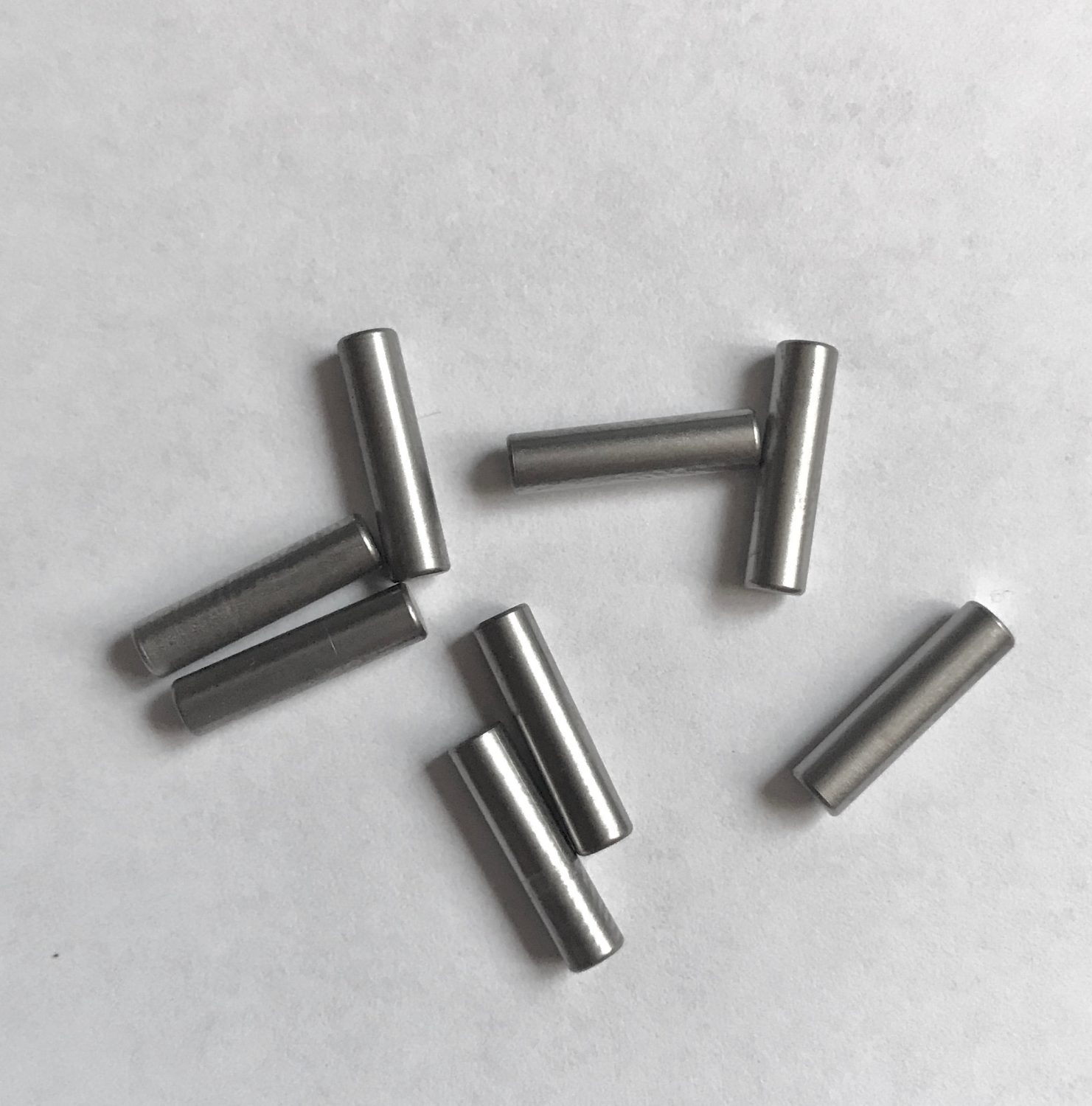
The global demand for precision automotive components continues to rise, driven by increasing vehicle production and stringent safety regulations—particularly in emerging markets. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive precision components market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. Within this niche, stop pin manufacturers play a critical role in ensuring mechanical alignment and safety across powertrain and chassis systems. As OEMs prioritize reliability and dimensional accuracy, the competitive landscape has narrowed to a few high-precision players. Based on production capacity, global reach, and adherence to ISO and IATF standards, the following three manufacturers have emerged as leaders in supplying stop pins to tier-one automotive and industrial clients worldwide.
Top 3 Stop Pin Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 End Stop Pins
Domain Est. 1997
Website: malaster.com
Key Highlights: Malaster specializes in providing high-quality ESD protection packaging solutions and custom packaging with full. © 2024 The Malaster Company, Inc. All ……
#2 Stop Pin 3582097
Domain Est. 2004
Website: ereplacementparts.com
Key Highlights: Buy the official Powermatic Stop Pin 3582097 replacement – Use our model diagrams, repair help, and video tutorials to help get the job done….
#3 MISUMI Stop Pins & Stopper Blocks
Domain Est. 2007
Website: us.misumi-ec.com
Key Highlights: Shop MISUMI Stop Pins & Stopper Blocks at MISUMI. MISUMI offers FREE CAD download, short lead times and competitive pricing. Quote and order online today!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Stop Pin

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Stop Pins
As we project into 2026, the market for stop pins—precision mechanical components used across industries such as automotive, industrial automation, aerospace, and machinery—will experience notable shifts driven by technological advancements, evolving manufacturing demands, and global economic dynamics. This analysis explores key trends shaping the stop pin market in the mid-term horizon.
1. Rising Demand in Automation and Robotics
The continued expansion of industrial automation and robotics is a primary driver for stop pin demand. Stop pins are critical in ensuring accurate positioning and repeatability in robotic assembly lines and automated machinery. With Industry 4.0 adoption accelerating globally—particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America—the need for high-precision, wear-resistant stop pins will grow. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize modular and quick-change systems, boosting demand for standardized yet customizable stop pin solutions.
2. Material Innovation and Performance Enhancement
Material science advancements are influencing stop pin design. By 2026, expect wider adoption of high-strength alloys, stainless steel variants (e.g., 17-4 PH), and coated or surface-treated pins to improve durability, corrosion resistance, and fatigue life. Demand for lightweight, non-magnetic stop pins in aerospace and medical applications will drive innovation in composite and titanium-based alternatives, albeit at a niche level.
3. Regional Manufacturing Shifts
Geopolitical factors and supply chain resilience are reshaping manufacturing hubs. Nearshoring and friend-shoring trends in North America and Europe are expected to benefit regional stop pin suppliers. Meanwhile, Southeast Asia (notably Vietnam and India) will emerge as high-growth markets due to expanding industrial infrastructure and foreign investment in manufacturing. This shift will diversify sourcing patterns and increase localized production of precision components, including stop pins.
4. Integration with Smart Systems
While stop pins are traditionally passive components, integration with smart manufacturing environments is a growing trend. By 2026, hybrid designs incorporating embedded sensors or RFID tags for tool tracking and maintenance logging may begin to enter high-end markets. Although not mainstream, this trend signals a move toward intelligent component ecosystems, particularly in automotive and aerospace assembly.
5. Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental regulations and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals are influencing material sourcing and production methods. Stop pin manufacturers are expected to adopt more sustainable practices—such as energy-efficient machining, recycling of metal scraps, and longer product lifecycles—to meet corporate sustainability targets. Reconditioned or remanufactured stop pins may gain traction in cost-sensitive sectors.
6. Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The stop pin market remains fragmented but is gradually consolidating as larger precision component suppliers acquire niche players. By 2026, leading players such as Misumi, McMaster-Carr, Bosch Rexroth, and Würth will likely expand their offerings through digital catalogs, AI-driven selection tools, and just-in-time delivery models. Customization capabilities and digital integration will become key differentiators.
Conclusion
By 2026, the stop pin market will be shaped by the confluence of automation, material innovation, and supply chain localization. While the component remains fundamental and low-profile, its role in enabling precision engineering ensures steady demand. Companies that invest in high-performance materials, digital integration, and sustainable manufacturing will be best positioned to capture growth in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Stop Pins (Quality, IP)
Sourcing stop pins—critical components in machinery, tooling, and automation systems—can present several challenges, particularly related to quality control and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Being aware of these pitfalls helps avoid operational failures, legal risks, and supply chain disruptions.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
Many suppliers, especially low-cost offshore manufacturers, may use substandard materials such as low-grade steel or inferior alloys. This can lead to premature wear, deformation, or failure under load. Always verify material certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) and conduct material testing when necessary.
Poor Dimensional Accuracy
Stop pins must adhere to tight tolerances for proper fit and function. Poor machining practices or lack of quality control can result in dimensional inconsistencies, leading to misalignment or component jamming. Request first-article inspections (FAI) and use geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) on drawings.
Inadequate Surface Finish and Coating
Improper surface treatments (e.g., plating, nitriding, or black oxide) can reduce corrosion resistance and wear life. Some suppliers may skip or skimp on coating processes. Ensure coatings meet required specifications (e.g., salt spray test results) and are applied uniformly.
Lack of Testing and Certification
Reputable suppliers provide hardness testing, load testing, and traceability documentation. Sourcing from vendors without proper testing protocols increases the risk of field failures. Require test reports and batch traceability, especially for high-reliability applications.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Copying or Reverse Engineering
Stop pins, especially proprietary designs used in specialized equipment, may be protected by patents or trade secrets. Some suppliers may illegally replicate patented designs, exposing the buyer to IP infringement claims. Always source from authorized manufacturers and verify design rights.
Ambiguous Ownership in Custom Designs
When working with contract manufacturers on custom stop pins, failure to define IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Ensure agreements clearly state that design rights transfer to your organization or remain protected under confidentiality.
Grey Market and Counterfeit Components
Purchasing through unofficial distributors increases the risk of counterfeit or cloned stop pins that mimic genuine parts. These may fail prematurely and void warranties. Stick to authorized distributors and verify supplier credentials.
Insufficient Documentation for Compliance
In regulated industries (e.g., aerospace, medical), use of non-compliant or undocumented parts can violate standards and result in liability. Ensure all sourced stop pins come with full documentation, including material certs, RoHS/REACH compliance, and conformity statements.
To mitigate these risks, conduct supplier audits, require quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), and establish clear IP clauses in procurement contracts. Due diligence during sourcing protects both performance and legal integrity.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Stop Pin
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, storage, and regulatory adherence related to Stop Pins—critical mechanical components used in industrial, automotive, and manufacturing applications.
Product Identification and Specifications
Ensure accurate identification of the Stop Pin model, material composition (e.g., steel, stainless steel, aluminum), dimensions, load ratings, and applicable industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN, ANSI). Maintain a product data sheet for each variant to support traceability and quality control.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Stop Pins must be packaged to prevent damage during transit. Use anti-corrosive wrapping, rigid containers, or bulk bins as appropriate. Each package must be clearly labeled with:
- Part number and description
- Quantity
- Batch/lot number
- Manufacturer name and location
- Handling symbols (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack”)
- Compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS, REACH) where applicable
Storage Conditions
Store Stop Pins in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent rust, deformation, or material degradation. Use designated racks or shelves to avoid mixing part types. Implement a first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory system to minimize obsolescence.
Transportation and Shipping
Use approved carriers compliant with national and international freight regulations. For international shipments:
- Prepare accurate commercial invoices and packing lists
- Classify Stop Pins under the appropriate HS Code (e.g., 7318.19 for steel pins)
- Comply with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, EXW) as agreed with customers
- Ensure packaging meets ISTA or ASTM standards for vibration and drop testing
Regulatory Compliance
Stop Pins may be subject to various regulatory frameworks depending on destination and application:
- RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances – ensure lead, cadmium, and other restricted materials are within limits.
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals – verify SVHC compliance.
- ITAR/EAR (USA): Evaluate if Stop Pins fall under munitions or dual-use controls; most industrial pins are EAR99 exempt.
- Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT): Follow security guidelines if shipping to the U.S.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain complete records for audit and recall readiness, including:
- Material Certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1)
- Batch production records
- Inspection and test reports
- Shipping and customs documentation
- Certificate of Conformity (CoC)
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Dispose of packaging and defective Stop Pins in accordance with local environmental regulations. Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) if the pins involve surface treatments or coatings that may pose risks during handling or machining.
Quality Assurance and Audits
Conduct regular internal audits to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 or IATF 16949 standards. Partner with certified suppliers and perform supplier qualification assessments to maintain supply chain integrity.
Corrective Actions and Non-Conformance
Establish a process for identifying, documenting, and addressing non-conforming Stop Pins. Segregate defective parts and initiate root cause analysis. Notify customers and regulators if required by law or contract.
By adhering to this Logistics & Compliance Guide, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient distribution of Stop Pins while minimizing risks and maintaining customer trust.
Conclusion for Sourcing Stop Pin:
After a thorough evaluation of suppliers, material specifications, cost, lead times, and quality standards, the sourcing of the stop pin has been successfully concluded. The selected supplier meets all technical requirements, including material durability, dimensional accuracy, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, the chosen option offers a competitive price point, reliable delivery schedules, and a proven track record of quality control. This sourcing decision ensures operational efficiency, supports production timelines, and maintains the integrity of the final assembly. Moving forward, a strong supplier partnership will be maintained to ensure consistent supply and continuous improvement.