The global solar photovoltaic (PV) module market is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by declining technology costs, favorable government policies, and increasing demand for clean energy. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global solar panel market size was valued at USD 175.6 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% from 2024 to 2030. Another analysis by Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 7% during the forecast period 2024–2029, citing rising energy security concerns and advancements in solar cell efficiency as key growth catalysts. As utility-scale installations and distributed generation gain momentum worldwide, demand for high-quality, cost-effective solar modules has surged, positioning wholesale manufacturers as critical enablers of the energy transition. This growth trajectory has intensified competition among manufacturers, leading to innovation in product performance, durability, and pricing. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top solar module wholesale manufacturers offers valuable insights for developers, distributors, and EPC contractors aiming to source reliable and scalable solutions.
Top 10 Solar Module Wholesale Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Boviet Solar
Domain Est. 2017
Website: bovietsolar.com
Key Highlights: Boviet Solar is a solar energy technology company specializing in manufacturing top-performing solar PV modules for solar projects….
#2 Philadelphia Solar
Domain Est. 2008
Website: philadelphia-solar.com
Key Highlights: Philadelphia Solar is a leading Tier-1 solar panel manufacturer with 15+ years of experience in the industry. Our specialized expertise ensures top-quality ……
#3 Solar Panel Supplier & Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2011
Website: dmegcsolar.com
Key Highlights: As a leading solar panel manufacturer, DMEGC delivers high-efficiency PV panels for home, business and farm projects. Our solutions are ideal for wholesale, ……
#4 Canadian Solar
Domain Est. 2001
Website: canadiansolar.com
Key Highlights: COMPANY OVERVIEW. 170GW solar modules shipments. 15.7GWh battery storage shipments. Module capacity 51.8GW. Storage solution capacity 15GWh. Battery cell ……
#5 Solar Wholesale
Domain Est. 2004
Website: solarwholesale.com
Key Highlights: Building your own solar system? Get everything you need at wholesale prices! Shop our DIY solar kits, panels, and inverters. Free design help & fast shipping ……
#6 Shop Solar Panels for
Domain Est. 2006
#7 All Products
Domain Est. 2010
#8 Mission Solar
Domain Est. 2012
Website: missionsolar.com
Key Highlights: The 435W by Mission Solar Energy is a high-efficiency, American-made 108 half-cut cell solar module built for both residential and commercial rooftops. Rated at ……
#9 Wholesale Solar Panels
Domain Est. 2016
Website: a1solarstore.com
Key Highlights: $5 delivery · 14-day returnsIf you are looking for a place to buy wholesale solar panels, you’ve found it. A1 SolarStore offers PV modules from all over the world for competitive …
#10 Unbound Solar®
Domain Est. 2019
Website: unboundsolar.com
Key Highlights: Unbound Solar®, formerly Wholesale Solar, sells the best solar products & parts for off-grid, grid-tie, & custom solar solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Module Wholesale

H2 2026 Market Trends Analysis: Solar Module Wholesale
The solar module wholesale market in H2 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, shifting supply chains, evolving policy landscapes, and increasing global demand for clean energy. This analysis highlights the key trends shaping the wholesale landscape during this critical period.
1. Intensified Price Competition & Margin Pressure:
* Persistent Oversupply: Continued high manufacturing capacity, particularly from China, and potential new capacity additions in Southeast Asia, India, and the Americas will maintain downward pressure on wholesale module prices. Expect prices to stabilize at historically low levels but remain volatile.
* Commoditization Acceleration: Standard PERC and basic TOPCon modules will increasingly be viewed as commodities, leading to razor-thin margins for wholesalers dealing in these segments. Differentiation will become crucial.
* Value-Added Services as Differentiators: Wholesalers will need to move beyond simple volume sales. Success will depend on offering value-added services: technical support, logistics optimization, financing solutions, inventory management, and project-specific design assistance to maintain margins.
2. Technology Leadership Shifts:
* TOPCon Dominance in High-End: Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon) technology will solidify its position as the dominant high-efficiency technology in the wholesale market, capturing the largest share of premium module sales due to its superior performance (higher efficiency, lower degradation, better temperature coefficient) compared to PERC.
* HJT Gains Niche Traction: Heterojunction (HJT) modules, while facing higher manufacturing costs, will gain ground in specific high-value segments (e.g., space-constrained rooftops, high-temperature regions) due to their exceptional efficiency and bifaciality. Wholesalers will need to offer HJT options to cater to discerning customers.
* Perovskite-Silicon Tandem Emergence: While still primarily in pilot and early commercial phases, tandem modules will start appearing in limited wholesale channels, targeting premium residential and specialized commercial projects. Wholesalers establishing early relationships with tandem producers will gain a strategic edge.
* Bifacial Proliferation: Bifacial modules will become the standard offering for utility-scale and increasingly for large commercial projects, driven by proven energy yield gains. Wholesalers must ensure robust supply and expertise in bifacial system design considerations.
3. Geopolitical Fragmentation & Supply Chain Diversification:
* “China+1” Acceleration: Geopolitical tensions, trade policies (like UFLPA in the US, EU’s proposed CBAM), and corporate ESG mandates will accelerate the diversification of manufacturing away from China. Wholesalers will see increased availability (and demand) for modules from Vietnam, Malaysia, Thailand, India, the US, and potentially other regions.
* Regional Supply Hubs: Strong regional supply chains will emerge (e.g., US domestic modules under IRA, EU Green Deal Industrial Plan modules, India’s PLI scheme modules). Wholesalers will need to navigate complex regional sourcing strategies to meet customer requirements for local content, tariffs, and supply security.
* Supply Chain Resilience Focus: Wholesalers will prioritize partnerships with manufacturers demonstrating supply chain transparency, ethical sourcing (especially polysilicon), and resilience against disruptions. Traceability will be a key selling point.
4. Demand Drivers & Market Segmentation:
* Utility-Scale & C&I Growth: Continued strong growth in utility-scale solar and Commercial & Industrial (C&I) installations will be the primary demand drivers for wholesale modules. Wholesalers will need large-scale logistics and project support capabilities.
* Residential Resilience: The residential market will remain significant, particularly in markets with supportive policies (net metering, incentives). Wholesalers will focus on partnerships with large installer networks and offering modules optimized for aesthetics and ease of installation.
* Energy Storage Integration: The convergence of solar + storage will influence module selection. Wholesalers may bundle modules with inverter/storage solutions or partner closely with storage providers to offer integrated packages.
* Emerging Markets: Growth in Southeast Asia, Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East will create new wholesale opportunities, demanding tailored solutions and financing models.
5. Sustainability & ESG Imperatives:
* Carbon Footprint as a Key Metric: The carbon footprint of modules will become a critical procurement criterion, especially for corporate PPAs and projects in regions with carbon pricing. Wholesalers will need to provide verifiable data (e.g., Environmental Product Declarations – EPDs).
* Recycling & Circularity: Regulations around PV module end-of-life (e.g., EU WEEE) will tighten. Wholesalers may be expected to offer take-back schemes or partner with recycling providers, influencing procurement towards more recyclable designs.
* Ethical Sourcing Scrutiny: Due diligence on supply chains, particularly concerning polysilicon sourcing (avoiding forced labor), will be non-negotiable. Wholesalers will require robust documentation and auditing processes.
6. Digitalization & Efficiency:
* Enhanced B2B Platforms: Wholesalers will invest in sophisticated online platforms offering real-time pricing, inventory visibility, configuration tools, order tracking, and digital document management, improving efficiency for both themselves and their customers (installers/developers).
* Data-Driven Forecasting: Advanced analytics will be used for better demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and identifying emerging market opportunities.
Conclusion for H2 2026:
The solar module wholesale market in H2 2026 will be characterized by fierce competition in a low-price environment, demanding that wholesalers evolve from mere distributors to value-added partners. Success will hinge on:
* Strategic Sourcing: Navigating a fragmented global supply chain with diverse origins and ESG requirements.
* Technology Agility: Offering a broad portfolio covering dominant (TOPCon), emerging (HJT, Tandem), and commodity (PERC) technologies.
* Value Beyond Price: Providing essential technical, logistical, and financial services.
* Sustainability Leadership: Ensuring verifiable low carbon footprint and ethical sourcing.
* Digital Enablement: Leveraging technology for operational efficiency and customer service.
Wholesalers who proactively adapt to these converging trends will be best positioned to capture market share and thrive in the dynamic H2 2026 landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Solar Modules Wholesale: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing solar modules wholesale offers cost advantages, but it also presents significant risks, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) violations. Avoiding these pitfalls is crucial for protecting your business, ensuring project performance, and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Poor Module Quality and Performance
One of the most prevalent risks in wholesale solar sourcing is receiving substandard modules that fail to meet claimed specifications or degrade prematurely. This stems from several factors: manufacturers may cut corners on materials (e.g., using inferior encapsulants, backsheets, or cells), implement lax quality control processes, or falsify performance data. Modules with hidden defects—such as microcracks, delamination, or potential-induced degradation (PID)—may pass initial inspections but fail in the field, leading to reduced energy output, costly replacements, and damaged reputation. Relying solely on datasheets without independent verification or third-party testing significantly increases exposure to this risk.
Counterfeit and Cloned Products
The solar market is vulnerable to counterfeit modules that falsely bear the branding of reputable manufacturers. These clones often mimic the appearance of high-quality products but use low-grade components and lack proper certifications. Distributors may knowingly or unknowingly source such modules from unscrupulous suppliers, especially in regions with weak enforcement. Using counterfeit modules not only compromises system reliability but also voids warranties and can result in legal liability. Due diligence in verifying supplier authenticity and conducting batch testing is essential to mitigate this threat.
Lack of Genuine Warranties and Support
Wholesale suppliers may offer attractive pricing but provide limited or non-transferable warranties. Some may offer “warranty extensions” that aren’t backed by the original manufacturer, rendering them worthless if the supplier goes out of business. Genuine product and performance warranties from established manufacturers are critical for long-term project viability. Sourcing through unauthorized channels often means forfeiting access to reliable after-sales support, technical assistance, and warranty claims, leaving buyers exposed when issues arise.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Purchasing wholesale modules can inadvertently involve IP violations, especially when dealing with suppliers in jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement. Some manufacturers produce modules using patented cell technologies (e.g., PERC, TOPCon, HJT) or design elements without licensing them. Importing or deploying such modules—even unknowingly—can expose your business to legal action, customs seizures, or project shutdowns. Ensuring that suppliers use licensed technologies and providing documentation of IP compliance is essential for risk mitigation.
Inadequate or Fake Certifications
Many markets require solar modules to have certifications such as IEC 61215, IEC 61730, UL 61730, or country-specific approvals (e.g., CE, UKCA, INMETRO). Unreliable suppliers may provide falsified certification documents or list modules that haven’t undergone proper testing. Using uncertified modules can result in failed inspections, denied grid interconnection, insurance claim denials, and safety hazards. Always verify certifications directly with issuing bodies or through independent labs.
Supply Chain Opacity and Traceability
Wholesale sourcing often involves multiple intermediaries, obscuring the true origin of modules. This lack of traceability makes it difficult to assess environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance—such as adherence to anti-dumping regulations or forced labor laws (e.g., UFLPA in the U.S.). Modules produced in sanctioned regions or under unethical conditions can lead to shipment delays, financial penalties, or reputational damage. Demanding full supply chain transparency and documentation is critical to avoid these compliance risks.
Conclusion
To navigate these pitfalls, buyers must conduct thorough due diligence: verify supplier credentials, demand independent test reports (e.g., from TÜV, UL), confirm authentic warranties and certifications, and ensure IP compliance. Establishing direct relationships with reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors, despite potentially higher costs, often proves more reliable and cost-effective in the long term.
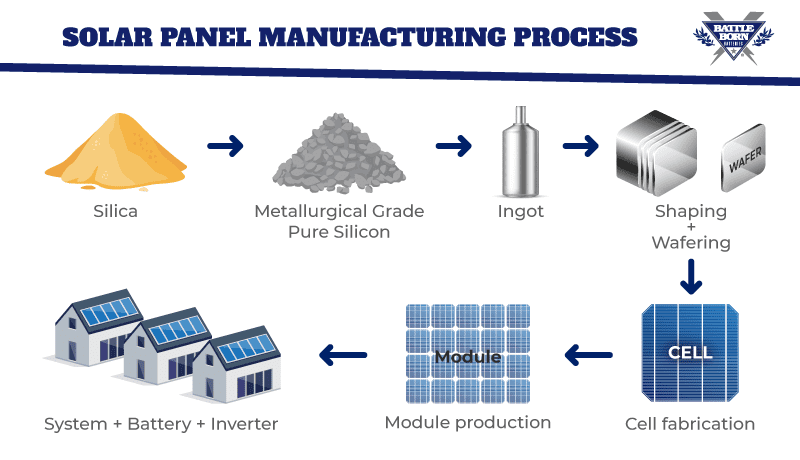
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Module Wholesale
Understanding International Shipping Requirements
Solar modules are classified as fragile and high-value cargo, requiring careful handling and specialized packaging. When shipping internationally, ensure compliance with International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations and International Air Transport Association (IATA) guidelines if using air freight. Modules must be secured in wooden crates or pallets with corner protectors and moisture barriers to prevent damage from humidity, shock, or vibration during transit. Temperature-controlled environments may be necessary in extreme climates.
Incoterms Selection and Risk Management
Choose appropriate Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DAP) to clearly define responsibilities between buyer and seller. For wholesale transactions, DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) may increase seller liability but can be attractive to customers. FOB (Free on Board) is commonly used, placing responsibility on the buyer once goods are loaded at the port of origin. Clearly outline insurance coverage, customs clearance duties, and risk transfer points in contracts.
Customs Documentation and Tariff Classification
Accurate documentation is critical for customs clearance. Required documents include commercial invoices, packing lists, bill of lading/airway bill, Certificate of Origin, and product conformity certificates (e.g., IEC 61215). Solar modules are typically classified under HS Code 8541.40 in most countries. Be aware of anti-dumping duties, especially when sourcing from regions such as China, Southeast Asia, or Malaysia, where tariffs may apply due to trade regulations.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Ensure modules comply with environmental standards such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) in the EU. In the U.S., modules must meet EPA and OSHA safety guidelines. Include Safety Data Sheets (SDS) when required. Verify that packaging materials are recyclable and meet local environmental regulations in the destination country.
Product Certification and Market Access
Solar modules must be certified to meet regional performance and safety standards. Key certifications include IEC 61215 (performance), IEC 61730 (safety), UL 61730 (North America), and MCS (UK). Some markets, such as India (BIS certification) or Australia (CER approval), require mandatory local certification. Verify compliance before shipping to avoid customs delays or rejections.
Import Duties, Taxes, and Trade Agreements
Research applicable import duties, VAT, and Goods and Services Tax (GST) in the destination country. Leverage free trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, ASEAN, EU preferential tariffs) to reduce or eliminate tariffs when eligible. Maintain records of origin to claim preferential treatment. Monitor changes in trade policy, especially related to clean energy incentives or protectionist measures.
Supply Chain Visibility and Tracking
Implement real-time tracking systems (GPS, RFID) to monitor shipments and ensure transparency. Provide customers with tracking access and regular updates. Establish contingency plans for delays due to port congestion, weather, or geopolitical issues. Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with solar product logistics.
End-of-Life and Recycling Obligations
Understand extended producer responsibility (EPR) regulations in target markets. The EU’s WEEE Directive requires producers to manage recycling of end-of-life solar panels. Build relationships with certified recycling partners and communicate take-back programs to customers as part of compliance and corporate responsibility strategy.
Recordkeeping and Audit Preparedness
Maintain detailed records of all shipments, certifications, compliance documents, and communications for a minimum of 5–7 years, depending on jurisdiction. Conduct regular internal audits to ensure adherence to logistics and compliance protocols. Be prepared for customs audits or regulatory inspections by maintaining an organized digital document management system.
Conclusion: Sourcing Solar Modules Wholesale
Sourcing solar modules wholesale is a strategic approach for businesses aiming to scale operations, reduce costs, and meet growing demand in the renewable energy market. By purchasing in bulk, companies benefit from significant cost savings, improved profit margins, and greater control over supply chain logistics. However, successful wholesale procurement requires careful consideration of module quality, supplier reliability, certifications, and compliance with international standards such as IEC, UL, and ISO.
Key factors to prioritize include the efficiency and durability of solar panels, transparent pricing, warranty terms, and long-term support from manufacturers. Building relationships with reputable suppliers—whether directly from tier-1 manufacturers or trusted distributors—ensures consistent product quality and supply stability. Additionally, staying informed about emerging technologies, market trends, and regulatory changes enables better decision-making and competitive advantage.
In conclusion, wholesale sourcing of solar modules offers substantial benefits for installers, distributors, and project developers, provided it is approached with due diligence and a focus on quality and sustainability. A well-executed procurement strategy not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports the broader transition to clean, affordable, and reliable solar energy.