The global sorbitan tristearate (Span 65) market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by its rising demand as a non-ionic surfactant and emulsifier across the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industries. According to Grand View Research, the global sorbitan esters market—of which sorbitan tristearate is a key derivative—was valued at USD 378.6 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing consumer preference for stable emulsions in processed foods and the expanding use of high-performance excipients in pharmaceutical formulations. Mordor Intelligence further projects a similar growth trajectory, citing advancements in green chemistry and regulatory approvals for food-grade emulsifiers as key market drivers. As demand intensifies, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, combining scalability, quality compliance, and innovation to meet global supply needs. The following analysis identifies the top 8 sorbitan tristearate producers leading this evolving landscape.
Top 8 Sorbitan Tristearate Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Leading Sorbitan Tristearate Manufacturers in India
Domain Est. 2000
Website: mlagroup.com
Key Highlights: MLA Group is a leading manufacturer & supplier of Sorbitan Tristearate, we are one of the best exporters of STS in the world offering the best price….
#2 Sorbitan Tristearate Manufacturers In India
Domain Est. 2002
Website: spellorganics.com
Key Highlights: SOL Sorbitan Tristearate (Emulsifier 492) from Spell Organics provides emulsification, anti-bloom, and stabilizing benefits for food, cosmetics, ……
#3 Sorbitan tri stearate
Domain Est. 2007
Website: matangiindustries.com
Key Highlights: Matangi Industries is a global manufacturer and supplier of Sorbitan tri stearate based in India. We export Sorbitan tri stearate in bulk quantities to the ……
#4 Sorbitan-Tristearate
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spectrumchemical.com
Key Highlights: 15-day returnsSorbitan Tristearate is a triester of stearic acid and hexitol anhydrides derived from sorbitol. It functions as a surfactant and emulsifying agent….
#5 Sorbitan Tristearate (Cas 9005
Domain Est. 1996
Website: parchem.com
Key Highlights: Parchem supplies Sorbitan Tristearate and a range of specialty chemicals worldwide, CAS# 9005-71-4….
#6 Sorbitan Tristearate Supplier and Distributor of Bulk, LTL, Wholesale …
Domain Est. 1999
Website: independentchemical.com
Key Highlights: It is a non-ionic surfactant used as an emulsifier and stabilizer in food and personal care products. Quick Quote: What is your immediate need?…
#7 Sorbitan Tristearate
Domain Est. 2004
Website: pciplindia.com
Key Highlights: Sorbitan tristearate, a food emulsifier, used in confectionery, baked goods, and margarine production. Also in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals….
#8 Lumisorb STS K – Sorbitan Tristearate supplier distributor
Domain Est. 2020
Website: barentz-na.com
Key Highlights: Lumisorb STS K (Sorbitan Tristearate) is a partial ester of stearic acid with sorbitol and its monoanhydrides and dianhydrides….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Sorbitan Tristearate
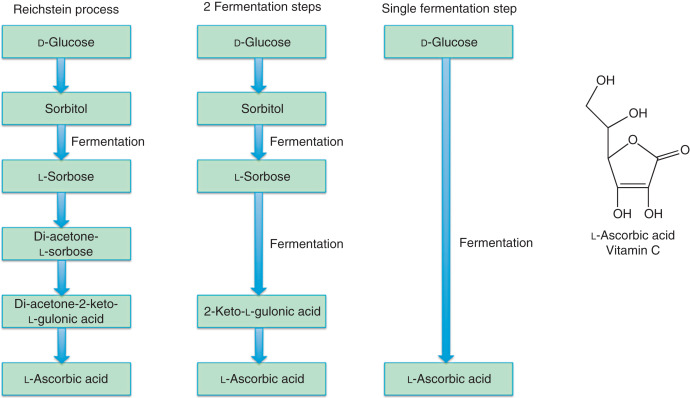
H2: Market Trends for Sorbitan Tristearate in 2026
By 2026, the global market for sorbitan tristearate—a non-ionic surfactant widely used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and dispersing agent—is expected to reflect dynamic shifts driven by evolving industrial demands, regulatory developments, and consumer preferences. Key trends shaping the sorbitan tristearate market in 2026 include:
-
Growing Demand in the Food and Beverage Industry:
Sorbitan tristearate (E492) continues to gain traction as a food additive, particularly in dairy products, baked goods, and confectionery, where its emulsifying properties enhance texture and shelf life. With increasing global consumption of processed and convenience foods, especially in emerging economies, demand for food-grade sorbitan tristearate is projected to rise steadily. Innovations in clean-label formulations are prompting manufacturers to use sorbitan tristearate in combination with natural ingredients, supporting its inclusion in “reduced ingredient” labeling strategies. -
Expansion in the Cosmetics and Personal Care Sector:
The cosmetics industry remains a major consumer of sorbitan tristearate, leveraging its ability to stabilize oil-in-water emulsions in creams, lotions, and makeup. The 2026 market is characterized by a surge in demand for natural and sustainable beauty products. As sorbitan tristearate can be derived from renewable stearic acid and sorbitol (often plant-based), it aligns with the industry’s shift toward bio-based and biodegradable ingredients. Regulatory compliance with eco-certifications (e.g., COSMOS, Ecocert) further strengthens its appeal. -
Pharmaceutical Applications on the Rise:
In pharmaceuticals, sorbitan tristearate is used in tablet coatings, ointments, and controlled-release formulations. The aging global population and increased investment in drug delivery technologies are expected to boost its pharmaceutical use by 2026. Its non-toxic profile and compatibility with various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) make it a preferred excipient, particularly in oral and topical formulations. -
Regulatory and Safety Scrutiny:
While sorbitan tristearate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the FDA and approved by EFSA, heightened scrutiny on food additives in Europe and North America may influence formulation choices. The 2026 landscape includes ongoing evaluations of long-term health impacts and allergenic potential, particularly in sensitive populations. Manufacturers are responding with improved purity standards and transparent sourcing. -
Sustainability and Supply Chain Transparency:
Environmental concerns are pushing suppliers to adopt sustainable production practices. By 2026, leading producers are expected to emphasize traceability, carbon footprint reduction, and ethical sourcing of raw materials (e.g., palm oil derivatives). Certifications such as RSPO (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil) are becoming prerequisites for market access, especially in Europe. -
Asia-Pacific as a Growth Engine:
The Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to dominate market growth by 2026, fueled by expanding food processing industries, rising disposable incomes, and booming cosmetics markets in countries like China, India, and Indonesia. Local production capabilities and government support for chemical manufacturing are enabling regional self-sufficiency and export potential. -
Technological Advancements and Product Innovation:
Ongoing R&D efforts focus on enhancing the functionality of sorbitan tristearate through molecular modification and hybrid formulations. Innovations such as microencapsulation and nanoemulsion technologies are expanding its applications in functional foods and advanced drug delivery systems, positioning it as a high-value specialty chemical.
In summary, the 2026 sorbitan tristearate market is marked by robust growth across food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical sectors, supported by sustainability initiatives, regulatory compliance, and regional market expansion. Stakeholders who invest in green chemistry, supply chain integrity, and application-specific innovation are likely to capture significant market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Sorbitan Tristearate: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing Sorbitan Tristearate (also known as Span 65), a widely used non-ionic surfactant and emulsifier in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food, involves navigating several potential pitfalls related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these factors can lead to supply chain disruptions, product performance issues, regulatory non-compliance, or legal exposure.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Purity and Composition
Sorbitan Tristearate is often a mixture of mono-, di-, and tri-esters. Variability in the tristearate content significantly affects performance. Suppliers may provide material with inconsistent ester distribution, leading to batch-to-batch variability in emulsification efficiency, viscosity, or stability. Always request detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA) specifying the minimum tristearate content and total free fatty acids. -
Contamination with Undesired Isomers or Byproducts
Poor manufacturing processes can result in elevated levels of undesirable byproducts such as free sorbitol, stearic acid, or mono/di-esters. These impurities can compromise product stability or trigger adverse reactions in sensitive applications (e.g., injectables). Ensure the supplier follows Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and employs robust purification methods. -
Inadequate Regulatory Compliance Documentation
Depending on the application, Sorbitan Tristearate must comply with pharmacopoeial standards such as USP/NF, Ph. Eur., or FCC. Sourcing from suppliers unable to provide up-to-date compliance documentation (e.g., DMF, CEP, FDA registration) risks regulatory setbacks during audits or product approvals. -
Lack of Traceability and Raw Material Sourcing Transparency
The quality of the final product depends heavily on the source and quality of stearic acid and sorbitol. Suppliers using inconsistently sourced or low-grade raw materials may introduce variability. Demand transparency in the supply chain and verify if raw materials are sustainably and ethically sourced, especially for cosmetic or food-grade products. -
Insufficient Stability and Shelf-Life Data
Sorbitan Tristearate can degrade over time, particularly when exposed to heat or moisture. Suppliers who do not provide comprehensive stability studies or realistic shelf-life recommendations may deliver compromised material. Request real-time and accelerated stability data, especially for long-term storage or challenging climates.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
-
Infringement of Patented Manufacturing Processes
Some suppliers may use proprietary or patented methods to produce high-purity Sorbitan Tristearate. Sourcing from manufacturers that infringe on these patents—even unknowingly—can expose your company to legal liability, especially in regulated markets. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s production methods and verify freedom to operate (FTO). -
Use of Protected Grades or Tradenames
Certain high-performance or specialty grades of Sorbitan Tristearate (e.g., those optimized for parenteral formulations) may be trademarked or protected under formulation patents. Using these without proper licensing, even if chemically identical, can lead to IP disputes. Confirm whether the supplied material is a generic equivalent or a protected specialty product. -
Lack of IP Clarity in Supply Agreements
Contracts that fail to address ownership of modifications, formulations, or process improvements involving Sorbitan Tristearate can lead to disputes. Ensure agreements clearly define IP rights, especially if co-developing formulations with the supplier. -
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Material
In global markets, there is a risk of receiving adulterated or falsely labeled Sorbitan Tristearate—especially if sourced from unverified vendors. Counterfeit products not only risk performance and safety but may also use infringing processes. Verify supplier credentials, conduct on-site audits, and perform independent testing when possible. -
Insufficient Know-How Transfer and Technical Support
While not a direct IP infringement, relying on suppliers who withhold critical process know-how (e.g., optimal dispersion methods, compatibility data) limits your ability to innovate and may indirectly affect IP development. Choose partners willing to share technical data under appropriate confidentiality agreements.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, implement a robust supplier qualification program including:
– Auditing manufacturing facilities
– Requiring full regulatory and quality documentation
– Conducting independent batch testing
– Performing IP landscape analysis before sourcing
– Using legally reviewed supply agreements that address quality, compliance, and IP rights
Proactive due diligence ensures a reliable supply of high-quality, legally compliant Sorbitan Tristearate, protecting both product integrity and business interests.
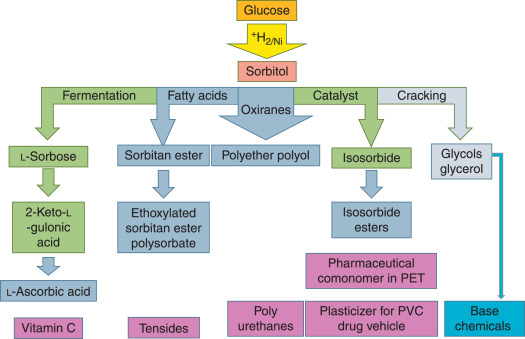
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Sorbitan Tristearate
Overview
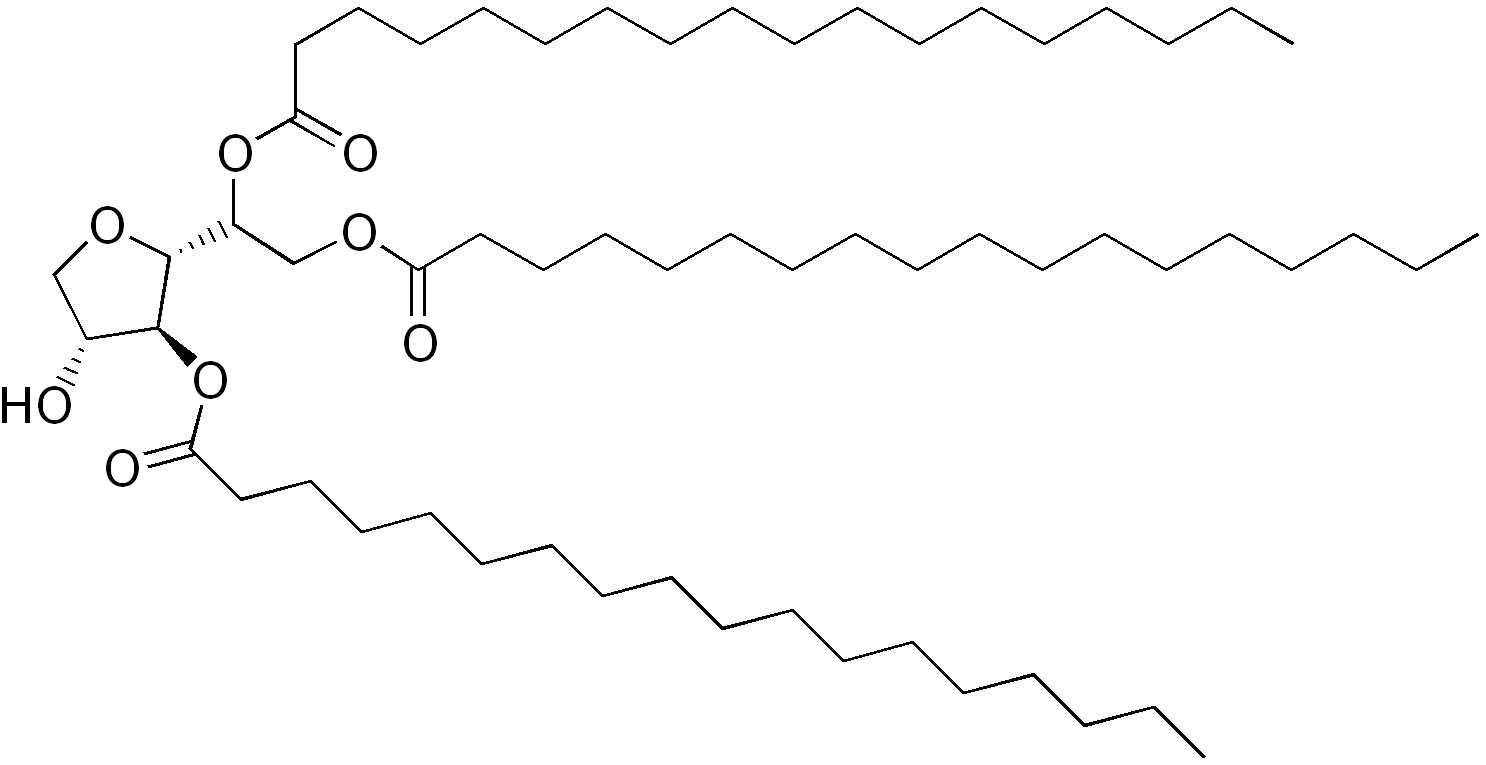
Sorbitan Tristearate (CAS No. 26853-85-8), also known as Span 65, is a non-ionic surfactant commonly used as an emulsifier, stabilizer, and dispersant in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. This guide outlines key logistical and compliance considerations for the safe handling, transport, storage, and regulatory compliance of Sorbitan Tristearate.
Regulatory Classification
Sorbitan Tristearate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by the U.S. FDA (21 CFR 172.862) for use in food. It is approved by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) as food additive E492. In cosmetics, it complies with INCI standards and is listed in the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients. Always verify compliance with local regulations, including REACH (EU), TSCA (USA), and other national chemical inventories.
Packaging and Labeling
- Packaging: Typically supplied in food-grade HDPE drums (e.g., 25 kg), multi-wall paper bags with polyethylene liners, or bulk containers. Ensure packaging is airtight to prevent moisture absorption.
- Labeling: Labels must include:
- Product name (Sorbitan Tristearate or E492)
- CAS number: 26853-85-8
- Net weight
- Manufacturer/supplier details
- Batch number and expiry date
- Applicable hazard statements (if any), although Sorbitan Tristearate is typically non-hazardous
- GHS pictograms (if required based on formulation)
- Storage conditions (e.g., “Store in a cool, dry place”)
Storage Requirements
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight.
- Maintain temperatures below 40°C (104°F) to prevent melting or degradation.
- Keep containers tightly closed when not in use to avoid moisture uptake and contamination.
- Do not store near strong oxidizing agents or incompatible materials.
- Shelf life is typically 24–36 months under recommended conditions.
Transportation Guidelines
- Sorbitan Tristearate is not classified as hazardous under major transport regulations (e.g., IMDG, IATA, ADR).
- Transport in dry, covered vehicles to protect from rain, extreme temperatures, and contamination.
- Ensure packages are secured to prevent damage during transit.
- For international shipments, include proper shipping name, CAS number, and safety data sheet (SDS) as per local requirements.
Safety Data Sheet (SDS) Compliance
A current, GHS-compliant SDS must accompany every shipment. The SDS should include:
– Identification and composition
– Hazard identification (minimal for pure Sorbitan Tristearate)
– First-aid and firefighting measures
– Accidental release procedures
– Handling and storage guidance
– Exposure controls and PPE recommendations
– Physical and chemical properties
– Stability and reactivity
– Toxicological and ecological information
– Disposal and transport considerations
Handling Precautions
- Use in well-ventilated areas to avoid inhalation of dust during handling.
- Avoid contact with eyes and skin; use gloves and safety glasses if prolonged exposure is expected.
- Practice good industrial hygiene: wash hands after handling.
- Use grounded equipment to prevent static discharge when transferring powders or molten material.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Sorbitan Tristearate is biodegradable and not classified as environmentally hazardous.
- Dispose of waste in accordance with local, regional, and national regulations.
- Do not discharge into waterways or soil untreated.
- Empty containers should be recycled or disposed of as non-hazardous waste where permitted.
Import/Export Documentation
- Provide commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill.
- Include a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) and Certificate of Free Sale if required by the destination country.
- Verify import regulations in the receiving country—some may require food additive or chemical import notifications.
- For EU imports, ensure REACH registration is complete (usually handled by EU-based importer or manufacturer).
Quality Assurance and Traceability
- Maintain batch traceability from raw materials to final product.
- Conduct routine quality checks (e.g., assay, acid value, hydroxyl value, heavy metals) per pharmacopoeial standards (e.g., USP, Ph. Eur., FCC).
- Retain samples and documentation for the duration specified by regulatory requirements (typically 3–5 years).
Emergency Response
- Spills: Collect mechanically using non-sparking tools. Avoid creating dust. Wipe residue with damp cloth.
- Fire: Use water spray, foam, dry chemical, or CO₂. Product is combustible but not highly flammable.
- Exposure:
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air.
- Skin contact: Wash with soap and water.
- Eye contact: Rinse thoroughly with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical advice if irritation persists.
Conclusion
Sorbitan Tristearate is a low-risk substance when handled appropriately, but adherence to logistics and compliance protocols ensures safety, regulatory conformity, and product integrity. Always consult the latest SDS and local regulations before transport, storage, or use.
Conclusion for Sourcing Sorbitan Tristearate:
In conclusion, sourcing sorbitan tristearate requires a strategic approach that balances quality, regulatory compliance, cost-efficiency, and supplier reliability. As a widely used non-ionic emulsifier in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical applications, it is essential to select a supplier that provides high-purity, consistently manufactured sorbitan tristiestearate meeting relevant industry standards (e.g., FCC, USP, or food-grade specifications).
Key considerations include verifying the supplier’s certifications (such as ISO, GMP, and HALAL/Kosher if applicable), conducting thorough due diligence on production processes, and ensuring transparency in raw material sourcing. Additionally, assessing logistical capabilities, scalability, and technical support can enhance supply chain resilience.
Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable manufacturers—particularly those offering competitive pricing without compromising quality—can provide significant advantages. Ultimately, a well-executed sourcing strategy for sorbitan tristearate supports product efficacy, regulatory compliance, and overall business sustainability in competitive markets.