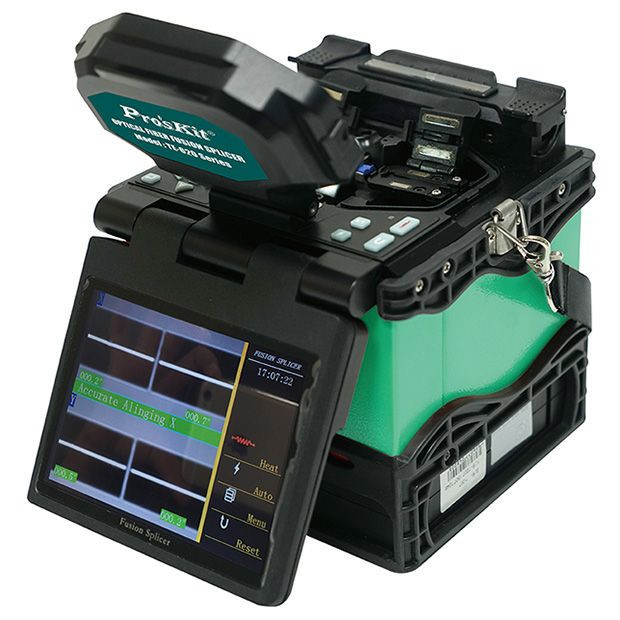
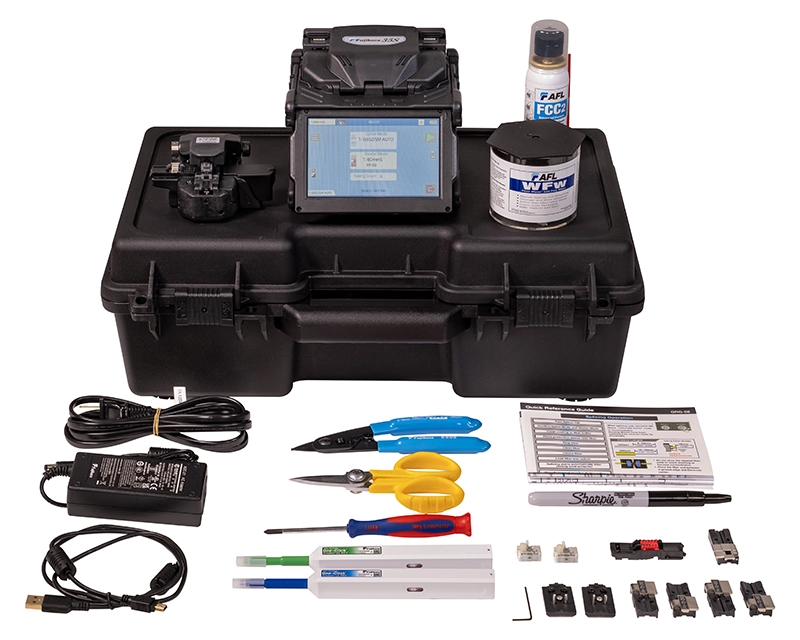
The global splicing machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across industries such as telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 1.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2028. This expansion is fueled by increasing investments in fiber optic infrastructure, stringent quality standards in manufacturing, and the growing need for reliable, high-precision joining technologies. Grand View Research further underscores this momentum, citing advancements in automation and the integration of IoT in splicing equipment as key drivers reshaping the competitive landscape. As industries prioritize efficiency and minimal signal loss in connectivity solutions, the role of innovative splicing machine manufacturers becomes increasingly critical. Below, we examine the top eight manufacturers leading this evolution through technological excellence, global reach, and strong R&D capabilities.
Top 8 Splicing Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 MADE IN JAPAN Fusion Splicers Supplied throughout the World
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sumitomoelectric.com
Key Highlights: The Sumitomo Electric Group is working on the establishment of a fusion splicing technology adaptable to all types of optical fiber….
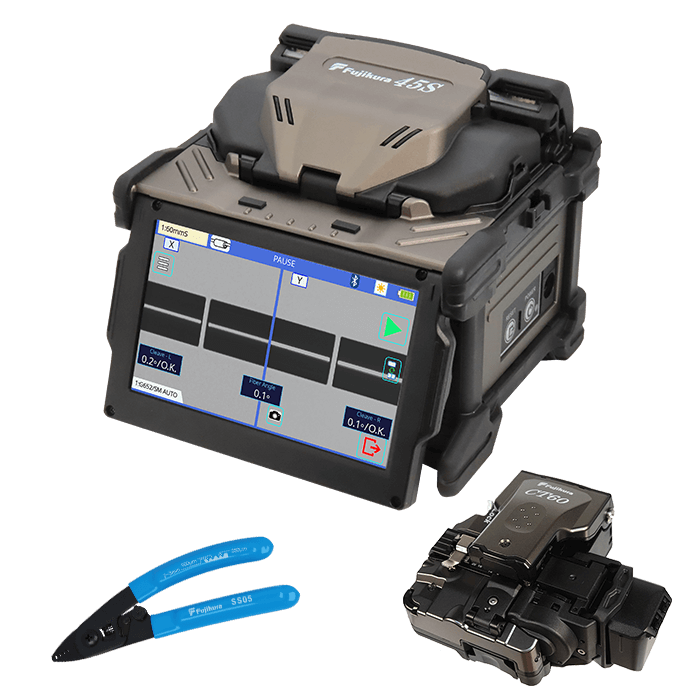
#2 Fujikura Fusion Splicing Systems
Domain Est. 2008
Website: aflglobal.com
Key Highlights: Superior technology, proven reliability and extraordinary service make Fujikura the world leader in fusion splicing products….
#3 Fiber Fusion Splicers,Fiber Optic Cleavers,Fiber Optical Equipment …
Domain Est. 2012
Website: xhfiber.com
Key Highlights: Professional manufacturer of various fusion splicers,fiber cleavers,OTDR and related fiber test equipment,as well as fiber tools….
#4 Fusion Splicer
Domain Est. 2014
Website: signalfiresplicer.com
Key Highlights: Factory Address: Building 18, Chengdu Hi-Tech International Enterprise Park. Liando U Valley,1111 Changsheng Bridge, Pidu District, Chengdu China Tel: (+86) ……
#5 Fusion Splicer Solutions, Tools, and Equipment
Domain Est. 2002
Website: ofsoptics.com
Key Highlights: Fusion splicer solutions for professionals. Highly accurate splicers to all fiber optic cable types. OFS is the official support center of Fitel splicers….
#6 Fusion Splicers|Sumitomo Electric(US)
Domain Est. 2009
Website: global-sei.com
Key Highlights: Fusion splicers, fiber cleavers and other accessories are introduced on the website of Sumitomo Electric. Sumitomo Electric’s fusion splicers product ……
#7 Fiberfox America
Domain Est. 2016
Website: fiberfoxamerica.com
Key Highlights: Accessories. Fusion Splicer. The Smallest and the Lightest Ribbon Fiber Fusion Splicer. Size: 4.8 x 4.88 x 5.4 (in). Weight: 3.8 lbs. (w/o battery). Fastest ……
#8 Fusion Splicer Solutions
Domain Est. 2018
Website: sumitomoelectriclightwave.com
Key Highlights: When it comes to optical fiber fusion splicers, no other company in the world can match Sumitomo Electric Lightwave for innovation, speed, and performance….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Splicing Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Splicing Machines
The global splicing machine market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and sustainability imperatives. Key trends shaping the market include:
1. Automation and Smart Integration: The integration of splicing machines with Industry 4.0 technologies will accelerate. By 2026, expect widespread adoption of IoT-enabled machines with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics. AI-driven optimization of splice parameters will enhance consistency and reduce waste, particularly in high-volume sectors like paper, textiles, and film.
2. Demand for High-Speed and Precision: Industries such as flexible packaging, nonwovens, and advanced materials will demand splicing systems capable of ultra-high speeds (>1,000 m/min) with micron-level accuracy. Automated tapeless splicing (e.g., butt splicing, ultrasonic welding) will gain traction to minimize material loss and improve product quality.
3. Sustainability-Driven Innovation: Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals will push manufacturers toward energy-efficient machines and waste-reducing technologies. Splicers designed for lightweight materials, recyclable substrates, and minimal adhesive/tape usage will see increased adoption. Closed-loop systems that recover and reuse splicing byproducts may emerge.
4. Customization and Modular Design: As end-user applications diversify (e.g., EV battery films, medical textiles), demand will grow for modular splicing solutions. OEMs will offer configurable platforms adaptable to niche materials and production line layouts, reducing downtime during changeovers.
5. Growth in Emerging Applications: Beyond traditional paper and textiles, splicing machines will expand into high-growth sectors:
– Renewable Energy: Splicing of solar panel backsheets and battery separator films.
– E-Mobility: Precision joining of lightweight composites and insulation materials.
– Biomedical: Sterile splicing for wound care and wearable sensors.
6. Regional Shifts: Asia-Pacific (especially China, India, and Southeast Asia) will remain the largest market due to manufacturing expansion. However, North America and Europe will see steady growth driven by automation upgrades in aging industrial infrastructure and reshoring initiatives.
7. Consolidation and Service Ecosystems: Market consolidation among key players (e.g., Fife, Tidland, Montalvo) will intensify. Competition will shift from hardware alone to integrated service offerings—cloud-based analytics, training, and performance-based maintenance contracts—creating recurring revenue streams.
By 2026, success in the splicing machine market will hinge on delivering intelligent, sustainable, and application-specific solutions that enhance operational efficiency across diverse global industries.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Splicing Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
When sourcing splicing machines—especially from international or less-regulated markets—buyers often encounter significant challenges related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Recognizing these pitfalls early can prevent costly delays, legal complications, and operational inefficiencies. Below are key issues to watch for:
Poor Build Quality and Component Sourcing
Many low-cost splicing machines use substandard materials and inferior components to cut production costs. This often results in premature wear, frequent breakdowns, and inconsistent splicing performance. Critical parts such as electrodes, alignment mechanisms, and control systems may lack precision, directly impacting splice loss and long-term reliability. Buyers may find that machines fail to meet advertised specifications, especially under continuous operation.
Inadequate Calibration and Testing Procedures
Reputable manufacturers rigorously calibrate and test each unit before shipment. However, some suppliers skip or minimize these steps, leading to machines that require extensive recalibration upon arrival. This not only delays deployment but may require third-party service technicians, increasing total cost of ownership. Lack of proper factory acceptance testing (FAT) is a red flag.
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance metrics such as splice loss (e.g., claiming 0.01 dB when real-world results are closer to 0.1 dB), splice speed, or fiber compatibility. These inaccuracies are often only discovered after field testing, by which time return or warranty options may be limited or voided due to import restrictions.
Lack of Genuine Firmware and Software Licenses
Splicing machines rely on proprietary software for operation, diagnostics, and data logging. Some sourced units come with pirated, modified, or unlicensed firmware. This poses cybersecurity risks, limits access to updates, and may violate software licensing agreements. In regulated industries, using unlicensed software can lead to compliance violations.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing splicing machines that copy patented designs, user interfaces, or internal technologies exposes buyers to potential IP liability. Even if unintentional, using or importing infringing equipment can result in legal action, customs seizures, or forced decommissioning. This is especially prevalent with machines that closely mimic well-known brands but lack official distribution channels.
Voided or Non-Existent Warranty Support
Many low-cost suppliers offer limited or ambiguous warranty terms. In some cases, warranties are invalid outside the country of manufacture, or support requires returning the unit at the buyer’s expense. Lack of local technical service partners further complicates repairs, leading to extended downtime.
Absence of Compliance and Certification Documentation
Reputable splicing machines come with certifications such as CE, RoHS, or FCC, confirming compliance with safety and environmental standards. Machines lacking proper documentation may fail customs inspections or violate local regulations, leading to delays or rejection upon import.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence: verify supplier credentials, request third-party test reports, inspect units in person if possible, ensure software authenticity, and consult legal experts regarding IP and compliance. Investing in reputable brands or authorized distributors, while potentially higher upfront, often proves more cost-effective and reliable in the long run.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Splicing Machine
General Overview
Splicing machines, used in industries such as fiber optics, telecommunications, and manufacturing, require careful handling, precise shipping, and adherence to regulatory standards during transportation and operation. This guide outlines best practices for logistics and compliance to ensure safe, efficient, and legal movement and use of splicing equipment.
Packaging & Handling
Proper packaging is essential to protect sensitive components during transit. Always use the original manufacturer’s packaging or a custom-made case with internal cushioning. Secure the splicing unit, electrodes, and accessories in foam inserts to prevent movement. Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up.” Avoid exposing the machine to extreme temperatures, moisture, or dust before and during shipment.
Transportation Requirements
Use reputable carriers experienced in handling high-precision equipment. For international shipments, ensure temperature-controlled and shock-monitored transport where applicable. Complete all required shipping documentation, including commercial invoices, packing lists, and equipment specifications. Maintain chain of custody records for traceability, especially when shipping across borders.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify export control regulations based on the splicing machine’s technical specifications. Equipment with advanced optical alignment or laser technology may be subject to export restrictions under frameworks such as the Wassenaar Arrangement or national regulations (e.g., U.S. EAR or EU Dual-Use Regulation). Obtain necessary export licenses prior to shipment. For imports, comply with customs requirements, including tariff classifications (HS codes), duties, and local technical standards.
Regulatory Standards & Certifications
Ensure the splicing machine complies with relevant international and local safety and performance standards. Common certifications include:
– CE marking (for EU markets)
– FCC compliance (for U.S. electromagnetic interference)
– RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
– IEC 60825 (laser safety standards)
Maintain certification documentation for inspection and customs clearance.
Power & Environmental Requirements
Confirm local voltage, frequency, and plug types at the destination. Use transformers or adapters if necessary. Operate the splicing machine within the manufacturer-specified environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, and dust levels) to ensure performance and longevity.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain a comprehensive compliance file including:
– Equipment manuals and technical specifications
– Certificate of Conformity
– Calibration records
– Export/import licenses
– Shipping and customs documentation
Proper recordkeeping supports audits and regulatory inspections.
On-Site Compliance & Training
Upon delivery, ensure qualified personnel install and calibrate the machine according to manufacturer guidelines. Provide operator training on safety protocols, maintenance, and compliance with local workplace regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.). Document all training and maintenance activities.
Disposal & End-of-Life Management
Follow local and international regulations for the disposal of electronic waste (WEEE Directive in the EU, EPA guidelines in the U.S.). Return or recycle components such as batteries, circuit boards, and laser modules through certified e-waste handlers to meet environmental compliance standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Splicing Machine:
In conclusion, sourcing a splicing machine requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term operational needs. It is essential to identify the specific type of splicing (e.g., mechanical, heat, ultrasonic, or adhesive) that aligns with your production process and material types. After comparing various suppliers and models based on reliability, service support, energy efficiency, and automation capabilities, the selected splicing machine should enhance productivity, ensure consistent splice quality, and integrate seamlessly into existing production lines.
Additionally, considering after-sales service, training, spare parts availability, and warranty terms will contribute to minimizing downtime and maximizing return on investment. By conducting thorough research and due diligence, the chosen splicing machine will not only meet current demands but also support scalability and future growth. Ultimately, the right sourcing decision leads to improved operational efficiency, product quality, and cost savings across the manufacturing process.