The global stainless steel market, driven by rising demand in construction, automotive, and industrial applications, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030, according to Grand View Research. Within this landscape, SS 304—known for its optimal balance of corrosion resistance, formability, and cost-effectiveness—accounts for nearly 60% of austenitic stainless steel consumption worldwide. As urbanization and infrastructure development accelerate across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, the demand for high-quality SS 304 material continues to rise. This surge has positioned leading manufacturers at the forefront of innovation and supply chain reliability. Based on production capacity, geographical reach, compliance with international standards (ASTM, ISO), and output consistency, the following eight companies have emerged as key players shaping the global SS 304 material composition market.
Top 8 Ss 304 Material Composition Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Quality 304 & 304L Stainless Steel Composition
Domain Est. 1997
Website: stanch.com
Key Highlights: Grade 304L is a low carbon chemistry of 304, it combined with an addition of nitrogen enables 304L to meet the mechanical properties of 304….
#2 Grade 304 Stainless Steel
Domain Est. 1999
Website: azom.com
Key Highlights: Stainless steel types 1.4301 and 1.4307 are also known as grades 304 and 304L respectively. Type 304 is the most versatile and widely used stainless steel….
#3 Stainless Steel Grades
Domain Est. 1999
Website: jindalstainless.com
Key Highlights: Stainless Steel 304 is a versatile austenitic alloy renowned for its remarkable corrosion resistance and durability. Its versatility shines in applications ……
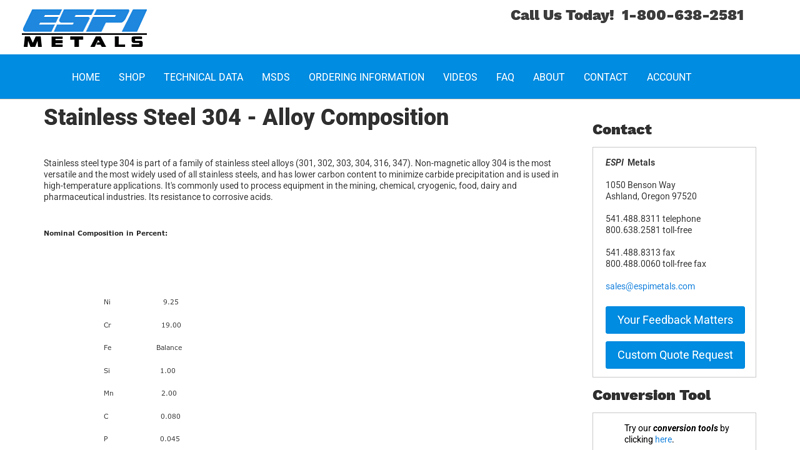
#4 Stainless Steel 304
Domain Est. 2000
Website: espimetals.com
Key Highlights: Type 304—the most common grade; the classic 18/8 (18% chromium, 8% nickel) stainless steel. Outside of the US it is commonly known as “A2 stainless steel”, in ……
#5 AISI 304
Domain Est. 2007
Website: stahlportal.com
Key Highlights: The stainless steel alloys AISI 304 and AISI 304L are the best known and most widely used chromium-nickel steels. Their excellent corrosion resistance, high ……
#6 304 Stainless Steel, AISI 304, EN 1.4301, S30400 …
Domain Est. 2009
Website: neonalloys.com
Key Highlights: 304 stainless steel is the most commonly use austenite steel. 304 SS usually contains 18% chromium, 8% nickel. 304 stainless steel has a very good resistance….
#7 Understanding stainless-steel grades
Domain Est. 2012
Website: essentracomponents.com
Key Highlights: 304 grade stainless steel referred to as 18/8. This refers to 304’s average composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel….
#8 Stainless Steel 304
Domain Est. 2017
Website: thyssenkrupp-materials.co.uk
Key Highlights: Stainless steel 304 and stainless steel 304L are also known as 1.4301 and 1.4307 respectively. Type 304 is the most versatile and widely used stainless steel. ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ss 304 Material Composition

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for SS 304 Material Composition
Stainless Steel 304 (SS 304), renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and versatility, remains one of the most widely used austenitic stainless steels across industries. As the global economy transitions toward sustainable manufacturing, infrastructure development, and advanced technology integration, the market dynamics for SS 304 are expected to evolve significantly by 2026. This analysis explores key trends shaping the demand, composition considerations, and supply chain factors influencing SS 304 in the coming years.
1. Growing Demand in Construction and Infrastructure
The construction sector is projected to be a major driver of SS 304 demand by 2026, especially in emerging economies across Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa. Urbanization, coupled with government initiatives promoting resilient and sustainable infrastructure, will increase the use of corrosion-resistant materials like SS 304 in architectural applications, water treatment systems, and building facades. The material’s balanced composition—typically 18% chromium and 8% nickel (18/8 stainless steel)—ensures longevity in harsh environments, making it a preferred choice for long-term projects.
2. Shift Toward Sustainable and Recyclable Materials
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing industries to adopt materials with high recyclability. SS 304 is 100% recyclable and retains its properties through multiple recycling cycles. This eco-friendly attribute is expected to boost its adoption in green building certifications (e.g., LEED) and circular economy models. By 2026, manufacturers may emphasize low-carbon production methods and transparent sourcing of raw materials, especially nickel and chromium, to meet ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards.
3. Fluctuations in Raw Material Supply and Composition Stability
The composition of SS 304 is sensitive to the availability and pricing of key alloying elements—primarily chromium, nickel, and iron. As of 2026, geopolitical tensions, mining restrictions, and supply chain disruptions in major producing regions (e.g., Indonesia for nickel, South Africa for chromium) could lead to price volatility. This may prompt some producers to explore minor compositional adjustments or substitute grades (e.g., SS 304L for enhanced weldability), though the core 18/8 ratio is expected to remain standard due to performance requirements and international standards (ASTM, JIS, etc.).
4. Expansion in Industrial and Consumer Applications
Beyond traditional uses in food processing, chemical equipment, and medical devices, SS 304 is gaining traction in emerging sectors such as renewable energy (e.g., solar panel frames, battery enclosures), electric vehicles (EV charging infrastructure), and smart home appliances. The material’s hygienic surface, non-reactivity, and aesthetic appeal align well with modern consumer expectations. By 2026, demand from high-tech manufacturing and consumer electronics is expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5–6%.
5. Technological Advancements in Manufacturing and Quality Control
Advances in metallurgical processing, such as argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) and smart monitoring systems, are enabling more consistent SS 304 composition and improved material properties. In 2026, digital twins and AI-driven quality assurance will allow producers to maintain tighter control over elemental composition, minimizing impurities and enhancing performance. This precision supports compliance with stringent industry standards in aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific will likely remain the dominant consumer and producer of SS 304 by 2026, led by China, India, and Japan. However, North America and Europe are expected to see renewed growth due to infrastructure revitalization programs and the reshoring of manufacturing. These regions may also enforce stricter material traceability requirements, influencing how SS 304 is produced and documented.
Conclusion
By 2026, the SS 304 material market will be shaped by sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and resilient demand across diverse sectors. While its fundamental composition is expected to remain stable, external pressures such as raw material costs and environmental regulations will drive efficiency improvements and responsible sourcing. Companies that invest in quality control, recycling infrastructure, and adaptive supply chains will be best positioned to capitalize on the evolving landscape of stainless steel demand.
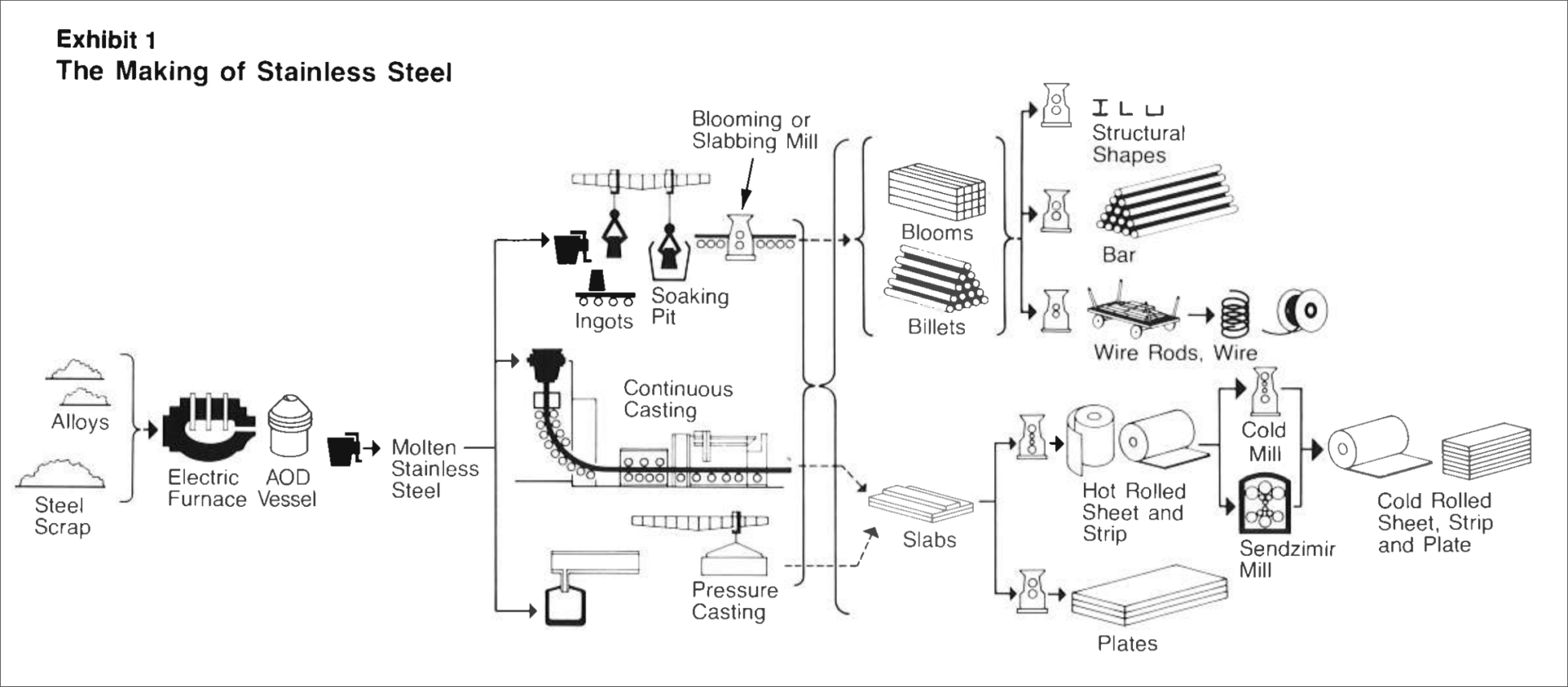
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing SS 304 Material Composition (Quality, IP)
Sourcing SS 304 (AISI 304 stainless steel) involves several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning material quality and intellectual property (IP) integrity. Understanding these risks ensures reliable procurement and compliance with industry standards.
Inadequate Verification of Chemical Composition
One of the primary pitfalls is assuming that the supplied material meets the standard SS 304 composition (typically 18% chromium and 8% nickel) without proper testing. Suppliers may provide substandard or misrepresented alloys. Without third-party material test reports (MTRs) or positive material identification (PMI) testing, buyers risk receiving materials with incorrect alloy content, leading to premature failure in corrosive environments.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
A common issue is the absence of full traceability and proper certification. Reputable suppliers should provide certified mill test reports (MTRs) that conform to ASTM A240 or equivalent standards. Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide documented traceability increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or non-compliant material, especially in global supply chains.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Materials
The stainless steel market is vulnerable to counterfeit products, where lower-grade steels (e.g., 200-series) are falsely labeled as SS 304. This misrepresentation affects corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Without rigorous supplier vetting and material verification protocols, companies may unknowingly incorporate inferior materials into critical applications.
Insufficient Quality Control in Manufacturing
Even with correct raw material composition, improper manufacturing processes (e.g., heat treatment, welding) can degrade material performance. Sourcing from vendors without certified quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001) increases the risk of inconsistencies and non-conformance, undermining the integrity of the final product.
Intellectual Property and Specification Risks
When sourcing custom-fabricated components, there’s a risk of IP leakage if design specifications or proprietary compositions are shared without proper legal safeguards. Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clear contractual terms are essential to protect sensitive information, especially when working with overseas suppliers.
Overlooking Regional Standards and Compliance
Different regions may have varying standards for SS 304 (e.g., ASTM in the U.S., EN in Europe, JIS in Japan). Sourcing without confirming compliance with the required regional or industry-specific standards can lead to regulatory or operational issues, particularly in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals or food processing.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should implement robust supplier qualification processes, demand verifiable documentation, conduct independent material testing, and protect intellectual property through legal agreements. Due diligence in sourcing SS 304 ensures material integrity, regulatory compliance, and long-term performance reliability.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for SS 304 Material Composition
Stainless Steel 304 (SS 304), also known as 1.4301 in the European standard, is one of the most widely used austenitic stainless steels due to its excellent corrosion resistance, formability, and weldability. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential when handling SS 304, particularly in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, construction, and chemical processing. This guide outlines key considerations for material handling, transportation, documentation, and regulatory compliance related to SS 304’s chemical composition.
Material Composition Overview
SS 304 is primarily composed of iron, chromium, and nickel, with small additions of other elements to enhance performance. The standard composition per ASTM A240/A240M and AISI specifications is as follows:
- Chromium (Cr): 18.0–20.0%
- Nickel (Ni): 8.0–10.5%
- Carbon (C): ≤ 0.08%
- Manganese (Mn): ≤ 2.0%
- Silicon (Si): ≤ 1.0%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤ 0.045%
- Sulfur (S): ≤ 0.030%
- Iron (Fe): Balance
This composition ensures corrosion resistance in a wide range of environments and provides good mechanical properties across various temperatures.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
ASTM and ASME Standards
- SS 304 must meet the requirements of ASTM A240/A240M for chromium and chromium-nickel stainless steel plate, sheet, and strip.
- For pressure-containing applications, compliance with ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC), Section II is mandatory.
- Material test reports (MTRs) must be provided to verify conformance to these standards.
ISO and EN Standards
- In Europe, SS 304 is designated as X5CrNi18-10 (1.4301) per EN 10088-2.
- Compliance with ISO 15510 for stainless steel chemical composition is required for international shipments.
- CE marking may be necessary depending on the application and regional regulations.
REACH and RoHS Compliance
- SS 304 is generally compliant with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations, as it contains no substances of very high concern (SVHCs) above threshold levels.
- For electrical and electronic applications, ensure the material meets RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, particularly regarding restricted heavy metals.
FDA and Food-Grade Compliance
- SS 304 is approved for food-contact applications under FDA 21 CFR §178.3297.
- Surfaces must be passivated and properly finished (e.g., 2B, BA, or polished) to prevent contamination.
- Documentation proving food-grade suitability must accompany shipments for use in food or pharmaceutical industries.
Logistics and Handling Guidelines
Packaging and Protection
- Protect SS 304 sheets, coils, bars, and pipes from moisture, contaminants, and mechanical damage.
- Use weather-resistant packaging for sea freight; plastic wrapping or VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper is recommended.
- Avoid contact with carbon steel to prevent cross-contamination and rust staining (e.g., use separate storage areas and handling tools).
Transportation and Storage
- Store materials in a dry, well-ventilated area, off the ground and away from corrosive chemicals.
- Separate from halide sources (e.g., salt, chloride-based cleaners) to prevent pitting corrosion.
- For international shipping, ensure compliance with IMDG Code (for sea) or ADR (for road in Europe) if transporting in bulk or as part of fabricated components.
Traceability and Documentation
- Maintain full traceability from melt batch to final product using heat numbers.
- Provide Mill Test Certificates (MTCs) or Material Test Reports (MTRs) per EN 10204 Type 3.1 or 3.2, depending on project requirements.
- Include chemical composition, mechanical properties, and applicable standard references in documentation.
Quality Assurance and Testing
- Conduct spectrometric analysis (OES or XRF) to verify chemical composition upon receipt.
- Perform intergranular corrosion testing (e.g., ASTM A262) if used in high-temperature or corrosive environments.
- For critical applications, consider additional tests such as PMI (Positive Material Identification) to confirm alloy grade.
Summary
Effective logistics and compliance for SS 304 require adherence to international material standards, proper handling to maintain integrity, and comprehensive documentation to ensure traceability and regulatory acceptance. By understanding the material’s composition and regulatory landscape, organizations can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient use of SS 304 across global supply chains.
Conclusion for Sourcing SS 304 Material Composition:
Sourcing SS 304 (AISI 304) stainless steel requires a clear understanding of its standard material composition to ensure quality, performance, and compliance with industry specifications. SS 304 is an austenitic stainless steel with a typical composition of 18–20% chromium and 8–10.5% nickel, along with a maximum of 0.08% carbon, 2% manganese, 1% silicon, and 0.045% phosphorus and sulfur each, with the remainder being iron. This composition provides excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and durability in a wide range of environments.
To ensure consistent quality and traceability, it is essential to source SS 304 from reputable suppliers who provide certified mill test reports (MTRs) compliant with standards such as ASTM A240, AISI, or ISO 15510. Verification through material testing methods like Positive Material Identification (PMI) can further confirm composition accuracy, especially for critical applications in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical handling.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of SS 304 depends on verifying its precise chemical composition, ensuring compliance with relevant standards, and maintaining rigorous quality control throughout the supply chain. This approach minimizes the risk of material substitution, ensures long-term performance, and supports the reliability and safety of the final product.