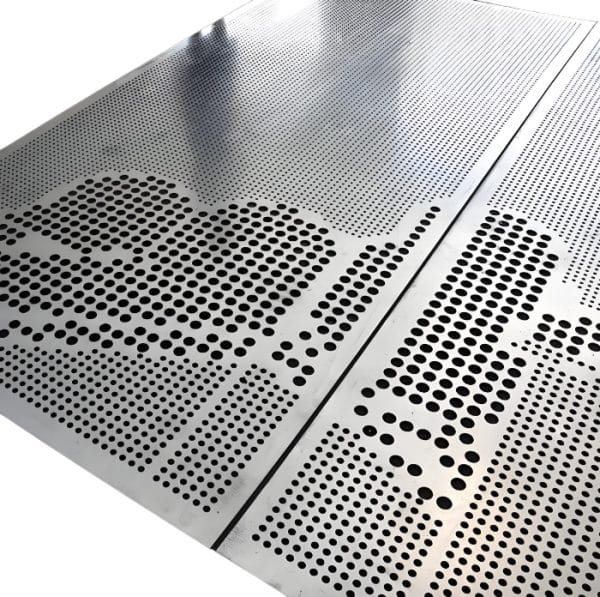
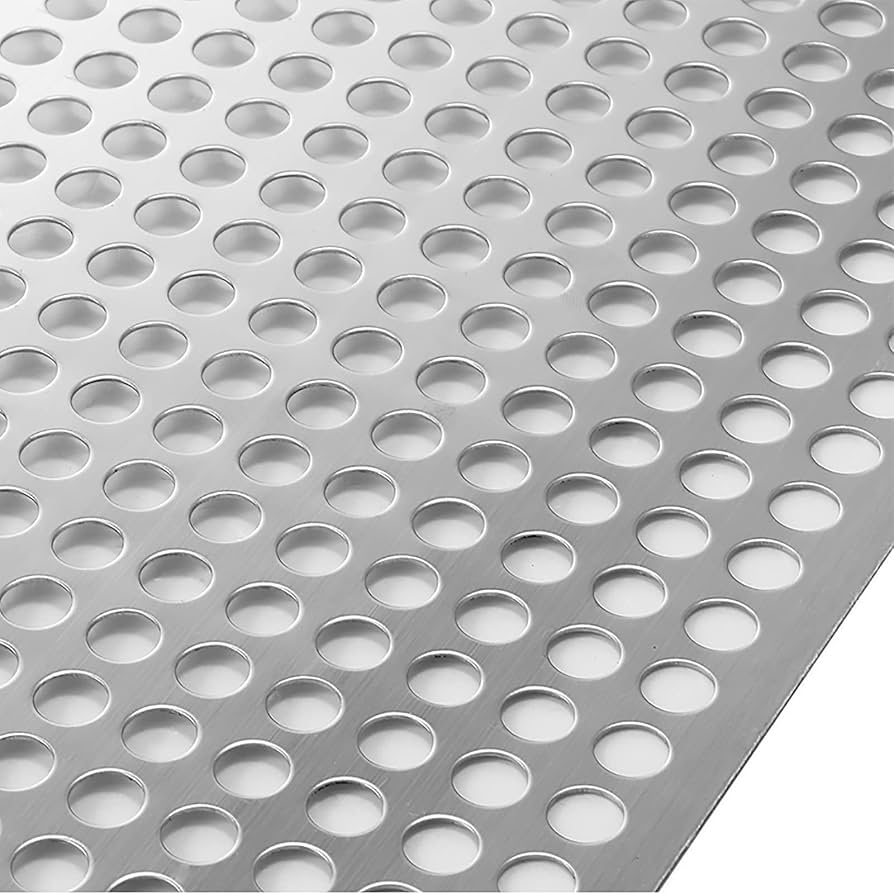
The global steel sheets market, including specialized products like perforated or steel sheets with holes, is witnessing steady expansion driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steel market was valued at approximately USD 1.1 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.2% from 2023 to 2030. A key driver behind this growth is the increasing need for lightweight, durable, and acoustically efficient materials, where perforated steel sheets play a critical role—especially in architectural cladding, filtration systems, and ventilation equipment. Mordor Intelligence also highlights a CAGR of over 3.8% for the steel products market, with Asia-Pacific leading both in production and consumption due to rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. As demand for customized steel solutions rises, selecting reliable manufacturers capable of precision perforation, scalable production, and international compliance becomes crucial. Below, we present a data-driven overview of the top 10 manufacturers of steel sheets with holes, recognized for their technological capabilities, product range, and global market reach.
Top 10 Steel Sheet With Holes Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Perforated Metal Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sss-steel.com
Key Highlights: We offer a superior range of perforated steel sheet, designed to meet various industrial, architectural, and decorative needs….
#2 Buy Perforated Steel Sheet Metal Online
Domain Est. 1999
Website: industrialmetalsupply.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsOrder Hole Perforated Metal Sheet Available in Southern CA, AZ & Northern Mexico. Industrial Metal Supply stocks a wide range of sizes of ……
#3 Perforated Metals Product Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2014
Website: amicoglobal.com
Key Highlights: STANDARD STOCK SHEETS. AMICO manufactures and carries a large inventory of the most common perforated metal panels in various alloys and gauges. shop now….
#4 Perforated Metal Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2015
Website: hendrickcorp.com
Key Highlights: We’re a top-rated perforated sheet metal manufacturer. We have a variety of perforation patterns and can create custom perforated sheet metal. Contact Us!…
#5 Stanch, Stainless Steel Perforated Sheet Supplier
Domain Est. 1997
Website: stanch.com
Key Highlights: Stanch offers custom perforated stainless steel sheet and plate that are stamped or punched, creating a uniform pattern of holes. Our stainless steel ……
#6 Perforated Metal
Domain Est. 1997
Website: metlx.com
Key Highlights: Perforated metal is manufactured by using punches or presses to create a series of holes, slots, bars, or decorative patterns in sheet metal….
#7 Perforated Metal Sheet Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: directmetals.com
Key Highlights: We carry perforated metal in many hole shapes, sizes, and materials. Perforated sheets are versatile and can be used for metal screens, diffusers, guards, ……
#8 Perforated Metal Products & Fabrication Services
Domain Est. 1999
Website: marcospecialtysteel.com
Key Highlights: Marco Specialty Steel stocks a wide variety of thicknesses, hole shapes, and patterns, plus our perforated fabrication services include custom punching….
#9 Custom Perforated Metal Panels & Sheets
Domain Est. 2002
Website: remalymfg.com
Key Highlights: Contact Remaly Manufacturing Company for small to medium-sized orders of high quality custom perforated sheets and perforated metal panels….
#10 Perforated Sheets Metal
Domain Est. 2014
Website: perforated-sheet.com
Key Highlights: Perforated sheet metal gives you a stunning effect with round, square, slot, hexagon and whatever designs you want. We can customize them for you….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Steel Sheet With Holes

H2: Projected Market Trends for Steel Sheet With Holes in 2026
The global market for steel sheets with holes is expected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across construction, industrial manufacturing, and infrastructure development sectors. These perforated steel sheets—valued for their strength, ventilation properties, aesthetic versatility, and lightweight structure—are gaining traction in both traditional and emerging applications.
One of the primary growth drivers is the expanding construction industry, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where urbanization and public infrastructure projects are accelerating. Perforated steel sheets are increasingly used in architectural facades, noise barriers, flooring grates, and sunscreens due to their functional and design advantages. The trend toward sustainable and energy-efficient building design further supports adoption, as perforated sheets contribute to natural lighting and airflow, reducing reliance on artificial systems.
In the industrial sector, steel sheets with holes are seeing increased use in machinery guards, filtration systems, conveyor belts, and acoustic enclosures. The rise of automation and smart manufacturing is spurring demand for durable, customizable protective components—areas where perforated steel excels. Additionally, advancements in laser and CNC perforation technologies are enabling more precise, complex patterns at lower costs, broadening the material’s appeal across high-end applications.
Automotive and transportation industries are also emerging as key end-users. Perforated steel is being integrated into vehicle components for weight reduction, heat dissipation, and noise control. Railway platforms, bus shelters, and EV charging stations are increasingly incorporating these materials for both safety and design purposes.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the market in 2026 due to rapid industrialization in countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by modernization of aging infrastructure and green building initiatives. Meanwhile, the Middle East is witnessing growing use in large-scale architectural projects, particularly in smart city developments.
However, market growth may face headwinds from fluctuating raw material prices and environmental regulations on steel production. Companies are responding by investing in recycled steel content and energy-efficient manufacturing processes to align with ESG standards.
In summary, the steel sheet with holes market in 2026 will be shaped by technological innovation, architectural trends, and infrastructure expansion, positioning it as a critical material in sustainable and industrial design. Suppliers who offer customization, rapid prototyping, and eco-friendly production methods are likely to gain a competitive edge.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Steel Sheet With Holes (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing steel sheets with pre-punched holes can streamline manufacturing, but it comes with several risks related to quality control and intellectual property. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure you receive reliable components while protecting your designs and legal interests.
Inconsistent Hole Quality and Dimensional Accuracy
One of the most frequent issues is variability in hole size, shape, and placement. Poor tooling maintenance, incorrect punch settings, or substandard equipment can lead to out-of-tolerance holes, burrs, or deformation. This compromises fit and function in assembly, potentially causing delays, rework, or product failure.
Material Quality and Certification Gaps
Suppliers may use lower-grade steel than specified or fail to provide proper material certifications (e.g., mill test reports). Without verified chemical composition and mechanical properties, the structural integrity and performance of the perforated sheets—especially in load-bearing or safety-critical applications—can be compromised.
Poor Edge and Surface Finish
Inadequate processing can result in rough edges, excessive burring, or surface damage around the holes. These imperfections not only affect aesthetics but can also create stress concentration points, reducing fatigue life and increasing the risk of cracking under load.
Lack of Traceability and Process Control
Some suppliers lack robust quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001), making it difficult to trace production batches or verify process consistency. This absence of traceability hampers root cause analysis and corrective actions when defects are discovered post-delivery.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Using custom hole patterns based on protected designs—such as patented perforation layouts or proprietary tooling—without proper licensing can expose your business to legal action. Suppliers may unknowingly (or knowingly) reproduce IP-protected patterns, implicating your company as the end user.
Unauthorized Use or Replication of Custom Tooling
When you commission custom punch tooling for unique hole patterns, there’s a risk the supplier may reuse, copy, or sell the tooling to competitors. Without clear contractual agreements, your design advantage can be quickly eroded, leading to market saturation and loss of competitive edge.
Inadequate Documentation and Design Transfer
Poor communication or incomplete technical documentation (e.g., missing GD&T, flat pattern files, or revision control) can result in misinterpretation of specifications. This often leads to incorrect hole layouts, spacing errors, or deviations from the intended design.
Overlooking Secondary Processes
Perforated steel sheets may require additional treatments like deburring, painting, galvanizing, or laser etching. If these processes are outsourced or poorly coordinated, inconsistencies in finish, coating adhesion, or dimensional accuracy can occur, affecting overall part quality.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, clear technical specifications, robust contracts with IP protections, and ongoing quality audits.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Steel Sheet With Holes
Overview
Steel sheets with holes—also known as perforated steel sheets—are widely used in construction, filtration, automotive, and architectural applications. Their unique structure presents specific handling, transportation, and regulatory considerations. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance requirements to ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations when transporting and using perforated steel sheets.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling are essential to prevent deformation, corrosion, and damage during transit.
– Bundling: Secure sheets into tightly strapped bundles using steel or polymer banding. Place edge protectors to avoid corner damage.
– Palletization: Stack bundles on wooden or recyclable plastic pallets. Use dunnage between layers to prevent scratching and ensure stability.
– Weather Protection: Wrap pallets in waterproof stretch film or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper to protect against moisture and rust.
– Handling Equipment: Use forklifts or cranes with wide clamps or lifting beams to avoid bending. Never drag sheets across surfaces.
Transportation Requirements
Transportation must account for weight, dimensions, and regulatory standards.
– Weight and Load Distribution: Perforated steel sheets are lighter than solid sheets of the same size, but loads must still be evenly distributed and secured to prevent shifting.
– Securement: Use load straps, dunnage, or load locks to immobilize cargo. Comply with FMCSA (U.S.) or equivalent regional securement regulations.
– Vehicle Type: Flatbed trucks, enclosed trailers, or shipping containers (for international transit) are common. Ensure vehicles are in good condition and suitable for heavy cargo.
– Stacking Limits: Do not exceed manufacturer-recommended stacking height to prevent bottom-layer deformation.
International Shipping & Documentation
For cross-border shipments, compliance with international standards and documentation is crucial.
– Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin. Clearly describe goods as “Perforated Steel Sheets” with material grade (e.g., ASTM A36, SS304).
– HS Code: Use appropriate Harmonized System code. Example: 7308.90 (for structural sections of iron or steel) or 7326.20 (for other articles of steel), depending on form and use.
– Export Controls: Verify if product is subject to export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.). Most standard perforated sheets are not controlled, but confirm based on alloy composition and end-use.
– Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities using standard Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) to avoid disputes.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
Adherence to safety and environmental regulations ensures legal operation and worker protection.
– OSHA (U.S.) / HSE (UK) / Local Standards: Follow guidelines for material handling, storage, and workplace safety. Provide PPE (gloves, eye protection) due to sharp hole edges.
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Confirm that steel composition complies with substance restrictions, especially for coated or galvanized perforated sheets.
– Hazard Communication: Label materials appropriately. While steel sheets are not hazardous, oil coatings or treatments may require SDS (Safety Data Sheets).
– Environmental Regulations: Recyclability of steel should be highlighted. Manage packaging waste responsibly under local recycling laws.
Storage Guidelines
Improper storage can lead to corrosion and physical damage.
– Indoor Storage: Store in a dry, ventilated warehouse. Elevate pallets off the floor using wooden blocks.
– Outdoor Storage: If unavoidable, cover with waterproof tarps and ensure proper drainage. Do not allow water pooling.
– Separation: Keep away from corrosive chemicals or high-humidity areas. Avoid contact with dissimilar metals to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Quality and Inspection
Pre-shipment checks help maintain compliance and customer satisfaction.
– Dimensional Accuracy: Verify hole pattern, spacing, sheet thickness, and overall dimensions against specifications.
– Surface Condition: Inspect for scratches, dents, rust, or coating defects.
– Certification: Provide mill test certificates (e.g., MTC 3.1 per EN 10204) when required, confirming material properties and compliance.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for steel sheets with holes ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and customer trust. By following best practices in packaging, transport, documentation, and safety, businesses can minimize risks and optimize supply chain performance. Always consult local regulations and industry standards for region-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing steel sheets with pre-punched holes requires careful consideration of material specifications, hole patterns, manufacturing standards, and supplier reliability. It is essential to clearly define project requirements — including steel grade, thickness, hole size, spacing, and coating or finishing needs — to ensure compatibility with the intended application. Engaging with reputable suppliers capable of precision punching and quality control helps minimize lead times, reduce waste, and ensure consistency in production. Additionally, evaluating cost efficiency through bulk ordering, logistics, and customization options contributes to an effective procurement strategy. Overall, a well-informed sourcing approach ensures the timely delivery of high-quality perforated steel sheets that meet both performance and budgetary goals.