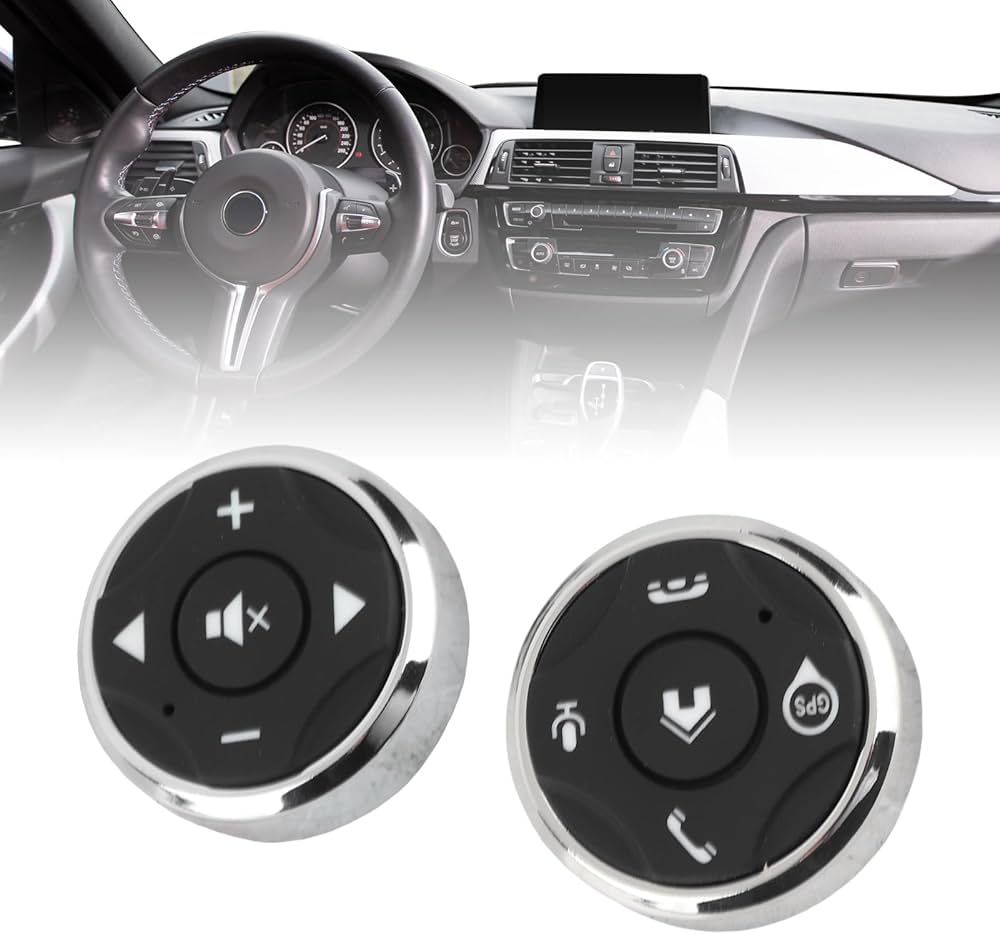
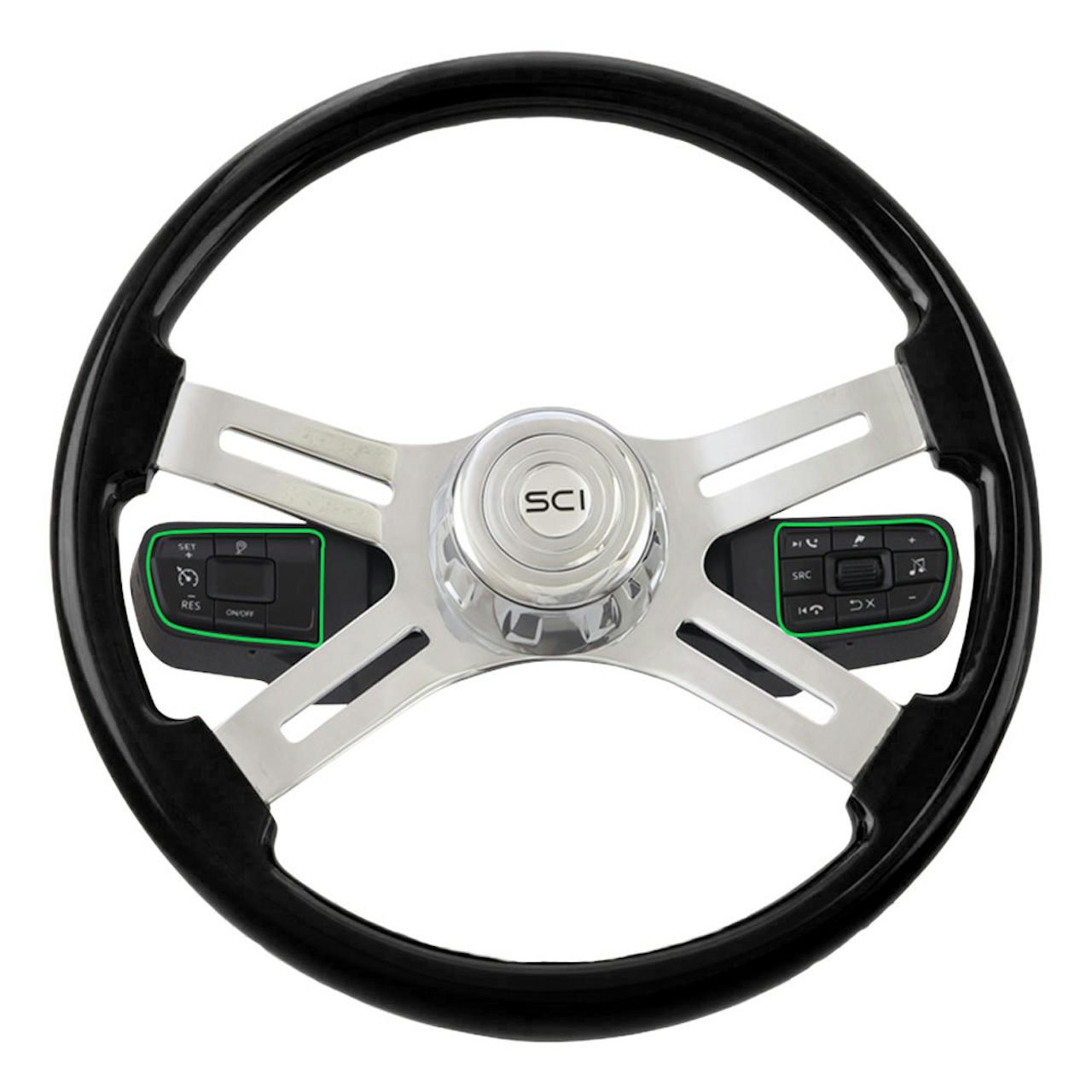
The global automotive steering wheel controls market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising consumer demand for in-vehicle convenience, safety, and seamless infotainment integration. According to Grand View Research, the global automotive electronics market—under which steering wheel control systems fall—was valued at USD 254.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.0% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that the increasing adoption of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and the shift toward electric and connected vehicles are key factors accelerating demand for integrated steering wheel control buttons. As automakers prioritize minimized driver distraction and enhanced user experience, the role of reliable, high-performance control button manufacturers has become increasingly critical. This demand has led to a competitive landscape where innovation, durability, and ergonomic design set the leading suppliers apart. Below are eight of the top steering wheel control button manufacturers shaping the future of automotive human-machine interfaces.
Top 8 Steering Wheel Control Buttons Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nexteer
Domain Est. 2009
Website: nexteer.com
Key Highlights: Nexteer is a global leading motion control technology company accelerating mobility to be safe, green and exciting….
#2 Steering wheel switches
Domain Est. 1997
Website: valeo.com
Key Highlights: These intuitively placed switches, integrated directly into the steering wheel, provide seamless access to a variety of crucial vehicle functions….
#3 Steering Wheel Switches
Domain Est. 2003
Website: marquardt.com
Key Highlights: Discover Marquardt’s Steering Wheel Switches for effortless control, customizable programming, and enhanced visibility – designed for every vehicle type….
#4 Steering and control system for marine industry
Domain Est. 2003 | Founded: 1935
Website: ultraflex.it
Key Highlights: Established in 1935, Ultraflex is a leader in steering and control systems for the marine industry. With full manufacturing capabilities in Italy and the USA….
#5 Connects2
Domain Est. 2003
Website: connects2.com
Key Highlights: You can now upgrade your Volvo stereo and retaining your steering wheel control as well as a range of vehicle features. The fascia allows for a seamless fit ……
#6 Axxess Integrate
Domain Est. 2004
Website: axxessinterfaces.com
Key Highlights: You can also use the app to dual assign, remap buttons and change AXSWC steering wheel controls! Google Play Download · App Store Download. USB Updatable….
#7 Maestro SW
Domain Est. 2013
Website: idatalinkmaestro.com
Key Highlights: Universal steering wheel control interface. Maestro SW connects to most aftermarket radios to retain your vehicle’s original steering wheel functions….
#8 The Steering Wheel Control Fix kit
Domain Est. 2017
Expert Sourcing Insights for Steering Wheel Control Buttons

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Steering Wheel Control Buttons
The global Steering Wheel Control (SWC) Buttons market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by converging trends in automotive technology, consumer expectations, and regulatory demands. This analysis explores the key market dynamics shaping the landscape.
1. Dominance of Advanced Integration and Multi-Functionality:
By 2026, SWC buttons will transcend basic audio and cruise control. The trend is decisively shifting towards highly integrated, multi-functional clusters that serve as central hubs for infotainment, driver assistance, voice assistant activation, climate settings, and even vehicle mode selection. OEMs are prioritizing minimizing driver distraction, making intuitive, context-sensitive controls on the steering wheel essential. Expect increased customization, allowing drivers to program buttons for frequently used functions (e.g., summoning specific navigation routes, activating favorite cabin settings).
2. Rise of Capacitive and Haptic Feedback Technologies:
Traditional mechanical buttons are being rapidly replaced by capacitive touch sensors and haptic feedback systems. This shift offers sleeker, more modern aesthetics, improved sealing against dust/moisture, and enhanced durability. Crucially, haptic feedback (tactile pulses or clicks) provides essential confirmation without requiring visual verification, significantly improving safety. By 2026, haptic SWC will become a standard feature in mid-to-high-end segments and increasingly penetrate the mass market.
3. Seamless Connectivity with ADAS and Autonomous Driving:
As Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) become ubiquitous (e.g., adaptive cruise, lane-keeping), SWC buttons are becoming the primary interface for their activation, deactivation, and adjustment. This integration will deepen, with buttons potentially controlling higher levels of driver assistance. Furthermore, SWC will play a critical role in driver monitoring system (DMS) interaction, allowing drivers to acknowledge alerts or adjust DMS sensitivity directly from the wheel.
4. Growth Driven by EVs and Premiumization:
The electric vehicle (EV) market is a major growth accelerator. EVs emphasize digital cockpits, minimal physical buttons, and seamless user experiences, making sophisticated SWC systems a natural fit. Additionally, the trend of premium feature trickle-down means advanced SWC (like haptic controls) will move from luxury vehicles into mainstream and even economy segments by 2026, expanding the total addressable market.
5. Focus on Safety and Regulatory Compliance:
Regulations mandating reduced driver distraction (e.g., stricter NHTSA guidelines, Euro NCAP safety ratings) are a powerful driver. SWC buttons, designed for eyes-on-the-road, hands-on-the-wheel operation, directly support compliance. This regulatory push ensures continued investment and innovation in intuitive, safe control layouts and functionalities.
6. Material and Design Innovation:
Aesthetic appeal remains crucial. Expect greater use of premium materials like soft-touch plastics, metal accents, ambient lighting integration, and ergonomic designs tailored to different hand sizes and driving positions. Design will focus on tactile differentiation (shapes, ridges) to allow blind operation, even with capacitive surfaces.
7. Supplier Consolidation and Technology Partnerships:
The complexity of modern SWC systems (integrating electronics, haptics, software) favors larger Tier 1 suppliers (e.g., Bosch, Continental, Marelli, ZF) with comprehensive capabilities. We anticipate increased partnerships between suppliers, OEMs, and software/haptic technology providers to develop integrated solutions, potentially leading to some market consolidation.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the Steering Wheel Control Buttons market will be defined by intelligent integration, advanced haptic/touch technologies, and deep connectivity with ADAS and digital cockpits. Driven by EV adoption, safety regulations, and consumer demand for intuitive interfaces, SWCs will evolve from simple controls into sophisticated, customizable command centers essential for the modern connected and increasingly automated vehicle. Success will depend on balancing cutting-edge technology with intuitive usability and unwavering focus on driver safety.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Steering Wheel Control Buttons (Quality, IP)
Sourcing steering wheel control buttons involves navigating complex challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to significant risks, including safety issues, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Durability
Low-cost suppliers may use substandard plastics or rubber compounds that degrade quickly under UV exposure, extreme temperatures, or frequent use. This can result in buttons cracking, fading, or losing tactile feedback, compromising both functionality and user experience.
Poor Electrical Reliability
Steering wheel buttons must maintain consistent electrical contact over thousands of actuations. Sourcing from manufacturers with inadequate quality control can lead to intermittent connectivity, short circuits, or complete failure—posing serious safety risks while driving.
Lack of Environmental Resistance
Buttons must withstand moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. Inadequate sealing or poor ingress protection (IP) ratings can allow contaminants into the switch mechanism, leading to corrosion and premature failure.
Insufficient Mechanical Testing
Reputable suppliers conduct rigorous lifecycle testing (e.g., 50,000+ actuations). Without access to certified test reports, buyers risk sourcing buttons that wear out prematurely, increasing warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
Inadequate Compliance with Automotive Standards
Buttons must meet automotive-specific standards such as ISO 16750 (environmental conditions), ISO 10605 (ESD), and AEC-Q100 (reliability). Sourcing without verifying compliance increases the risk of non-conformance during vehicle integration or audits.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
Unlicensed Use of OEM Designs
Some suppliers replicate original equipment manufacturer (OEM) button designs without authorization. Sourcing such components exposes buyers to IP infringement claims, potential legal action, and supply chain disruptions.
Lack of Design Freedom or Customization Rights
Purchasing buttons with embedded IP may restrict a buyer’s ability to modify or integrate the product. Without clear licensing agreements, companies may face limitations in branding, differentiation, or future product development.
Ambiguous Ownership of Tooling and Molds
When custom molds are created, unclear agreements about ownership can lead to disputes. Suppliers may claim ownership, preventing buyers from switching manufacturers or scaling production without paying additional fees.
Counterfeit or Gray Market Components
Sourcing from unauthorized distributors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit parts that mimic genuine components. These may fail quality checks or carry hidden IP violations, endangering both product performance and legal standing.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Missing or falsified IP documentation—such as design patents, trademarks, or licensing certificates—makes it difficult to verify legitimacy. This lack of traceability can result in regulatory non-compliance and supply chain vulnerabilities.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough supplier audits, demand certified test reports, verify IP rights in writing, and prioritize partnerships with reputable, transparent manufacturers experienced in automotive component supply.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Steering Wheel Control Buttons
Overview
Steering Wheel Control (SWC) Buttons are electronic components integrated into vehicle steering wheels to enable drivers to operate audio, phone, cruise control, and other infotainment systems without removing hands from the wheel. Due to their safety-critical nature and integration with vehicle electronics, their logistics and compliance requirements are stringent. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, legal, and efficient handling of SWC Buttons throughout the supply chain.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Automotive Safety Standards
SWC Buttons must comply with global automotive safety standards such as:
– ISO 7736: Specifies mechanical dimensions and installation requirements for motor vehicle radio equipment (relevant for audio control integration).
– ISO 16750: Environmental conditions and electrical testing for automotive electronics (vibration, temperature, humidity).
– ISO 26262: Functional safety for road vehicles, particularly relevant if buttons interface with ADAS or safety systems. Compliance may require ASIL (Automotive Safety Integrity Level) assessment.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
SWC Buttons must meet EMC regulations to prevent interference with vehicle systems:
– CISPR 25: Limits radio interference from electronic components in vehicles.
– ISO 11452 & ISO 7637: Standards for immunity to electrical disturbances and transient voltages.
Environmental & Chemical Regulations
- REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals. Ensure no restricted substances (e.g., lead, cadmium, phthalates) are present above thresholds.
- RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances in electrical equipment. Applies to electronic components and PCBs within SWC Buttons.
- ELV Directive (EU): End-of-Life Vehicles directive requiring recyclability and marking of materials.
Regional Homologation
- ECE Regulations (UNECE): Required for vehicles sold in Europe; SWC Buttons may fall under broader vehicle type approval.
- FMVSS (USA): Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, particularly FMVSS 101 (controls and displays) and FMVSS 208 (occupant protection, relevant for airbag integration).
- China GB Standards: GB/T and CCC certification may be required for components in vehicles manufactured or sold in China.
Logistics Handling & Storage
Packaging Requirements
- Use anti-static packaging (ESD-safe materials) for all electronic sub-assemblies.
- Secure buttons in rigid, cushioned containers to prevent mechanical damage during transit.
- Include desiccants and moisture barrier bags if components are sensitive to humidity.
Temperature & Environmental Controls
- Store and transport within specified temperature range (typically -40°C to +85°C for automotive-grade components).
- Avoid condensation; maintain relative humidity below 70% unless otherwise specified.
- Protect from direct sunlight and corrosive atmospheres.
Labeling & Traceability
- Each unit or batch must have a unique traceable identifier (e.g., barcode, QR code).
- Labels must include: part number, revision, manufacturing date, country of origin, and compliance markings (e.g., CE, RoHS).
- Support full traceability for recall management and warranty claims.
Transportation & Supply Chain Considerations
Mode of Transport
- Air freight: Preferred for time-sensitive shipments; ensure compliance with IATA regulations for lithium batteries if applicable (e.g., in wireless buttons).
- Ocean/land freight: Use climate-controlled containers; monitor for shock, vibration, and moisture ingress.
Customs & Import Compliance
- Provide accurate HS (Harmonized System) codes—typically under 8537 (control panels) or 8708 (parts and accessories of motor vehicles).
- Prepare Certificates of Conformity (CoC), test reports (EMC, environmental), and material declarations (RoHS, REACH) for customs clearance.
- Comply with Importer Security Filing (ISF) and other border regulations in destination countries.
Quality Assurance & Documentation
Incoming Inspection
- Verify conformity to purchase order specifications.
- Check for physical damage, correct labeling, and packaging integrity.
- Perform functional testing on sample batches (e.g., conductivity, button actuation force, LED functionality).
Required Documentation
- Technical Datasheets and Test Reports (EMC, environmental, durability).
- Certificates of Compliance (CoC) for RoHS, REACH, and ISO standards.
- Bill of Materials (BOM) with substance declarations.
- Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT), if applicable under U.S. Dodd-Frank Act.
End-of-Life & Sustainability
Recycling & Disposal
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) guidelines in the EU.
- Partner with certified e-waste recyclers for proper disassembly and material recovery.
- Design for disassembly to support circular economy goals.
Sustainable Logistics
- Optimize packaging size and weight to reduce carbon footprint.
- Use recyclable or biodegradable materials where possible.
- Consolidate shipments to minimize transport emissions.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for Steering Wheel Control Buttons require a coordinated approach across regulatory, environmental, and supply chain domains. Adherence to international standards, proper handling, and complete documentation ensures product safety, legal market access, and customer satisfaction. Regular audits and supplier collaboration are essential to maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
In conclusion, sourcing steering wheel control buttons requires a careful balance between quality, compatibility, cost, and supplier reliability. Whether for original equipment manufacturing (OEM), aftermarket solutions, or replacement parts, it is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to industry standards and offer consistent product performance. Factors such as material durability, electrical connectivity, integration with vehicle systems (e.g., CAN bus), and compliance with safety regulations must be thoroughly evaluated. Additionally, considering long-term supply chain stability and scalability ensures uninterrupted production or service. By conducting thorough due diligence and leveraging strategic supplier relationships, businesses can secure high-performing steering wheel control buttons that enhance user experience, ensure driver safety, and support overall vehicle functionality.