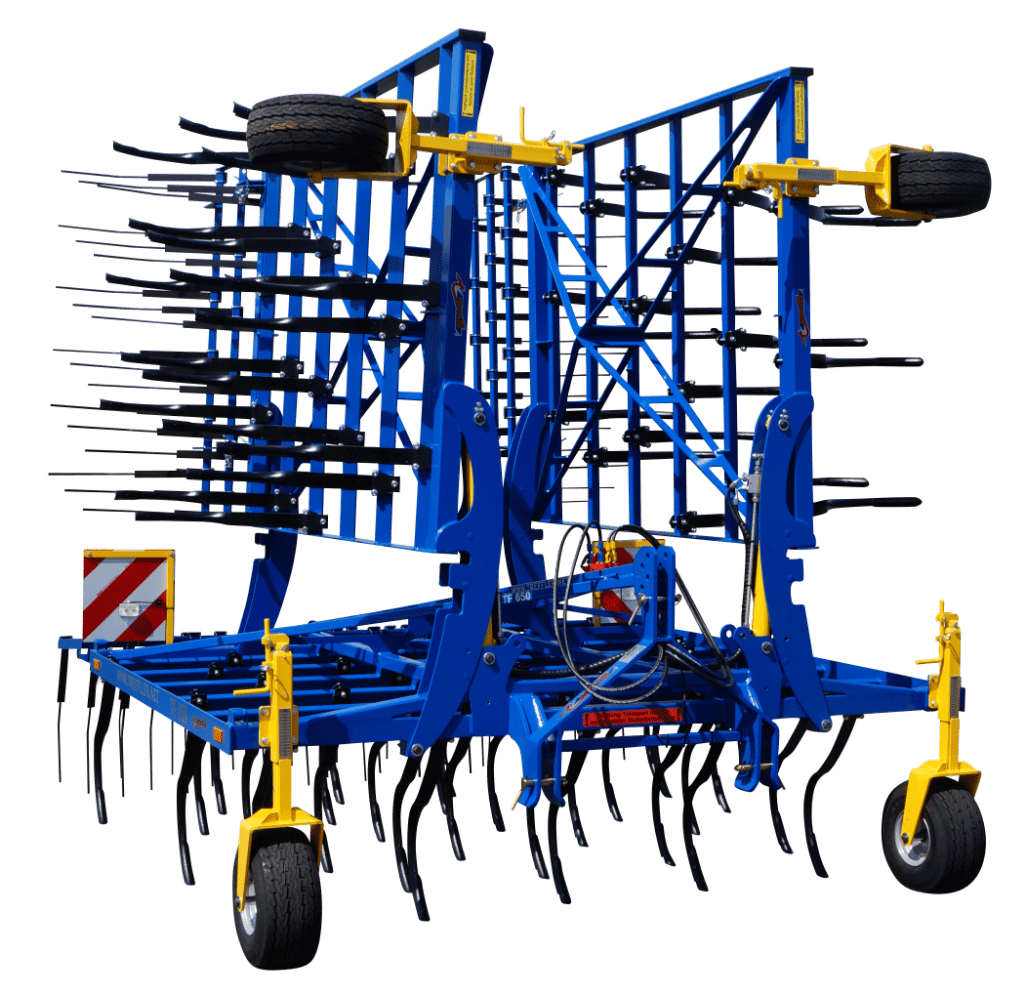
The global agricultural machinery market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for efficient farming equipment to boost crop yields and address labor shortages. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the agricultural machinery market was valued at USD 176.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% through 2029. Within this expanding landscape, spring tooth cultivators have become essential tools for primary and secondary tillage, offering farmers improved soil aeration, weed control, and residue management. Their adaptability across soil types and compatibility with a range of tractors have contributed to increasing adoption, particularly in large-scale row crop operations. With North America and Europe leading in precision farming adoption and emerging economies investing in modernization, demand for high-performance cultivators continues to rise. This growth trajectory has fostered a competitive manufacturing environment, with innovation in tine durability, frame strength, and adjustability becoming key differentiators. Based on market presence, product range, technological advancement, and global distribution, the following nine companies represent the leading spring tooth cultivator manufacturers shaping the future of mechanized tillage.
Top 9 Spring Tooth Cultivator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Spring-tooth cultivator for seedbed preparation
Domain Est. 2011
Website: treffler.net
Key Highlights: The Treffler spring-tooth cultivator is the proven solution for optimum seedbed preparation. The latest technology for careful, flat soil cultivation….
#2 Agriculture
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kongskilde.com
Key Highlights: Rigid tine stubble cultivator. The Kongskilde Delta Flex is a heavy-duty rigid tine cultivator designed for efficient stubble cultivation and seedbed ……
#3 cm
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rinieri.com
Key Highlights: Spring tine cultivator “CM” with special supports “Stone-Jumper” of working groups equipped with antishock springs, the frame is width adjustable….
#4 Agricultural Products from Remlinger Manufacturing
Domain Est. 1999
Website: remlingermfg.com
Key Highlights: Remlinger designs and manufactures farm tillage and land management equipment, with over 60 years of experience….
#5 Not Your Grandfather’s Spring Tooth
Domain Est. 2003
Website: hillcotechnologies.com
Key Highlights: The Hillco Spring Tooth solves the trash clearance problem by using S-tines instead of C-tines which are a taller style of shank allowing for ……
#6 Heavy Duty Spring Loaded Tine Cultivator
Domain Est. 2005
Website: brabereq.com
Key Highlights: Heavy Duty Spring Loaded Tine Cultivator. Part Number: BE-FC7S. • Cat 2, 3PT hitch • 7 double coil ……
#7 Spring Tine Cultivator
Domain Est. 2017
Website: mgeweb.com
Key Highlights: Spring tine cultivator with adjustable ripper points. Frame is width adjustable (manually) to fit a wide range of row spacings in both vineyards and orchards….
#8 Spring Shank Cultivator
Domain Est. 2018
Website: fieldkingusa.com
Key Highlights: Spring Shank Cultivator medium Series suitable for loosening and aerating the soil to a depth of nine inches. know more features, specifications and more….
#9 Treffler TF Spring
Domain Est. 2019
Website: organicmachinery.net
Key Highlights: The Treffler precision spring-tooth cultivator is available in various models with working widths of 3.00 m to 7.50 m. With innovative and patented flat steel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Spring Tooth Cultivator

2026 Market Trends for Spring Tooth Cultivators
The global Spring Tooth Cultivator market is poised for steady evolution by 2026, shaped by a confluence of agricultural challenges, technological advancements, and shifting farming practices. While facing competition from newer tillage implements, spring tooth cultivators maintain a significant niche, with market dynamics pointing towards incremental growth, regional variation, and increasing demand for enhanced, durable equipment.
1. Sustained Demand in Conservation and Secondary Tillage:
Spring tooth cultivators will continue to play a vital role in conservation tillage systems and as secondary tillage tools. Their ability to effectively manage crop residue, break up soil crusts, level seedbeds, and control early weeds without inverting the soil profile aligns perfectly with the growing global emphasis on soil health and erosion reduction. This sustained utility in minimum and reduced-till systems will underpin steady demand, particularly in regions with established conservation farming practices like North America and parts of Europe.
2. Focus on Durability and Heavy-Duty Designs:
The trend towards larger farm sizes and the need to cover more ground efficiently will drive demand for larger, heavier-duty spring tooth cultivators. Manufacturers will prioritize robust construction using high-strength steels to withstand high-speed operation (10-12+ mph) and challenging field conditions. Expect continued innovation in shank design, frame reinforcement, and wear protection (e.g., replaceable points, hardened teeth) to extend lifespan and reduce maintenance costs, a key factor for cost-conscious operators.
3. Integration with Technology (Limited but Growing):
While not as technologically advanced as planters or combines, the 2026 market will see a gradual increase in tech integration. Basic features like hydraulic folding for transport, improved depth control systems, and potentially simple monitoring for downforce or section control may become more common on mid-to-high-end models. However, widespread adoption of sophisticated telematics or automated guidance integration specific to the cultivator itself is likely still limited compared to other machinery, focusing instead on compatibility with existing tractor guidance systems.
4. Regional Market Divergence:
Market growth will be uneven. North America (especially the US) will remain a significant market, driven by large-scale row crop farming (corn, soybeans) and established conservation tillage adoption. Europe will see steady demand, influenced by environmental regulations favoring reduced tillage. Asia-Pacific (particularly India, China, Southeast Asia) presents the highest growth potential due to rising mechanization rates, the need for efficient residue management (especially post-rice), and government support for modern agriculture. Demand in Latin America and Africa will grow but may be constrained by economic factors and infrastructure.
5. Competitive Pressure and Niche Consolidation:
Spring tooth cultivators face ongoing competition from alternative implements like field cultivators with coulters, vertical tillage tools, and high-speed disc harrows, which often offer faster operation and better residue incorporation. This pressure will push spring tooth manufacturers to emphasize their unique advantages: superior trash clearance in heavy residue, effective soil fracturing at speed, and excellent soil leveling. The market may see some consolidation, with manufacturers focusing on specialized, high-performance models rather than a broad range of basic units.
6. Sustainability and Longevity as Key Selling Points:
The inherent simplicity and durability of well-made spring tooth cultivators contribute to their sustainability profile. Their long operational life and relatively straightforward repairability will be increasingly marketed as advantages in an era of rising equipment costs and focus on reducing the total cost of ownership. This positions them favorably against more complex, potentially less durable alternatives.
In conclusion, the 2026 Spring Tooth Cultivator market will not experience explosive growth but will maintain relevance through adaptation. Success will depend on manufacturers delivering robust, efficient, and increasingly feature-enhanced implements that meet the specific needs of conservation tillage and residue management, particularly in large-scale farming and rapidly mechanizing regions, while effectively competing against evolving alternative tillage technologies.
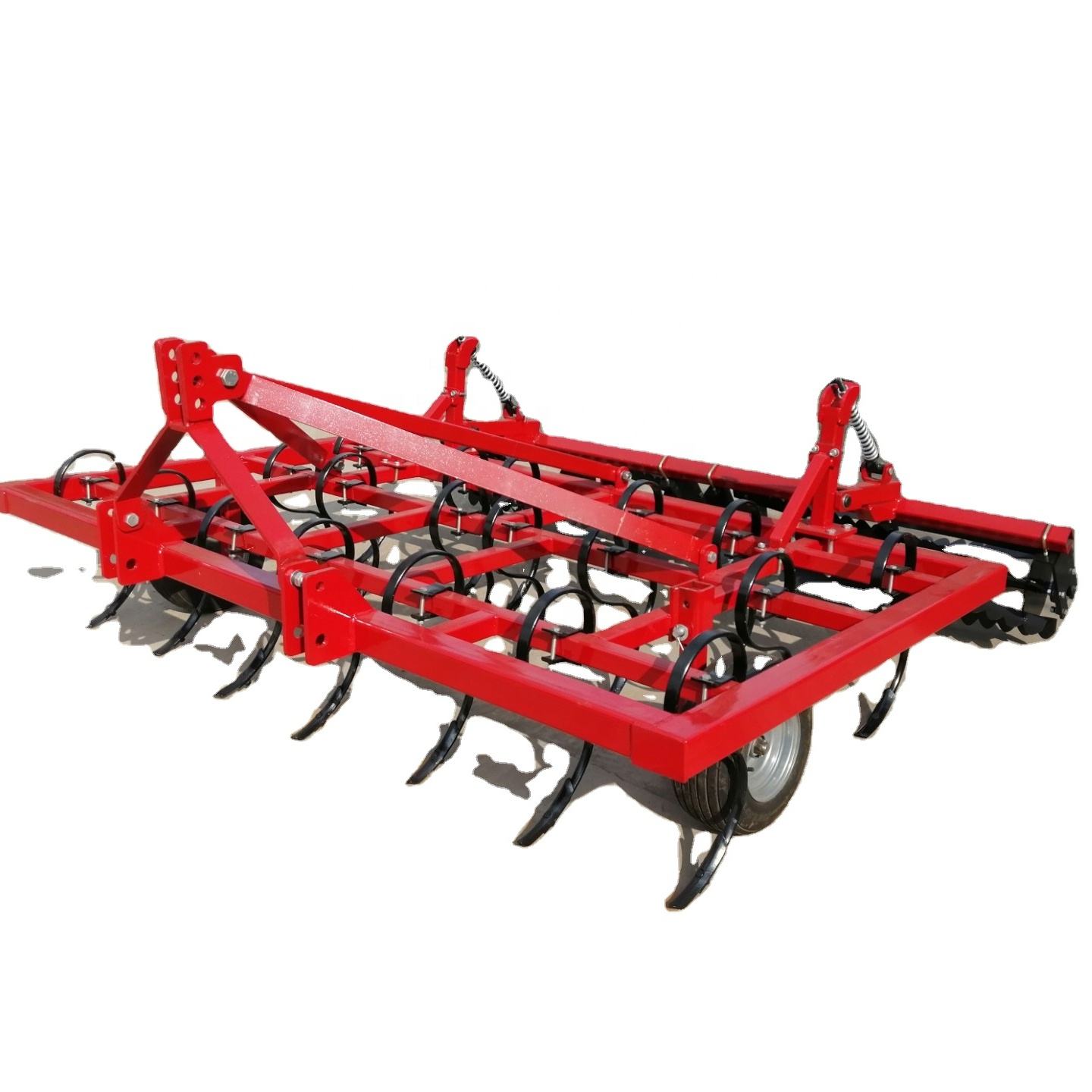

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Spring Tooth Cultivators: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Specifications
One of the most frequent pitfalls when sourcing spring tooth cultivators is failing to verify the quality of materials and construction. Low-cost suppliers may use substandard steel for tines and frames, leading to premature wear, breakage, and reduced field performance. Buyers should insist on verified material certifications (e.g., high-tensile or boron steel) and inspect weld quality, heat treatment processes, and overall finish. Skipping factory audits or sample testing increases the risk of receiving machinery that fails under operational stress.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers who replicate patented designs—especially those mimicking well-known agricultural brands—exposes buyers to legal and reputational risks. Many spring tooth cultivators incorporate proprietary tine configurations, frame geometries, or adjustment mechanisms protected by patents. Purchasing counterfeit or cloned equipment may result in customs seizures, lawsuits, or market bans. Due diligence should include verifying the originality of design and requesting IP compliance documentation from suppliers.
Relying Solely on Price as a Selection Criterion
Focusing exclusively on low purchase price often leads to higher total cost of ownership. Inferior spring tooth cultivators require frequent repairs and part replacements, and downtime during planting seasons can be costly. Buyers should evaluate long-term value, including durability, warranty terms, spare parts availability, and technical support—factors often sacrificed by unscrupulous suppliers.
Inadequate Verification of Supplier Credentials
Many sourcing failures stem from insufficient vetting of suppliers. Fake certifications, fabricated references, and misleading factory photos are common. Third-party inspections, site visits, and checks through trade databases or industry associations are essential to confirm legitimacy. Without this, buyers risk dealing with brokers posing as manufacturers or companies with poor quality control systems.
Lack of Standardization and Compatibility Assurance
Spring tooth cultivators must integrate with existing tractors and implements. Sourcing units without verifying hitch types, working widths, and depth control mechanisms can result in incompatibility. Suppliers may offer “custom” solutions that deviate from industry standards, complicating maintenance and limiting aftermarket support.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality cultivators require maintenance and replacements. Sourcing from suppliers without a reliable spare parts network or technical support can lead to extended downtime. Buyers should confirm spare parts lead times, availability of wear components (like tines and shanks), and access to service manuals before finalizing procurement.
Failing to Address Warranty and Liability Terms
Ambiguous or absent warranty terms leave buyers exposed if defects emerge post-purchase. Poorly drafted contracts may exclude critical components or limit liability unreasonably. It’s crucial to negotiate clear warranty coverage, define responsibilities for defects, and include penalties for non-compliance to protect investment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Spring Tooth Cultivator
Product Classification & HS Code
The Spring Tooth Cultivator is classified under agricultural machinery. The standard Harmonized System (HS) Code is 8433.51.00, which covers “other agricultural, horticultural or forestry machinery for soil preparation or cultivation.” Confirm the exact code with local customs authorities, as regional variations may apply.
Import/Export Documentation Requirements
Ensure the following documents are prepared for international shipments:
– Commercial Invoice (detailing product description, value, and quantity)
– Packing List (specifying weight, dimensions, and packaging type)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin (often required for tariff determination)
– Import/Export License (if mandated by destination country)
Regulatory Compliance Standards
The Spring Tooth Cultivator must comply with relevant safety and technical standards in the target market:
– CE Marking (EU): Conformity with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and applicable EN standards (e.g., EN ISO 4254-1 for safety of agricultural machinery).
– EPA & DOT (USA): No engine emissions requirements for non-powered implements, but ensure compliance with DOT regulations for transport safety.
– Other Regions: Verify national agricultural equipment regulations (e.g., Australia’s ASAE standards, Canada’s CSA B349).
Packaging & Handling Guidelines
- Secure cultivator on wooden pallets or in crates to prevent movement during transit.
- Use protective wrapping to prevent rust and damage to tines.
- Label packages with handling instructions: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and weight specifications.
- Include clear product identification tags with model number and serial number (if applicable).
Transportation & Freight Considerations
- Classify shipment under freight class 70–85 (NMFC code 172160 for agricultural tools) for LTL (Less-Than-Truckload) in North America.
- For ocean freight, calculate volume accurately to optimize container space (20’ or 40’ containers).
- Anchor equipment firmly in containers or trailers to prevent shifting.
- Consider demurrage and detention charges when planning delivery timelines.
Customs Clearance Procedures
- Provide accurate product description: “Spring Tooth Cultivator – Agricultural Soil Cultivation Implement.”
- Declare correct country of manufacture.
- Anticipate duties based on trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN). Use a licensed customs broker for efficient clearance.
- Be prepared for physical inspection, especially in regulated markets.
After-Sales & Warranty Compliance
- Include multilingual operation and safety manuals as required by destination country.
- Comply with local warranty and service obligations—retain records of shipped units and serial numbers.
- Ensure spare parts (e.g., replacement spring tines) are available and compliant with same standards.
Environmental & Disposal Regulations
- Design and document with end-of-life recyclability in mind (steel content >90%).
- Comply with EU End-of-Life Vehicles (ELV) Directive if applicable, or local scrap metal regulations.
- Avoid hazardous coatings or substances restricted under RoHS or REACH in component manufacturing.
Adhering to this guide ensures smooth logistics operations and regulatory compliance for the global distribution of Spring Tooth Cultivators. Always consult local legal and customs experts for market-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Spring Tooth Cultivator
In conclusion, sourcing a spring tooth cultivator requires careful consideration of several key factors, including soil type, tillage requirements, compatibility with existing machinery, durability, and cost-effectiveness. By evaluating suppliers based on product quality, warranty, after-sales support, and customer reviews, agricultural operations can secure a reliable and efficient implement that enhances soil preparation and promotes optimal crop growth. Additionally, choosing a cultivator with adjustable tines, robust spring mechanisms, and easy maintenance features ensures long-term performance and adaptability across varying field conditions. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing decision will contribute to improved farm productivity, reduced operational downtime, and a strong return on investment.