The global spot welding machines market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand in the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the spot welding equipment market was valued at USD 6.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is fueled by increasing automation in production lines, stricter quality control standards, and the growing adoption of resistance welding in electric vehicle (EV) battery manufacturing. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights that advancements in inverter-based and robotic spot welding technologies are further accelerating market growth, with a particular emphasis on energy efficiency and precision. As industries prioritize high-speed, repeatable, and reliable joining processes, the need for advanced spot welding solutions has never been greater—making the selection of leading manufacturers crucial for ensuring performance and innovation.
Top 10 Spot Welding Machines Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 1999
Website: nimak.com
Key Highlights: Industrial joining technology: Resistance welding, welding robots, gluing and dosing technology. Manual welding guns · Overview classicGUN basicGUN servoGUN….
#2 Spot Welding
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cntrline.com
Key Highlights: Spot Welding. Resistance spot welding gun technology has advanced considerably since the introduction of the Transgun, transformer weld gun package….
#3 Tecna
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tecna.net
Key Highlights: Car body repair technologies. Our spot welders are the perfect tool for body shop works. High precision, durability and SMART Technology are the keys that will ……
#4 Spot Weld, Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: spotweldinc.com
Key Highlights: Spot Weld Inc. offers new and remanufactured welding equipment, as well as all of your resistance welding supply needs. We sell spot welders, projection welders ……
#5 Equipment & Systems
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
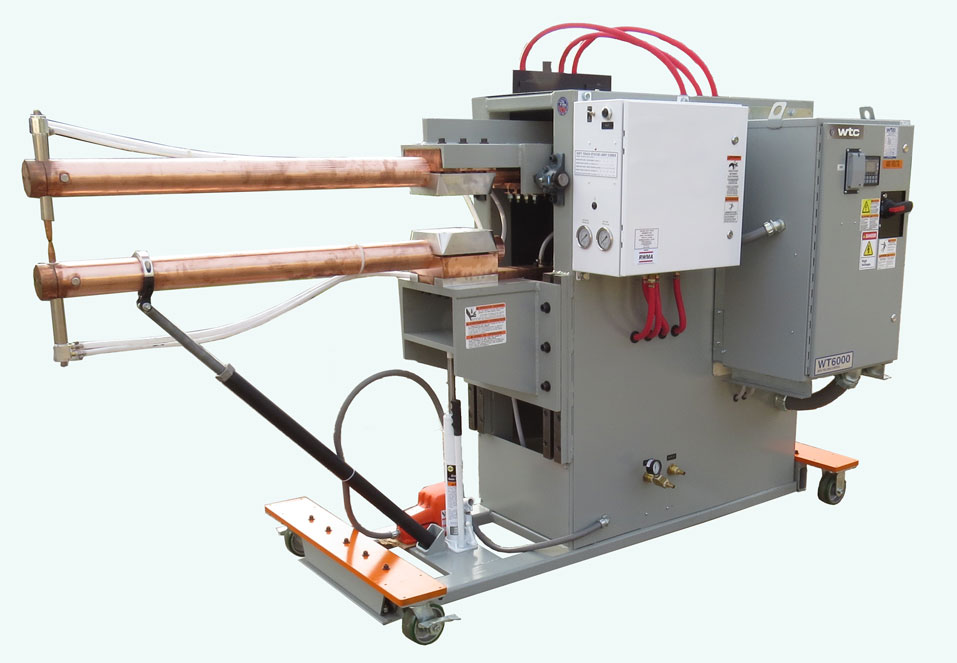
#6 Resistance Welders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tjsnow.com
Key Highlights: T. J. Snow offers a complete line of standard and custom designed resistance spot welders and projection welders, including automated multi-gun and special ……
#7 Resistance Welding
Domain Est. 1997
Website: spotco.com
Key Highlights: We provide state-of-the-art spot welding equipment that delivers fast, efficient, and strong welds. Our spot welders are suitable for a wide range of industries ……
#8 Sunstone Welders
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
#9 Seedorff ACME
Domain Est. 2010
Website: seedorffacme.com
Key Highlights: ACME Rocker Arm Welders. Acme air-operated rocker arm spot welders offer the advantages of faster production, uniform spot welds and elimination of operator ……
#10 SUNKKO
Domain Est. 2017
Website: sunkko.net
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsPro Tool Picks · Laser Welder · Capacitor Spot Welder · Pneumatic Spot Welder · AC Spot Welder · Battery Equalizer · Battery Tester….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Spot Welding Machines

H2: Emerging Market Trends in Spot Welding Machines for 2026
The global spot welding machines market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Automation and Robotics Integration
By 2026, fully automated and robotic spot welding systems will dominate high-volume manufacturing sectors, especially automotive and EV production. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with smart welding heads will enable flexible, human-safe operations in smaller workshops, boosting productivity and precision while reducing labor costs.
2. Surge in Demand from the Electric Vehicle (EV) Sector
The rapid expansion of EV manufacturing is a primary growth catalyst. Spot welding remains critical for battery pack assembly—particularly for connecting lithium-ion cells—and lightweight vehicle frame construction. Machines tailored for aluminum and mixed-material joining will see increased demand, prompting OEMs to develop specialized, high-precision systems.
3. Advancements in Inverter and Mid-Frequency DC (MFDC) Technology
Energy-efficient inverter-based and MFDC spot welders will gain market share due to their superior control, faster cycle times, and lower power consumption. These technologies offer enhanced weld consistency and reduced heat distortion, aligning with quality demands in aerospace and electronics manufacturing.
4. Integration of IoT and Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
Smart welding machines embedded with sensors and IoT connectivity will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data analytics. By 2026, cloud-based platforms will allow remote diagnostics and process optimization, improving uptime and weld quality traceability across global supply chains.
5. Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will drive demand for energy-efficient welding solutions. Manufacturers will prioritize low-emission, high-efficiency models and explore regenerative energy systems. Recyclable components and reduced consumable waste will also influence product design.
6. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Growth in Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—will outpace other regions due to expanding manufacturing bases and infrastructure development. Nearshoring trends in North America and Europe will stimulate localized production of welding equipment, reducing dependency on global supply chains.
7. Rise of Portable and Compact Systems
Demand for lightweight, portable spot welders will grow in maintenance, repair, and small-scale fabrication industries. Advances in battery technology will enable high-performance cordless models, offering flexibility in field applications.
In summary, by 2026, the spot welding machines market will be defined by intelligence, efficiency, and adaptability—closely aligned with the needs of next-generation manufacturing, especially in transportation, energy, and advanced electronics.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Spot Welding Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing spot welding machines, especially from international or lower-cost suppliers, can expose buyers to significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and legal safety.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Build Quality and Material Standards
Many low-cost manufacturers may use substandard materials—such as inferior copper electrodes, low-grade transformers, or poor insulation—to cut costs. This results in reduced machine lifespan, inconsistent welds, frequent maintenance, and potential safety hazards. Buyers may receive units that vary significantly from one batch to another due to lax quality control processes.
Lack of Compliance with International Standards
Reputable spot welding machines should comply with standards such as CE, UL, or ISO. However, some suppliers may falsely claim certification or provide counterfeit documentation. Non-compliant machines can fail safety inspections, lead to workplace accidents, or cause liability issues.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Technical Documentation
Low-cost suppliers may not offer comprehensive technical support, spare parts availability, or detailed operation manuals. This can result in prolonged downtime during failures and challenges in integration or troubleshooting.
Overstated Performance Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate key performance metrics like duty cycle, welding force, or current output. Machines that underperform can disrupt production lines and lead to rework or product defects.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Counterfeit or Clone Machines
A major concern when sourcing from certain regions is the prevalence of cloned machines that mimic well-known brands. These copies often replicate design elements, control systems, or software without authorization, infringing on patents and trademarks.
Use of Unlicensed Software or Firmware
Some spot welding machines incorporate proprietary control algorithms or user interfaces. Unauthorized use of such software constitutes IP theft and may expose the buyer to legal liability, especially in regulated industries.
Limited Recourse in Case of IP Disputes
Purchasing a machine that violates IP rights—even unknowingly—can lead to seizure of equipment, legal action, or reputational damage. Buyers may find it difficult to pursue claims against overseas suppliers due to jurisdictional challenges.
Absence of IP Warranty or Indemnification
Many suppliers, particularly smaller or offshore vendors, do not provide warranties protecting buyers from third-party IP claims. This leaves the end-user exposed to potential litigation risks.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and reference checks.
- Verify certifications through independent means or third-party inspection services.
- Request detailed technical documentation and perform performance testing upon delivery.
- Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
- Work with reputable distributors or original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) to minimize exposure.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires careful supplier evaluation and proactive risk management, ensuring both operational reliability and legal compliance.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Spot Welding Machines
Overview
Spot welding machines are critical industrial tools used primarily in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics for joining metal sheets through electrical resistance. Due to their electrical components, weight, and operational safety requirements, transporting and deploying these machines involves careful logistics planning and adherence to compliance standards.
International Shipping & Transportation
When shipping spot welding machines internationally, proper packaging, labeling, and documentation are essential. Machines should be crated in wooden or metal cases with shock-absorbing materials to prevent damage during transit. Use standardized pallets and secure loads for container or flatbed transport. Ensure compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) and International Air Transport Association (IATA) regulations, particularly when batteries or capacitors are part of the system.
Export Documentation & Regulatory Compliance
Prepare accurate export documentation, including a commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading or airway bill, and a certificate of origin. Verify whether the destination country requires an export license or special permits. Spot welding machines may fall under export control classifications (e.g., ECCN 3A991 under the U.S. Commerce Control List), so check applicable dual-use regulations such as the Wassenaar Arrangement or national export control laws.
Electrical Safety & Certification
Spot welding machines must meet electrical safety standards in both the country of origin and the destination. Key certifications include:
– CE Marking (European Union): Compliance with the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive.
– UL/CSA Certification (United States and Canada): Required for electrical safety and market access.
– CCC Certification (China): Mandatory for electrical equipment sold in China.
Ensure machines are tested and certified by accredited labs prior to shipment.
Environmental & Hazardous Materials Compliance
While spot welding machines themselves are not typically classified as hazardous, certain components (e.g., transformers with insulating oil or capacitors containing PCBs) may be regulated. Confirm that materials used comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations in the EU, or TSCA in the U.S. Avoid shipping outdated or non-compliant models.
Import Regulations & Duties
Research import tariffs, value-added taxes (VAT), and customs duties applicable in the destination country. Use Harmonized System (HS) codes for accurate classification—common codes for spot welding machines include 8515.21 (resistance welding machines). Provide technical specifications to avoid delays or misclassification at customs.
On-Site Installation & Operational Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure proper site preparation including stable power supply (voltage, phase, frequency), grounding, and ventilation. Follow the manufacturer’s installation guidelines and conduct safety training for operators. Comply with local occupational safety regulations such as OSHA (U.S.), WHMIS (Canada), or the EU’s Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC. Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures and use personal protective equipment (PPE).
Maintenance & Regulatory Audits
Maintain detailed service records and schedule regular maintenance to meet insurance and safety audit requirements. Keep copies of all compliance certificates and update them as needed. Periodic inspections help ensure continued conformity with safety and environmental standards.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for spot welding machines involve careful coordination across shipping, regulatory, safety, and operational domains. Proactive planning and adherence to international standards ensure timely delivery, legal compliance, and safe operation in the end-user environment.
Conclusion for Sourcing Spot Welding Machines:
Sourcing the right spot welding machines requires a comprehensive evaluation of production needs, material specifications, automation requirements, and long-term operational costs. After assessing various suppliers, machine types, and technological features, it is evident that selecting a reliable, energy-efficient, and scalable solution is crucial for maintaining high-quality welds and ensuring productivity. Factors such as electrode force, current control, duty cycle, and integration capabilities with existing manufacturing systems play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Prioritizing suppliers with strong technical support, proven industry experience, and compliance with international safety and quality standards will contribute to minimal downtime and long-term cost savings. Additionally, considering future expansion and technological advancements—such as inverter-based or robotic spot welding systems—ensures adaptability in an evolving production environment.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that balances initial investment with performance, durability, and after-sales service will lead to the successful implementation of spot welding machines, enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency and product quality.