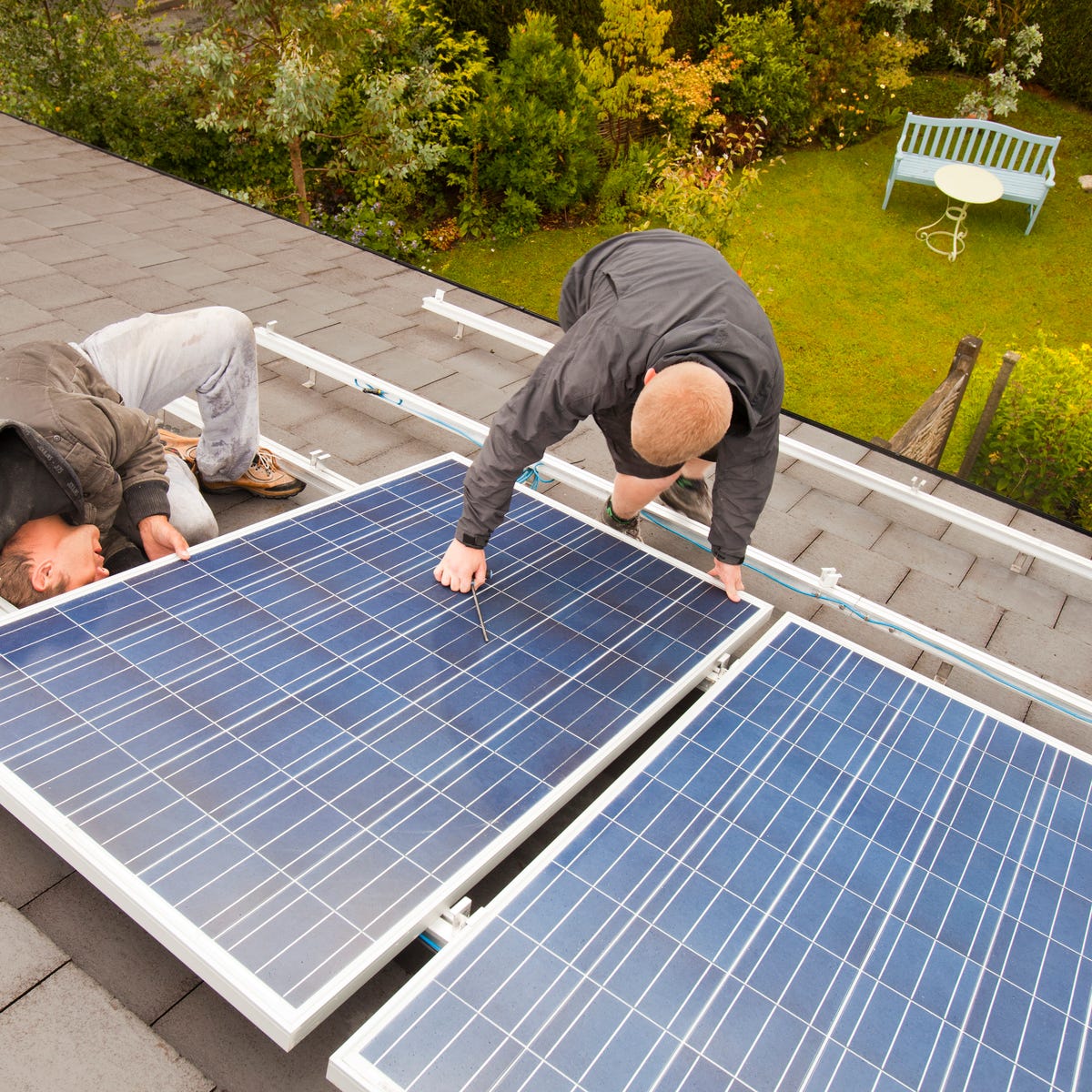
The solar power roof shingles market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient building materials and supportive government policies. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) market—of which solar roof shingles are a key segment—was valued at USD 12.4 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence projects similar momentum, forecasting a CAGR of over 13% between 2023 and 2028, fueled by advancements in solar technology and increasing residential solar adoption. As homeowners and builders seek aesthetically pleasing, dual-function roofing solutions, solar shingles have emerged as a compelling alternative to traditional panels. This surge in market potential has paved the way for innovation and competition, with a select group of manufacturers leading in product development, cost efficiency, and scalability. Below, we explore the top 9 solar power roof shingles manufacturers based on technological capability, pricing competitiveness, and market footprint.
Top 9 Solar Power Roof Shingles Cost Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 GAF Roofing
Domain Est. 1996
Website: gaf.com
Key Highlights: The right solution for any project · Asphalt shingles · Asphaltic system components · Solar roofing · TPO roofing systems · Roof coating systems · Low-slope asphalt ……
#2 Solar Roof
Domain Est. 1992
Website: tesla.com
Key Highlights: Power your home with a fully integrated solar and energy storage system. The glass solar tiles and steel roofing tiles look great up close and from the street….
#3 Solarstone
Domain Est. 1997
Website: solarstone.com
Key Highlights: SOLARSTONE develops and manufactures integrated solar roofs that combine energy production, durability, and architectural integrity….
#4 How Much Do Solar Shingles Cost? Pros, Cons, and ROI
Domain Est. 2000
Website: modernize.com
Key Highlights: The average cost to install solar roof shingles is $42,000 to $50,000 for a 2,000-square-foot roof, or $21 to $25 per square foot ($2,100 to $2 ……
#5 Trinity Solar
Domain Est. 2005
Website: trinitysolar.com
Key Highlights: Premium solar and roofing installed by experts. For over 30 years, Trinity Solar has provided custom solutions and outstanding service….
#6 Solar
Domain Est. 2007
Website: certainteed.ca
Key Highlights: Highly efficient panels and shingles needn’t compromise on aesthetics to deliver clean energy while also preventing water intrusion. Solstice® Solar Systems ……
#7 LUMA Solar
Domain Est. 2016
Website: lumasolar.com
Key Highlights: Luxury solar roofs for beautiful structures and forever homes. We developed the first fully-integrated solar shingle system in North America….
#8 Solar Shingles 101
Domain Est. 2007
Website: solarpowerauthority.com
Key Highlights: The cost of a solar shingle system varies greatly with your home’s square footage, energy needs, shingle manufacturer and the solar installer. Some systems, ……
#9 Solar Roof Shingles Cost and Homeowners Guide 2026
Domain Est. 1998
Website: ecowatch.com
Key Highlights: The average cost of solar roof shingles ranges between $25,000 to $60,000, or between $15 to $35 per square foot, for the average U.S. roof size of 1,700 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Power Roof Shingles Cost

2026 Market Trends for Solar Power Roof Shingles Cost
By 2026, the market for solar power roof shingles is expected to undergo significant transformation, driven by technological innovation, policy shifts, and growing consumer demand. These factors are converging to influence the cost trajectory of this emerging building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) technology.
Declining Production Costs and Economies of Scale
A primary driver behind projected cost reductions by 2026 is the anticipated expansion in manufacturing capacity. As major producers like GAF Energy, Tesla, and newer entrants scale up production, economies of scale are expected to lower per-unit manufacturing expenses. Increased automation and improvements in materials processing—such as more efficient thin-film or perovskite-silicon tandem cells—could further reduce material waste and assembly times. These efficiencies are likely to translate into lower upfront costs for consumers, potentially bringing prices closer to parity with conventional solar panels plus traditional roofing materials.
Falling Installation and Soft Costs
Beyond hardware, “soft costs” such as permitting, design, and labor currently represent a significant portion of solar shingle installations. By 2026, streamlined permitting processes, wider installer training programs, and standardized installation protocols are expected to reduce labor time and complexity. With more roofing contractors becoming certified to install solar shingles, competition in the installation market may intensify, leading to lower labor rates. Additionally, integration with roofing replacements—where solar shingles are installed during re-roofing projects—could reduce overall project costs by eliminating the need for separate roof and solar installations.
Policy Incentives and Tax Credits
Government incentives will continue to play a crucial role in shaping affordability. In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) extends the 30% federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) through 2032, which applies to solar shingles as a qualified technology. Many states and municipalities are expected to introduce or expand additional rebates and property tax exemptions by 2026, especially in regions prioritizing clean energy and building decarbonization. These incentives can significantly reduce the net cost to homeowners, improving return on investment and payback periods.
Competitive Pressure and Market Expansion
The solar shingle market is poised for increased competition, with traditional solar companies, roofing manufacturers, and tech startups entering the space. This growing competition is likely to drive price reductions and stimulate innovation in both performance and aesthetics. As product differentiation increases—offering various styles, colors, and energy outputs—manufacturers may adopt value-based pricing strategies, making entry-level options more accessible. Greater consumer awareness and demand for seamless solar integration will further accelerate market growth and cost efficiency.
Integration with Smart Home and Storage Systems
By 2026, solar shingles are increasingly being marketed as part of broader home energy ecosystems, including battery storage and smart energy management systems. While these integrations may raise the initial system cost, they enhance long-term value by increasing energy self-sufficiency and resilience. The bundling of solar shingles with financing options, such as solar leases or power purchase agreements (PPAs), could also lower barriers to entry and spread costs over time, making the technology more financially viable for average homeowners.
Conclusion
By 2026, solar power roof shingles are expected to become more cost-competitive due to declining production and installation expenses, robust policy support, and intensified market competition. While they may still carry a premium over traditional solar panels, the gap is projected to narrow significantly. As technology matures and adoption increases, solar shingles are likely to transition from a niche luxury product to a mainstream residential energy solution, offering both aesthetic appeal and long-term economic benefits.

H2. Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solar Power Roof Shingles: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing solar power roof shingles involves more than just comparing prices—overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to significant long-term risks. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Quality and Durability
Many buyers focus on upfront cost savings, opting for cheaper, unproven brands. Low-quality shingles may degrade faster, offer lower energy efficiency, or fail under environmental stress (hail, wind, temperature swings). This leads to higher lifetime costs due to maintenance, repairs, or early replacement.
2. Lack of Third-Party Certifications
Failing to verify certifications such as UL 1703, IEC 61215, or ENERGY STAR can expose buyers to substandard products. Certified shingles have undergone rigorous safety, performance, and durability testing—essential for both residential safety and warranty validity.
3. Inadequate Warranty Coverage
Some manufacturers offer long-term power output warranties (e.g., 25 years), but the fine print may exclude workmanship, weather damage, or proper installation. A comprehensive warranty should cover both product defects and performance degradation.
4. Overlooking Compatibility with Existing Roofing Systems
Solar shingles must integrate seamlessly with underlayment, flashing, and roofing materials. Poor compatibility leads to leaks, structural damage, or voided roofing warranties. Always confirm system integration requirements before procurement.
5. Ignoring Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing from manufacturers with unclear IP ownership—especially in regions with weak IP enforcement—can lead to legal exposure. Using shingles that infringe on patented technologies (e.g., Tesla’s integrated solar tile designs) may result in cease-and-desist orders or liability for end users and installers.
6. Relying on Unverified Suppliers or OEMs
Many suppliers rebrand solar shingles from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) without transparency. This can obscure the true origin, quality control processes, and support availability. Always verify the manufacturer and request test reports or factory audits.
7. Underestimating Installation Expertise Requirements
Solar shingles require specialized installation knowledge. Choosing products without certified installer networks increases the risk of improper installation, which can compromise performance, safety, and warranty claims.
8. Neglecting Long-Term Support and Spare Parts Availability
Some emerging brands may lack the infrastructure for ongoing support. If the supplier goes out of business or discontinues a product line, obtaining replacement shingles or technical support becomes difficult.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, conduct thorough due diligence: vet suppliers, demand certification documentation, validate IP legitimacy, and prioritize products with strong warranties and installer support. Investing time upfront ensures reliable performance, legal safety, and better return on investment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Power Roof Shingles: Cost Considerations
When integrating solar power roof shingles into residential or commercial construction, understanding the logistics and compliance aspects is essential to accurately estimate and manage costs. This guide outlines key factors affecting the total cost, from transportation and installation to permitting and regulatory requirements.
Transportation and Supply Chain Logistics
The cost of solar roof shingles is influenced significantly by logistical challenges in transportation and supply chain management. These specialized materials are often manufactured in limited facilities and may require careful handling due to their fragility.
- Shipping Costs: Solar shingles are heavier and more delicate than traditional roofing materials, increasing freight charges. International sourcing can lead to tariffs and longer lead times, impacting project timelines and expenses.
- Storage Requirements: On-site storage must protect shingles from weather, breakage, and theft. Climate-controlled or secure staging areas may be needed, adding to overhead.
- Inventory Management: Just-in-time delivery is ideal to reduce storage costs, but supply chain disruptions can cause delays and cost overruns. Maintaining buffer stock increases capital costs.
Installation and Labor Logistics
Installation of solar shingles requires specialized skills and coordination between roofing and electrical contractors, directly affecting labor costs.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: Certified installers for integrated solar roofing are limited, leading to higher labor rates and potential scheduling delays.
- Integration Complexity: Unlike traditional solar panels, solar shingles are installed like roofing materials while simultaneously forming an electrical system. This dual function increases installation time and complexity.
- Equipment and Tools: Specialized tools for cutting, sealing, and wiring solar shingles may require additional investment or rental fees.
Permitting and Regulatory Compliance
Navigating local, state, and federal regulations is a crucial—and often costly—part of solar shingle projects.
- Building Permits: Most jurisdictions require permits for structural and electrical modifications. Fees vary by location, and application processes can delay project start dates.
- Electrical Codes: Compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC), including rapid shutdown requirements and grounding standards, may necessitate additional components and inspections.
- Interconnection Agreements: Utility companies require approval before connecting solar systems to the grid. This process includes fees, technical reviews, and potential upgrade costs to the electrical service panel.
Incentives, Tax Credits, and Rebates
While not a direct cost, understanding compliance with incentive programs can significantly reduce net expenses.
- Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC): As of 2024, the ITC allows for a 30% tax credit on the total installed cost of solar shingles, including labor and permitting. Proper documentation is required to claim the credit.
- State and Local Incentives: Many regions offer rebates, property tax exemptions, or sales tax waivers. Eligibility often depends on using certified installers and approved equipment.
- Net Metering Policies: Compliance with utility-specific net metering rules affects long-term energy savings and return on investment.
Inspection and Certification Requirements
Post-installation compliance ensures system safety and eligibility for incentives.
- Municipal Inspections: Local building and electrical departments conduct inspections to verify code compliance. Failed inspections result in rework and added labor costs.
- UL and Building Code Certification: Solar shingles must meet Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standards (e.g., UL 1703) and local building codes for fire resistance, wind uplift, and electrical safety.
- Performance Monitoring Compliance: Some incentives require integration with certified monitoring systems to track energy production.
Environmental and Disposal Compliance
End-of-life management and environmental regulations also influence long-term cost planning.
- Recycling and Disposal: Solar shingles contain hazardous materials (e.g., cadmium telluride in some models). Disposal must comply with EPA and state regulations, potentially incurring fees.
- Roof Decommissioning: Removal and replacement of solar shingles at end-of-life require careful handling to avoid damage and ensure environmental compliance.
Conclusion
The total cost of solar power roof shingles extends beyond the product price to include logistics, labor, and compliance expenses. Proactive planning, engagement with certified professionals, and thorough understanding of regulatory requirements are critical to controlling costs and ensuring a successful installation. By accounting for these elements early in the project lifecycle, stakeholders can optimize both financial and operational outcomes.
In conclusion, sourcing solar power roof shingles involves a careful evaluation of both upfront costs and long-term benefits. While the initial investment is significantly higher than traditional roofing materials—typically ranging from $15 to $25 per square foot—solar shingles offer the dual advantage of energy generation and aesthetic integration with the roof. Key cost factors include the type of solar shingles (e.g., Tesla Solar Roof, GAF Energy, or CertainTeed), roof size and complexity, local labor rates, permitting, and available incentives such as the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which can offset up to 30% of installation costs.
Additionally, long-term savings on electricity bills, increased home value, and environmental benefits contribute to the overall value proposition. However, cost-effectiveness varies by region, sunlight exposure, and energy consumption patterns. Conducting a detailed site assessment and obtaining multiple quotes from certified installers are essential steps to ensure accuracy in projected costs and returns.
Ultimately, solar roof shingles represent a premium, sustainable roofing solution best suited for homeowners seeking energy independence, a seamless roof design, and a long-term commitment to renewable energy.