The global steel water pipe market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising urbanization, increasing infrastructure investments, and stringent regulations around water quality and distribution efficiency. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global steel pipes market size was valued at USD 71.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029, with water transmission emerging as a key application segment. Similarly, Grand View Research highlights that the global water and wastewater pipes market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by aging water infrastructure and the need for corrosion-resistant, high-strength materials like steel. Amid this growth, manufacturers specializing in steel water pipes are playing a critical role in delivering durable, high-performance solutions for municipal, industrial, and agricultural water systems. Based on production capacity, global reach, compliance with international standards, and technological innovation, the following nine companies have established themselves as leaders in the steel water pipe manufacturing landscape.
Top 9 Steel Water Pipe Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#2
Domain Est. 2008 | Founded: 1905
Website: american-usa.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1905 in Birmingham, Alabama, AMERICAN is a manufacturer of fire hydrants, valves, ductile iron pipe and spiral-welded steel pipe for the waterworks….
#3 U.S. Pipe
Domain Est. 1995
Website: uspipe.com
Key Highlights: US Pipe, a Quikrete company, offers a complete range of Ductile Iron Pipe, Restrained Joint Pipe, Fabrication, Gaskets, and Fittings….
#4 Permapipe
Domain Est. 1996
Website: permapipe.com
Key Highlights: PERMA-PIPE manufactures and supplies pre-insulated piping solutions, containment systems, anti-corrosion coatings, custom fabrication and leak detection systems ……
#5 United Pipe & Steel
Domain Est. 1996
Website: unitedpipe.com
Key Highlights: United Pipe & Steel is the leading master distributor of Domestic steel pipe, globally sourced steel pipe, copper tubing, plastic pipe, electrical conduit and ……
#6 Kelly Pipe
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kellypipe.com
Key Highlights: Since 1898, Kelly Pipe Co., LLC has been the industry leader among carbon steel pipe suppliers in the United States and abroad….
#7 Northwest Pipe Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nwpipe.com
Key Highlights: Northwest Pipe leads the industry in providing innovation solutions to a variety of municipal water and infrastructure applications. View Solutions. homepage ……
#8 American Piping Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: amerpipe.com
Key Highlights: American Piping Products is the largest supplier of steel pipe, tube, fittings & flanges in the United States. View our product catalog & request a quote….
#9
Domain Est. 1998
Website: consolidatedpipe.com
Key Highlights: A national leader in piping, fittings, valves, and all accessories for the energy, oil & gas, utility, construction, water and sewer industries….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Steel Water Pipe

H2: Projected Market Trends for Steel Water Pipes in 2026
The global steel water pipe market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by infrastructural expansion, urbanization, sustainability initiatives, and technological advancements. Below are key trends expected to shape the market in that year:
1. Rising Infrastructure Investment in Emerging Economies
Developing regions such as Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America are accelerating investments in water supply and sanitation infrastructure. Governments in countries like India, Indonesia, and Nigeria are launching large-scale water pipeline projects to address water scarcity and improve public health. This surge in public and private funding is expected to boost demand for durable steel water pipes, particularly large-diameter line pipes used in municipal and intercity water transmission.
2. Shift Toward Corrosion-Resistant and Coated Steel Pipes
By 2026, the market will see increased adoption of coated and lined steel pipes—such as cement mortar-lined (CML), fusion-bonded epoxy (FBE), and galvanized variants—due to their enhanced longevity and resistance to internal and external corrosion. Utilities and municipalities are prioritizing lifecycle cost reduction, prompting a shift away from uncoated carbon steel pipes in favor of protective solutions that extend service life beyond 50 years.
3. Integration of Smart Water Management Systems
The convergence of digital infrastructure and water networks will drive demand for “smart” steel pipes embedded with sensors for real-time monitoring of pressure, flow, and leak detection. By 2026, integration with IoT-enabled water management platforms will become a value-added differentiator, especially in smart city projects across North America, Europe, and parts of East Asia.
4. Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental regulations and green building standards (e.g., LEED, BREEAM) are pushing the adoption of recyclable and low-impact materials. Steel, being 100% recyclable, holds a competitive advantage over alternatives like PVC or concrete. Additionally, tightening regulations on lead and plastic leaching in drinking water systems will further support the preference for high-quality steel pipes in potable water applications.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Post-pandemic disruptions and geopolitical tensions have prompted a reevaluation of supply chains. By 2026, there will be a growing trend toward regional manufacturing hubs to reduce dependency on imports, especially in the U.S., EU, and India. This localization will support faster project turnaround and reduce freight costs, benefiting domestic steel pipe producers.
6. Competition from Alternative Materials
Despite its strengths, steel will continue to face competition from ductile iron, HDPE, and composite pipes—particularly in smaller-diameter distribution lines. However, steel maintains dominance in high-pressure, large-diameter transmission mains, where strength and fire resistance are critical. Innovation in hybrid systems (e.g., steel-concrete composite pipes) may emerge as a niche growth area.
7. Price Volatility and Raw Material Costs
Fluctuations in iron ore, scrap metal, and energy prices will remain a challenge. However, advancements in electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking and increased use of recycled content are expected to stabilize production costs and improve environmental performance, making steel pipes more economically viable in the long term.
Conclusion
By 2026, the steel water pipe market will be characterized by a blend of traditional demand drivers—urbanization and infrastructure development—and modern imperatives such as digital integration and sustainability. Companies that invest in advanced coatings, smart technologies, and resilient supply chains are likely to gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Steel Water Pipes (Quality & IP)
Sourcing steel water pipes involves navigating complex quality standards and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to project delays, safety risks, legal issues, and financial losses. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
H2: Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
Failing to verify mill test certificates (MTCs) or material test reports (MTRs) is a critical error. Without proper documentation, there’s no proof the pipe meets required standards (e.g., ASTM A53, API 5L, or ISO 3183). Poor traceability also complicates quality audits and liability determination in case of failure.
2. Non-Compliance with Regional Standards and Codes
Using pipes that meet international standards but not local regulations (e.g., NSF/ANSI 61 for potable water in the U.S. or WRAS approval in the UK) can result in rejected shipments or non-compliant installations. Always verify regional certification requirements before procurement.
3. Substandard Coatings and Corrosion Protection
Improper or inconsistent internal/external coatings (e.g., cement mortar lining, fusion-bonded epoxy, or galvanizing) compromise pipe longevity. Suppliers may cut costs by applying inadequate coating thickness or skipping pre-treatment, leading to early corrosion and water contamination.
4. Poor Weld Quality in ERW and SSAW Pipes
Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) and Submerged Arc Welded (SAW) pipes are prone to weld defects like incomplete penetration, slag inclusions, or lack of fusion. Without rigorous non-destructive testing (NDT) such as ultrasonic or radiographic inspection, these flaws may go undetected.
5. Inconsistent Dimensional Tolerances
Variations in outer diameter, wall thickness, or straightness affect joint integrity and installation. Pipes outside specified tolerances can cause leaks, misalignment, or increased stress in piping systems.
H2: Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Designs or Trademarks
Sourcing pipes bearing counterfeit or unauthorized brand names (e.g., fake API Monogram) infringes on IP rights. This exposes buyers to legal action, customs seizures, and reputational damage. Always verify manufacturer credentials and licensing.
2. Reverse Engineering and Patent Infringement
Some suppliers may replicate patented pipe technologies (e.g., specialized joint systems or alloy compositions) without permission. Purchasing such products—even unknowingly—can entangle the buyer in infringement disputes, especially in cross-border transactions.
3. Misuse of Certification Marks
Forged or unlicensed use of certification marks (e.g., API, ISO, CE) misrepresents product compliance. Buyers assuming authenticity based on labels alone risk acquiring substandard or non-compliant products. Direct verification with certification bodies is essential.
4. Lack of Due Diligence on Supplier IP Compliance
Failing to audit a supplier’s IP practices—such as checking for active patents, trademarks, and licensing agreements—can lead to unintentional complicity in IP violations. Conduct thorough background checks and request IP compliance declarations.
5. Ambiguous Contracts Without IP Clauses
Procurement contracts that omit clear terms on IP ownership, liability for infringement, and responsibilities in case of counterfeit discovery leave buyers vulnerable. Ensure contracts specify warranties related to IP rights and remedies for violations.
Conclusion
Mitigating these pitfalls requires proactive due diligence, supplier vetting, third-party inspections, and legal review of IP terms. Prioritizing certified suppliers, demanding full documentation, and validating compliance with both quality standards and IP regulations ensures reliable and legally sound procurement of steel water pipes.
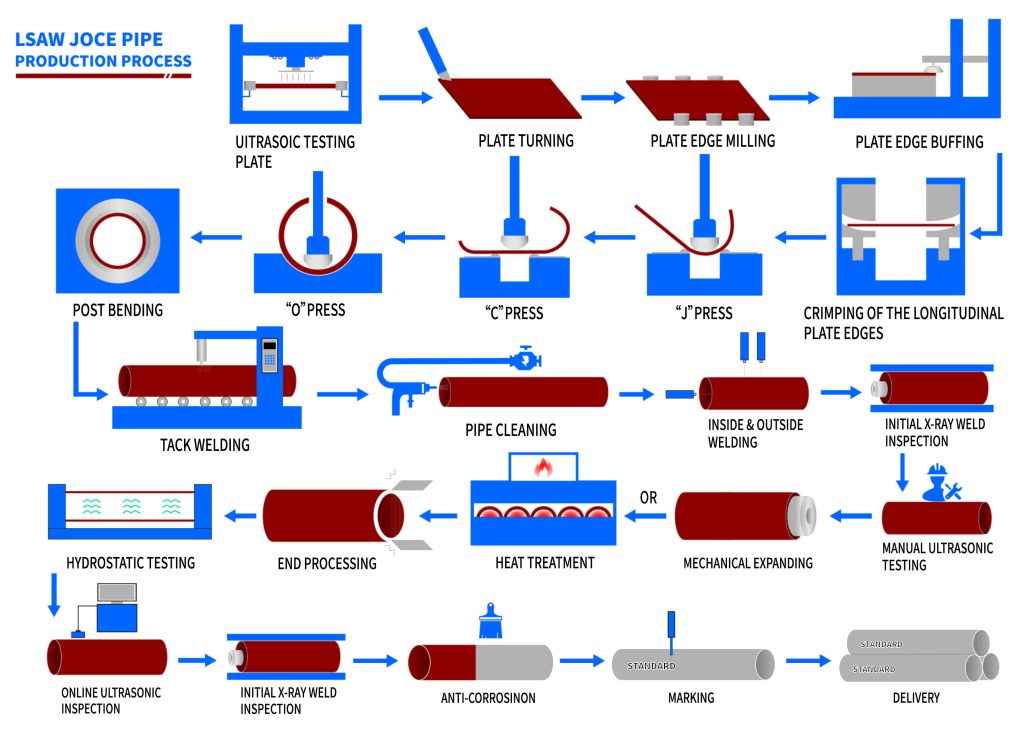
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Steel Water Pipe
Overview of Steel Water Pipe Transportation and Regulatory Requirements
Steel water pipes are essential components in infrastructure projects such as municipal water supply, irrigation systems, and industrial applications. Due to their size, weight, and material composition, the logistics and compliance involved in transporting and handling steel water pipes require careful planning and adherence to international, national, and regional regulations.
Transportation Logistics
Packaging and Unitization
Steel water pipes are typically transported in bundles secured with steel or synthetic strapping. Protective caps are used on pipe ends to prevent damage. Coated pipes may require additional wrapping or crating to preserve the anti-corrosion coating. Pipes are often loaded on flatbed trailers, open-top containers, or bulk carriers depending on shipment mode.
Mode of Transport
- Road: Most common for domestic or regional delivery. Flatbed or lowboy trailers are used for long or heavy sections. Oversize load permits may be required.
- Rail: Suitable for long-distance, high-volume shipments within continents. Special railcars support heavy and long pipe lengths.
- Sea: Used for international shipments. Pipes are loaded in break-bulk cargo holds or on deck using dunnage and lashing systems. ISO containers may be used for smaller-diameter pipes.
- Intermodal: Combines rail, road, and sea transport. Requires standardization of handling equipment and securement methods.
Handling and Storage
- Use proper lifting equipment (slings, cranes, forklifts with pipe clamps).
- Store pipes on level, well-drained surfaces; elevate from ground using timber dunnage to prevent moisture contact.
- Avoid stacking too high to prevent deformation or damage, especially for coated pipes.
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
Steel water pipes must comply with recognized international standards such as:
– ISO 3183: Petroleum and natural gas industries – Steel pipes for pipeline transportation systems (often referenced for water applications).
– ASTM A53/A135/A500: Standard specifications for pipe types used in structural and water applications.
– EN 10217: European standard for welded steel tubes for pressure purposes.
– API 5L: Commonly used for line pipe, sometimes adapted for water service.
National and Regional Regulations
- United States: Compliance with DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations for hazardous materials (if coated with hazardous substances), FMCSA rules for oversized loads, and OSHA safety standards for handling.
- European Union: Must comply with CE marking requirements under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) if used in construction-related water systems.
- Canada: Transport adheres to CN/CP rail standards and provincial road regulations; CSA standards apply for pipe quality.
- Other Regions: Check local standards (e.g., AS/NZS in Australia, GOST in Russia, JIS in Japan).
Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Coatings and Linings: Epoxy, cement-mortar, or polyethylene coatings must comply with potable water safety standards (e.g., NSF/ANSI 61 in the U.S., WRAS in the UK).
- Hazardous Materials: If pipes are coated with substances containing VOCs or heavy metals, proper labeling and documentation under ADR (Europe), IMDG (sea), or 49 CFR (U.S.) may be required.
- Spill Prevention: Contingency plans for coating material spills during transport or storage.
Documentation and Certification
Required Shipping Documents
- Bill of Lading (BOL)
- Packing List (detailing pipe dimensions, weight, coating type, bundle count)
- Certificate of Compliance (CoC) or Mill Test Certificate (MTC) per EN 10204 Type 3.1 or 3.2
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS/SDS) for coated pipes
- Phytosanitary Certificate (if wooden dunnage or crates are used internationally)
Customs and Import Compliance
- Accurate HS Code classification (e.g., 7303.00 for cast iron or steel pipes, 7305.11–7306.90 for specific steel pipe types).
- Adherence to anti-dumping or countervailing duties where applicable (e.g., U.S. or EU import tariffs on certain steel products).
- Proof of origin documentation for preferential trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP).
Quality Assurance and Inspection
Pre-Shipment Inspection
Third-party inspections may be required to verify:
– Dimensions and tolerances
– Coating integrity (holiday detection test)
– Weld quality (for welded pipes)
– Marking and traceability (heat number, size, standard)
In-Transit Monitoring
Use GPS tracking and shock/vibration sensors for high-value or critical shipments to monitor handling conditions.
Risk Management
Common Risks
- Corrosion during marine transport due to salt exposure
- Mechanical damage from improper handling
- Delays due to customs clearance or permit issues
- Theft or loss in transit
Mitigation Strategies
- Use desiccants and moisture barriers in containers.
- Train personnel in safe lifting and rigging practices.
- Work with certified freight forwarders experienced in heavy cargo.
- Obtain marine cargo insurance covering all risks.
Conclusion
Efficient logistics and strict compliance are vital for the safe and timely delivery of steel water pipes. By adhering to international standards, maintaining proper documentation, and implementing robust handling and transportation protocols, companies can ensure product integrity, regulatory approval, and customer satisfaction across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Steel Water Pipes:
Sourcing steel water pipes requires a comprehensive evaluation of quality, cost, supplier reliability, compliance with industry standards, and long-term performance. Selecting the right supplier involves verifying product certifications (such as ISO, ASTM, or ASME), ensuring material suitability for specific applications (e.g., galvanized, carbon, or stainless steel), and assessing delivery timelines and logistical support. Establishing strong relationships with reputable manufacturers or distributors helps guarantee consistent quality, competitive pricing, and timely project execution. Furthermore, considering sustainability, corrosion resistance, and lifecycle costs enhances the overall value and durability of the water infrastructure. In conclusion, a strategic and well-informed sourcing approach ensures the procurement of high-quality steel water pipes that meet technical specifications, regulatory requirements, and project objectives efficiently and reliably.