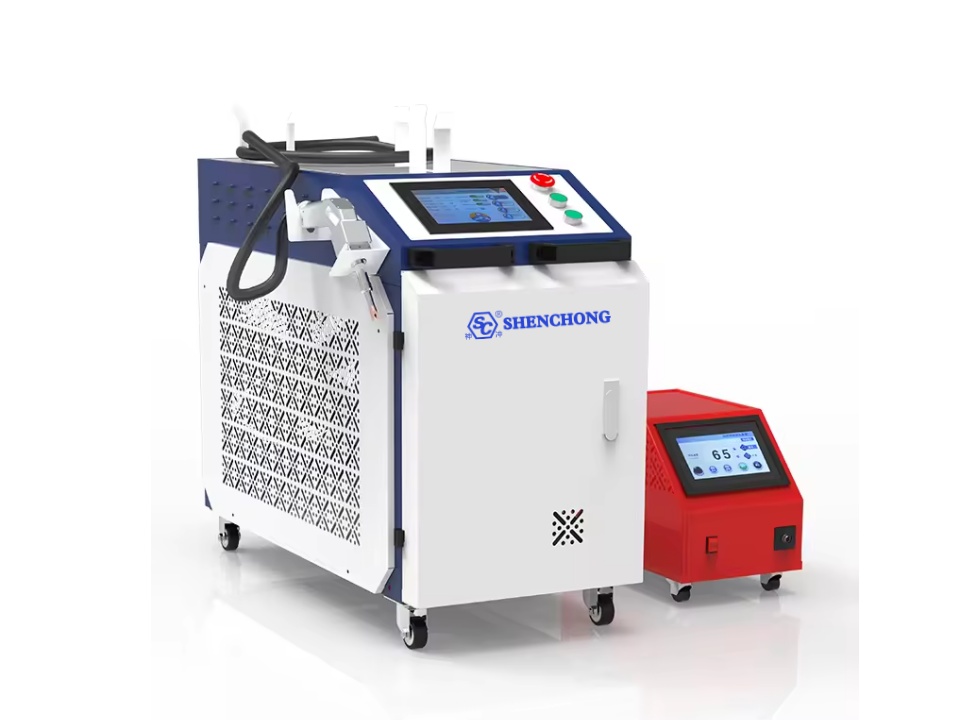
The global laser welding equipment market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining technologies across automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 2.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by the rising adoption of automation in manufacturing and the need for cleaner, more efficient welding processes. As manufacturers seek reliable performance and advanced integration capabilities, a handful of key players have emerged as leaders in innovation and sales. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and global distribution, here are the top 10 laser welding machine manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Soldadoras A Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Laser Technology
Website: luxinar.com
Key Highlights: Luxinar develops, manufactures and sells industrial laser sources. The company has been at the forefront of laser technology for over 25 years….
#2 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a leading manufacturer of mobile, flexible, and high-performance laser systems for laser welding, laser hardening, powder deposit welding and additive metal ……
#3 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#4 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#5 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#6 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#7 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#8 IPG Photonics
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: IPG Photonics manufactures high-performance fiber lasers, amplifiers, and laser systems for diverse applications and industries. Discover your solution….
#9 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#10 Laser machines for cutting, engraving, marking and …
Website: elettrolaser.com
Key Highlights: Laser machines for welding, engraving, marking, and cutting. Elettrolaser creates laser welding machines with engraving lasers that are among the best i……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Soldadoras A Laser
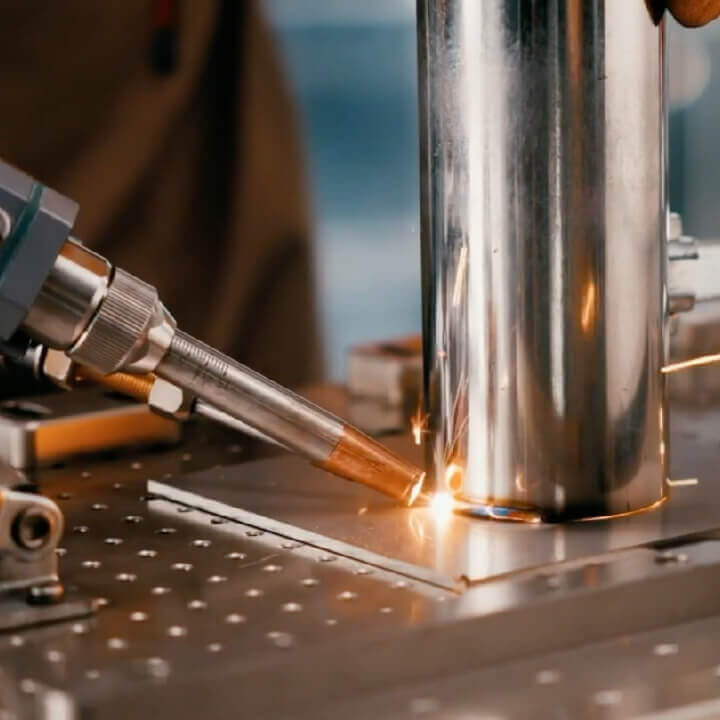

H2: Market Trends for Laser Welding Machines (Soldadoras a Láser) in 2026
By 2026, the global market for laser welding machines (soldadoras a láser) is expected to experience robust growth, driven by technological advancements, expanding industrial automation, and rising demand across key manufacturing sectors. Several critical trends are shaping the trajectory of this market:
-
Increased Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The rapid expansion of the electric vehicle industry is a major catalyst for laser welding demand. Laser welding offers high precision, speed, and strength—essential for battery pack assembly, powertrain components, and lightweight body structures. As EV production scales globally, especially in North America, Europe, and Asia, manufacturers are investing heavily in high-power fiber laser welding systems, boosting market growth. -
Growth in Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Integration of laser welding machines with Industry 4.0 technologies—such as AI-driven process monitoring, IoT-enabled predictive maintenance, and robotic automation—is becoming standard. By 2026, smart laser welding cells capable of real-time quality control and adaptive parameter adjustment are expected to dominate advanced production lines, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. -
Advancements in Fiber and Hybrid Laser Technologies
Fiber lasers continue to gain market share due to their superior energy efficiency, lower maintenance, and higher beam quality compared to traditional CO₂ lasers. Additionally, hybrid laser-arc welding systems are gaining traction in heavy industries like shipbuilding and construction, combining the penetration depth of arc welding with the precision of lasers. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Countries in Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America are modernizing their manufacturing infrastructure, creating new opportunities for laser welding equipment. Government initiatives to promote domestic manufacturing (e.g., “Make in India” or “Industry 4.0 Mexico”) are accelerating the adoption of advanced welding technologies. -
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient laser systems to meet environmental regulations and reduce operational costs. By 2026, laser welding machines with optimized power consumption and recyclable components are expected to appeal to environmentally conscious industries. -
Consolidation and Innovation Among Key Players
The competitive landscape is seeing increased consolidation, with major players like TRUMPF, IPG Photonics, and Han’s Laser acquiring smaller innovators to enhance their technology portfolios. Simultaneously, startups are introducing compact, cost-effective laser welders for SMEs, democratizing access to high-precision welding. -
Rising Demand in Medical and Aerospace Sectors
High-precision applications in medical device manufacturing (e.g., stents, implants) and aerospace (e.g., turbine components, structural assemblies) continue to drive demand for pulsed and ultrafast laser welding systems, known for minimal heat distortion and superior weld quality.
In conclusion, by 2026, the soldadoras a láser market will be characterized by technological sophistication, deeper integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems, and broadening applications across high-growth industries. Companies that invest in innovation, sustainability, and regional market expansion are poised to lead in this dynamic landscape.
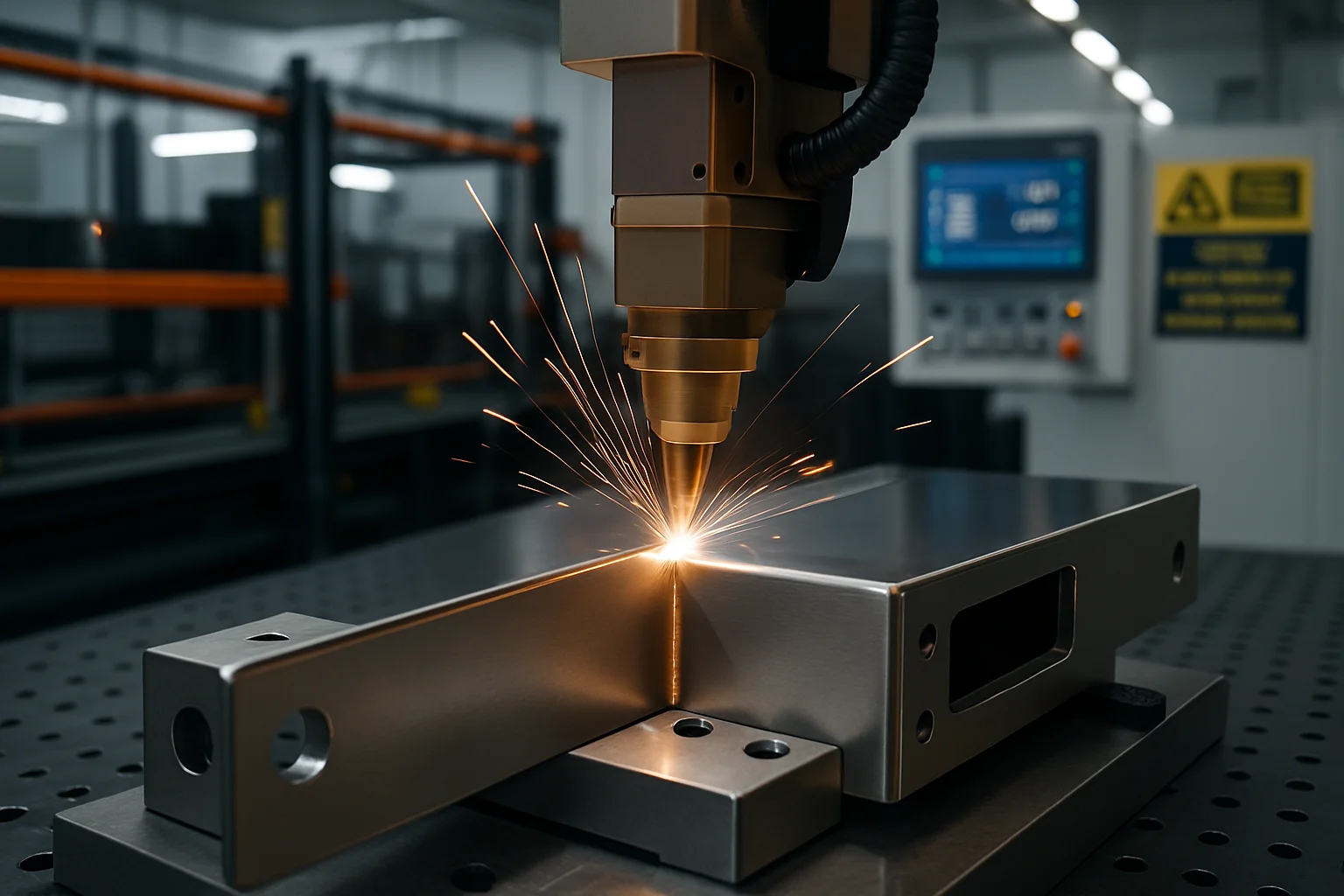

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Soldadoras a Láser (Quality and IP Considerations)
Sourcing laser welding machines (soldadoras a láser) involves significant technical, quality, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Avoiding these common pitfalls is crucial for ensuring long-term operational success and legal compliance.
Inadequate Quality Verification and Testing
Many buyers focus solely on price and specifications without validating the actual performance and durability of the laser welding machine. This can lead to receiving units that fail to meet production standards, suffer from frequent breakdowns, or produce subpar welds. Key issues include:
- Lack of On-Site Testing: Failing to request or perform real-world welding trials under conditions similar to your production environment.
- Overreliance on Brochures: Assuming advertised power, precision, and speed ratings reflect real performance without third-party validation.
- Poor Quality Control in Manufacturing: Especially with suppliers from regions with inconsistent manufacturing standards, where component quality (e.g., optics, cooling systems, control boards) may be substandard.
Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing from certain markets—particularly where IP enforcement is weak—exposes buyers to significant legal and reputational risks:
- Counterfeit or Cloned Technology: Some suppliers offer machines that replicate patented designs, software, or components from leading brands (e.g., Trumpf, IPG, or Han’s Laser) without authorization. Using such equipment may expose your company to infringement claims.
- Embedded Proprietary Software: Machines may include unlicensed control software or firmware, which can lead to compliance issues, lack of updates, or sudden operational failures.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Lack of visibility into component origins increases the risk of inadvertently using equipment with stolen IP, particularly in high-tech subsystems like laser sources or motion control systems.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines can become liabilities if reliable technical support and spare parts are unavailable:
- Limited Local Service Networks: Many suppliers, especially smaller or overseas-based ones, lack trained technicians nearby, leading to long downtimes.
- Obsolescence Risk: Machines may use proprietary components that are discontinued quickly, making long-term maintenance difficult.
- Language and Communication Barriers: Can delay troubleshooting and increase error rates during setup or repairs.
Overlooking Safety and Certification Standards
Laser welding machines must comply with regional safety standards (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO 60825). Sourcing non-compliant units can lead to:
- Workplace Safety Hazards: Inadequate enclosures, interlocks, or ventilation systems increase the risk of accidents.
- Customs or Regulatory Rejection: Machines may be detained or banned from operation if they lack proper certifications.
- Insurance and Liability Issues: Non-certified equipment may void workplace insurance policies in the event of an incident.
Failure to Verify Supplier Credentials and Long-Term Viability
Partnering with unreliable suppliers can jeopardize your investment:
- Short-Term Suppliers: Some vendors operate temporarily, disappearing after the sale and leaving buyers without support.
- Lack of References or Case Studies: Reputable suppliers should provide verifiable customer testimonials and successful installation examples in your industry.
- Unclear Warranty Terms: Ambiguous or restrictive warranties can limit recourse in case of defects or performance issues.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—prioritizing verified quality, conducting due diligence on IP compliance, ensuring support availability, confirming certifications, and vetting suppliers—companies can make more secure and effective sourcing decisions for laser welding equipment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Soldadoras a Láser (Laser Welders)
Product Classification and Regulatory Overview
Laser welding machines (soldadoras a láser) are classified as industrial machinery and laser products, subject to multiple international and regional regulations. Key classifications include HS Code 8515.21 for electric welding equipment and compliance with IEC 60825-1 for laser safety. Exporters must verify country-specific requirements, including conformity assessments, labeling, and technical documentation.
Safety and Technical Compliance
Ensure all laser welding systems comply with IEC 60825-1 (laser radiation safety) and IEC 60204-1 (safety of machinery – electrical equipment). Machines must feature proper interlocks, emergency stops, and laser warning labels in the local language of the destination country. CE marking is mandatory for EU imports, while FDA registration is required for U.S. market entry under 21 CFR 1040.10/1040.11.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Use robust, climate-resistant packaging with shock-absorbing materials to protect sensitive optical and electronic components. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and laser warning symbols. Include desiccants if shipping to humid regions. Secure all moving parts and optics, and anchor the unit within the crate to prevent shifting during transit.
Export Documentation
Prepare a complete export dossier including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, certificate of origin, and technical specifications. For regulated markets, include a Declaration of Conformity (DoC), CE certificate, or FDA accession number. Some countries may require pre-shipment inspection (PSI) or a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) from authorized bodies.
Import Regulations by Key Markets
- European Union: CE marking required; comply with the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and EMC Directive (2014/30/EU). Notify a Notified Body if necessary.
- United States: Register with FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH); submit a product report and annual certification.
- Canada: Comply with the Radiation Emitting Devices Act (REDA); provide a detailed technical report to Health Canada.
- Mexico: NMX-SE-002-SCFI-2013 applies; NOM-024-SCFI-2016 may require import licensing.
Transportation and Freight Considerations
Use freight forwarders experienced in handling high-value industrial equipment. Opt for sea freight (FCL/LCL) for cost efficiency or air freight for urgent deliveries. Ensure cargo insurance covers damage, theft, and delays. Monitor shipments via GPS tracking, especially for units with sensitive optics or control systems.
Customs Clearance and Duties
Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes to avoid delays. In the U.S., laser welders typically face a duty rate of 1.7%; EU rates vary by member state (usually 0–2.5%). Be prepared for customs inspections—maintain digital copies of all compliance documents accessible to agents at ports of entry.
After-Sales and Technical Support Compliance
Offer multilingual user manuals and safety instructions. Ensure remote diagnostics and software updates comply with local data privacy laws (e.g., GDPR in Europe). Provide on-site technician training where required, adhering to local labor and immigration regulations for service personnel.
Environmental and End-of-Life Compliance
Adhere to WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive in the EU for end-of-life take-back obligations. Inform customers of proper disposal procedures. Avoid hazardous substances in accordance with RoHS (EU) or similar regulations in target markets.
Audit and Continuous Compliance
Conduct annual internal audits of export processes and regulatory updates. Subscribe to regulatory intelligence services to monitor changes in laser safety, machinery, or trade policies. Maintain a compliance management system (CMS) to track certifications, renewals, and product modifications.
Conclusión sobre la Fuente de Soldadoras a Láser
La selección y adquisición de soldadoras a láser requiere un enfoque estratégico que considere no solo el costo inicial del equipo, sino también factores clave como la calidad del proceso de soldadura, la precisión, la automatización, el soporte técnico, la disponibilidad de repuestos y la capacitación del personal. Tras evaluar diferentes proveedores y tecnologías disponibles en el mercado, se concluye que invertir en soldadoras a láser de origen confiable — ya sea de fabricantes europeos, asiáticos o norteamericanos — representa una ventaja competitiva significativa en sectores como la automotriz, aeroespacial, médica y de fabricación de precisión.
Las soluciones de última generación ofrecen mayor eficiencia energética, integración con sistemas de fabricación inteligente (Industria 4.0) y una relación costo-beneficio favorable a mediano y largo plazo, gracias a su bajo mantenimiento y alta repetibilidad. Asimismo, establecer alianzas con proveedores que ofrezcan asistencia técnica local y garantías amplias minimiza tiempos de inactividad y asegura la continuidad operativa.
En definitiva, la decisión de aprovisionarse de soldadoras a láser debe basarse en un análisis técnico-económico integral, priorizando la calidad, el soporte postventa y la escalabilidad tecnológica, con el fin de maximizar la productividad y mantener altos estándares de fabricación en un mercado cada vez más exigente.