The global solid carbide end mills market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision machining across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and mold-making. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in CNC machining and rising adoption of high-performance cutting tools. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the broader end mills market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand significantly over the next decade, underpinned by the superior wear resistance, thermal stability, and longevity of solid carbide tools compared to traditional high-speed steel variants. As manufacturing standards become more exacting, leading producers are investing in innovative coatings, geometries, and manufacturing processes to enhance tool performance and efficiency. In this competitive landscape, ten manufacturers have emerged as key players, setting industry benchmarks for quality, precision, and technological advancement.
Top 10 Solid Carbide End Mills Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PROMAX Tools
Domain Est. 2003
Website: promaxtools.com
Key Highlights: CERATIZIT Sacramento (formerly PROMAX Tools) is a premium manufacturer of solid carbide End Mills located in Rancho Cordova, California (in Sacramento County)….
#2 SPEED TIGER
Domain Est. 2020 | Founded: 1998
Website: speedtigertools.com
Key Highlights: Speed Tiger, founded in 1998, is the leading manufacturer of carbide end mills and the largest cutting tools manufacturer in Taiwan….
#3 High
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kennametal.com
Key Highlights: High-performance solid carbide end mills from Kennametal are the perfect choice for cutting aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, or other tough materials….
#4 Solid Carbide End Mills
Domain Est. 1996
Website: secotools.com
Key Highlights: Premium solid carbide end mills bring unmatched cutting performance, long tool life and high process security to demanding parts production in industry segments ……
#5 Solid Carbide End Mills for Any Milling Operation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: fullertontool.com
Key Highlights: Our Intimidator high-performance end mill excels in slotting, roughing, and finishing applications in difficult-to-machine materials….
#6 Solid carbide end mills
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sandvik.coromant.com
Key Highlights: The full assortment of our high-quality solid carbide end mills includes tools from roughing to finishing and thread milling within Versatile, Optimized and ……
#7 Harvey Tool
Domain Est. 1997
Website: harveytool.com
Key Highlights: For over 30 years Harvey Tool has been providing specialty carbide end mills and cutting tools to the metalworking industry. Find your local cutting tool ……
#8 Carbide End Mills
Domain Est. 1997
Website: consumables.alliedhightech.com
Key Highlights: Made of solid carbide for maximum performance and durability, carbide end mills are used to cut metal (copper, aluminum, gold, solder, steel, NiCo), ……
#9 Solid Carbide End Mills
Domain Est. 2014
Website: morsect.com
Key Highlights: MORSE offers complete selections of solid carbide endmills for many milling applications. Tools are available for roughing, semi-finishing and finishing ……
#10 YG
Domain Est. 2001
Website: yg1usa.com
Key Highlights: CBN 2 FLUTE 30 DEGREE HELIX BALL END MILL · CBN 2 FLUTE 30 DEGREE HELIX … THREAD MILLS SOLID CARBIDE · INDEXABLE INSERTS. YG MILL; APKT, ADKT, AOMT, APMT ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solid Carbide End Mills
H2: Projected Market Trends for Solid Carbide End Mills in 2026
The global market for solid carbide end mills is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, shifting manufacturing demands, and regional industrial growth. These high-performance cutting tools, essential in precision machining across aerospace, automotive, medical, and mold & die industries, are expected to witness robust expansion fueled by several key trends.
-
Rising Demand from High-Precision Industries
Industries requiring tight tolerances and superior surface finishes—such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing—are projected to be major growth drivers. The increasing use of difficult-to-machine materials like titanium, Inconel, and high-strength steels necessitates advanced solid carbide end mills with enhanced durability and cutting efficiency. By 2026, demand from these sectors is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 6%, particularly in North America and Asia-Pacific. -
Technological Innovation in Coating and Geometry
Innovation in PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) coatings, such as AlTiN, TiSiN, and diamond-like carbon (DLC), will continue to improve tool life and performance under extreme conditions. Additionally, optimized flute geometries and variable helix/helix core designs will enhance chip evacuation and reduce vibration, enabling higher feed rates and longer tool life. These advancements will be critical in supporting high-speed and hard milling applications. -
Growth in Asia-Pacific Manufacturing Hubs
China, India, and Southeast Asian countries are expanding their manufacturing capabilities, especially in electronics and electric vehicle (EV) production. This industrial growth will boost local demand for solid carbide end mills. By 2026, the Asia-Pacific region is forecasted to account for over 45% of global consumption, driven by investments in smart factories and industrial automation. -
Sustainability and Tool Reconditioning
Environmental and cost pressures are pushing manufacturers toward sustainable practices. Tool reconditioning (regrinding and recoating) is gaining traction as a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to new tool purchases. Leading suppliers are expected to expand their refurbishment services, offering certified reconditioned end mills with near-original performance—contributing to a circular economy in metalworking. -
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Digital Tool Management
Smart manufacturing trends are leading to the integration of digital tool management systems. By 2026, an increasing number of solid carbide end mills will come equipped with RFID tags or QR codes, enabling real-time tracking of tool life, usage conditions, and performance data. This digitalization improves process predictability, reduces downtime, and supports predictive maintenance strategies. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted companies to diversify sourcing and localize production. Tool manufacturers are expected to establish regional production facilities closer to key markets to reduce lead times and mitigate risks. This shift will influence pricing strategies and inventory models in the solid carbide end mill sector.
In conclusion, the 2026 market for solid carbide end mills will be shaped by innovation, digital transformation, and strategic regional growth. Companies that invest in R&D, sustainability, and digital integration will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic and competitive landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solid Carbide End Mills: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing solid carbide end mills can significantly impact machining performance, tool life, and overall production costs. While cost savings may be tempting, overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to severe downstream consequences. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Inconsistent Performance
Many low-cost suppliers use substandard carbide grades or inconsistent manufacturing processes. This results in tools with poor wear resistance, chipping, or premature failure. Inconsistent flute geometry, edge preparation, and coating application further degrade cutting performance and reduce tool life. Using such tools leads to increased downtime, scrapped parts, and higher total cost of ownership despite lower initial prices.
Counterfeit or Misrepresented Brand-Name Tools
A major IP risk is the proliferation of counterfeit end mills falsely branded as premium manufacturers (e.g., Sandvik, Kennametal, or Mitsubishi). These copies often mimic packaging and labeling but use inferior materials and processes. Purchasing counterfeit tools violates IP laws, exposes companies to legal liability, and undermines trust with customers and partners. Additionally, performance falls drastically short of genuine products, leading to reliability issues.
Lack of Traceability and Certifications
Reputable suppliers provide material certifications, batch traceability, and quality assurance documentation. Many low-tier suppliers lack these, making it difficult to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO, DIN). Without traceability, diagnosing tool failure becomes nearly impossible, and compliance with regulated industries (aerospace, medical) cannot be assured.
Inadequate Coating Technology and Application
High-performance end mills rely on advanced coatings (e.g., TiAlN, AlCrN) applied via precision methods like PVD. Some suppliers cut corners by using outdated or improperly applied coatings, which fail under high heat or pressure. This not only reduces tool life but can also lead to workpiece contamination or surface defects.
Weak IP Protection in Supply Chain Contracts
Sourcing agreements often fail to address IP ownership, especially when custom tools are involved. Without clear contractual terms, suppliers may reuse tool designs, replicate geometries, or sell them to competitors. This erodes competitive advantage and exposes companies to design theft.
Overlooking Geopolitical and Compliance Risks
Sourcing from regions with lax IP enforcement increases exposure to counterfeit production and unauthorized replication. Additionally, trade regulations, import restrictions, and sanctions may apply—particularly when dealing with advanced tooling technologies that have dual-use applications.
To mitigate these risks, buyers should conduct thorough supplier vetting, request samples and certifications, verify authenticity through authorized distributors, and include strong IP protection clauses in procurement contracts. Prioritizing long-term performance and legal compliance over initial cost savings ensures better outcomes in manufacturing operations.
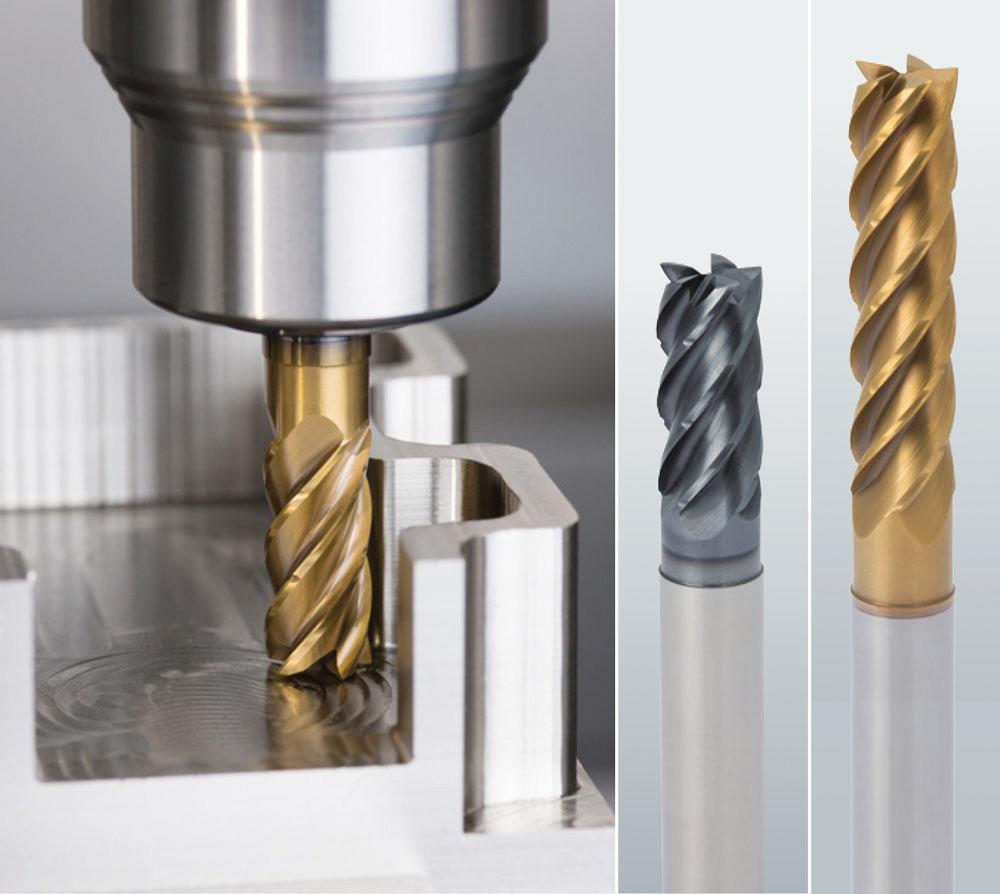

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solid Carbide End Mills
Overview
Solid carbide end mills are high-precision cutting tools widely used in metalworking, aerospace, automotive, and mold-making industries. Due to their composition, value, and international trade implications, proper logistics and compliance procedures are essential for their import, export, and domestic distribution.
Classification & Tariff Codes
Correct product classification ensures compliance with customs regulations and accurate duty assessment.
– HS Code (Harmonized System) Example: 8207.50 (for interchangeable tools for hand tools or machine tools, of which the working part is of ceramics, sintered metal carbides, or hard steel)
– Specific Sub-Categories: 8207.50.30 (for end mills of sintered metal carbides) — applicable in many jurisdictions, including the United States.
Note: HS codes may vary by country; verify with local customs authorities.
Export Controls & Licensing
Solid carbide end mills may be subject to export control regulations due to potential dual-use applications (civilian and military/strategic).
– EAR (Export Administration Regulations – U.S.):
– Classified under ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) 2B116 or 9A991, depending on specifications such as precision, diameter, coating, and intended use.
– Items under 2B116 may require a license for export to certain countries, especially embargoed nations or those of concern.
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): Generally not applicable unless used in defense-related applications.
– EU Dual-Use Regulation (EU) 2021/821: Similar controls apply; check Annex I for classification.
Always conduct screening against denied party lists (e.g., BIS, OFAC, EU Consolidated List).
Material & Environmental Compliance
Carbide end mills contain tungsten carbide and cobalt, which may be regulated under environmental and safety frameworks.
– REACH (EU):
– Cobalt (a binder in carbide) is listed as a Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC). Suppliers must provide a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and comply with SCIP notification requirements if cobalt content exceeds thresholds.
– RoHS (EU): Generally not applicable to industrial tools, but verify coatings or packaging materials.
– TSCA (U.S.): Confirm that chemical components are listed or exempt under the Toxic Substances Control Act.
– Conflict Minerals (Dodd-Frank Act): Tungsten is a 3TG mineral; companies must conduct due diligence and file annual reports if products contain conflict minerals from covered regions.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging ensures product integrity and regulatory compliance.
– Packaging Standards:
– Use anti-corrosion packaging (VCI paper or desiccants) to prevent moisture damage.
– Individual or grouped packaging in sealed plastic or cardboard with protective inserts.
– Labeling:
– Include product ID, specifications (diameter, length, coating), manufacturer details, and country of origin.
– Mark “Fragile” and “This Side Up” as needed.
– Shipping Documentation:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Export License (if required)
– SDS (for hazardous component disclosure)
Import Regulations
Importers must comply with destination country rules.
– Customs Valuation: Ensure accurate declared value; transfer pricing must reflect arm’s-length transactions.
– Duties & Taxes: Calculate based on HS code and trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU FTAs).
– Product Standards: Verify conformity with local standards (e.g., ANSI in the U.S., DIN in Germany).
– Inspection Requirements: Some countries may require pre-shipment inspection for high-value or regulated tools.
Transportation & Insurance
- Mode of Transport: Air freight for urgent, high-value shipments; ocean freight for bulk orders.
- Incoterms: Clearly define responsibilities (e.g., FOB, DDP) in contracts.
- Cargo Insurance: Cover full value against loss, theft, or damage during transit. Include war risk and strike clauses if shipping to high-risk regions.
Recordkeeping & Audits
Maintain records for compliance and traceability.
– Retain export documentation for a minimum of 5 years (U.S. requirement under EAR).
– Document compliance screenings, license applications, and internal audits.
– Implement a compliance management system (CMS) for tracking regulatory changes.
Best Practices
- Conduct regular training for logistics and export compliance teams.
- Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with tooling and dual-use goods.
- Perform annual compliance audits to ensure adherence to evolving regulations.
- Use automated compliance software to monitor sanctions lists and classification updates.
Conclusion
Solid carbide end mills require careful attention to classification, export controls, environmental regulations, and logistics protocols. Proactive compliance mitigates legal risks, ensures smooth international trade, and safeguards business continuity. Always consult with legal and customs experts to address jurisdiction-specific requirements.
In conclusion, sourcing solid carbide end mills requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, performance, and supplier reliability. These high-precision cutting tools are essential for achieving excellent surface finishes, tight tolerances, and efficient material removal rates in industries such as aerospace, automotive, mold-making, and medical device manufacturing. When selecting a supplier, it is crucial to evaluate factors such as material quality (e.g., grain size, coating technology), tool geometry, consistency in manufacturing, technical support, and delivery lead times.
Opting for reputable manufacturers—whether domestic or international—can significantly enhance machining performance and reduce tooling-related downtime. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership rather than just upfront price helps in identifying solutions that offer better durability and longer tool life. Partnerships with suppliers that provide application engineering support and customization options can further optimize tool performance for specific machining operations.
Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy for solid carbide end mills contributes to improved productivity, reduced operational costs, and enhanced competitiveness in high-precision manufacturing environments. Regular evaluation of supplier performance and staying updated on advancements in cutting tool technology will ensure continued success in sourcing the right tools for evolving manufacturing demands.