The global speed control sensor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising automation across automotive, industrial, and aerospace sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global sensor market size was valued at USD 237.4 billion in 2023 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.9% from 2024 to 2030, with speed control sensors representing a critical segment due to their role in optimizing performance and energy efficiency. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the automotive speed sensor market alone to grow at a CAGR of over 7.2% through 2029, fueled by increasing demand for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles. As precision and real-time monitoring become non-negotiable in modern machinery, leading manufacturers are innovating to meet performance, durability, and integration demands. This evolving landscape has elevated the importance of reliable speed control sensor suppliers—companies that combine engineering excellence with scalable production. Below, we spotlight the top 10 speed control sensor manufacturers shaping this high-growth industry.
Top 10 Speed Control Sensor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1
Domain Est. 1997
Website: smith-systems-inc.com
Key Highlights: Smith Systems Inc. is a privately owned manufacturer of speed sensors, motion sensors and temperature sensors, as well as sensor controls, custom ……
#2 Speed sensors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: ifm.com
Key Highlights: Speed sensors are used to safely detect standstill, overspeed and underspeed of drives or belt break on conveyors.Missing: control manufacturer…
#3 Sensors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: murata.com
Key Highlights: Murata develops and manufactures high-performance inertial sensors, including accelerometers, inclinometers, and combined gyroscope-accelerometer sensors….
#4 Electro
Domain Est. 1996
Website: electro-sensors.com
Key Highlights: Electro-Sensors Rugged Speed Switches, Industrial Sensors, and Hazard Monitoring Systems. Trade Shows and Events….
#5 Custom Speed Sensor Solutions from Motion Sensors Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: motionsensors.com
Key Highlights: Motion Sensors designs and manufactures speed sensors across a variety of industries, including aerospace, rail, military, and power….
#6 Speed Sensors – Automation
Domain Est. 1988
Website: automation.honeywell.com
Key Highlights: Honeywell offers speed sensors designed for enhanced reliability and an extended life. These technologies offer the ability to detect speed, direction, or ……
#7 Sensors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: allegromicro.com
Key Highlights: Allegro’s inductive sensors deliver precision motor position sensing with unmatched configurability, enabling tailored performance for diverse applications….
#8 Piher Sensing Systems
Domain Est. 2000
Website: piher.net
Key Highlights: We are experts in contactless and contacting sensor technologies for position, tilt, speed and current measurement. With over 70 years’ experience….
#9 SSI Technologies, LLC
Domain Est. 2011
Website: ssi-sensors.com
Key Highlights: Speed and Position Sensors. SSI Technologies, LLC Sensors & Controls Division is a leader in the design, development, and manufacturing of passive (Variable ……
#10 Telemecanique Sensors
Domain Est. 2014
Website: telemecaniquesensors.com
Key Highlights: As experts in the detection industry for over a century, Telemecanique Sensors tailors its vast range of sensor products, so they will address the various ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Speed Control Sensor
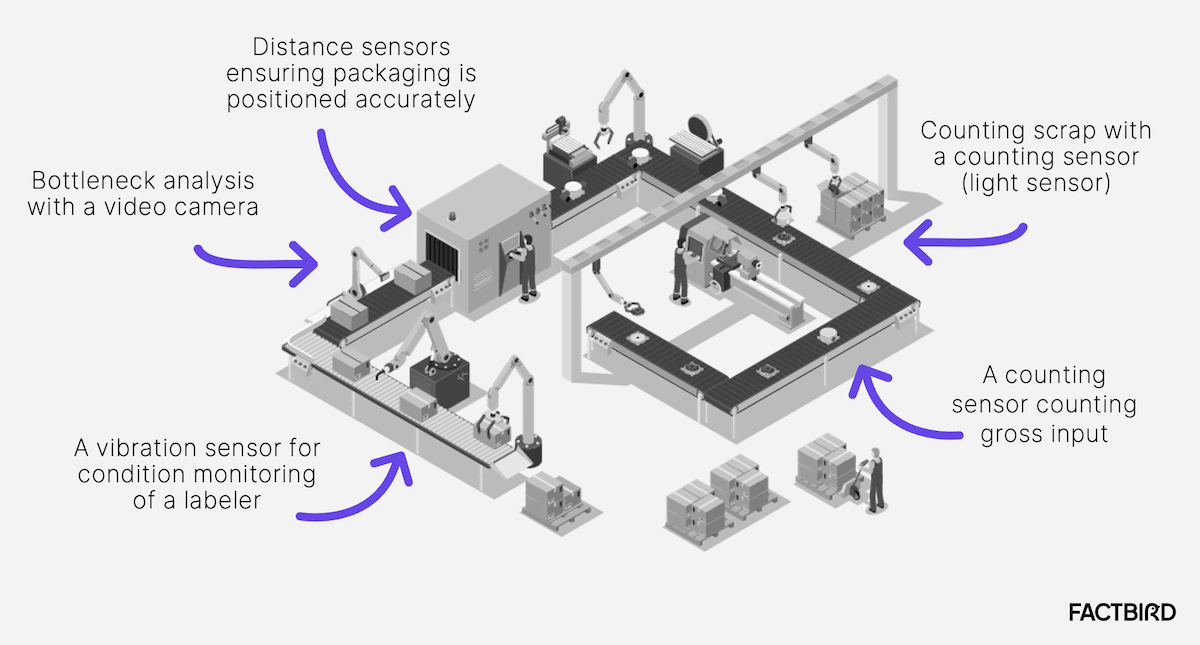
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Speed Control Sensors
The global speed control sensor market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing automation across industries, and the rising demand for energy efficiency and precision in mechanical systems. As industries continue to prioritize smart manufacturing, electric mobility, and intelligent transportation systems, speed control sensors are becoming integral components in a wide range of applications. Below are the key market trends expected to shape the speed control sensor landscape in 2026:
-
Growing Adoption in Electric and Autonomous Vehicles
The automotive sector is a major driver of demand for speed control sensors. With the global push toward electric vehicles (EVs) and the development of autonomous driving technologies, precise speed monitoring and control are critical. Speed control sensors are essential in motor control units, regenerative braking systems, and traction control. By 2026, the integration of advanced sensor systems in EVs is expected to accelerate, supported by government regulations promoting clean transportation. -
Expansion in Industrial Automation and Industry 4.0
The ongoing transition to Industry 4.0 is fueling demand for smart sensors, including speed control sensors, in manufacturing and process industries. These sensors are used in robotic arms, conveyor systems, CNC machines, and automated assembly lines to ensure optimal speed regulation and operational efficiency. The integration of IoT-enabled speed sensors allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced system reliability—key components of smart factories. -
Technological Advancements in Sensor Design
By 2026, speed control sensors are expected to feature enhanced accuracy, miniaturization, and improved durability. Innovations such as Hall-effect sensors, optical encoders, and magnetoresistive technologies are becoming more prevalent due to their non-contact operation, high resolution, and resistance to harsh environments. Additionally, the development of wireless and energy-efficient sensors will support broader deployment in remote or hard-to-access locations. -
Increased Demand in Renewable Energy Systems
Wind turbines and solar tracking systems rely heavily on speed control sensors to optimize energy output. With global investments in renewable energy infrastructure rising, the need for reliable speed sensing in variable-speed generators and motorized solar panels is expanding. This trend is expected to gain momentum through 2026, particularly in emerging markets investing in sustainable energy solutions. -
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Safety Requirements
Governments and regulatory bodies are enforcing stricter safety and performance standards in transportation and industrial machinery. This is increasing the adoption of high-precision speed control sensors to comply with safety regulations such as ISO 26262 (functional safety in automotive) and IEC 61508 (industrial systems). Sensor manufacturers are responding by developing fault-tolerant and safety-certified products. -
Regional Market Growth Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the speed control sensor market by 2026, driven by rapid industrialization in China, India, and Southeast Asia, along with strong automotive production. North America and Europe will maintain robust growth due to high adoption of automation technologies and stringent emission norms. Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East are emerging as potential growth markets due to infrastructure development and energy sector investments. -
Integration with AI and Predictive Analytics
Speed control sensors are increasingly being paired with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to enable predictive analytics. This allows systems to anticipate performance deviations, optimize speed profiles, and reduce wear and tear. By 2026, AI-integrated sensor solutions are expected to become standard in high-value applications such as aerospace, rail transport, and heavy machinery.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for speed control sensors will be characterized by innovation, diversification, and integration with digital technologies. As demand rises across automotive, industrial, energy, and transportation sectors, manufacturers must focus on scalability, reliability, and smart connectivity to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Speed Control Sensors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing speed control sensors requires careful attention to both quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these factors can lead to system failures, safety hazards, and increased lifecycle costs. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate IP Rating for Operating Environment
Selecting a sensor with an insufficient IP rating for the application environment is a frequent error. For example, using an IP65-rated sensor in a washdown or outdoor setting where high-pressure water and dust are present may result in internal contamination and premature failure. Always match the IP rating to environmental conditions—such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes—to ensure long-term reliability.
Overlooking Sensor Build Quality and Materials
Focusing solely on price or availability can lead to sourcing sensors with substandard materials or poor construction. Low-quality housings, seals, or connectors may not withstand mechanical stress or corrosive environments, even if the IP rating appears adequate. Verify the sensor’s mechanical durability, use of corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., stainless steel, robust polymers), and adherence to international quality standards (e.g., ISO, IEC).
Misinterpreting IP Ratings
A common mistake is assuming a higher first digit (solids protection) ensures protection against liquids, or vice versa. For instance, IP54 offers limited dust protection and splash resistance but is not suitable for submersion. Always interpret both digits of the IP code correctly and validate the sensor’s suitability for specific exposure conditions such as continuous moisture, high-pressure jets, or fine particulates.
Sourcing from Unverified Suppliers
Procuring sensors from uncertified or unverified suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit or misrepresented products. Some suppliers may falsely claim IP ratings or use inferior components. Always source from reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors and request certification documentation, such as test reports or third-party validation.
Neglecting Long-Term Reliability and Testing
Failing to evaluate sensor performance under real-world conditions can result in unexpected downtime. Sensors may pass basic IP tests in labs but fail under prolonged exposure or thermal cycling. Request field performance data, conduct pilot testing, and consider mean time between failure (MTBF) metrics when assessing quality.
Incompatibility with System Requirements
Even with proper IP and quality, a sensor may fail if it’s electrically or mechanically incompatible with the control system. Check output signal type (e.g., analog, digital, PNP/NPN), voltage requirements, response time, and mounting dimensions to ensure seamless integration and reliable speed feedback.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures the selected speed control sensor delivers accurate, durable, and safe performance throughout its operational life.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Speed Control Sensor
This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, import/export, and use of Speed Control Sensors in accordance with international and regional regulations.
Product Classification & Documentation
Ensure accurate classification of the Speed Control Sensor under the Harmonized System (HS) Code for customs clearance. Typical classifications may fall under 8543.70 (Electrical Apparatus for Switching/Protection) or 9032.89 (Automatic Regulation/Control Instruments), depending on function. Maintain complete technical documentation including datasheets, user manuals, CE/UKCA declarations (if applicable), and safety certifications.
Export Controls & Sanctions
Verify whether the sensor contains controlled technologies subject to export regulations such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) in the U.S. or dual-use controls under EU Regulation (EU) 2021/821. Sensors with high-precision measurement capabilities or intended for military/aerospace applications may require export licenses. Screen end-users and destinations against national sanctions lists to ensure compliance.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Package sensors securely to prevent damage during transit, using anti-static materials where applicable. Label packages with handling symbols (e.g., fragile, avoid moisture) and include proper shipping names, UN numbers (if applicable), and hazard class information—especially if sensors contain restricted substances. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if batteries or hazardous components are integrated.
Import Regulations & Duties
Research import requirements in the destination country, including conformity assessments, local certification (e.g., CCC in China, KC in South Korea, PSE in Japan), and potential import duties. Provide accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin. Some markets may require third-party testing or registration prior to import.
Environmental & Safety Compliance
Ensure the Speed Control Sensor complies with environmental directives such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization of Chemicals), and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) in the EU. Declare substance content as required and provide end-of-life disposal instructions. Confirm compliance with EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) and low-voltage safety standards (e.g., IEC 61010) where applicable.
Transportation & Storage Conditions
Store and transport sensors in dry, temperature-controlled environments within the specified operating/storage range (typically -20°C to +70°C unless otherwise stated). Avoid exposure to vibration, dust, or corrosive atmospheres during logistics operations. Monitor shelf life for sensors with sensitive internal components or batteries.
End-Use Restrictions
Clearly communicate any restrictions on the use of the Speed Control Sensor, particularly in safety-critical systems (e.g., transportation, industrial automation). Provide compliance statements indicating suitability for intended applications and warn against unauthorized modifications that could void certifications.
Recordkeeping & Audit Readiness
Maintain records of all compliance documentation, shipping logs, export licenses, and certifications for a minimum of five years. Ensure traceability of serial numbers or batch identifiers for recall readiness and regulatory audits.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, organizations can ensure the lawful, safe, and efficient global distribution of Speed Control Sensors.
Conclusion for Sourcing Speed Control Sensor:
After a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers, technical specifications, cost considerations, and reliability factors, the sourcing of the speed control sensor has been successfully concluded. The selected supplier offers a high-quality sensor that meets all required performance standards, including accuracy, durability, and compatibility with existing systems. The chosen solution provides a favorable balance between cost-efficiency and long-term reliability, ensuring optimal functionality within the intended application. Additionally, the supplier demonstrates strong supply chain stability and responsive technical support, reducing procurement risks. This strategic sourcing decision supports operational efficiency and lays a solid foundation for system integration and future scalability.