The global solenoid starter relay market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising automotive production and increased demand for reliable engine starting systems. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive relay market—which includes solenoid starter relays—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% between 2023 and 2028, fueled by advancements in vehicle electrification and the integration of advanced electronic control units. Additionally, Grand View Research estimates that the global automotive relay market size was valued at USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth trajectory underscores the critical role of high-performance solenoid starter relays in modern vehicles. As demand escalates, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining innovation, reliability, and global reach to dominate the landscape. Below, we highlight the top six solenoid starter relay manufacturers shaping the future of automotive and industrial starting systems.
Top 6 Solenoid Starter Relay Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Woodward
Domain Est. 1995
Website: woodward.com
Key Highlights: Woodward teams around the world design and build innovative energy control solutions for aerospace and industrial applications that put the world in motion….
#2 Powersports Vehicle Manufacturers and Starter Solenoid Suppliers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: johnsonelectric.com
Key Highlights: Johnson Electric offers robust starter solenoid solutions for manufacturers of jet skis, ATVs, snowmobiles, and other powersports vehicles. These solutions ……
#3 RS
Domain Est. 2001
Website: us.rs-online.com
Key Highlights: RS, formerly Allied Electronics, is an omni-channel provider of industrial and electronics products and solutions to industrial customers across the ……
#4 Starter Relay Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2017
Website: startersolenoid.net
Key Highlights: T&X relay starter are long lasting, being made from tough corrosion-resistant materials. A highly efficient design allows for improved operation….
#5 DENSO Auto Parts
Domain Est. 2006
Website: densoautoparts.com
Key Highlights: DENSO is a global choice for top automakers, with multiple vehicle models rolling off the assembly line with DENSO auto parts under the hood….
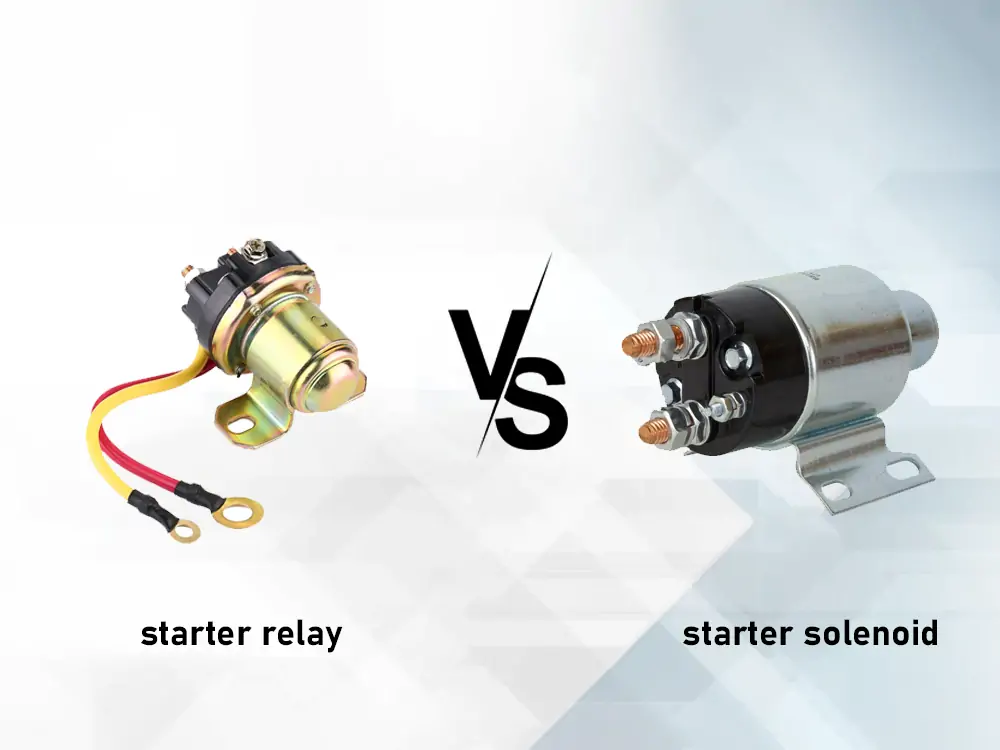
#6 Starter Relay vs Starter Solenoid
Domain Est. 2014
Website: kynix.com
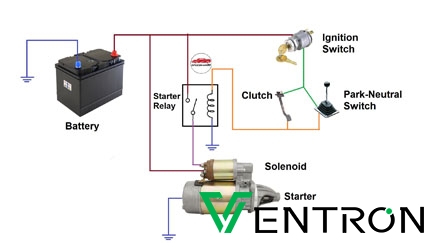
Key Highlights: The starter relay and starter solenoid function nearly identically. An electromagnetic field is created when a current flows through the coil ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solenoid Starter Relay
H2: Market Trends for Solenoid Starter Relay in 2026
1. Market Growth and Demand Outlook
The global solenoid starter relay market is projected to experience steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing vehicle production, advancements in automotive electrical systems, and rising demand for reliable ignition components. According to industry forecasts, the market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.5% from 2022 to 2026. The expansion of the automotive aftermarket and the continued reliance on internal combustion engines (ICE) in emerging markets remain key demand drivers.
2. Regional Demand Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to dominate the solenoid starter relay market in 2026, with China, India, and Southeast Asian countries leading due to high vehicle production and increasing ownership rates. North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, primarily driven by vehicle maintenance and replacement needs in aging vehicle fleets. Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East are emerging as growth markets due to infrastructure development and expanding transportation networks.
3. Technological Advancements
In 2026, solenoid starter relays are expected to incorporate enhanced durability, improved thermal resistance, and better electromagnetic efficiency. Manufacturers are focusing on miniaturization and integration with smart vehicle systems, enabling diagnostics and predictive maintenance. Some next-generation relays may feature embedded sensors or communication interfaces compatible with onboard vehicle networks, supporting the industry’s move toward connected and semi-autonomous vehicles.
4. Impact of Electrification and EV Trends
While the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a long-term challenge to traditional starter relay demand—since EVs do not require starter motors—the market will remain resilient through 2026. Most EVs still utilize auxiliary relays for battery management and power distribution, creating a niche opportunity. Additionally, hybrid vehicles, which combine ICE and electric powertrains, continue to require solenoid starter relays, ensuring sustained demand during the transition period.
5. Supply Chain and Manufacturing Shifts
Automotive component manufacturers are increasingly localizing production to reduce logistics costs and mitigate supply chain disruptions. In 2026, we expect to see more regional manufacturing hubs for solenoid starter relays, particularly in Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe. Automation and Industry 4.0 technologies will enhance production efficiency, allowing for higher quality control and scalability.
6. Competitive Landscape
The market will remain consolidated with key players such as Bosch, Denso, Delphi (Aptiv), and HELLA dominating global supply. However, regional manufacturers in China and India are gaining market share through cost-effective solutions and partnerships with local automakers. Competition will intensify around product reliability, pricing, and customization for specific vehicle platforms.
7. Regulatory and Environmental Influences
Stricter emissions and vehicle safety regulations are prompting automakers to adopt more reliable and energy-efficient components. While solenoid starter relays are not directly regulated, their performance affects overall vehicle efficiency and cold-start emissions. As a result, compliance with ISO/TS 16949 and other automotive quality standards will be critical for market access.
8. Aftermarket Expansion
The automotive aftermarket for solenoid starter relays is expected to grow faster than the OEM segment by 2026, fueled by the increasing average age of vehicles and higher rates of component replacement. E-commerce platforms and digital distribution channels will play a larger role in reaching end-users, especially in developing economies.
Conclusion
By 2026, the solenoid starter relay market will continue to evolve amid technological progress and automotive industry transformation. While electrification poses a long-term structural challenge, ongoing demand from ICE and hybrid vehicles, coupled with innovation in relay design and regional market growth, will sustain the sector’s relevance. Companies that invest in R&D, supply chain agility, and aftermarket strategies will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solenoid Starter Relays (Quality & IP)
Sourcing solenoid starter relays—critical components in vehicle starting systems—requires careful attention to both quality and ingress protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking these factors can lead to premature failures, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Low Cost Over Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting relays based solely on price. Cheap, low-quality relays often use inferior materials such as substandard copper windings, weak spring mechanisms, or poor-grade contacts. These can result in:
- Intermittent starting or failure to engage
- Overheating under normal load
- Reduced lifespan due to rapid contact erosion
Always verify manufacturer reputation, certifications (e.g., ISO/TS 16949), and component material specifications.
2. Ignoring Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
The IP rating defines a relay’s resistance to dust and moisture—critical for under-hood environments exposed to rain, road spray, and temperature fluctuations. Common pitfalls include:
- Using IP20-rated relays in outdoor or engine bay applications: These offer minimal protection and are prone to moisture ingress, leading to short circuits or corrosion.
- Assuming all “automotive-grade” relays are weatherproof: Not all are; always confirm the specific IP rating (e.g., IP65, IP67) suitable for the installation environment.
3. Mismatched Electrical Specifications
Selecting a relay with incorrect voltage, current, or coil resistance can damage the relay or connected systems. Pitfalls include:
- Using a 12V relay in a 24V system (or vice versa)
- Exceeding the maximum continuous load current, causing overheating
- Incompatible coil resistance leading to weak actuation or excessive draw on control circuits
Always cross-reference the relay’s specs with the vehicle or equipment manufacturer’s requirements.
4. Overlooking Environmental and Thermal Ratings
Relays must perform across a wide temperature range. Sourcing relays without checking their operational temperature range (e.g., -40°C to +85°C) can result in:
- Failure in extreme cold (e.g., coil not energizing)
- Contact welding or insulation breakdown in high heat
Ensure the relay is rated for the actual under-hood or installation environment.
5. Falling for Counterfeit or Unverified Suppliers
Purchasing from unverified online marketplaces or third-party suppliers increases the risk of counterfeit relays. These may:
- Lack proper internal components or use recycled parts
- Display fake certifications or incorrect labeling
- Fail prematurely under real-world conditions
Always source from authorized distributors or reputable suppliers with traceable supply chains.
6. Neglecting Mechanical Compatibility
Even with correct electrical specs, a relay may not fit the socket or mounting configuration. Issues include:
- Incorrect terminal layout (e.g., ISO 280, Bosch-style)
- Wrong physical dimensions or mounting style
Verify footprint and pin configuration before procurement.
7. Skipping Life Cycle and Durability Testing Data
High-quality relays provide data on mechanical and electrical life cycles (e.g., 100,000 operations). Sourcing without this information risks:
- Early wear-out in frequent-start applications (e.g., fleet vehicles)
- Unpredictable failure modes
Request and review reliability test reports when available.
By avoiding these common pitfalls—particularly by prioritizing verified quality and appropriate IP ratings—you ensure reliable, long-term performance of solenoid starter relays in demanding automotive and industrial environments.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solenoid Starter Relay
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legal handling, transportation, and distribution of Solenoid Starter Relays.
Product Classification and Documentation
Ensure accurate product classification for customs and regulatory purposes. Solenoid starter relays typically fall under HS Code 8536.50 (Relays) or similar, depending on regional tariff schedules. Maintain detailed technical specifications, including voltage ratings, current capacity, and dimensions. Required documentation includes commercial invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin, and safety compliance certificates (e.g., UL, CE, RoHS).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package relays in static-dissipative or anti-static materials to prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. Use robust inner packaging (e.g., molded trays or bubble wrap) to prevent physical damage during transit. Outer packaging should be sturdy corrugated cardboard with appropriate cushioning. Clearly label packages with product identifiers, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “Do Not Drop”), and orientation arrows. Avoid excessive stacking to prevent compression damage.
Transportation and Storage Conditions
Transport and store relays in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 10°C to 40°C). Avoid exposure to moisture, dust, and corrosive atmospheres. Ensure vehicles used for transport are clean and protected from weather. For long-term storage, use climate-controlled warehouses with humidity levels below 75% RH to prevent condensation and corrosion. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure relays comply with relevant regional and international standards:
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of Hazardous Substances; confirm lead, cadmium, and other restricted substances are within limits.
– REACH (EU): Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals; provide SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) declarations if applicable.
– CE Marking: Required for sale in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– UL/CSA (North America): Compliance with safety standards for electrical components.
– EAC (Eurasian Customs Union): Required for markets such as Russia and Belarus.
– CCC (China): Mandatory for products sold in China, if applicable.
Import/Export Controls
Verify whether solenoid starter relays are subject to export control regulations, such as EAR (Export Administration Regulations) in the U.S. Most relays are classified under ECCN 8A992 (civil aircraft-related items) or EAR99 (low-risk general items), but confirm based on technical specs. Obtain necessary export licenses if required. Screen end-users and destinations against denied party lists (e.g., OFAC, BIS).
Labeling and Marking
Each relay unit must be permanently marked with manufacturer name or trademark, model number, voltage/current ratings, and applicable safety certifications (e.g., UL, CE). Packaging labels must include product description, quantity, batch/lot number, manufacturing date, and compliance marks. Use multilingual labels when shipping to non-English-speaking regions.
Returns and Reverse Logistics
Establish a clear returns policy for defective or non-conforming relays. Use traceable return shipping methods and inspect returned units for damage or misuse. Segregate non-compliant or recalled items in secure quarantine areas. Follow local e-waste regulations for disposal or recycling, particularly due to RoHS compliance requirements.
Risk Mitigation and Audits
Conduct regular audits of logistics partners and compliance documentation. Maintain insurance coverage for transport and storage risks. Keep updated records of all compliance certifications and renewals. Train logistics staff on proper handling and regulatory requirements to minimize compliance breaches and shipment delays.
Conclusion for Sourcing Solenoid Starter Relay:
Sourcing a solenoid starter relay requires a careful evaluation of technical specifications, quality standards, supplier reliability, and cost-effectiveness. It is essential to ensure compatibility with the specific vehicle or equipment make and model, including correct voltage, current ratings, and physical dimensions. Prioritizing components from reputable manufacturers or certified suppliers helps guarantee durability, safety, and performance under varied operating conditions.
Additionally, considering factors such as supply chain stability, lead times, and after-sales support contributes to minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Whether sourcing for OEM, aftermarket, or replacement purposes, a strategic approach that balances quality and cost will lead to reliable engine starting performance and long-term operational efficiency. Therefore, the optimal sourcing decision involves a thorough supplier assessment and adherence to industry standards to ensure the solenoid starter relay meets both technical and operational requirements.