The global steel sheets market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global steel market was valued at USD 1.47 trillion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2024 to 2030. This surge is further amplified by increasing infrastructure investments and rapid urbanization, particularly in emerging economies. As one of the most widely used forms of flat-rolled steel, steel sheet rolls play a critical role in applications ranging from roofing and cladding to appliance manufacturing and automotive body panels. With the Asia Pacific region dominating production and consumption—accounting for over 50% of global demand—manufacturers are scaling capacities and investing in advanced coating and processing technologies to meet evolving industry standards. Based on production scale, export volume, technological capabilities, and market presence, the following ten companies have emerged as leaders in the global steel sheet rolls manufacturing landscape.
Top 10 Steel Sheet Rolls Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 American Steel Products :: Cleveland
Domain Est. 2004
Website: clevelandcliffs.com
Key Highlights: Cleveland-Cliffs is the largest flat-rolled steel producer in North America and the largest supplier of automotive-grade steel in the US….
#2 SSAB high
Domain Est. 1996
Website: ssab.com
Key Highlights: SSAB is a specialized steel manufacturer. We only make steel grades with qualities that are fine-tuned to make applications stronger, lighter, safer, easier to ……
#3 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#4 Farwest Steel Service Center
Domain Est. 1995
Website: farweststeel.com
Key Highlights: Farwest is a full line steel service center. Farwest’s steel inventory of plate, sheet, tube, bars and wide flange beam are available for next day shipment….
#5 Atlas Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: atlassteel.com
Key Highlights: Atlas provides stainless steel sheets and coil products that are available in a variety of finishes, cut-to-length and blanks, as well as tub products. Learn ……
#6 Ryerson: Online Metals Supplier
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ryerson.com
Key Highlights: Ryerson is an online metal supplier, metal processor and distributor, offering more than 65000 varieties of stainless, aluminum, carbon and alloys in all ……
#7 Steel Dynamics
Domain Est. 1999
Website: steeldynamics.com
Key Highlights: Our steel operations produce steel products, including hot roll, cold roll, and coated sheet steel, structural steel beams and shapes, rail, engineered special ……
#8 Alliance Steel: Flat Rolled Steel Sheet Supplier & Distributor
Domain Est. 2006
Website: alliancesteel.net
Key Highlights: A leading flat rolled steel sheet supplier and metal coil processor. Alliance Steel provides full-scale steel service offering large volumes of flat rolled ……
#9 Wheeling
Domain Est. 2020
Website: wheeling-nipponsteel.com
Key Highlights: Wheeling-Nippon Steel is a leader in hot-dip and hot rolled coated steel products, offering high-quality corrosion-resistant sheets for endless ……
#10 JFE Steel Corporation
Website: jfe-steel.co.jp
Key Highlights: JFE Steel and thyssenkrupp Steel Europe Launch High-tensile Steel Sheets Capable of Cold Forming for Use in Automobile Frames…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Steel Sheet Rolls
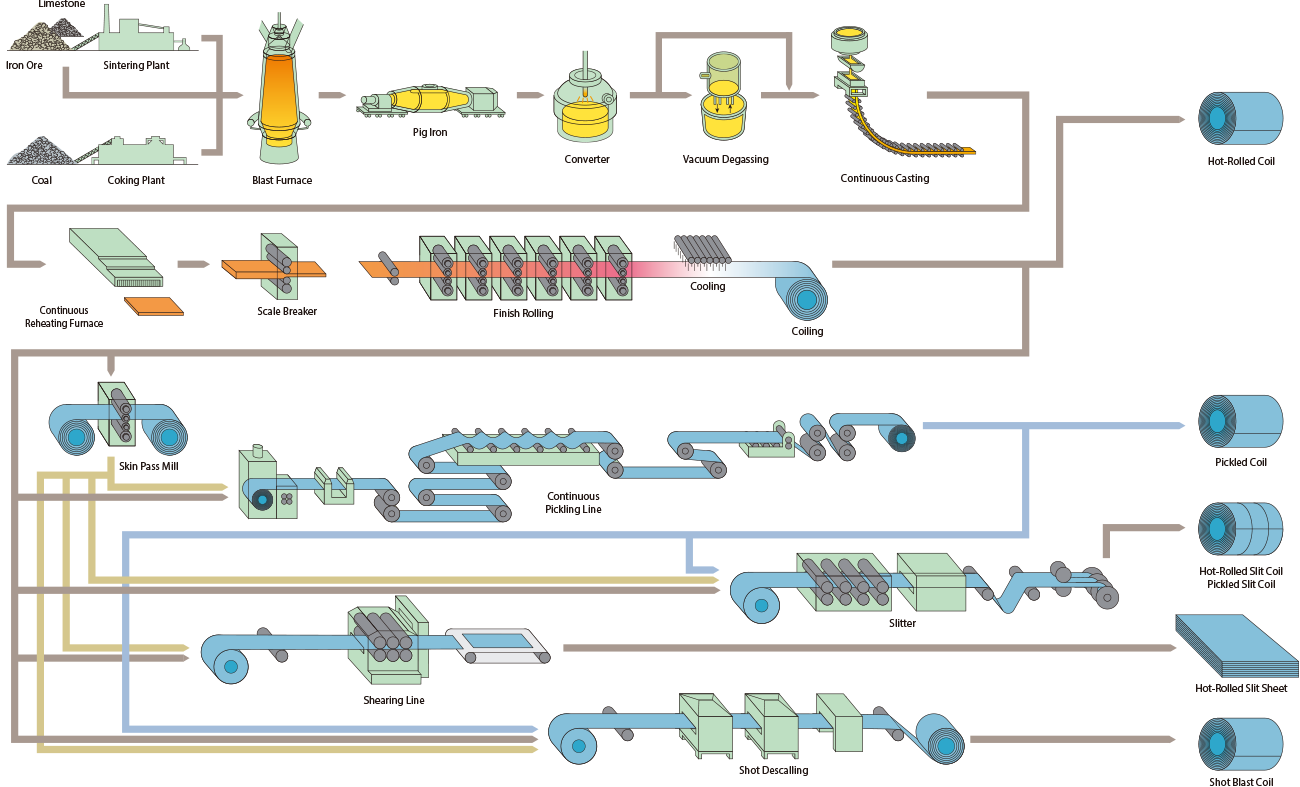
H2: Projected Market Trends for Steel Sheet Rolls in 2026
The global steel sheet rolls market is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, and macroeconomic shifts. Key trends shaping the market include increasing infrastructure development, growth in automotive and construction sectors, and a rising emphasis on sustainable production.
-
Growing Demand from Construction and Infrastructure
By 2026, rapid urbanization—particularly in Asia-Pacific and Africa—will continue to fuel demand for steel sheet rolls in residential, commercial, and public infrastructure projects. Governments investing in smart cities and transportation networks will further boost consumption, especially in cold-rolled and galvanized steel sheets used for roofing, cladding, and structural applications. -
Automotive Industry Transition and Lightweighting
The automotive sector remains a major consumer of steel sheet rolls. As automakers strive to meet fuel efficiency and emission standards, there is a shift toward advanced high-strength steel (AHSS) in vehicle manufacturing. By 2026, demand for AHSS sheet rolls is expected to rise significantly, particularly in electric vehicle (EV) production, where durability and weight reduction are critical. -
Expansion of Renewable Energy Projects
The global push for clean energy will increase the use of steel sheet rolls in wind turbines, solar panel mounting structures, and energy storage systems. Galvanized and corrosion-resistant steel grades will see heightened demand due to their durability in outdoor environments. -
Sustainability and Green Steel Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing steel producers toward low-carbon manufacturing processes. By 2026, the adoption of hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) technologies and increased use of recycled scrap in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) are expected to expand, leading to the growth of “green steel” sheet rolls. Buyers in Europe and North America will increasingly prioritize carbon footprint data, influencing procurement decisions. -
Regional Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Geopolitical factors and trade policies will continue to affect the global steel trade. Countries like India and Southeast Asian nations are expected to ramp up domestic steel production, reducing reliance on imports. Meanwhile, nearshoring trends in North America—supported by policies such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act—will stimulate local steel sheet roll manufacturing to serve clean energy and infrastructure projects. -
Price Volatility and Raw Material Constraints
Fluctuations in iron ore, coking coal, and energy prices will remain a challenge. By 2026, supply chain diversification and long-term contracts with raw material suppliers will be critical for steel producers to maintain stable pricing and ensure consistent output. -
Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing
Steel manufacturers are increasingly adopting AI, IoT, and predictive maintenance in rolling mills to enhance efficiency and product quality. By 2026, digital twin technologies and real-time monitoring systems will become standard in leading steel plants, improving yield rates and reducing downtime in sheet roll production.
In summary, the 2026 steel sheet rolls market will be characterized by strong demand from infrastructure and green technologies, a shift toward high-performance and sustainable products, and enhanced operational efficiency through digital transformation. Producers who adapt to these trends—particularly in sustainability and innovation—will be best positioned for long-term growth.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Steel Sheet Rolls (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing steel sheet rolls involves navigating a complex landscape where quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) risks can significantly impact supply chain reliability, production efficiency, and legal compliance. Failing to address these pitfalls can result in costly delays, product defects, and exposure to litigation.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Material Specifications
One of the most frequent issues is receiving steel sheet rolls that do not conform to specified standards (e.g., ASTM, JIS, or EN). Variations in chemical composition, tensile strength, thickness tolerance, or surface finish can compromise product performance. Buyers may assume supplier certifications are reliable, but without independent verification, non-compliant material can enter production.
Poor Surface Quality and Coating Defects
Surface imperfections such as scratches, roll marks, oil residue, or inconsistent coating (e.g., galvanized or galvalume) are common, especially with lower-tier mills. These flaws can affect downstream processes like painting, welding, or forming, leading to rework or rejection of finished goods.
Inadequate Quality Control and Certification
Some suppliers, particularly in less-regulated markets, provide falsified or incomplete mill test certificates (MTCs). Relying solely on paperwork without third-party inspection or batch testing exposes buyers to substandard materials. Traceability issues may also arise if heat numbers or batch IDs are missing or inaccurate.
Hidden Damage During Transit
Steel sheet rolls are susceptible to mechanical damage (dents, edge crimping) and corrosion if not properly packaged or shipped. Moisture exposure during ocean freight can lead to rust, especially without vapor corrosion inhibitors (VCI) or proper wrapping. Damage may not be evident until unpacking, causing production delays.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Steel Grades
Some suppliers may falsely claim to produce or supply patented steel grades (e.g., high-strength low-alloy steels or specialized coatings) without proper licensing. Using such materials exposes the buyer to IP infringement claims, even if unintentional, potentially resulting in legal action and supply chain disruption.
Reverse-Engineered or Counterfeit Materials
In certain regions, mills produce “copycat” versions of branded steels (e.g., mimicking Nippon Steel or ArcelorMittal formulations). While chemically similar, these materials may not meet the performance or durability benchmarks of the original, and their use may violate IP rights held by the innovating companies.
Lack of IP Clauses in Supply Agreements
Many procurement contracts fail to include clear indemnification clauses protecting the buyer from IP infringement. Without these, the buyer may bear legal and financial responsibility if sourced materials violate third-party patents or trademarks.
Supply Chain Opacity and Substitution Risks
Complex supply chains involving multiple intermediaries increase the risk of unauthorized material substitution. A supplier might source from a mill that infringes on IP, leaving the end buyer vulnerable—even if the direct supplier was unaware. Lack of transparency makes it difficult to audit the origin and legitimacy of the steel.
Mitigating these pitfalls requires rigorous supplier vetting, independent quality testing, clear contractual terms, and due diligence on the provenance and IP status of the steel products being sourced.
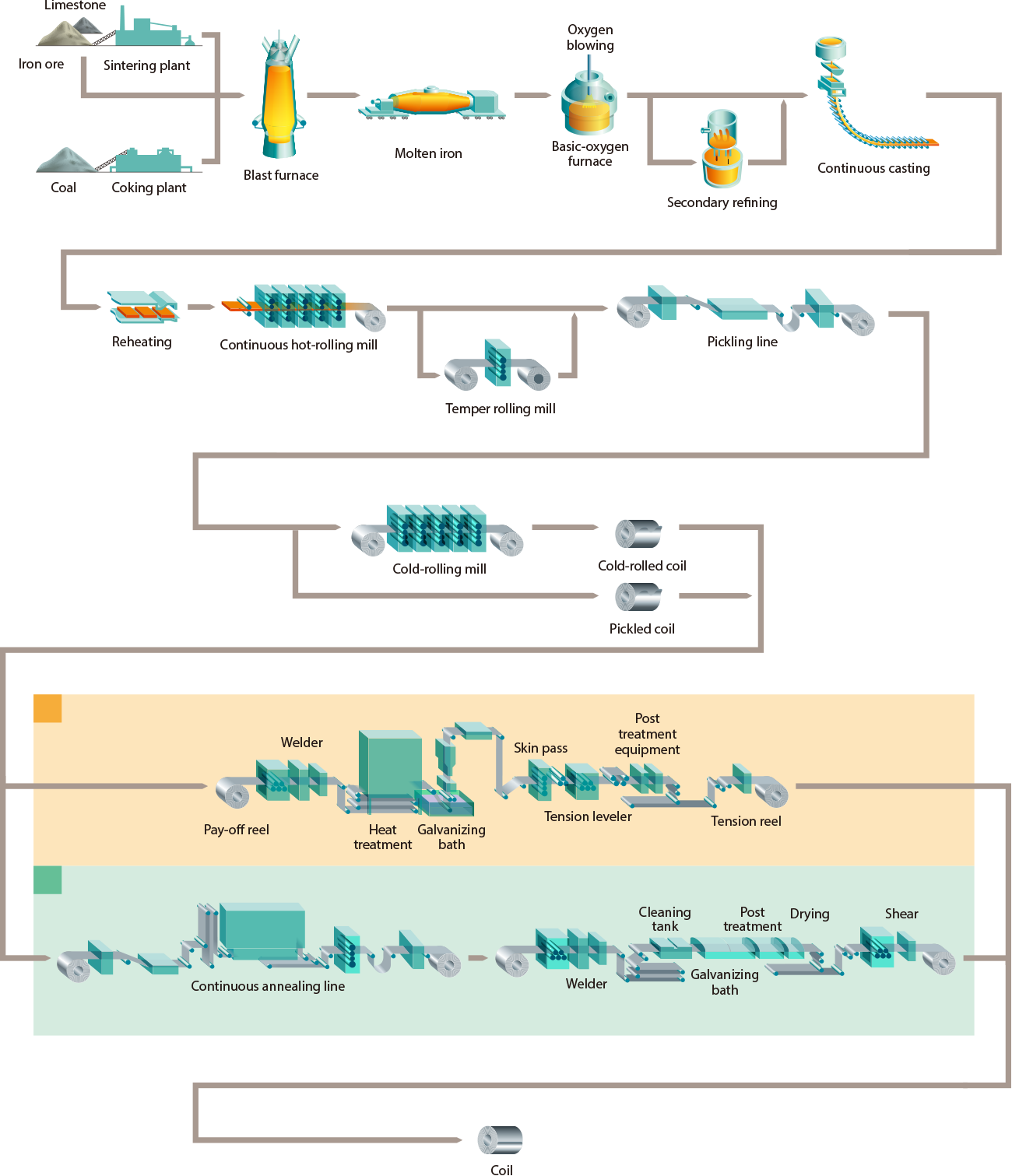
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Steel Sheet Rolls
Overview
Steel sheet rolls are heavy, high-value commodities commonly used in automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries. Safe, efficient logistics and regulatory compliance are essential to prevent damage, ensure timely delivery, and meet international and domestic standards.
Packaging and Securing
Steel sheet rolls must be properly packaged to prevent corrosion, mechanical damage, and shifting during transit.
– Core Protection: Use plastic end caps and moisture-resistant wrapping (e.g., VCI paper) to protect roll ends and prevent rust.
– Coiling and Wrapping: Rolls should be tightly coiled and wrapped with steel or plastic strapping. Waterproof outer wrapping is recommended for ocean or open-air transport.
– Palletization: Place rolls on robust wooden or steel pallets designed to support heavy loads. Avoid stacking unless specifically designed for vertical stacking.
– Load Securing: Use steel straps, lashing belts, or dunnage bags in containers or trailers to prevent movement. Ensure even weight distribution and secure anchoring to floor points.
Transportation Modes
Select the appropriate transport method based on destination, volume, and cost.
– Road Transport: Use low-bed or flatbed trailers with proper load securing. Confirm axle weight limits and route restrictions.
– Rail Transport: Ideal for long distances and large volumes. Use gondola or flatcars with chocks and restraints.
– Maritime Shipping: Containerized (20’ or 40’ flat rack or open-top) or breakbulk depending on roll size. Comply with IMO and IMSBC Code requirements for heavy cargo.
– Intermodal Handling: Ensure compatibility between transport modes. Avoid unnecessary handling to reduce risk of edge damage.
Handling and Storage
Proper handling prevents deformation and workplace injuries.
– Lifting Equipment: Use cranes, forklifts with roller clamps, or spreader beams. Never lift by the core alone.
– Storage Conditions: Store indoors or under cover on level, dry ground. Use wooden blocks to elevate rolls and prevent moisture contact.
– Stacking Guidelines: If stacking is required, follow manufacturer recommendations. Use alignment pads and limit stack height to prevent collapse.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to global and local regulations for transport and export.
– Weight and Dimension Regulations: Comply with road weight limits (e.g., USDOT, EU Directive) and oversized load permits where applicable.
– Export Documentation: Include commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and bill of lading. For exports, provide mill test certificates (e.g., EN 10204 3.1).
– Hazard Classification: While not hazardous, steel rolls may be subject to cargo securing rules under the CTU (Cargo Transport Unit) Code.
– Customs Compliance: Ensure Harmonized System (HS) code accuracy (e.g., 7209.15–7209.90 for flat-rolled products). Be prepared for anti-dumping or safeguard duties in certain regions (e.g., EU, USA).
Safety and Risk Management
Prioritize worker safety and cargo integrity.
– Training: Train personnel in safe lifting, strapping, and forklift operation.
– Inspection: Conduct pre-shipment checks for packaging integrity, rust, and securing.
– Insurance: Secure marine, inland transit, and liability insurance covering damage, loss, and third-party risks.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
- Recyclability: Steel is fully recyclable—communicate this in compliance and CSR reporting.
- Emissions Tracking: Monitor and report transportation emissions, especially for international shipments.
- Packaging Waste: Use recyclable or reusable strapping and dunnage where possible.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for steel sheet rolls depend on meticulous planning, adherence to regulations, and investment in proper equipment and training. By following this guide, shippers can minimize risks, reduce costs, and ensure reliable delivery across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing Steel Sheet Rolls
In conclusion, sourcing steel sheet rolls requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, supply reliability, and compliance with industry standards. A thorough evaluation of suppliers—considering factors such as manufacturing capabilities, material certifications, lead times, and logistical support—is essential to ensure consistent product performance and project success. Additionally, building strong relationships with reputable suppliers, conducting regular quality audits, and staying informed about market trends can enhance procurement efficiency and mitigate supply chain risks. By implementing a structured and proactive sourcing strategy, organizations can secure high-quality steel sheet rolls that meet technical specifications while supporting long-term operational and financial objectives.