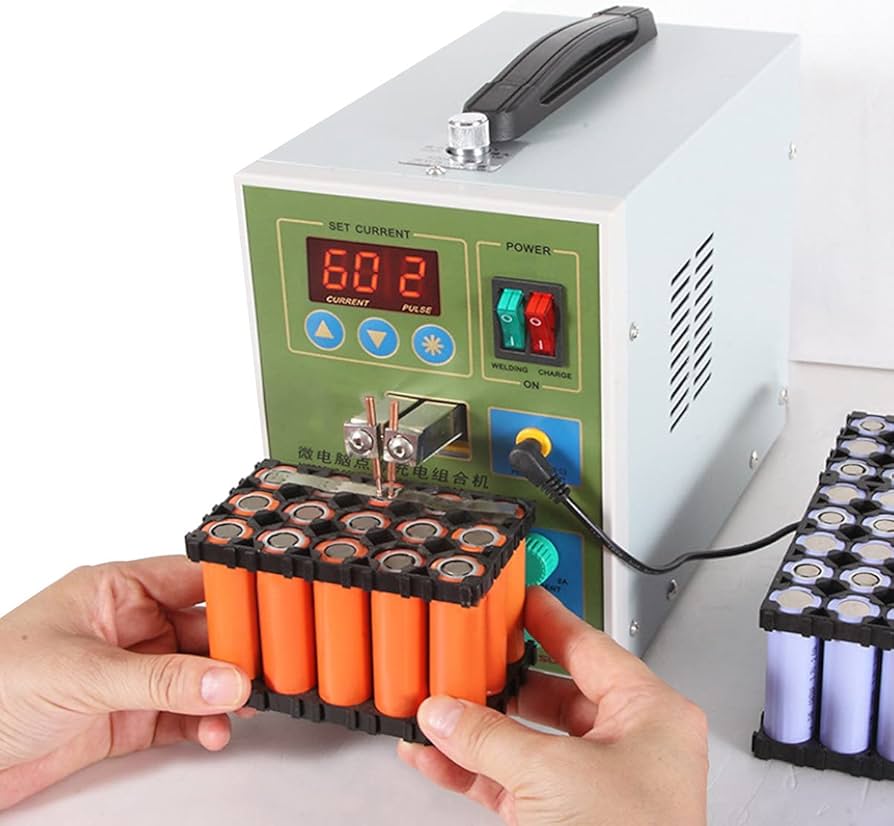
The global demand for spot welders in the battery manufacturing sector is surging, driven by the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy storage markets. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global spot welder market was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% through 2029, with battery pack assembly representing one of the fastest-growing application segments. This growth is fueled by the increasing production of lithium-ion batteries, which require high-precision, repeatable welding processes for cell interconnection—particularly in nickel and copper tab welding. As battery manufacturers scale up production to meet EV OEM demands, the need for reliable, automated, and energy-efficient spot welders has become mission-critical. In this evolving landscape, selecting the right equipment can significantly impact production throughput, weld quality, and long-term operational costs. Here’s a data-driven look at the top nine spot welders shaping efficiency and performance in modern battery manufacturing facilities worldwide.
Top 9 Spot Welder For Battery Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 spot
Website: powerstream.com
Key Highlights: The welder can be operated on standard household voltage and powers. Battery manufacturers require spot welders for tab welding and battery pack assembly….
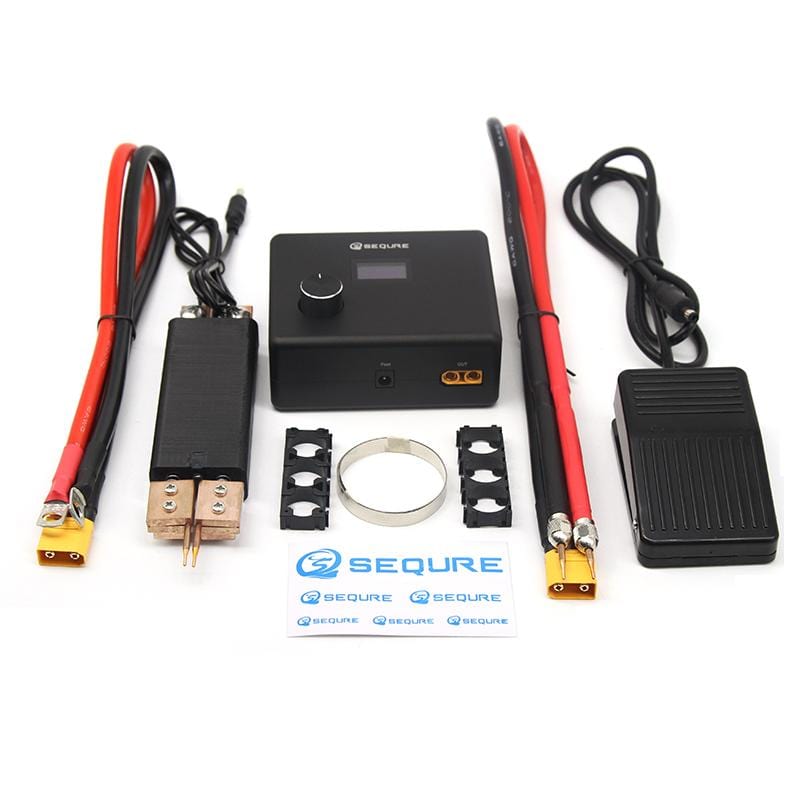
#2 Mini Intelligent DIY Spot Welder OLED Automatic Manual Switching …
Domain Est. 2019
Website: sequremall.com
Key Highlights: Out of stock Rating 5.0 (19) SQ-SW1 is battery powered, OLED display can show high and low voltage warnings. Using the new spot welding technology, and intelligently switching au…
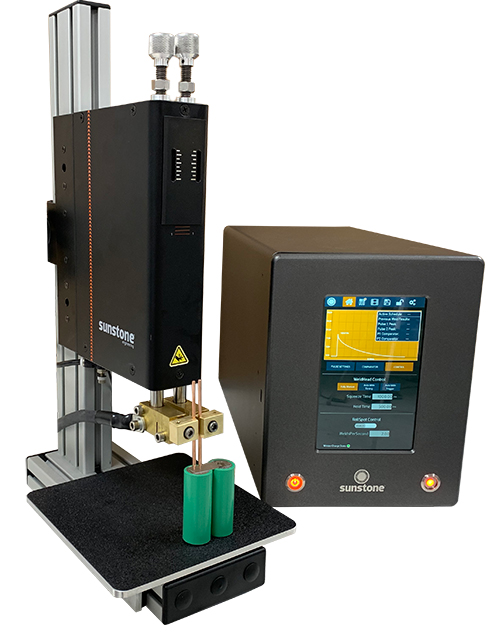
#3 Sunstone Welders
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
#4 Battery Spot Welder
Domain Est. 2010
Website: ussolid.com
Key Highlights: Out of stock Rating 4.5 (2) Product Features The newly designed U.S. Solid USS-BSW00006 high-frequency inversion battery spot welder equips with the two super capacitors for ener…
#5 The Hybrid Welding Station
Domain Est. 2011
Website: ai-mfg.com
Key Highlights: The Hybrid Welding Station is a groundbreaking, patented, OE Accepted**, DC battery-based spot welder has demonstrated itself to be a cost-effective, robust ……
#6 Electroweld Pedal Operated Battery Tab Spot Welder 5KVA (BSP
Domain Est. 2014
Website: electroweld.com
Key Highlights: Electroweld Pedal Operated Battery Tab Spot Welder 5KVA (BSP-5). Regular price $552.00. Prices include Shipping to destination port (Via CIF-named port of ……
#7 battery
Domain Est. 2016
Website: tmaxcn.com
Key Highlights: Tmax Battery Equipments Limited. offers an extensive range of high quality Battery Spot Welder and much more. Please visit: www.tmaxcn.com….
#8 Battery Industry
Domain Est. 2019
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: For each battery spot welding application and type of battery manufactured, AMADA WELD TECH offers a production solution: resistance welding, laser welding, ……
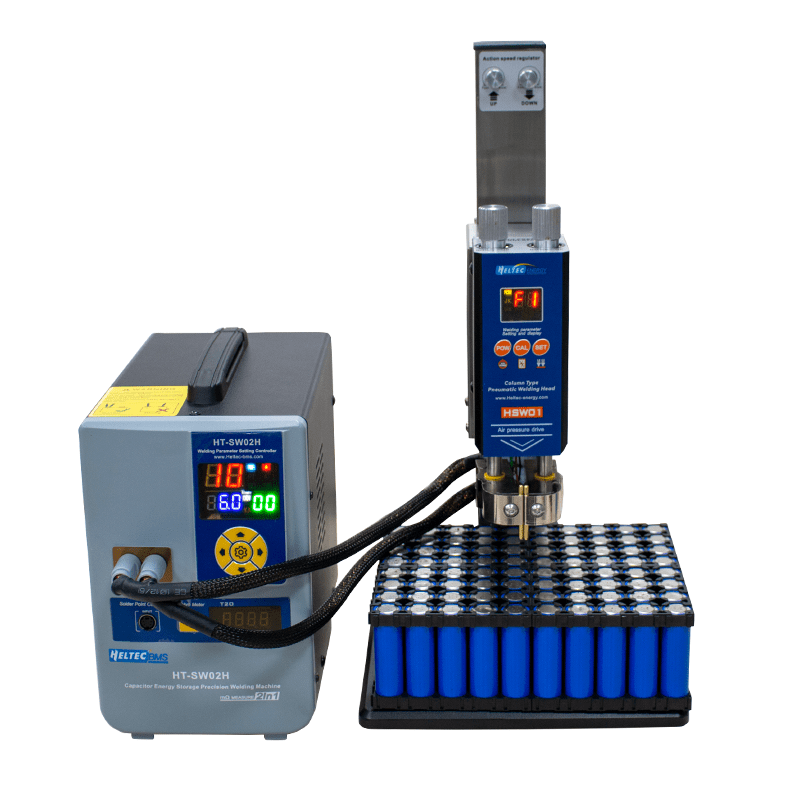
#9 High
Domain Est. 2023
Website: heltec-energy.com
Key Highlights: Designed with precision and efficiency in mind, this mini spot welder is perfect for welding batteries in various applications. Whether you are involved in DIY ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Spot Welder For Battery
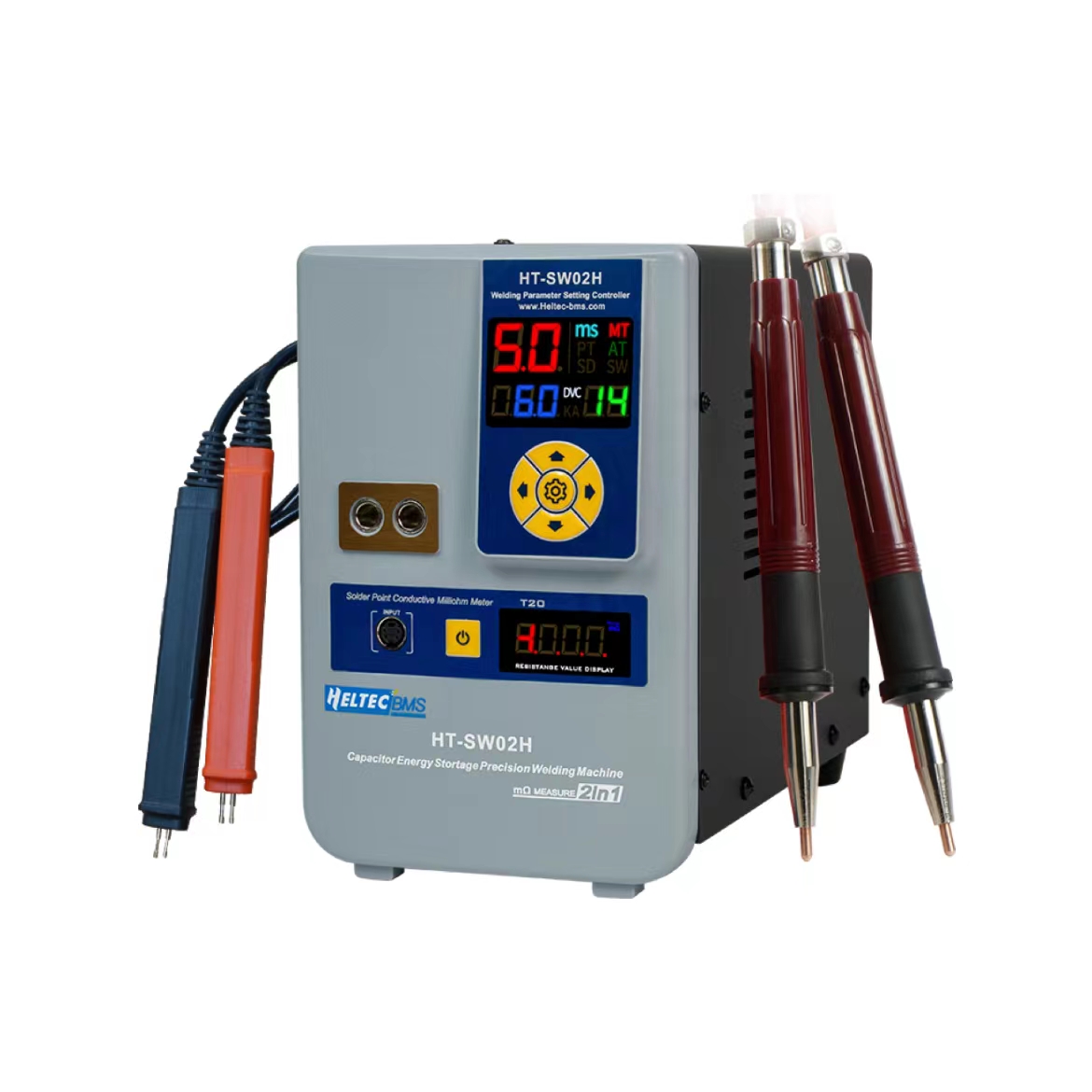

2026 Market Trends for Spot Welder for Battery
Rising Demand from Electric Vehicle and Energy Storage Sectors
The global market for spot welders for battery applications is projected to experience significant growth by 2026, primarily driven by the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle (EV) and renewable energy storage industries. As automakers worldwide accelerate their transition to electric mobility, the demand for high-precision, reliable battery manufacturing equipment—especially resistance spot welding systems—continues to surge. Battery packs in EVs require thousands of individual cell interconnections, and spot welding remains the dominant method for joining nickel, copper, and aluminum tabs due to its speed, consistency, and low heat impact.
Advancements in Automation and Smart Welding Technologies
By 2026, spot welders for battery manufacturing are increasingly integrating advanced automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Manufacturers are adopting fully automated welding cells equipped with real-time monitoring, adaptive control systems, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These smart welding solutions improve weld quality, reduce defects, and enhance process traceability—critical factors in meeting the stringent safety and performance standards of battery production. Integration with Industry 4.0 platforms enables seamless data exchange between welding equipment and manufacturing execution systems (MES), supporting mass customization and higher throughput.
Shift Toward High-Precision and Low-Damage Welding
As battery cell designs become more compact and energy-dense, the need for high-precision, low-thermal-impact welding grows. In 2026, market trends show a strong preference for mid-frequency direct current (MFDC) and capacitor discharge (CD) spot welders, which offer finer control over weld parameters and minimize spatter and electrode wear. Innovations such as servo-controlled welding heads and closed-loop feedback systems are becoming standard, allowing sub-millimeter accuracy and consistent weld strength—essential for maintaining the integrity of sensitive battery materials.
Regional Manufacturing Expansion and Supply Chain Localization
Geopolitical dynamics and supply chain resilience are shaping regional market trends. North America and Europe are investing heavily in localized battery gigafactories to support domestic EV production, driving demand for spot welding equipment. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, South Korea, and Japan—remains the largest market, benefiting from established battery manufacturing ecosystems. Equipment suppliers are responding by expanding regional service networks and offering modular, scalable welding solutions tailored to local production scales and regulatory requirements.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency in Equipment Design
Environmental considerations are influencing equipment design. By 2026, energy-efficient spot welders with lower power consumption and reduced cooling requirements are gaining favor. Manufacturers are prioritizing eco-friendly materials, recyclable components, and longer equipment lifecycles. Additionally, the push for green manufacturing is encouraging the adoption of welding systems compatible with sustainable battery chemistries, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and solid-state batteries, which may require modified welding parameters and electrode technologies.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation Drivers
The competitive landscape is evolving, with established industrial equipment providers competing against specialized battery-focused technology firms. Key players are investing in R&D to differentiate through software integration, remote diagnostics, and customizable welding profiles. Strategic partnerships between welding equipment manufacturers and battery cell producers are accelerating innovation, leading to application-specific solutions that improve yield rates and reduce total cost of ownership.
In summary, the 2026 market for spot welders in battery applications is characterized by technological sophistication, automation, and alignment with the global energy transition. As battery production scales to meet future demand, spot welding technology will continue to play a pivotal role in ensuring quality, efficiency, and scalability across the value chain.
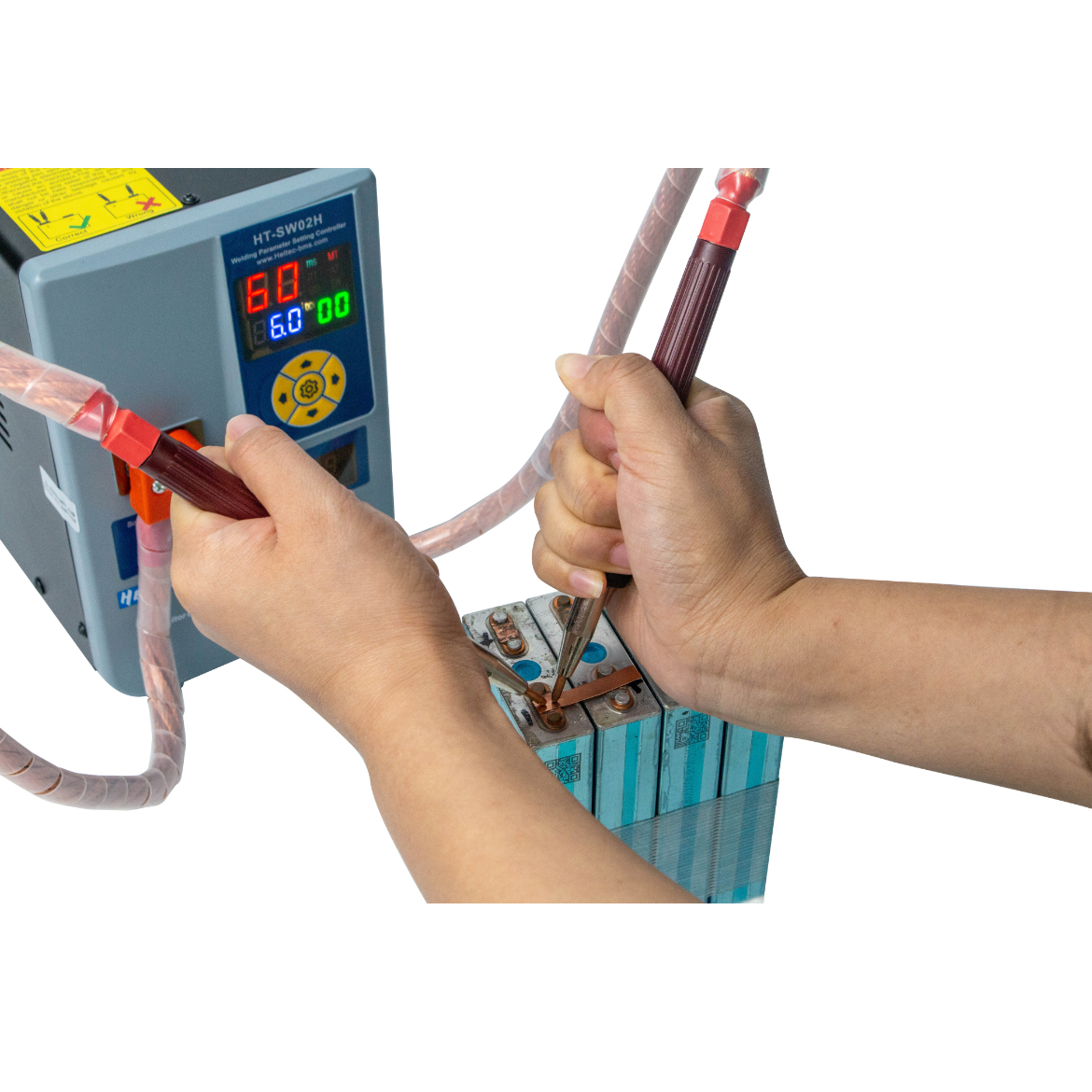

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Spot Welder for Battery Applications (Quality & IP Considerations)
Sourcing a spot welder for battery manufacturing—especially for lithium-ion cells—requires careful evaluation beyond basic functionality. Overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to production delays, safety risks, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Weld Quality and Process Consistency
Many low-cost or poorly engineered spot welders fail to deliver consistent, high-integrity welds essential for battery safety and performance. Inconsistent weld strength can result in cell damage, internal short circuits, or reduced battery life. Watch out for machines lacking real-time monitoring, feedback control, or precise current/voltage regulation. Without robust process validation (e.g., weld tear testing, resistance monitoring), you risk undetected weld defects that compromise pack reliability.
Inadequate Ingress Protection (IP) Rating for Industrial Environments
Battery production environments often involve coolant splashes, metal particulates, and humidity. Using a spot welder with insufficient IP rating (e.g., less than IP54) exposes sensitive electronics to contamination and short circuits. Ensure the welder’s control units, transformers, and cabling are appropriately sealed. An IP65-rated enclosure, for example, provides dust-tight protection and resistance to water jets, crucial for maintaining uptime and safety in cleanroom or high-humidity settings.
Hidden IP Risks from Copycat or Reverse-Engineered Equipment
Some suppliers offer spot welders that mimic branded models but infringe on patented technologies—such as waveform control algorithms, electrode force mechanisms, or safety interlocks. Purchasing such equipment exposes your company to third-party IP litigation. Always verify the manufacturer’s design ownership, request documentation of licensed technologies, and avoid vendors unwilling to provide transparency about their engineering sources.
Lack of Traceability and Data Logging Capabilities
Modern battery production demands full process traceability for quality control and compliance (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949). Spot welders without integrated data logging—recording parameters like current, duration, resistance, and weld count per joint—hinder root cause analysis during failures. This lack of documentation can also impede certification efforts and recalls, increasing liability risks.
Insufficient Service Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality equipment can fail. Sourcing from vendors with poor after-sales support or limited regional service networks leads to extended downtime. Verify whether the supplier offers firmware updates, calibration services, and readily available spare parts—especially consumables like electrodes and insulation tips. Poor support often correlates with IP issues, as unauthorized manufacturers rarely sustain long-term service commitments.
Overlooking Safety Certification and Compliance
Battery welding involves high currents and potential fire hazards. Using non-certified equipment (e.g., lacking CE, UL, or relevant regional safety marks) risks non-compliance with workplace safety regulations. Certified welders integrate safety features like emergency stop circuits, overcurrent protection, and interlocked guards. Ensure the equipment meets international standards such as IEC 60204-1 for machinery safety.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, you can select a spot welder that ensures reliable, safe, and legally sound battery production.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Spot Welders Used in Battery Manufacturing
Overview
Spot welders are critical equipment in battery production, particularly for joining battery cells, tabs, and busbars in lithium-ion and other rechargeable battery systems. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure safety, operational efficiency, and adherence to international regulations throughout the supply chain.
International Shipping & Transportation
Transporting spot welders—especially those designed for battery manufacturing—requires careful planning due to their electrical components, weight, and potential inclusion of hazardous materials (e.g., capacitors). Key considerations include:
- Packaging: Use robust, moisture-resistant, and shock-absorbent packaging with protective foam or crating. Secure internal components to prevent movement during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”) and include product identifiers, model numbers, and serial numbers.
- Modes of Transport: Evaluate suitability of air, sea, or ground freight based on size, urgency, and destination. Air freight is faster but more costly; sea freight is economical for large units.
- Export Documentation: Prepare commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and export declarations. Ensure Harmonized System (HS) codes are correctly assigned (e.g., 8515.21 for resistance welding machines).
Regulatory Compliance
Spot welders used in battery manufacturing must comply with safety and performance standards in both origin and destination countries.
- Electrical Safety Standards:
- IEC 60204-1: Safety of machinery – Electrical equipment of machines.
- UL 508A (North America): Standard for industrial control panels.
- CE Marking (Europe): Compliance with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU).
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
- IEC 61326-1: EMC requirements for electrical equipment used in industrial environments.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance:
- Ensure materials used in construction (e.g., wiring, insulation, coatings) are free from restricted substances (lead, cadmium, etc.) per EU RoHS and REACH regulations.
- Battery-Specific Standards:
- Although the welder itself isn’t a battery, its use in battery assembly may require alignment with UN 38.3-related safety protocols in manufacturing environments, particularly regarding spark control and grounding.
Import Requirements by Region
Different markets have specific import regulations for industrial equipment:
- United States:
- FCC certification for electromagnetic interference (if applicable).
- Compliance with OSHA workplace safety standards.
- No NRTL (Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory) certification may be required depending on state regulations (e.g., UL listing via Intertek or TUV).
- European Union:
- CE marking with technical file, EU Declaration of Conformity, and involvement of a Notified Body if required.
- Compliance with the EU Machinery Regulation (EU) 2023/1230 (upcoming replacement for 2006/42/EC).
- China:
- CCC (China Compulsory Certification) may apply depending on power specifications and end-use.
- GB standards alignment (e.g., GB 5226.1 for electrical safety).
- Southeast Asia & Other Regions:
- Verify local requirements; some countries accept CE or UL marks, while others require local certifications (e.g., PSE in Japan, KC in South Korea).
Customs Clearance & Duties
- Provide accurate product classification (HS Code: typically 8515.21.00 for spot welders).
- Be prepared for customs inspections, especially for electrical machinery.
- Calculate and budget for import duties, VAT, and potential anti-dumping taxes based on country of origin.
- Use Incoterms® clearly (e.g., FOB, DDP) to define responsibilities between buyer and seller.
Installation & On-Site Compliance
Upon delivery, ensure:
– Equipment is installed by qualified personnel following manufacturer guidelines.
– Proper grounding and electrical supply compatibility (voltage, frequency, phase).
– Integration with facility safety systems (e.g., emergency stop circuits, interlocks).
– Training for operators on safe operation and maintenance, per OSHA or local occupational health and safety regulations.
Environmental & End-of-Life Considerations
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive guidelines in the EU for disposal or recycling.
- Ensure recyclable materials (metals, wiring) are separated and handled by certified e-waste processors.
- Avoid landfill disposal of components containing hazardous substances.
Summary
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of spot welders for battery manufacturing involves coordinated attention to international shipping standards, regional regulatory requirements, and safe handling practices. Proactive documentation, certification, and adherence to safety protocols ensure smooth operations and legal compliance across global markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Spot Welder for Battery Manufacturing or Assembly
After evaluating various factors such as welding quality, consistency, automation capabilities, cost, and compatibility with battery materials (e.g., nickel, copper, or aluminum tabs on Li-ion or NiMH cells), sourcing the right spot welder is critical for ensuring reliable and safe battery pack assembly. Both manual and automated resistance spot welding systems have their place, depending on production volume and precision requirements.
For low to medium-scale operations, a pulse-type spot welder with adjustable current, pulse duration, and dual-transformer design offers a cost-effective and flexible solution. High-volume or industrial applications benefit significantly from fully automated systems with electrode monitoring, real-time feedback, and integration into production lines for improved repeatability and throughput.
Key considerations when sourcing include electrode material and tip design, power supply stability, maintenance requirements, and safety certifications. Investing in a reputable brand with technical support and spare parts availability ensures long-term reliability.
In conclusion, selecting a spot welder tailored to your specific battery cell type and production goals will enhance welding consistency, improve battery pack performance, reduce failure rates, and ultimately support the overall quality and safety of the end product. Proper sourcing today lays the foundation for scalable, efficient, and compliant battery assembly processes tomorrow.