The global electronics manufacturing industry continues its upward trajectory, driven by increasing demand for consumer electronics, automotive systems, and advanced telecommunications infrastructure. A critical yet often overlooked component in this ecosystem is solder flux, with the global solder flux market valued at USD 1.48 billion in 2022 and projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% through 2030, according to Grand View Research. This growth is fueled by rising miniaturization of electronic components, expanded PCB complexity, and the proliferation of surface mount technology (SMT) processes—trends that are elevating the importance of precision application tools such as flux pens. As manufacturers seek consistent, no-mess flux delivery for rework and prototyping, the demand for high-performance solder flux pens has surged. In this evolving landscape, a select group of suppliers has emerged as leaders, combining formulation expertise with ergonomic design to meet the needs of professionals across industries. Based on market presence, product innovation, and technical performance, the following nine companies stand out as the top solder flux pen manufacturers shaping today’s electronics assembly workflows.
Top 9 Solder Flux Pen Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Flux pen manufacturer
Domain Est. 2005
Website: en.jufengxi.com
Key Highlights: Shenzhen Jufeng is a manufacturer of soldering flux pens. We provide high-quality soldering flux pen products with excellent thermal conductivity and stable ……
#2 TAIYO ELECTRIC IND.CO.,LTD.|A comprehensive manufacturer of …
Domain Est. 2001
Website: en.goot.jp
Key Highlights: We are a one-stop soldering iron manufacturer that conducts research, development, design, manufacturing, and sales in a wide range of fields from household ……
#3 Kester
Domain Est. 1995
Website: kester.com
Key Highlights: Solder Wire · Liquid Solder Flux · Solder Paste · Tacky Solder Flux · Preforms · Bar Solder · Other · ALPHA HiTech · SMD Adhesives · Underfills · Edgebond….
#4 Chemtronics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: chemtronics.com
Key Highlights: Chemtronics is the leader in solutions for the electronics, telecommunications and critical environments markets. Products include degreasers, flux removers ……
#5 SRA Soldering Products
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sra-solder.com
Key Highlights: 1–6 day delivery 30-day returnsWelcome to the SRA web site. We offer a wide selection of soldering and brazing alloys in paste and wire form. We carry Aoyue soldering, desoldering….
#6 Products |HAKKO
Domain Est. 1998
Website: hakko.com
Key Highlights: Product Search Lineup, Auto-Sodering System, Auto-Sodering System, Soldering Iron, Soldering Iron, Desoldering/Rework, Desoldering/Rework, FUME EXTRACTOR, Fume ……
#7 Priben Soldering Electronics Equipment and Materials
Domain Est. 2012
Website: priben.co.za
Key Highlights: Priben Distribution offers one of the largest range of soldering paste and flux product lines to the African markets….
#8 Solder Flux & Liquid Flux Products
Domain Est. 2018
Website: macdermidalpha.com
Key Highlights: Our liquid flux products improve wetting, minimize defects, and ensure strong, electrochemically reliable joints, enhancing overall quality and performance….
#9 MaxxPamma
Domain Est. 2023
Website: maxxpamma.com
Key Highlights: SOLDERING STATION & IRON · HOT AIR GUN · SOLDERING – PPD PASTE / FLUX & SPRAY · ELECTRONIC CLEANER · LED LAMP / UV LIGHTS · BLOWER · SCREW DRIVER & SHEARS ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solder Flux Pen
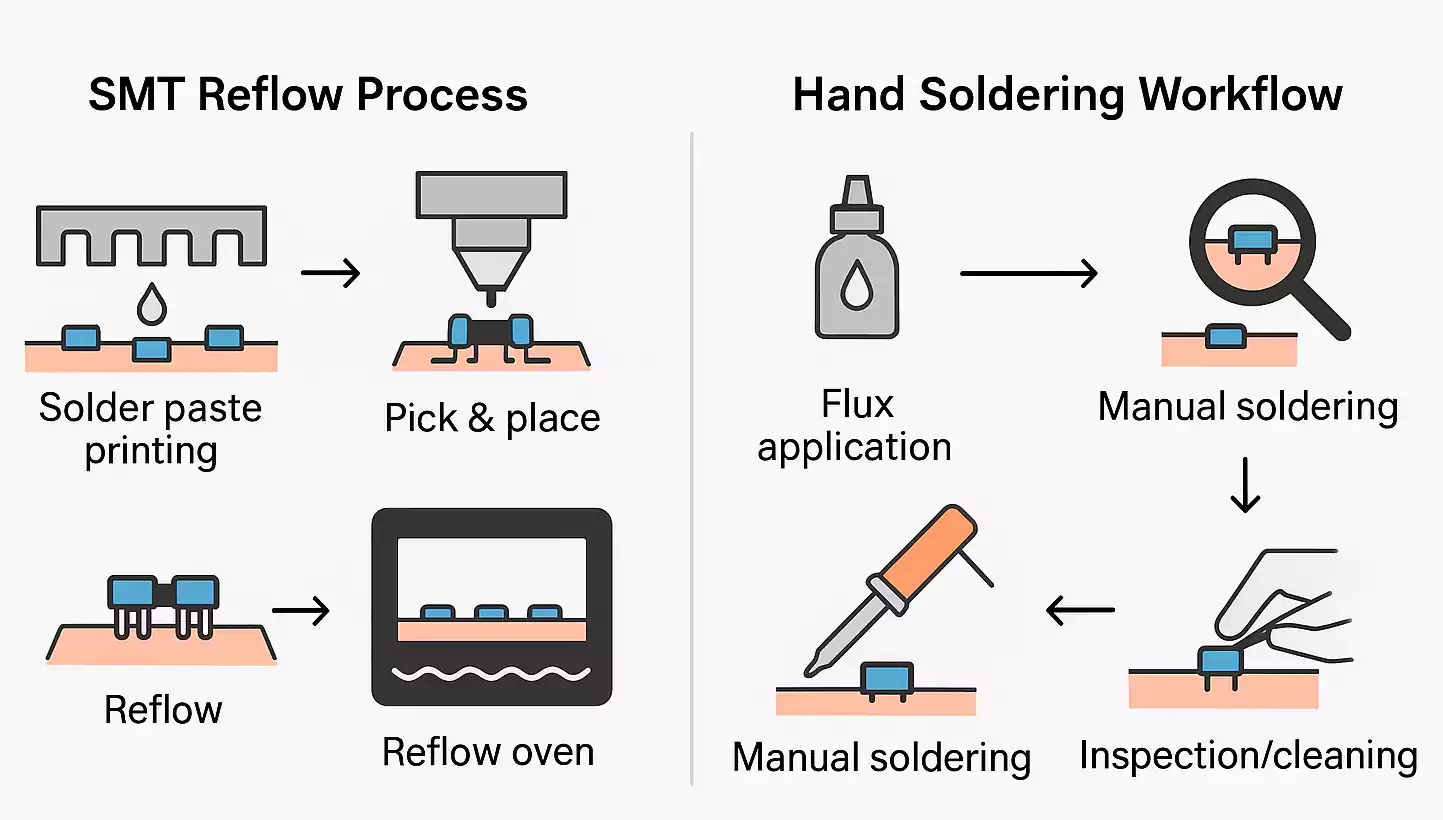
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Solder Flux Pens
The global solder flux pen market is poised for steady growth through 2026, driven by increasing demand for compact, user-friendly tools in electronics manufacturing, repair, and prototyping. As electronic devices become more miniaturized and complex, precision soldering tools like flux pens are gaining prominence. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape by 2026.
1. Rising Demand in Electronics Repair and DIY Markets
The proliferation of consumer electronics and the growing do-it-yourself (DIY) culture are fueling demand for solder flux pens. These tools offer controlled application of flux, reducing waste and improving solder joint quality. With the Right-to-Repair movement gaining momentum globally, especially in North America and Europe, more individuals and independent repair shops are adopting flux pens for efficient and accurate repairs.
2. Expansion in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, particularly countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia, is expected to witness strong market growth due to expanding electronics manufacturing and rising investments in consumer electronics. Localized production and affordable flux pen variants are making the product accessible to a broader base of technicians and small-scale manufacturers.
3. Product Innovation and Formulation Advancements
Manufacturers are focusing on eco-friendly, no-clean flux formulations that comply with environmental regulations such as RoHS and REACH. Additionally, improvements in viscosity and residue control are enhancing performance, especially for high-density circuit boards. Refillable and ergonomic pen designs are also becoming more common, appealing to professional and hobbyist users alike.
4. Integration with Smart and Automated Tools
While flux pens remain primarily manual tools, there is a trend toward integration with digital soldering stations and smart prototyping kits. Some advanced models now include features like flow control indicators and compatibility with IoT-enabled workbenches, catering to automated and semi-automated production environments.
5. Competitive Landscape and Brand Differentiation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with both established chemical suppliers (e.g., MG Chemicals, Kester) and niche brands vying for market share. Differentiation is being achieved through specialized formulations (e.g., for lead-free soldering, high-temperature applications), packaging innovations, and bundled kits targeting educational and training sectors.
6. Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers to reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and adopt biodegradable packaging. By 2026, compliance with stricter environmental standards is expected to be a key purchasing criterion, particularly in regulated markets like the EU and North America.
In conclusion, the solder flux pen market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, sustainability, and broader accessibility. Driven by trends in repair, miniaturization, and environmental responsibility, the segment is projected to maintain a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5–7% through the forecast period, solidifying its role in modern electronics assembly and maintenance.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solder Flux Pens (Quality & IP)
Sourcing solder flux pens may seem straightforward, but overlooking key factors can lead to significant quality issues, production delays, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these common pitfalls ensures reliable performance and legal compliance.
Poor Flux Formulation and Inconsistent Quality
One of the most frequent issues is selecting flux pens with subpar or inconsistent chemical formulations. Low-quality flux may contain excessive residues, have poor thermal stability, or fail to provide adequate wetting during soldering. This results in weak solder joints, bridging, or component damage. Additionally, inconsistent viscosity or flow rate across different pen units leads to unreliable application, impacting process repeatability and product reliability in high-volume manufacturing.
Lack of Compliance with Industry Standards
Many sourced flux pens do not meet critical industry standards such as IPC-J-STD-004 or RoHS. Non-compliant flux may contain banned substances like lead or halides, risking regulatory penalties and product recalls. Furthermore, using flux that doesn’t align with your assembly process (e.g., no-clean vs. water-soluble) can lead to cleaning challenges or long-term reliability concerns such as electrochemical migration.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Suppliers, particularly from unverified sources, often fail to provide adequate technical documentation—such as Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), flux composition, or batch traceability. This lack of transparency complicates quality audits, failure analysis, and regulatory compliance. Without batch-specific data, identifying the root cause of soldering defects becomes nearly impossible.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks from Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Products
Sourcing from unauthorized or dubious suppliers increases the risk of purchasing counterfeit flux pens that mimic well-known brands. These products not only underperform but may also infringe on IP rights, exposing your company to legal liability. Using counterfeit or unlicensed products in your manufacturing process could compromise your own product certifications and damage your brand reputation.
Poor Dispensing Mechanism and Packaging
Low-cost flux pens often feature unreliable dispensing tips that clog easily, leak, or deliver inconsistent amounts of flux. This results in operator frustration and inconsistent application, leading to rework and increased defect rates. Additionally, poor packaging can expose the flux to moisture or contamination, degrading its effectiveness before use.
Insufficient Supplier Vetting and Supply Chain Transparency
Relying on suppliers without proper vetting—especially those offering unusually low prices—can lead to supply chain disruptions and hidden quality issues. Lack of transparency in the supply chain makes it difficult to ensure ethical sourcing, consistent quality, and responsiveness to technical support needs.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, including requesting samples, verifying certifications, reviewing supplier audits, and ensuring IP compliance before integrating flux pens into your production process.
H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solder Flux Pen
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal handling, storage, transportation, and use of Solder Flux Pens. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, safety, and product integrity.
H3: Regulatory Classification & Documentation
- GHS/SDS Compliance:
- Mandatory SDS: A current, supplier-provided Safety Data Sheet (SDS) compliant with the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) is required for every flux pen product.
- Classification: Review Section 2 (Hazard Identification) of the SDS. Common classifications include:
- Flammability: Many fluxes contain flammable solvents (e.g., alcohols). Look for H225 (Highly flammable liquid and vapour) or H226 (Flammable liquid and vapour).
- Health Hazards: Potential for skin irritation (H315), serious eye irritation (H319), respiratory irritation (H335), or specific target organ toxicity (H370, H372 – less common, but check).
- Environmental Hazards: Potential aquatic toxicity (H400, H410).
- Labeling: Ensure the flux pen container and its immediate packaging display GHS-compliant labels with Pictograms (e.g., Flame, Exclamation Mark), Signal Word (e.g., “Danger”, “Warning”), Hazard Statements (H-phrases), and Precautionary Statements (P-phrases) as per the SDS and local regulations (e.g., OSHA HazCom, CLP in EU/UK).
- Transportation Regulations (Dangerous Goods):
- Classification: Determine if the flux pen is classified as Dangerous Goods for transport based on its SDS (Section 14: Transport Information).
- Common UN Numbers:
- UN 1133: PAINT related material, n.o.s. (including fluxes with flammable liquids).
- UN 1263: FLAMMABLE LIQUID, N.O.S. (if the flux is primarily flammable solvent).
- UN 3065: ENVIRONMENTALLY HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCE, LIQUID, N.O.S. (if aquatic toxicity is the primary hazard).
- Mode-Specific Rules:
- Air (IATA DGR): Strict limits on quantity per package and per consignment (often limited to “Excepted Quantities” or “Limited Quantities” for small pens). Requires specific packaging, labeling, and documentation (Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods if exceeding limits).
- Road/Rail (ADR/RID): Similar classification; requires proper labeling, packaging, and potentially a transport document if exceeding Limited Quantity thresholds.
- Sea (IMDG Code): Classification and packaging requirements apply; documentation needed if exceeding Limited Quantity.
- Limited/Excepted Quantities: Small flux pens (e.g., < 500ml) often qualify for simplified regulations under “Limited Quantities” (LQ – packaging code “Y”) or “Excepted Quantities” (EQ – packaging code “E”). Crucially verify eligibility based on UN number, packing group, and quantity per inner/outer packaging using the applicable regulations. Even under LQ/EQ, specific packaging and marking requirements apply.
- Country-Specific Regulations: Be aware of national variations (e.g., REACH/SVHC in EU, TSCA in US, K-REACH in Korea). Check for substance restrictions or registration requirements.
H3: Storage Requirements
- Location: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight, heat sources, and ignition sources (open flames, sparks, hot surfaces). Designated flammable storage cabinets are often required for significant quantities.
- Segregation: Store away from oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases, and incompatible materials (check SDS Section 10: Stability and Reactivity).
- Containment: Use secondary containment (e.g., spill trays) if storing significant quantities to contain leaks.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access for inspection and emergency response. Keep storage areas clean and organized.
- Temperature: Adhere to the storage temperature range specified on the SDS or product label. Avoid freezing.
H3: Handling & Use
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandatory use as specified in SDS Section 8:
- Gloves: Chemically resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile rubber). Check SDS for specific recommendations.
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or a face shield, especially when dispensing or if splashing is possible.
- Respiratory Protection: Usually not required for occasional use in well-ventilated areas. Required if ventilation is inadequate, during large-scale use, or if SDS specifies (e.g., H335). Use appropriate respirators (e.g., N95 for particulates, organic vapor cartridge for solvents) based on risk assessment.
- Protective Clothing: Lab coat or apron to protect skin and clothing.
- Ventilation: Use in a well-ventilated area. Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) like a fume extractor is highly recommended, especially for frequent or prolonged use, to control solvent vapors and flux fumes generated during soldering.
- Minimizing Exposure:
- Only apply the necessary amount of flux.
- Avoid skin contact. Wash hands thoroughly after handling, even when wearing gloves.
- Do not eat, drink, or smoke in handling areas.
- Clean up spills immediately using appropriate absorbents (e.g., spill pillows, vermiculite). Dispose of contaminated materials as hazardous waste.
- Soldering: Be aware that heating flux generates fumes. Ensure adequate ventilation/fume extraction during soldering operations.
H3: Transportation (Internal & External)
- Internal Movement: Use secondary containment (trays, bins) when moving pens within a facility. Secure loads to prevent tipping or leakage. Follow designated safe routes.
- External Shipment:
- Classification: Confirm UN number, Proper Shipping Name, Hazard Class, Packing Group, and applicable quantity limits (LQ/EQ) using the SDS and transport regulations.
- Packaging: Use UN-certified packaging appropriate for the hazard and quantity (e.g., robust outer box, inner leak-proof containers, cushioning). For LQ/EQ, use packaging meeting the specific requirements (e.g., triple packaging for EQ).
- Marking & Labeling: Apply correct hazard labels (e.g., Class 3 Flammable Liquid) and, for LQ/EQ, the specific Limited Quantity mark (diamond-shaped black & white) or Excepted Quantity mark (square-on-point black & white). Mark outer packaging with Proper Shipping Name, UN number, and shipper/consignee information.
- Documentation: Prepare required shipping papers (e.g., Air Waybill, Bill of Lading) with accurate description, UN number, class, and quantity. A Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods is mandatory if shipping outside LQ/EQ limits. Include the SDS with the shipment or make it readily available to carriers.
- Carrier Notification: Inform the carrier of the hazardous nature of the shipment if required by regulations or carrier policy.
H3: Waste Disposal
- Classification: Spent flux, contaminated rags, spill cleanup materials, and empty containers are likely hazardous waste due to flammability and/or toxicity (check SDS Section 13: Disposal Considerations).
- Procedure:
- Collect waste in compatible, labeled, closed containers (e.g., metal can with tight lid for flammable waste).
- Never dispose of down drains or in regular trash.
- Never mix with other waste streams unless authorized.
- Dispose of through a licensed hazardous waste contractor following local, state/provincial, and national regulations (e.g., RCRA in the US).
- Empty containers should be disposed of as hazardous waste unless thoroughly cleaned and rendered non-hazardous (check local rules – “RCRA Empty” in US).
H3: Key Responsibilities
- Supplier: Provide accurate, up-to-date SDS and compliant product labeling.
- Importer/Distributor: Ensure correct classification, labeling, and documentation for the target market. Verify supplier SDS accuracy.
- End User (Company): Obtain and maintain SDS. Implement safe storage, handling, and use procedures. Train employees. Comply with transport regulations for shipments. Manage waste disposal legally. Conduct risk assessments.
Disclaimer: Regulations vary significantly by country, region, and quantity. This guide provides general principles. Always consult the specific SDS for the product, relevant national and international regulations (e.g., OSHA, EPA, DOT, IATA, ADR, REACH), and qualified safety/regulatory professionals to ensure full compliance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Solder Flux Pen:
After evaluating various suppliers, product specifications, cost factors, and performance requirements, it is concluded that sourcing a reliable and high-quality solder flux pen is essential for ensuring consistent soldering results, improving efficiency, and maintaining the integrity of electronic assemblies. The selected flux pen should offer precise application, be compatible with common solder types (e.g., lead-free or rosin-based), and meet industry standards for safety and cleanliness (e.g., low residue, non-corrosive).
Supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and availability of technical support are key criteria in the final decision. Reputable suppliers such as MG Chemicals, Kester, or Chemtronics provide trusted options that balance performance with value. In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach focusing on quality, compatibility, and supplier credibility will ensure optimal performance in both prototyping and production environments, ultimately enhancing overall product reliability and reducing rework rates.