The global stainless steel market continues to expand at a robust pace, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer goods sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 135.6 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence forecasts sustained growth, citing increased infrastructure investments and the material’s corrosion resistance and recyclability as key market drivers. As competition intensifies and production capacities shift toward Asia-Pacific—particularly China and India—the role of leading manufacturers becomes increasingly pivotal in shaping supply chains, innovation, and sustainability standards. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top stainless steel producers is essential for stakeholders across industries. Here are the top 10 stainless steel manufacturers leading the charge in output, technology, and global reach.
Top 10 Stain Steel Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Stainless Steel Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: stainlesssteelmanufacturers.org
Key Highlights: Easily find the top stainless steel manufacturers and industrial suppliers who offer complex stainless steel products with years of experience and are ISO ……
#2 U.S. Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: ussteel.com
Key Highlights: We’re bringing industry-leading steelmaking talent and technology together to help customers solve, innovate and excel. Just one example: lighter, stronger ……
#3 Metals Supplier & Service Center
Domain Est. 1997
Website: sss-steel.com
Key Highlights: Triple-S Steel is one of the largest metals distributor and service center in North and South America. Whether your project is large or small, local or global,…
#4 North American Stainless
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1990
Website: northamericanstainless.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1990, North American Stainless (NAS) has undertaken several phases of expansion to become the largest, fully integrated stainless steel producer in ……
#5 SSINA
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ssina.com
Key Highlights: Designing stainless steel structures is now a lot easier! Stainless steel has a well-established track record for a wide range of structural applications—large ……
#6 Outokumpu
Domain Est. 1996
Website: outokumpu.com
Key Highlights: Outokumpu is a global leader in sustainable stainless steel manufacturing. We manufacture a variety of stainless steel products. Discover our offering….
#7 Atlas Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: atlassteel.com
Key Highlights: Atlas Steel is one of the leading steel service centers for quality steel products that are used in a wide variety of applications for different industries….
#8 Specialty Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: univstainless.com
Key Highlights: Universal Stainless, headquartered in Bridgeville, PA, produces semi-finished and finished specialty steel long products and plate including stainless steel….
#9 of stainless steels
Domain Est. 2000
Website: worldstainless.org
Key Highlights: worldstainless.org is the most comprehensive site for anyone interested in stainless steels. You will find documentation on the properties, ……
#10 Valbruna Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 2002
Website: valbruna-stainless-steel.com
Key Highlights: Valbruna Steelworks is a leader in the production of special steel and in the processing of inoxidisable construction steel and metal alloys – Enter ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Stain Steel
H2: Projected Stainless Steel Market Trends for 2026
Based on current trajectories, technological advancements, and macroeconomic forecasts, the global stainless steel market in 2026 is expected to be shaped by several key trends, moving towards greater sustainability, digitalization, and demand diversification.
1. Sustainability & Decarbonization as Core Drivers
- Green Premium & Regulatory Pressure: Stringent global carbon regulations (e.g., EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism – CBAM) will make low-carbon stainless steel a competitive necessity, not just a niche product. Producers investing in electric arc furnaces (EAF) using recycled scrap and renewable energy will gain significant market advantage.
- Hydrogen-Based Reduction (H-DRI): Pilot projects for hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (H-DRI) feeding EAFs will scale, moving closer to commercial viability. This technology is crucial for decarbonizing the primary production route reliant on blast furnaces.
- Circular Economy Focus: Recycling rates (already high at ~85-90%) will be further optimized. Demand for high-quality recycled scrap will intensify, driving investment in advanced sorting and cleaning technologies. “Cradle-to-cradle” lifecycle assessments will become standard.
- ESG Reporting & Transparency: Investors and customers (especially in automotive and construction) will demand verified data on Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions, pushing producers towards greater supply chain transparency.
2. Digital Transformation & Smart Manufacturing
- AI & Predictive Analytics: AI will be deeply integrated for predictive maintenance of rolling mills and furnaces, optimizing energy consumption, forecasting demand fluctuations, and improving quality control (e.g., real-time defect detection).
- Digital Twins: Widespread adoption of digital twins for entire production lines will enable simulation, optimization, and faster troubleshooting, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Blockchain and IoT will enhance traceability of raw materials (nickel, chromium, scrap) and finished products, improving transparency, combating fraud, and building resilient supply chains in a volatile geopolitical environment.
3. Shifting Demand Dynamics
- Renewable Energy Infrastructure Boom: Significant growth driven by demand for stainless steel in solar panel frames, wind turbine components (especially offshore), hydroelectric plants, and hydrogen production/storage equipment (requiring highly corrosion-resistant grades).
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) Expansion: Increased use of stainless steel in EV battery housings (for safety and thermal management), exhaust systems for hybrids, and structural components. Demand for specific high-strength, lightweight grades will rise.
- Infrastructure & Construction Resilience: Continued strong demand in emerging markets for urbanization and infrastructure development. Focus on sustainable building (LEED certification) will favor stainless steel’s longevity and recyclability. Demand for architectural applications (facades, roofing) will grow.
- Consumer Goods & Hygiene: Persistent demand in appliances, cookware, and food processing equipment due to stainless steel’s durability, hygiene, and aesthetic appeal. Growth in water treatment and sanitation infrastructure globally.
4. Raw Material & Cost Volatility Management
- Nickel Market Evolution: The dominance of Class 1 nickel (for stainless) may face pressure from Class 2 nickel (for EV batteries), creating competition. Producers will seek long-term nickel supply agreements and explore alternative alloys (e.g., higher manganese, lower nickel grades like 200-series where feasible).
- Chromium & Ferroalloy Security: Geopolitical risks (e.g., South Africa, Kazakhstan) will necessitate diversified sourcing strategies and potential stockpiling. Recycling remains the primary source of chromium.
- Energy Cost Hedging: With energy being a major cost component (especially for EAF), producers will actively hedge against electricity price volatility and accelerate on-site renewable energy generation (solar, wind).
5. Geopolitical & Trade Landscape
- Regionalization & Reshoring: Ongoing supply chain reevaluation may lead to increased regional production capacity (e.g., in North America, Europe, India) to mitigate trade disputes (e.g., ongoing US Section 232) and logistics risks, though Asia (especially China) will remain dominant.
- Trade Policy Impact: CBAM and potential retaliatory measures will significantly influence trade flows and pricing. Producers outside the EU will need to adapt quickly to carbon cost inclusion.
Conclusion
By 2026, the stainless steel market will be characterized by a fundamental shift towards sustainability as a value driver, enabled by digitalization and shaped by demand growth in green technologies and resilient infrastructure. Success will depend on producers’ ability to decarbonize rapidly, manage volatile input costs, embrace digital tools for efficiency, and adapt to a fragmented but growing global demand landscape. The industry will move beyond being a commodity supplier to becoming an essential enabler of the clean energy transition.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Stainless Steel: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Concerns
Sourcing stainless steel can be a complex process, particularly when balancing cost, quality, and legal compliance. Companies often face challenges related to material authenticity, performance standards, and intellectual property rights. Below are key pitfalls to be aware of when procuring stainless steel, with a focus on quality assurance and IP risks.
1. Substandard Material Quality
One of the most common issues in stainless steel sourcing is receiving material that does not meet specified grades or mechanical properties. Suppliers—especially in competitive markets—may provide:
- Counterfeit or mislabeled grades (e.g., passing off 201 as 304 stainless steel).
- Inconsistent chemical composition, leading to reduced corrosion resistance or structural integrity.
- Lack of proper certification, such as mill test reports (MTRs) or material test certificates (MTCs).
Impact: Use of substandard steel can result in product failure, safety hazards, increased maintenance costs, and reputational damage.
Mitigation: Require third-party testing, conduct on-site audits, and insist on certified material with traceable documentation (e.g., EN 10204 3.1 or 3.2).
2. Inadequate Understanding of Grade Specifications
Stainless steel grades (e.g., 304, 316, 430) vary significantly in composition and application suitability. Buyers may assume interchangeability without recognizing performance differences.
Pitfall: Using a lower-grade alloy in corrosive environments can accelerate degradation.
Mitigation: Clearly define required specifications in procurement contracts and verify supplier expertise in metallurgy.
3. Non-Compliance with International Standards
Different regions follow different standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, JIS, GB). Sourcing from suppliers unfamiliar with or disregarding these standards can lead to non-compliant materials.
Risk: Imported steel may not meet local regulatory or industry requirements (e.g., food-grade, medical, or marine applications).
Mitigation: Ensure suppliers certify compliance with relevant standards and conduct independent quality inspections.
4. Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
When sourcing specialized stainless steel products (e.g., patented alloys, engineered components), IP concerns arise:
- Unauthorized production of proprietary alloys (e.g., imitation of branded steels like Outokumpu’s or Acerinox’s high-performance grades).
- Use of patented manufacturing processes without licensing.
Consequence: Buyers may unknowingly import or use infringing materials, exposing themselves to legal liability, product seizures, or customs delays.
Mitigation: Conduct due diligence on suppliers’ IP compliance; request proof of licensing where applicable; include IP warranties in procurement contracts.
5. Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of raw materials and verify ethical sourcing practices.
Pitfall: Risk of sourcing steel produced using unethical labor practices or conflict materials, leading to reputational and regulatory risks.
Mitigation: Partner with suppliers who provide full traceability and adhere to responsible sourcing standards (e.g., ISO 20400, OECD guidelines).
6. Overreliance on Price Over Performance
Choosing suppliers solely based on low cost increases the risk of receiving inferior or non-compliant materials.
Pitfall: Initial savings are offset by long-term costs from failures, rework, or downtime.
Mitigation: Adopt a total cost of ownership (TCO) approach, factoring in durability, maintenance, and lifecycle performance.
Conclusion
To avoid quality and IP pitfalls in stainless steel sourcing, organizations must implement rigorous supplier vetting, demand transparent documentation, and prioritize compliance over cost savings. Establishing long-term relationships with reputable, certified suppliers reduces risk and ensures material integrity across the supply chain.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Stainless Steel
Overview
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for handling, transporting, storing, and processing stainless steel across international and domestic supply chains. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
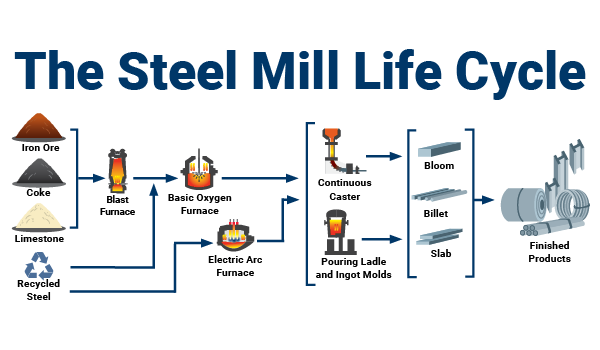
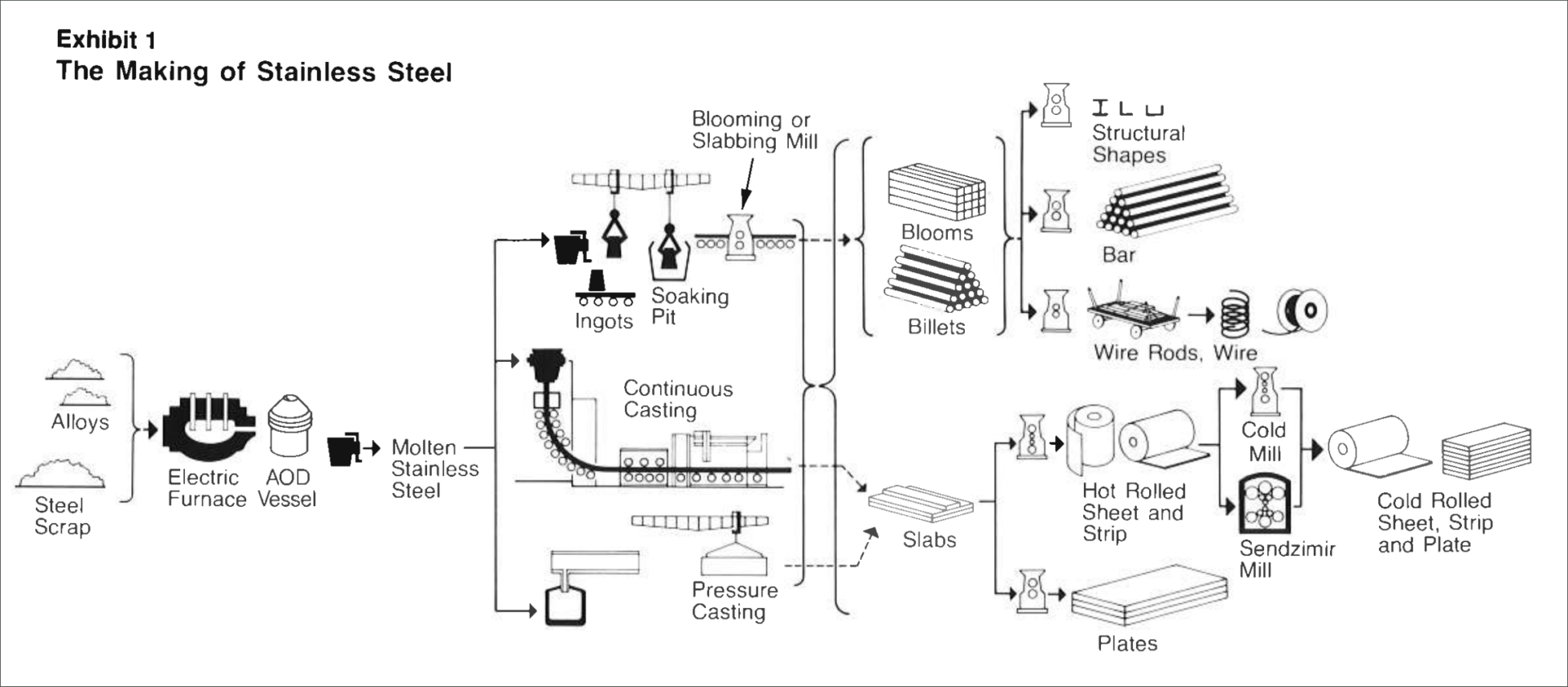
Material Classification and Properties
Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium (minimum 10.5%), nickel, and other elements. It is available in various grades (e.g., 304, 316, 430) and forms (sheet, coil, bar, tube). Understanding the specific grade and form is essential for appropriate handling and regulatory classification.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents surface damage, contamination, and corrosion during transit. Use protective films, edge guards, wooden skids, and moisture barriers. Avoid contact with carbon steel to prevent cross-contamination (e.g., rust transfer). Lifting equipment must be non-abrasive and clean to maintain surface finish, especially for polished or brushed grades.
Storage Conditions
Store stainless steel indoors in a dry, well-ventilated area. Keep materials elevated on pallets to avoid ground moisture. Segregate from carbon steel and corrosive substances (e.g., chlorides, acids). For coastal or high-humidity environments, implement additional moisture control measures such as desiccants or sealed wrapping.
Transport and Logistics
Use enclosed trucks or containers for long-distance shipments to prevent exposure to rain and contaminants. Secure loads to prevent movement and surface abrasion. For international shipments, ensure compliance with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) and provide accurate weight, dimensions, and material certifications. Special handling may be required for oversized or heavy coils and plates.
Regulatory Compliance
Stainless steel products must conform to regional and international standards, including:
– ASTM A240/A480 (USA)
– EN 10088 (Europe)
– JIS G4304 (Japan)
Ensure Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Mill Certificates (e.g., 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204) are available to verify chemical composition and mechanical properties.
Export and Import Regulations
Check destination country requirements for customs classification (HS codes—typically 7219 or 7220 for flat-rolled products). Some countries impose anti-dumping duties or require product certification (e.g., CE marking in the EU, CRN in Canada). Accurate documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is critical.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Adhere to OSHA (USA), REACH (EU), and GHS regulations regarding worker safety and hazardous substances. Although stainless steel is generally inert, cutting, grinding, or welding may produce hazardous dust or fumes. Provide proper PPE and ventilation. Recyclability of stainless steel must be documented to support environmental compliance and sustainability reporting.
Traceability and Documentation
Maintain full traceability from mill to end-user. Each batch or heat number should be documented and linked to quality certificates, inspection records, and shipping details. Digital tracking systems (e.g., ERP or blockchain) enhance transparency and support audits.
End-of-Life and Recycling
Stainless steel is 100% recyclable. Logistics plans should include take-back or recycling programs where applicable. Comply with local waste regulations and provide recycling documentation to customers seeking sustainable sourcing.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for stainless steel require attention to material specifications, handling protocols, regulatory standards, and documentation. By following this guide, stakeholders can ensure safe, legal, and efficient movement of stainless steel products through the supply chain.
Conclusion on Sourcing Stainless Steel
Sourcing stainless steel requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. The selection of the appropriate grade (e.g., 304, 316, 430) must align with the specific application requirements, such as corrosion resistance, strength, and environmental conditions. Engaging with reputable suppliers who adhere to international quality standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) ensures material integrity and performance consistency.
Cost considerations should go beyond initial pricing to include total landed costs, logistics, lead times, and long-term durability. Building strong relationships with suppliers, potentially diversifying sourcing geographically, mitigates risks related to geopolitical instability, trade tariffs, and supply disruptions. Additionally, increasing emphasis on sustainability calls for evaluating suppliers based on environmental practices, recycling capabilities, and responsible sourcing of raw materials.
In conclusion, successful stainless steel sourcing hinges on a comprehensive evaluation of technical, economic, and ethical factors. A well-informed, proactive procurement strategy not only ensures high-quality materials but also enhances operational efficiency, supports sustainability goals, and strengthens supply chain resilience.