The global split phase motor market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across household appliances, HVAC systems, and industrial equipment. According to Grand View Research, the global single-phase induction motor market—of which split phase motors are a key subset—was valued at USD 13.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 4.8% for the broader single-phase motor market during the forecast period of 2024–2029, fueled by increasing automation, energy efficiency regulations, and the proliferation of consumer electronics. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining precision engineering, scalable production, and innovation to dominate supply chains worldwide. The following list highlights the top 8 split phase motor manufacturers shaping this evolving landscape.
Top 8 Split Phase Motor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Leading Split Phase Electric Motor Manufacturer in China
Domain Est. 2023
Website: dagaomotors.com
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer and factory in China, we specialize in producing high-quality split phase electric motors that are both efficient and powerful….
#2 Split
Domain Est. 1994
Website: grainger.com
Key Highlights: Keep things running smoothly with a magnet motor or save money with an energy-efficient, three-phase motor. Shop Grainger today for all general-purpose ……
#3 Single phase Motor
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mitsubishielectric.com
Key Highlights: The Mitsubishi Electric Single-Phase Induction Motors are designed with versatility and user-centric innovation in mind. Developed to meet a wide range of ……
#4 Shop Electric AC Motors From Bodine Electric Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bodine-electric.com
Key Highlights: 3-day deliveryBodine manufactures four basic types of AC motors: · Permanent split capacitor (PSC) gear motors require a continuous-duty, motor run-capacitor to provide ……
#5 Split Phase
Domain Est. 1999
Website: blowerwheel.com
Key Highlights: Electric Motor – Split Phase – AO Smith – F501 -1/2 hp 1725 rpm 115 volts. $367.59. Add to Cart. Standard Lead Time Applies….
#6 Split phase induction motor
Domain Est. 2013
Website: sogears.com
Key Highlights: Split phase induction motor generally refers to the single-phase ac power supply (AC220V) supply of small power Split phase induction motor….
#7 Split Phase Motors
Domain Est. 2015
#8 LEESON Brand
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: The LEESON band spans thousands of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors, gearmotors, washdown and variable-speed control solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Split Phase Motor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Split Phase Motors
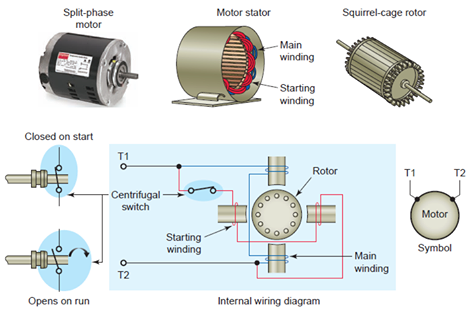
The split phase motor market in 2026 is characterized by a complex interplay of declining demand in traditional applications, driven by regulatory and technological shifts, alongside resilience and niche growth in specific segments. While facing significant headwinds from energy efficiency mandates and competition from more advanced motor types, split phase motors maintain a foothold due to their inherent simplicity, reliability, and low cost in applications where high starting torque or variable speed is not critical.
Key Trends Shaping the 2026 Market:
-
Continued Pressure from Energy Efficiency Regulations: Global standards (like IE3/IE4 minimum efficiency levels mandated in many regions) remain the dominant force. Split phase motors, typically classified as IE1 or low IE2, are increasingly non-compliant for new equipment in regulated sectors. This accelerates their replacement by higher-efficiency alternatives like Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motors, Electronically Commutated Motors (ECMs/BLDC), or IE2+ induction motors, particularly in HVAC, appliances, and industrial fans/pumps.
-
Stagnation and Decline in Core Applications: Major end-use markets show limited growth or contraction for split phase motors:
- Appliances: Washing machines, dryers, and some older refrigerator models are rapidly shifting to PSC or direct-drive inverter motors for better efficiency and performance. Split phase use is largely confined to lower-cost or replacement parts.
- HVAC: Furnace blowers and basic air handlers are overwhelmingly moving to high-efficiency PSC or ECM motors. Split phase motors are rare in new installations.
- Industrial Fans & Pumps: Efficiency regulations push adoption of IE2+ induction motors or variable speed drives, reducing split phase market share.
-
Resilience in Niche and Cost-Sensitive Applications: Despite pressures, the market persists due to key advantages:
- Low Cost & Simplicity: Unmatched low upfront cost and simple construction make them ideal for price-sensitive consumer goods and basic industrial tools where high efficiency isn’t paramount.
- Reliability & Robustness: Proven design with fewer failure points (no starting switch in some variants, simpler windings) ensures longevity in non-demanding applications.
- Specific Applications: They remain relevant in:
- Small Power Tools: Bench grinders, small drill presses, sanders.
- Basic Compressors: Smaller air compressors.
- Conveyors: Low-power, constant-speed lines.
- Agricultural Equipment: Some irrigation pumps, feed mixers.
- Replacement Market: Significant demand exists for replacing failed motors in older equipment still in service globally.
-
Geographic Market Divergence: The trend impact varies significantly:
- Developed Markets (North America, EU, Japan): The decline is most pronounced due to strict regulations and faster technology adoption. The market is primarily replacement and niche industrial.
- Developing Markets (Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Africa): Slower regulatory enforcement and higher sensitivity to initial cost sustain a larger market share. Split phase motors are still common in new, lower-cost appliances and industrial machinery, though the transition to PSC is accelerating.
-
Competition from PSC Motors: The primary competitor is the Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor. While slightly more expensive due to the run capacitor, PSC motors offer higher efficiency (typically IE2), smoother operation, less noise, and no centrifugal switch (reducing failure points). This makes PSC the dominant choice for most new applications where a single-phase induction motor is suitable, further squeezing the split phase market.
Outlook for 2026:
The 2026 split phase motor market is one of managed decline in volume within developed economies but sustained relevance through cost leadership and niche applications globally. Overall market growth is expected to be flat or slightly negative in volume terms, potentially showing modest nominal growth only due to inflation or specific regional industrial activity. The focus for manufacturers is shifting towards:
- Cost Optimization: Further reducing manufacturing costs to maintain competitiveness.
- Replacement Market Focus: Catering to the vast installed base of older equipment.
- Niche Application Development: Targeting specific industrial and agricultural segments where their simplicity and cost are decisive.
- Geographic Targeting: Focusing sales efforts on regions with less stringent regulations or higher price sensitivity.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the split phase motor is firmly established as a legacy technology in many high-volume applications, displaced by more efficient alternatives driven by regulation and performance demands. However, its fundamental advantages of low cost, simplicity, and reliability ensure it will not disappear. The market evolves into a specialized segment, serving cost-driven applications, specific industrial needs, and the critical replacement market, particularly in developing regions. Success for split phase motor manufacturers depends on operational efficiency and strategic focus on these resilient niches.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Split Phase Motors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing split phase motors—especially with attention to quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings—can present several challenges. Overlooking these pitfalls may lead to performance issues, premature failure, or safety hazards. Below are key concerns to consider:
Inadequate Quality Control from Suppliers
Many low-cost manufacturers, particularly in regions with less stringent oversight, may lack robust quality assurance processes. This can result in inconsistent winding techniques, substandard insulation materials, or poor bearing assembly. Without proper documentation or third-party certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), buyers risk receiving motors with short lifespans or unreliable performance under load.
Misrepresentation of IP Ratings
IP (Ingress Protection) ratings are often inaccurately claimed by suppliers. A motor advertised as IP54 or higher may not have been tested in accredited labs, leading to vulnerability to dust and moisture. This is especially problematic in industrial or outdoor environments where protection against contaminants is critical. Always request test reports or certification from recognized bodies to verify IP claims.
Use of Inferior Materials
To cut costs, some manufacturers substitute high-grade copper windings with aluminum or use lower-temperature-rated insulation. This reduces motor efficiency, increases heat generation, and shortens operational life. Similarly, low-quality bearings or housings may fail prematurely under continuous duty cycles.
Lack of Compliance with Regional Standards
Split phase motors must meet regional electrical and safety standards (e.g., UL in North America, CE in Europe, CCC in China). Sourcing motors without proper certification can lead to legal issues, voided insurance, or installation rejections. Ensure the motor complies with the target market’s regulatory requirements.
Insufficient Thermal and Load Testing Data
Reliable performance data—such as temperature rise under full load, duty cycle tolerance, and starting torque—is often missing or incomplete. Without this, it’s difficult to assess whether the motor will perform reliably in the intended application, especially in high-ambient-temperature environments.
Poor Documentation and Traceability
Inadequate datasheets, missing wiring diagrams, or lack of serial traceability can complicate installation, maintenance, and warranty claims. Reputable suppliers should provide comprehensive technical documentation and support.
Supply Chain and Lead Time Risks
Relying on single-source or distant suppliers may expose buyers to long lead times and logistical disruptions. This can delay production or maintenance schedules. Establishing relationships with multiple qualified vendors and verifying production capacity helps mitigate this risk.
By carefully vetting suppliers, demanding verifiable certifications, and validating technical specifications, buyers can avoid these common pitfalls and ensure reliable, long-term performance from split phase motors.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Split Phase Motors
Overview
Split phase motors are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability in single-phase power systems. Ensuring proper logistics handling and regulatory compliance is essential for safe transportation, import/export, and end-use installation. This guide outlines key considerations across the supply chain.
Packaging and Handling
- Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., corrugated cardboard with internal foam or wooden crates) to protect the motor from physical damage and environmental exposure.
- Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and motor specifications (voltage, RPM, horsepower).
- Avoid stacking excessive weight on packaged motors to prevent housing deformation or internal component damage.
- Handle with care using appropriate lifting equipment—avoid dragging or dropping.
Storage Conditions
- Store motors in a clean, dry, and temperature-controlled environment (ideally 10°C to 35°C or 50°F to 95°F).
- Keep motors away from dust, moisture, and corrosive chemicals to prevent insulation degradation and bearing contamination.
- If stored long-term, rotate shafts periodically (every 3–6 months) to prevent bearing brinelling.
Transportation
- Secure motors in transit using straps or dunnage to prevent shifting during road, rail, or sea transport.
- For international shipments, comply with IATA (air) or IMDG (sea) regulations—though split phase motors are generally non-hazardous, verify classification based on components (e.g., lubricants).
- Use climate-controlled containers when transporting through extreme climates to prevent condensation.
Import/Export Compliance
- Verify customs classification using the Harmonized System (HS) Code—typically 8501.40 for AC motors under 750W or 8501.31/32 for higher outputs.
- Obtain necessary documentation: commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin.
- Comply with destination-country energy efficiency standards (e.g., DOE in the U.S., MEPS in Australia, Ecodesign in the EU).
- Confirm compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH regulations for materials used in motor construction.
Electrical and Safety Standards
- Ensure motors meet regional safety certifications:
- UL or CSA (North America)
- CE (Europe, including Low Voltage and EMC Directives)
- CCC (China)
- ISI Mark (India)
- Verify insulation class (e.g., Class B or F) and duty cycle match application requirements.
- Motors must comply with applicable efficiency standards (e.g., IE2 minimum under IEC 60034-30 for many regions).
Labeling Requirements
- Permanent nameplate must include:
- Manufacturer name and model number
- Voltage, frequency, phase (single-phase)
- Horsepower or kilowatt rating
- Full load amperage (FLA)
- RPM and duty cycle
- Insulation class and IP (Ingress Protection) rating
- Safety certification marks (e.g., UL, CE)
End-of-Life and Environmental Compliance
- Follow WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions for proper disposal or recycling.
- Motors may contain recyclable materials (copper windings, steel housing); coordinate with certified e-waste handlers.
- Avoid landfill disposal; separate hazardous components (e.g., capacitors) per local regulations.
Documentation and Record Keeping
- Maintain compliance records, test reports, and certificates for a minimum of 5–10 years depending on jurisdiction.
- Provide user manuals with installation, operation, and maintenance instructions in the local language(s) of the destination market.
Summary
Proper logistics and compliance management for split phase motors ensures product integrity, regulatory adherence, and safe operation. Adhering to packaging, handling, transportation, and certification standards minimizes risks and supports global market access.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Split-Phase Motor
In conclusion, sourcing a split-phase motor requires a thorough evaluation of application requirements, performance specifications, and environmental conditions. These motors are widely used in applications such as fans, blowers, pumps, and small compressors due to their simple design, cost-effectiveness, and reliable starting torque for light-duty tasks. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to consider factors such as motor efficiency, durability, availability of spare parts, compliance with industry standards (e.g., NEMA or IEC), and technical support.
Sourcing from reputable manufacturers or certified distributors ensures product quality and long-term reliability. Additionally, evaluating total cost of ownership—rather than just initial price—helps in making an informed decision that balances performance and cost. With proper selection and sourcing strategy, a split-phase motor can provide efficient and dependable operation for a wide range of single-phase AC applications.