The global stainless steel market, driven by increasing demand in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, automotive, and chemical processing, is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.8% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. With SS316L—a low-carbon variant of 316 stainless steel known for superior corrosion resistance and weldability—becoming a material of choice in critical applications, demand for high-quality SS316L has surged across medical devices, marine components, and high-purity industrial systems. This growth is further amplified by stringent regulatory standards and the push for durable, hygienic materials in advanced manufacturing. As a result, leading producers are scaling production, investing in precision processing technologies, and enhancing quality certifications. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, product consistency, and industry reputation, the following nine manufacturers have emerged as key players in the global SS316L landscape.
Top 9 Ss316L Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 UNS S31603
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ulbrich.com
Key Highlights: Ulbrich is a manufacturer of 316L Stainless Steel UNS S31603, which is a s a low carbon austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel….
#2 Bonney Forge
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bonneyforge.com
Key Highlights: Bonney Forge is a leading manufacturer of Forged and Cast Steel Valves,Olets*/Pipets*, Forged Steel Fittings and Unions, and Specialty Products….
#3 Stainless steel tubing
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tubacex.com
Key Highlights: Tubacex stainless steel pipe manufacturers. Stainless steel tubing suppliers, stainless steel pipe, seamless tube. Stainless steel pipe fittings ……
#4 North American Stainless
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1990
Website: northamericanstainless.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1990, North American Stainless (NAS) has undertaken several phases of expansion to become the largest, fully integrated stainless steel producer ……
#5 Gibson Stainless & Specialty Inc.
Domain Est. 2002 | Founded: 1995
Website: gibsonstainless.com
Key Highlights: Founded in 1995, Gibson Stainless is a family-owned and operated company that focuses exclusively on manufacturing the highest quality stainless steel ……
#6 Outokumpu
Domain Est. 1996
Website: outokumpu.com
Key Highlights: Outokumpu is a global leader in sustainable stainless steel manufacturing. We manufacture a variety of stainless steel products. Discover our offering….
#7 316 / 316L Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: smithmetal.com
Key Highlights: Type 316 is an austenitic stainless steel with added molybdenum which gives the alloy improved corrosion resistance….
#8 316 / 316L Stainless Steel Pipe
Domain Est. 1997
Website: twmetals.com
Key Highlights: 316/316L stainless steel pipe can withstand elevated temperatures longer than grade 304/304L, has better corrosion resistance, and offers excellent weldability….
#9 Best 316L Stainless Steel Suppliers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: stanch.com
Key Highlights: Grade 316L (UNS S31603, EN 1.4404) is molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steels, which is more resistant to general corrosion and pitting/crevice corrosion ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ss316L

H2 2026 Market Trends for SS316L
Based on current trajectories, industry analysis, and macroeconomic factors, the SS316L (austenitic stainless steel with enhanced corrosion resistance due to molybdenum) market in the second half of 2026 is expected to be characterized by a stabilization following earlier volatility, driven by persistent demand in key sectors, ongoing supply chain adaptations, and the increasing influence of sustainability and technological advancements.
Key Trends Shaping H2 2026:
-
Stabilized but Elevated Prices: After significant volatility driven by raw material costs (nickel, molybdenum, chromium), energy prices, and geopolitical disruptions (particularly impacting nickel supply from key producers), prices for SS316L are anticipated to stabilize in H2 2026. However, they are likely to remain at a relatively elevated level compared to pre-2022 averages. This reflects:
- Continued Demand Pressure: Strong underlying demand (see below) supports prices.
- Persistent Cost Base: Higher energy costs for melting and processing, along with potentially tighter scrap availability for high-grade 316L, contribute to sustained production costs.
- Supply Discipline: Producers may exercise more pricing discipline following the lessons of recent boom-bust cycles.
-
Demand Resilience in Core Sectors:
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology: Remains the primary growth driver. The expansion of biologics manufacturing, increasing R&D, and stringent hygiene/sanitation requirements continue to fuel demand for high-purity SS316L in reactors, piping, and equipment. Demand for seamless tubes and specialized fittings is particularly strong.
- Chemical & Petrochemical: Steady demand persists for handling corrosive media, especially in sulfuric acid, acetic acid, and chloride-containing environments. Expansion in specialty chemicals and downstream petrochemicals in Asia supports this.
- Medical Devices: Growth in minimally invasive surgery, implants, and advanced diagnostics relies heavily on the biocompatibility and corrosion resistance of medical-grade SS316L. 3D printing (additive manufacturing) using SS316L powder is a significant growth niche.
- Food & Beverage: Strict hygiene standards maintain consistent demand for processing equipment, tanks, and piping, particularly in dairy, brewery, and high-acidity food processing.
- Emerging Energy: Demand from specific segments like hydrogen infrastructure (transportation, storage – where purity is critical) and certain components in advanced nuclear projects (e.g., coolant systems) is emerging, though not yet dominant.
-
Supply Chain Resilience & Regionalization:
- Diversification: Manufacturers and end-users have actively diversified supply sources over the past few years to mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks. This trend solidifies in H2 2026, with increased sourcing from Southeast Asia, India, and regional hubs.
- Inventory Management: Companies have shifted towards more strategic inventory management, holding higher safety stocks of critical grades like 316L compared to the “just-in-time” models prevalent pre-pandemic, adding a floor to demand.
- Logistics Normalization: While disruptions haven’t vanished, global logistics (shipping, port congestion) are expected to be more predictable and less disruptive than during peak pandemic or conflict periods, improving supply reliability.
-
Technological Advancements & Processing:
- Additive Manufacturing (AM): Demand for high-quality, spherical SS316L powder for AM (particularly Laser Powder Bed Fusion) grows significantly, driven by aerospace, medical, and complex industrial part manufacturing. Quality consistency and traceability are paramount.
- Processing Efficiency: Steelmakers invest in technologies to improve yield, reduce energy consumption, and enhance quality control (e.g., advanced melting techniques, better process monitoring) to maintain competitiveness under margin pressure.
- Surface Finishing: Demand for specialized surface finishes (electropolishing, passivation) remains high, especially in pharmaceutical and semiconductor applications, driving value-added services.
-
Sustainability & Regulatory Pressure:
- Circular Economy: Increased focus on scrap recycling efficiency, particularly for high-nickel, high-molybdenum grades like 316L. Traceability of recycled content becomes more important for ESG reporting.
- Decarbonization: Pressure on steel producers to reduce CO2 emissions (Scope 1 & 2) intensifies. Adoption of electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and exploration of hydrogen-based reduction technologies gain traction, though impacting costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter global regulations on material purity (e.g., for pharmaceuticals, food contact) and environmental standards (emissions, wastewater) necessitate continuous investment in quality control and process upgrades.
Outlook for H2 2026:
The SS316L market in the second half of 2026 is expected to be stable and fundamentally strong, underpinned by resilient demand from high-value, performance-critical industries. While price volatility should subside compared to previous years, costs are likely to remain firm. Success will depend on:
* Supply Chain Agility: Maintaining diversified and resilient sourcing.
* Quality & Certification: Meeting stringent and evolving standards, especially in pharma and medical.
* Sustainability Credentials: Demonstrating progress in decarbonization and circularity.
* Technological Adoption: Leveraging AM and efficient processing to capture value.
Overall, H2 2026 represents a period of consolidation and adaptation for the SS316L market, moving beyond crisis response towards a more resilient, technologically advanced, and sustainable future, driven by its irreplaceable properties in critical applications.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing SS316L (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing SS316L stainless steel—especially for critical applications in industries like medical devices, aerospace, and high-performance engineering—requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Failing to address these areas can lead to product failures, regulatory non-compliance, legal disputes, or reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Poor Material Quality and Non-Compliance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing SS316L is receiving substandard or non-compliant material. This often stems from inadequate supplier vetting or cost-driven procurement decisions.
-
Inadequate Certification and Traceability: Many suppliers provide mill test reports (MTRs) that are falsified, incomplete, or lack proper traceability (e.g., heat/lot numbers). Always verify that certifications comply with recognized standards such as ASTM A240, ASTM A479, or ISO 15510 and include full chemical analysis and mechanical properties.
-
Incorrect Alloy Composition: SS316L must have low carbon content (typically ≤ 0.03%) to resist sensitization and intergranular corrosion. Some suppliers may deliver standard 316 instead of 316L, or use off-spec materials with higher carbon or lower molybdenum content, compromising corrosion resistance.
-
Poor Surface Finish and Contamination: For medical or food-grade applications, surface finish (e.g., Ra value) and cleanliness are crucial. Poor finishing or contamination (e.g., iron embedding from shared machining tools) can lead to premature corrosion or failure.
-
Counterfeit or Gray Market Materials: Especially in global supply chains, counterfeit materials labeled as SS316L may actually be inferior grades. These often enter through unauthorized distributors or lack proper documentation.
Intellectual Property and Design Risks
Sourcing components made from SS316L—particularly custom-machined or fabricated parts—can expose companies to IP infringement if proper safeguards are not in place.
-
Unauthorized Use of Protected Designs: When outsourcing manufacturing, there’s a risk that suppliers may replicate or reverse-engineer your designs and sell them to competitors. This is especially prevalent in regions with weaker IP enforcement.
-
Lack of IP Clauses in Contracts: Many procurement agreements fail to include clear IP ownership terms. Without explicit clauses stating that all designs, tooling, and process developments remain the buyer’s property, suppliers may claim partial ownership or reuse the work.
-
Tooling and Process Replication: Suppliers may retain molds, jigs, or proprietary processes developed for your project. Without legal agreements forbidding reuse, they can produce identical or similar parts for third parties.
-
Data Security and Digital File Exposure: Sharing CAD files or technical specifications with suppliers increases the risk of data leaks. Ensure NDAs are in place and limit access to need-to-know information. Consider using watermarked or simplified design files when possible.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls:
– Audit suppliers regularly and require third-party material testing (e.g., PMI—Positive Material Identification).
– Insist on full traceability and original mill certifications.
– Use legally binding contracts with strong IP protection, including clauses on ownership, confidentiality, and post-contract obligations.
– Partner with reputable, certified suppliers (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100, or ISO 13485 for medical applications).
– Conduct incoming material inspections and maintain a documented quality assurance process.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns ensures reliable performance of SS316L components and protects your organization’s innovations and compliance standing.
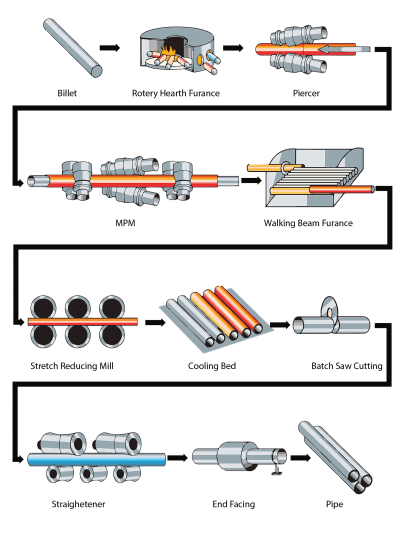
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for SS316L (Stainless Steel 316L)
SS316L, a low-carbon variant of austenitic stainless steel 316, is widely used in demanding environments due to its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and acids. Proper logistics and compliance management are crucial to maintain material integrity, ensure safety, and meet regulatory requirements throughout the supply chain.
H2: Key Logistics Considerations for SS316L
-
Material Handling & Storage:
- Separation: Store SS316L physically separated from carbon steel and other metals to prevent galvanic corrosion and iron contamination. Use dedicated racks, pallets, or storage areas with non-metallic barriers (e.g., wood, plastic).
- Cleanliness: Keep material clean and dry. Protect from dirt, dust, moisture, and corrosive atmospheres. Cover with breathable tarps if stored outdoors; avoid plastic sheeting that can trap moisture.
- Handling Equipment: Use clean, dedicated lifting equipment (slings, clamps, forklifts). Ensure equipment is free of carbon steel grit or rust. Avoid dragging or sliding material.
- Surface Protection: Protect polished or critical surfaces with protective films, caps, or plugs. Avoid contact with bare hands (use gloves) to prevent fingerprint corrosion.
-
Packaging & Transportation:
- Internal Protection: Use clean, dry, non-abrasive materials (e.g., VCI paper, plastic wraps, foam inserts) to prevent scratching, denting, and moisture ingress during transit.
- External Protection: Securely bundle or crate material to prevent movement. Use weatherproof covering for open transport. Clearly label packages.
- Contamination Prevention: Ensure transport vehicles (trucks, containers, railcars) are clean and free of residues from previous cargo (especially chlorides, acids, or abrasive materials). Avoid mixed loads with incompatible materials.
- Temperature & Humidity: While SS316L is robust, avoid prolonged exposure to extreme temperatures or high humidity during transit if possible, especially for precision components.
-
Traceability & Documentation:
- Maintain clear Material Test Reports (MTRs) or Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) for each batch/lot. These must include chemical composition (confirming low carbon, Mo content), mechanical properties, heat number, and applicable standards (e.g., ASTM A240, A276, A312).
- Implement a robust traceability system (e.g., heat number tagging) from supplier through processing and delivery to the end user.
- Accurate packing lists, shipping documents, and certificates of conformance are essential.
H2: Critical Compliance Requirements for SS316L
-
Material Standards & Specifications:
- Mandatory: Adhere strictly to the relevant national/international standards specified in the purchase order or project requirements. Common standards include:
- ASTM Standards: A240 (Plate), A276 (Bar), A312 (Pipe), A479 (Bar for Pressure Vessels), A580 (Wire).
- ASME Standards: SA-240, SA-276, SA-312, SA-479 (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code).
- EN/DIN Standards: EN 10088-2 (X2CrNiMo17-12-2), 1.4404.
- Certification: Provide valid and complete MTRs/MTCs (typically 3.1 or 3.2 per EN 10204) verifying compliance with the specified standard.
- Mandatory: Adhere strictly to the relevant national/international standards specified in the purchase order or project requirements. Common standards include:
-
Industry-Specific Regulations:
- Food & Beverage (FDA, EU 1935/2004): Ensure surfaces are suitable for food contact. Material must meet requirements for non-toxicity, cleanability, and resistance to food acids. Often requires specific surface finishes (e.g., electropolished) and documentation proving suitability.
- Pharmaceutical & Biotech (cGMP, ASME BPE): Requires ultra-high purity, specific surface finishes (Ra values), passivation, and documentation. Compliance with ASME BPE (Bioprocessing Equipment) standard is often mandatory for process equipment.
- Marine & Offshore: Must withstand saltwater environments. May require additional testing or certification (e.g., NORSOK M-650 for sour service, though 316L has limitations here).
- Oil & Gas: Subject to stringent codes like API, NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 (for sour service – Note: 316L has limited resistance to sulfide stress cracking and may not be suitable for all sour environments). Compliance with pressure vessel codes (ASME BPVC) is critical.
- Medical Devices: Must comply with biocompatibility standards (e.g., ISO 10993) and relevant medical device regulations (e.g., FDA 21 CFR, EU MDR). Requires rigorous traceability and quality management (ISO 13485).
-
Environmental, Health & Safety (EHS):
- Handling Safety: While solid SS316L is inert, machining/grinding generates dust/fumes containing chromium (VI) and nickel, which are carcinogenic. Implement engineering controls (ventilation), PPE (respirators, gloves), and safe work practices per OSHA (US) or local regulations (e.g., COSHH in UK).
- Waste Disposal: Metal swarf and grinding dust are classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions due to heavy metal content. Dispose of according to local hazardous waste regulations (e.g., RCRA in US). Recycling is preferred.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure compliance with REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) regarding Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) like Nickel. RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) may apply to electronic components using SS316L.
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG): While SS316L itself is not typically classified as dangerous goods for transport, machining waste (dust, swarf) often is (UN3089, Environmentally Hazardous Substance, Solid, n.o.s.). Proper classification, packaging, labeling, and documentation (e.g., SDS) are required for waste shipment.
-
Quality Management Systems (QMS):
- Adherence to recognized QMS standards like ISO 9001 is fundamental for ensuring consistent quality and process control throughout logistics and handling.
- Industry-specific QMS (e.g., ISO 13485 for medical devices, API Q1 for oil & gas) may be required.
Key Takeaway: Successful logistics and compliance for SS316L hinge on preventing contamination (especially iron), maintaining rigorous traceability, adhering strictly to material standards, and understanding the specific regulatory landscape of the end-use industry. Always consult the specific project specifications and applicable local, national, and international regulations.
Conclusion for Sourcing SS316L:
Sourcing SS316L stainless steel requires a strategic approach that balances material quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. SS316L, with its superior corrosion resistance, particularly in chloride environments, and excellent performance at elevated temperatures, is critical for demanding applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, marine engineering, and chemical processing.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include verifying material certifications (e.g., Mill Test Certificates, compliance with ASTM/ASME standards), ensuring traceability, and evaluating the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities and quality control systems. Engaging with reputable suppliers—preferably those with proven experience in providing SS316L for high-specification applications—minimizes the risk of material failure and ensures long-term performance.
Additionally, factors such as lead times, logistics, and total cost of ownership (including fabrication and maintenance costs) should be assessed to support sustainable and efficient procurement. By adopting a thorough and due diligence-driven sourcing strategy, organizations can secure high-quality SS316L that meets technical requirements, regulatory standards, and project timelines, ultimately contributing to product reliability and operational safety.