surface multi stage impeller monoblock pump for clean water to increase water pressure, gardening and ……
#7 Zoeller Pump Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: zoellerpumps.com
Key Highlights: The best-in-class 3/10 HP Zoeller M63 automatic Sump Pump is designed to remove groundwater from basement sump applications….
#8 Flint & Walling
Domain Est. 2000
Website: flintandwalling.com
Key Highlights: Well Submersible. Efficient and durable, our well submersible pumps ensure reliable water movement in any environment. 4″ Submersible Motors · 4″ Deep Set Pump ……
#9 Submersible Well Pumps
Domain Est. 2009
Website: franklinwater.com
Key Highlights: Franklin Electric offers a variety of submersible pumps designed for the movement of water providing superior performance for many different applications….
#10 Tuhorse Pumps
Domain Est. 2012
Website: tuhorse.us
Key Highlights: Free delivery 15-day returnsFeatured Products ; 2″ 370W Solar Submersible Deep Well Pump and Control Box · US$1,590.00 US$866.00 ; Tuhorse 2HP TS4-013-18 230V 1-Phase S.S. Complete…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Submersible Pump For Well

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Submersible Pumps for Wells
By 2026, the global market for submersible pumps for wells is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological innovation, increasing demand for efficient water management, and global shifts toward sustainability. Key trends shaping the industry include:
-
Growth in Residential and Agricultural Water Demand
Expansion in rural electrification and irrigation projects—particularly in emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America—is fueling demand for reliable well water extraction. As populations grow and climate variability intensifies, submersible pumps are becoming essential for secure water access in both household and farming applications. -
Adoption of Smart and IoT-Enabled Pumps
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into submersible pumps is a defining trend. By 2026, smart pumps equipped with sensors, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities are gaining traction. These systems enable real-time performance tracking, reduce downtime, and optimize energy use—particularly valued in large-scale agricultural and municipal water supply operations. -
Rise of Solar-Powered Submersible Pumps
With increasing focus on renewable energy, solar-powered submersible pumps are expected to capture a growing market share. These systems are cost-effective in off-grid areas and align with global decarbonization goals. Governments and NGOs are supporting solar pump adoption through subsidies and rural development programs, especially in India, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia. -
Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Standards
Stricter energy efficiency regulations, such as the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) and EU Ecodesign directives, are pushing manufacturers to develop high-efficiency motors and variable frequency drives (VFDs). By 2026, pumps meeting IE4 and IE5 efficiency standards are anticipated to become mainstream, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. -
Material Innovation and Durability Enhancements
Manufacturers are increasingly using corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, thermoplastics, and advanced composites to extend pump lifespan in challenging well conditions. This is particularly important in saline or mineral-rich groundwater environments, where reliability and maintenance intervals are critical. -
Consolidation and Competitive Landscape Shifts
The market is witnessing consolidation among key players—such as Grundfos, Xylem, Franklin Electric, and KSB—as companies seek to expand their product portfolios and geographic reach. At the same time, regional manufacturers are gaining ground by offering cost-competitive, localized solutions. -
Aftermarket Services and Digital Support Platforms
By 2026, service ecosystems—including remote diagnostics, digital spare parts platforms, and mobile-enabled technician networks—are becoming vital differentiators. Customers increasingly expect end-to-end lifecycle support, driving vendors to invest in cloud-based service infrastructures.
In summary, the 2026 submersible pump for well market is being reshaped by digitalization, sustainability imperatives, and evolving end-user needs. Companies that innovate in energy efficiency, smart integration, and renewable compatibility are likely to lead the market, while addressing affordability and accessibility will remain critical in developing regions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Submersible Pumps for Wells (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a submersible pump for a well demands careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Choosing Low-Quality Pumps Based on Price Alone
Prioritizing cost over quality often results in pumps built with inferior materials, substandard motors, and poor manufacturing tolerances. These pumps may fail prematurely, require frequent repairs, deliver inconsistent performance, and consume more energy, ultimately increasing the total cost of ownership.
Ignoring IP Protection and Authenticity
Procuring pumps from unauthorized suppliers or counterfeit sources poses serious IP risks. Counterfeit or cloned products not only violate intellectual property rights but also lack reliability, safety certifications, and manufacturer warranties. Using such equipment can expose buyers to legal liability and operational risks.
Overlooking Certification and Compliance
Failing to verify compliance with international standards (such as ISO, CE, or NSF) can result in pumps unsuitable for the intended application—especially in drinking water or hazardous environments. Non-compliant pumps may not meet efficiency, safety, or environmental regulations.
Inadequate Supply Chain Due Diligence
Sourcing from suppliers without transparent origins or verifiable manufacturing practices increases the risk of receiving reconditioned, fake, or non-original equipment. Always audit suppliers and demand proof of authenticity, including serial numbers, manufacturer documentation, and chain-of-custody records.
Neglecting After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost or off-brand pumps often lack reliable technical support and spare parts infrastructure. This can lead to extended downtime during failures, especially in remote or critical applications where maintenance responsiveness is crucial.
Assuming All “Branded” Pumps Are Genuine
Even when dealing with well-known brands, counterfeit products are prevalent in the market. Without verifying the distribution channel and obtaining proper documentation, buyers may inadvertently purchase fake pumps that mimic genuine products but fail under operation.
Disregarding Warranty and Service Terms
Some suppliers offer attractive pricing but provide limited or voidable warranties. Always review warranty conditions carefully—especially regarding installation requirements, authorized service providers, and exclusions that could render the warranty useless.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, buyers can ensure they source reliable, high-quality submersible pumps that meet performance needs and respect intellectual property rights.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Submersible Pumps for Wells
Overview
Submersible pumps for wells are critical equipment used in water extraction for residential, agricultural, industrial, and municipal applications. Proper logistics and compliance management ensures the safe, legal, and efficient transport, installation, and operation of these devices. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, shipping, regulatory compliance, and documentation.
Classification and Harmonized System (HS) Code
Submersible pumps for wells typically fall under the following HS Code:
8413.70 – Pumps for liquids, whether or not fitted with a measuring device, submersible, electrically powered.
– Confirm the exact HS code with local customs authorities, as classification may vary slightly by country.
– Accurate classification is essential for import/export duties, tariffs, and trade compliance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
- Protective Packaging: Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging (wooden crates or heavy-duty cardboard with internal foam padding) to prevent damage during transit.
- Orientation Labels: Mark packages with “This Side Up” and “Fragile” labels; submersible pumps must not be stored or transported upside down.
- Environmental Protection: Seal electrical components and motor casings to prevent exposure to dust, moisture, and corrosive elements.
- Weight and Dimensions: Clearly label gross weight, dimensions, and center of gravity for safe lifting and stacking. Use certified lifting points if provided.
Transportation Modes and Considerations
- Road Transport: Ensure vehicles are equipped with suspension systems to reduce vibration. Secure pumps to prevent shifting.
- Maritime Shipping: Use dry, ventilated containers. Comply with IMO regulations if transporting hazardous materials (e.g., lubricants in some pump models).
- Air Freight: Subject to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries or flammable components are included. Typically not required for standard electric submersible pumps.
- Cold Chain/Climate Control: Not typically required unless components are sensitive to extreme temperatures.
Import and Export Documentation
Ensure the following documents are prepared and accurate:
– Commercial Invoice (with declared value, quantity, and HS code)
– Packing List (detailed itemization of contents)
– Bill of Lading (sea freight) or Air Waybill (air freight)
– Certificate of Origin
– Import/Export License (if required by country)
– Customs Declaration Form
Regulatory Compliance
Electrical Safety Standards
- North America: Must comply with UL/CSA standards (e.g., UL 507 for electric motors).
- European Union: CE marking required under the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and RoHS compliance.
- Other Regions: Check local standards (e.g., CCC in China, BIS in India, S-Mark in Singapore).
Environmental and Material Restrictions
- RoHS (EU): Restricts use of hazardous substances (lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.).
- REACH (EU): Requires declaration of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC).
- Proposition 65 (California, USA): Requires warning labels if pump contains listed chemicals.
Water Quality and Usage Regulations
- Ensure pumps meet NSF/ANSI 61 (Drinking Water System Components) if used for potable water.
- Certain regions may require certification for agricultural or irrigation use (e.g., Water Efficiency Labelling Scheme in Australia).
Installation and Operational Compliance
- Follow manufacturer’s installation guidelines to ensure safety and warranty validity.
- Grounding and electrical wiring must comply with local codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC standards internationally).
- Pumps used in protected aquifers may require environmental permits or reporting.
Warranty and After-Sales Support
- Provide warranty documentation in local language.
- Include contact information for technical support and service centers.
- Maintain records of serial numbers and shipment details for traceability.
Disposal and End-of-Life Considerations
- Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU for proper recycling.
- Inform end-users of environmentally responsible disposal options.
- Remove and recycle oil or lubricants according to local hazardous waste regulations.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for submersible pumps for wells require careful attention to classification, packaging, transport safety, and regional regulations. Proactive documentation and adherence to electrical, environmental, and water safety standards mitigate risks and support smooth international trade and reliable operation.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Submersible Pump for a Well
After evaluating technical specifications, operational requirements, cost considerations, and long-term maintenance needs, sourcing the appropriate submersible pump for a well requires a balanced approach that prioritizes efficiency, durability, and suitability for site-specific conditions. Key factors such as well depth, required flow rate, water quality, power availability, and pump material compatibility must be carefully assessed to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Sourcing from reputable suppliers or manufacturers with proven experience in water well applications ensures product reliability, access to technical support, and warranty coverage. Additionally, considering energy-efficient models can lead to significant cost savings over time, especially in continuous or high-demand operations.
Ultimately, investing time in proper pump selection, professional installation, and routine maintenance will maximize water output, reduce downtime, and extend the system’s service life. A well-informed sourcing decision today contributes directly to the sustainability and reliability of the entire water supply system.