The global stainless steel market, driven by rising demand in construction, automotive, and industrial applications, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. Within this landscape, SS316—a molybdenum-containing austenitic stainless steel renowned for its superior corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments—has become a material of critical importance. As industries from marine engineering to pharmaceuticals prioritize durability and compliance, demand for high-purity, consistently composed SS316 has intensified. With the Asia Pacific region accounting for over 50% of global stainless steel production, competition among manufacturers to deliver precise, reliable compositions has escalated. Based on production capacity, quality certifications, R&D investment, and global supply footprint, the following analysis identifies the top seven SS316 composition manufacturers shaping the future of high-performance stainless steel.
Top 7 Ss316 Composition Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 UNS S31603
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ulbrich.com
Key Highlights: Ulbrich is a manufacturer of 316L Stainless Steel UNS S31603, which is a s a low carbon austenitic chromium-nickel stainless steel….
#2 High
Domain Est. 1998
Website: specialtysteel.com
Key Highlights: 316 Stainless Steel Features and Chemical Composition: Key Features: Contains up to 0.08% carbon, offering excellent tensile strength and corrosion resistance….
#3 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: azom.com
Key Highlights: Grade 316 is the standard molybdenum-bearing grade, second in importance to 304 amongst the austenitic stainless steels….
#4 Stainless Steel 316
Domain Est. 2000
Website: espimetals.com
Key Highlights: The 316 family is a group of austenitic stainless steels with superior corrosion resistance to 304 stainless steel. This alloy is suitable for welding….
#5 AISI 316L
Domain Est. 2007
Website: stahlportal.com
Key Highlights: Material grade 1.4435, also called 316L stainless steel, is described as a non-magnetic steel. The Delta ferrite content is max. 0.5%. It can be used in ……
#6 The different grades of stainless steel
Domain Est. 2014
Website: beal-inox.com
Key Highlights: Stainless steel or inox steel is an alloy of iron and carbon containing more than 50% iron, at least 10.5% chromium and less than 1.2% carbon….
#7 Stainless Steel 316L
Domain Est. 2017
Website: thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk
Key Highlights: This data sheet applies to stainless steel 316L / 1.4404 hot and cold-rolled sheets/plates and strip, semi-finished products, rods, rolled wire and profiles….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ss316 Composition
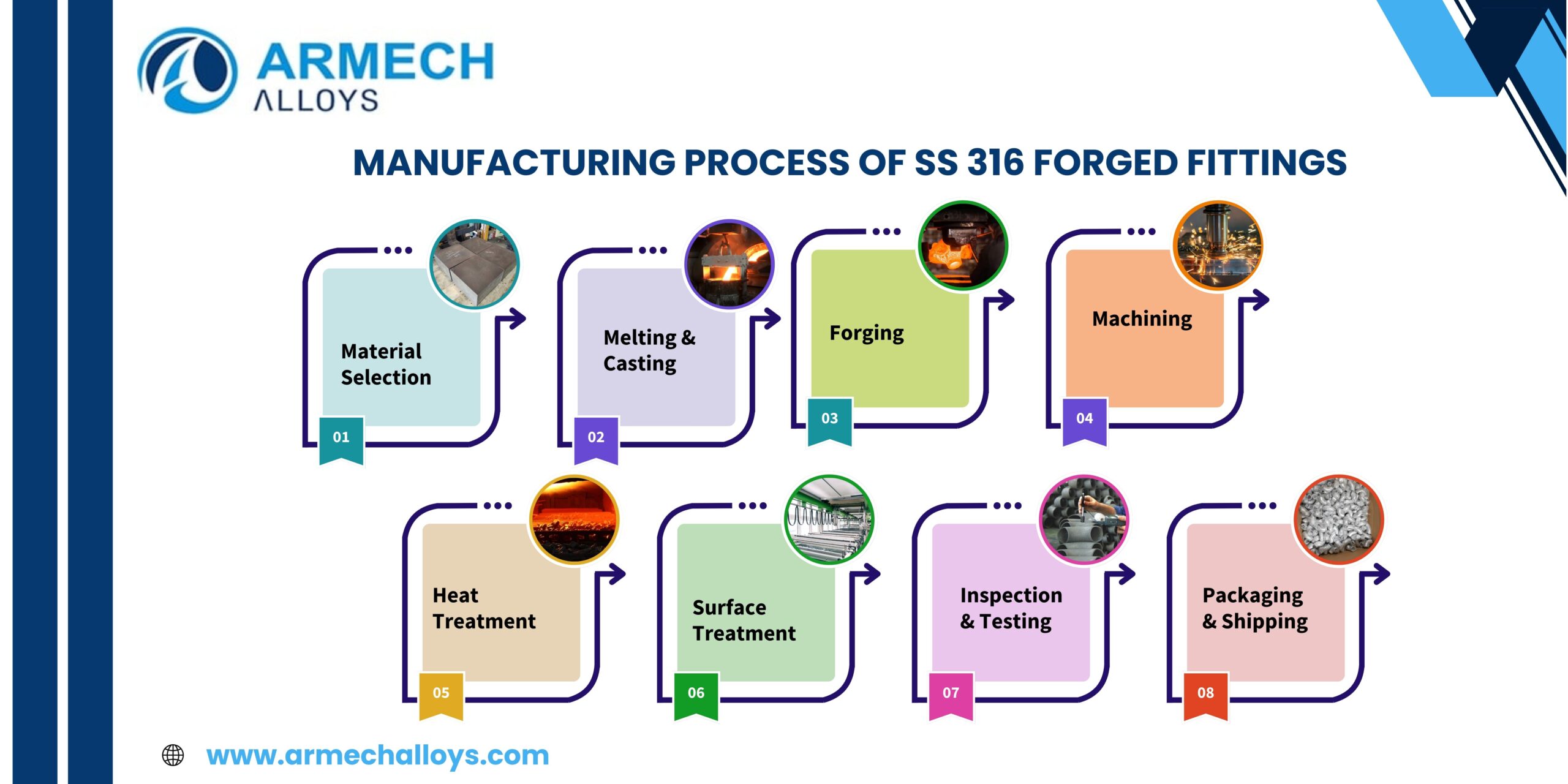
H2: Market Trends for SS316 Composition in 2026
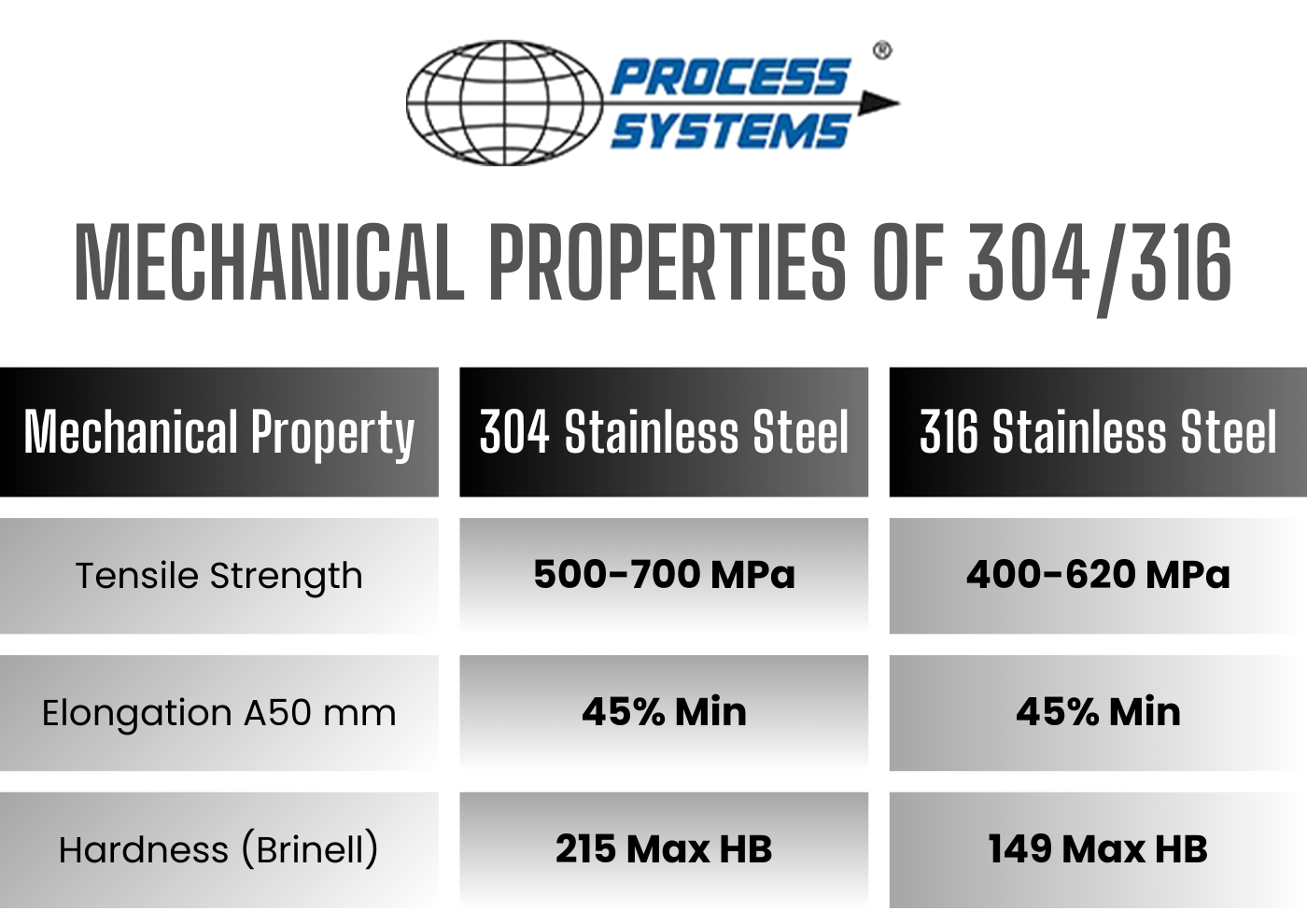
As the global industrial landscape evolves, the demand and application trends for stainless steel grade SS316—known for its superior corrosion resistance due to molybdenum-enhanced composition—are set to experience significant shifts by 2026. The composition of SS316, typically consisting of 16–18% chromium, 10–14% nickel, 2–3% molybdenum, and trace elements in a balanced iron base, positions it as a critical material across high-performance sectors. Below are the key market trends shaping the SS316 composition landscape in 2026:
1. Rising Demand in Sustainable Infrastructure
With global emphasis on green construction and infrastructure resilience, SS316 is increasingly specified in coastal developments, wastewater treatment plants, and desalination facilities. The molybdenum content (2–3%) in SS316 enhances resistance to chloride-induced pitting—making it ideal for marine and high-humidity environments. By 2026, government initiatives promoting sustainable urban development are projected to drive up SS316 consumption, particularly in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East.
2. Shift Toward High-Performance Alloys in Energy Transition
The clean energy transition is influencing material selection in offshore wind farms, hydrogen production systems, and carbon capture infrastructure. SS316’s composition offers excellent performance under corrosive conditions associated with saline environments and chemical exposure. By 2026, increasing investments in renewable energy are expected to boost demand for SS316, especially in electrolyzers and piping systems where chloride resistance is critical.
3. Supply Chain Volatility and Raw Material Costs
Nickel and molybdenum—key alloying elements in SS316—are subject to price volatility due to geopolitical tensions and mining constraints. By 2026, fluctuations in nickel prices (influenced by electric vehicle battery demand) and molybdenum supply chains may pressure manufacturers to explore optimized compositions or alternative grades. However, SS316’s established performance profile will likely preserve its market dominance in critical applications.
4. Advancements in Recycling and Circular Economy
Growing emphasis on sustainability is pushing the steel industry toward higher recycling rates. SS316’s composition allows for efficient recycling without significant degradation in quality. In 2026, improved sorting technologies and regulatory frameworks are expected to enhance scrap utilization, reducing reliance on primary raw materials and lowering the carbon footprint of SS316 production.
5. Regional Production Shifts and Localized Manufacturing
Trade policies, tariffs, and supply chain resilience strategies are driving regionalization of stainless steel production. In 2026, countries like India, Vietnam, and Mexico are expanding SS316 manufacturing capacity to serve local and nearshore markets. This shift is prompting refinements in composition standards to meet regional regulatory and environmental requirements.
6. Innovation in Composition for Enhanced Performance
While the standard SS316 composition remains widely used, there is growing R&D into modified variants (e.g., SS316L for low carbon, or enhanced molybdenum versions) to improve weldability and corrosion resistance. By 2026, nano-alloying and precision melting technologies may enable tighter control over composition, leading to next-generation SS316 grades with extended service life.
Conclusion
By 2026, SS316 composition will remain a cornerstone of high-corrosion-resistance applications, with market dynamics shaped by sustainability mandates, energy transition needs, and supply chain innovations. While cost and material availability challenges persist, the fundamental advantages of its chemical makeup—particularly chromium, nickel, and molybdenum synergy—will ensure continued demand across critical industries.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing SS316 Composition (Quality, IP)
Sourcing SS316 (Stainless Steel 316) requires careful attention to both material quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations, especially in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and aerospace where material integrity is critical. Failing to address common pitfalls can lead to compromised performance, regulatory non-compliance, and legal risks. Below are key challenges related to quality and IP when procuring SS316.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inadequate Material Certification
One of the most frequent issues is receiving SS316 without proper certification, such as Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) compliant with standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10204. Without valid documentation, it’s impossible to verify the chemical composition and mechanical properties, increasing the risk of using substandard material.
Inconsistent Chemical Composition
SS316 must meet specific alloy requirements (typically 16–18% chromium, 10–14% nickel, 2–3% molybdenum). Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in material that falls outside these ranges, reducing corrosion resistance—especially in chloride-rich environments.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Material
Some suppliers may label lower-grade stainless steel (e.g., SS304) as SS316 to cut costs. This misrepresentation can lead to premature failure in corrosive applications. Positive Material Identification (PMI) testing is essential to confirm the actual composition upon delivery.
Poor Manufacturing Practices
Even with correct alloy composition, poor fabrication—such as improper heat treatment or welding—can degrade SS316’s performance. Sourcing from vendors without certified manufacturing processes increases the risk of microstructural defects.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Alloys
Certain high-performance variations of SS316 (e.g., super-austenitic grades with enhanced molybdenum content) may be protected by patents or trade secrets. Using such variants without licensing can expose companies to IP infringement claims.
Reverse Engineering Risks
Attempting to replicate a competitor’s SS316-based component without understanding IP protections may lead to unintentional infringement, especially if the original design incorporates patented processing techniques or proprietary heat treatments.
Lack of Traceability in Supply Chain
Without clear documentation of material origin and processing history, organizations risk using materials that incorporate protected technologies. This becomes a critical issue in regulated or litigious environments where full traceability is required.
Mitigation Strategies
- Always require certified material test reports and conduct third-party PMI verification.
- Source from reputable, audited suppliers with ISO or AS9100 certification.
- Perform due diligence on alloy specifications to ensure they do not infringe on active patents.
- Maintain full documentation throughout the supply chain to support quality and IP compliance.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures the structural integrity, regulatory compliance, and legal safety of SS316 components in critical applications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for SS316 Composition
Material Overview
SS316 (also known as AISI 316 or 1.4401) is a molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steel known for its enhanced corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and acidic environments. Its composition typically includes chromium (16–18%), nickel (10–14%), molybdenum (2–3%), and trace amounts of other elements such as manganese, silicon, and carbon. This makes SS316 ideal for marine, pharmaceutical, food processing, and chemical industries.
Regulatory Compliance
- ASTM Standards: SS316 must comply with ASTM A240 (for plate, sheet, and strip) or ASTM A276 (for bars and shapes). These standards define chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing requirements.
- ISO Standards: ISO 15510 specifies the chemical composition of stainless steels, with SS316 designated as X5CrNiMo17-12-2.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: SS316 is generally compliant with EU regulations on hazardous substances (RoHS) and chemical registration (REACH), as it contains no restricted heavy metals like lead or cadmium. However, suppliers should provide documentation confirming compliance.
- FDA Approval: SS316 is acceptable for food contact applications under FDA 21 CFR §178.3297, provided it meets surface finish and fabrication standards.
Shipping & Handling Requirements
- Packaging: SS316 products must be protected from moisture and contamination during transit. Use waterproof wrapping, wooden crates, or pallets with plastic covers to prevent surface corrosion or scratches.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with material grade (e.g., “SS316” or “316 Stainless”), heat number, dimensions, weight, and supplier information. Include handling symbols (e.g., “Do Not Stack” or “Protect from Moisture”) as needed.
- Transportation: Suitable for standard land, sea, and air freight. Avoid prolonged exposure to saltwater or highly humid environments during shipping, especially for extended durations.
Storage Guidelines
- Environment: Store in a dry, indoor area with controlled humidity. Avoid direct contact with carbon steel to prevent cross-contamination and rust transfer.
- Racking: Use non-metallic or coated racks to prevent galvanic corrosion. Keep materials elevated from the floor to reduce moisture exposure.
- Inventory Rotation: Follow a first-in, first-out (FIFO) policy to minimize long-term storage risks and ensure material traceability.
Documentation & Traceability
- Mill Test Certificates (MTC): Require MTCs (typically Type 3.1 per EN 10204) for each batch, certifying chemical composition, mechanical properties, and compliance with applicable standards.
- Material Traceability: Maintain records linking heat/lot numbers to specific shipments and end uses, especially in regulated industries like aerospace or medical devices.
- Customs Documentation: For international shipments, include commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. SS316 may be classified under HS Code 7219 or 7222, depending on form (sheet, bar, etc.).
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- Recyclability: SS316 is 100% recyclable. Encourage recycling programs and proper disposal to meet sustainability goals.
- Dust & Fume Hazards: During cutting, grinding, or welding, SS316 produces hazardous fumes (containing chromium and nickel compounds). Use proper ventilation, respirators, and comply with OSHA or local safety regulations.
- Waste Management: Metal swarf and offcuts should be collected and recycled through certified metal reprocessors. Avoid landfill disposal.
Supplier & Quality Assurance
- Approved Suppliers: Source SS316 only from certified suppliers with quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Incoming Inspection: Verify material composition using PMI (Positive Material Identification) testing and review accompanying documentation upon receipt.
- Non-Conformance Reporting: Establish procedures for handling off-spec materials, including quarantine, supplier notification, and corrective actions.
Adhering to this guide ensures safe, compliant, and efficient handling of SS316 throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion on Sourcing SS316 Composition:
Sourcing SS316 (also known as AISI 316 or 1.4401) stainless steel requires a thorough understanding of its precise chemical composition to ensure material performance, regulatory compliance, and suitability for intended applications—particularly in aggressive environments such as marine, chemical processing, or pharmaceutical industries. The standard composition of SS316 includes key elements such as chromium (16–18%), nickel (10–14%), molybdenum (2–3%), and low carbon content (≤0.03% in the L variant, i.e., 316L), which together provide excellent corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and acidic conditions.
To ensure reliable sourcing, procurement should be based on certified material test reports (MTRs) conforming to recognized international standards such as ASTM A240, ISO 15510, or EN 10088. Verified suppliers with proven quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certified) should be prioritized to minimize risks of material substitution or non-conformance. Additionally, spectral analysis (e.g., PMI testing) upon receipt is recommended for quality assurance.
In summary, successful sourcing of SS316 hinges on strict adherence to compositional specifications, traceability, and collaboration with reputable suppliers to guarantee material integrity and long-term performance in critical applications.