The global solar photovoltaic (PV) module market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by declining costs, supportive government policies, and increasing demand for clean energy. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global solar panel market size was valued at USD 137.6 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This sustained growth is fueled by rising energy demands, technological advancements in solar efficiency, and aggressive renewable energy targets set by countries across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe. As the transition to renewable energy accelerates, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as market leaders, commanding significant shares through scale, innovation, and global distribution networks. The following list highlights the top 10 solar module manufacturers based on annual shipment volumes, manufacturing capacity, and market presence in 2023–2024, reflecting their pivotal role in shaping the future of solar energy.
Top 10 Solar Module Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Boviet Solar
Domain Est. 2017
Website: bovietsolar.com
Key Highlights: Boviet Solar is a solar energy technology company specializing in manufacturing top-performing solar PV modules for solar projects….
#2 Solar panel manufacturer, trusted since 1996
Domain Est. 2004
Website: recgroup.com
Key Highlights: REC Group is a solar panel manufacturer, trusted for almost three decades. Since its founding in 1996, REC has been a true pioneer in the solar industry….
#3 Suniva
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 2007
Website: suniva.com
Key Highlights: Suniva is America’s oldest and largest monocrystalline solar cell manufacturer in North America. Suniva was founded in 2007….
#4 SEG Solar
Domain Est. 2012
Website: segsolar.com
Key Highlights: We are a Leading US Solar Module Manufacturer with A Fully Integrated Supply Chain. About us. 1GW+. Global Cumulative Module Shipments. 1GW. Global PV Module ……
#5 Illuminate USA
Domain Est. 2019
Website: illuminateusa.com
Key Highlights: Illuminate USA is the largest single-site solar panel manufacturer in North America, using advanced manufacturing to supply the American solar market….
#6 First Solar
Domain Est. 1999
#7 Solar Manufacturing Map
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: The US Solar Photovoltaic Manufacturing Map shows only active manufacturing sites that contribute to the solar photovoltaic supply chain….
#8 Canadian Solar
Domain Est. 2001
Website: canadiansolar.com
Key Highlights: COMPANY OVERVIEW. 170GW solar modules shipments. 15.7GWh battery storage shipments. Module capacity 51.8GW. Storage solution capacity 15GWh. Battery cell ……
#9 Solar for , Utility, and Commercial
Domain Est. 2004
Website: trinasolar.com
Key Highlights: Trina Solar is a world leader in solar energy innovation and reliability. Power your energy future with industry-leading solar panels and solutions….
#10 PowerFilm Solar
Domain Est. 2005
Website: powerfilmsolar.com
Key Highlights: PowerFilm designs and manufactures custom solar cells, panels, and power solutions for energy harvesting, portable, and remote power applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Module

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Solar Modules
The global solar module market in 2026 is poised for robust expansion, driven by accelerating clean energy transitions, supportive government policies, technological innovation, and declining costs. As nations intensify efforts to meet climate targets under frameworks such as the Paris Agreement and RE100 initiatives, solar energy continues to emerge as a cornerstone of decarbonization strategies. The following analysis outlines key trends shaping the solar module market in 2026:
-
Continued Cost Reductions and Economies of Scale
By 2026, solar module prices are expected to remain under pressure due to sustained manufacturing scale-up, particularly in China, Southeast Asia, and India. Average prices for crystalline silicon (c-Si) modules are projected to stabilize between $0.10 and $0.13 per watt, down from $0.15/W in 2023. Advances in manufacturing efficiency, reduced material waste, and automation are contributing to lower levelized costs of electricity (LCOE), making solar increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. -
Dominance of High-Efficiency Technologies
PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) technology remains widely deployed, but market leadership is shifting toward next-generation cells such as TOPCon (Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact), HJT (Heterojunction), and eventually IBC (Interdigitated Back Contact). In 2026, TOPCon modules are expected to capture over 40% of global market share due to their higher efficiency (24–25%), faster scalability, and compatibility with existing production lines. HJT adoption is growing steadily, especially in premium and distributed markets. -
Expansion of Bifacial and Large-Format Modules
Bifacial solar modules, which generate power from both sides, are becoming standard in utility-scale deployments. When combined with single-axis trackers and high albedo surfaces, bifacial gains of 5–20% improve project ROI. Furthermore, large-format wafers (182mm and 210mm) dominate new installations, enabling higher power outputs per module (600W+), reduced balance-of-system (BOS) costs, and optimized logistics. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Regionalization
Geopolitical tensions and trade barriers (e.g., UFLPA in the U.S.) are reshaping supply chains. In 2026, there is increased investment in solar manufacturing outside China, particularly in India (via PLI Scheme), the U.S. (Inflation Reduction Act incentives), and the EU (Net-Zero Industry Act). Vertical integration—from polysilicon to module assembly—is becoming a strategic priority to ensure supply security and compliance with local content requirements. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Pressures
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are influencing procurement decisions. Manufacturers are responding with lower-carbon production methods, such as using green electricity in manufacturing and reducing silver content in cells. Additionally, solar panel recycling is gaining traction, with EU and upcoming U.S. state regulations mandating end-of-life management, spurring innovation in module design for recyclability. -
Integration with Energy Storage and Smart Grids
The rise of hybrid solar-plus-storage projects is affecting module design and deployment strategies. In 2026, solar modules are increasingly being paired with lithium-ion and emerging storage technologies (e.g., flow batteries) to provide dispatchable renewable power. Smart inverters and module-level power electronics (MLPE) are becoming more common, enhancing system monitoring, safety, and grid compatibility. -
Growth in Distributed and Emerging Markets
While utility-scale solar continues to dominate capacity additions, distributed solar (residential and commercial) is growing rapidly in markets such as the U.S., Germany, Australia, Japan, and Brazil. Simultaneously, emerging economies in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are leveraging modular and off-grid solar solutions to expand energy access, supported by international development funding and innovative financing models. -
Policy-Driven Demand Surge
Ambitious national targets—such as China’s 1,200 GW wind and solar goal by 2030, India’s 500 GW non-fossil target by 2030, and the EU’s REPowerEU plan—are driving long-term demand visibility. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) continues to unlock domestic solar investments through tax credits (ITC at 30–40% with bonuses), further boosting module demand through 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the solar module market is characterized by technological sophistication, global diversification, and integration into broader energy systems. While price competition remains intense, differentiation through efficiency, reliability, sustainability, and compliance will define market leaders. With global annual solar installations projected to exceed 400 GW, the solar module sector is not only central to the energy transition but also a critical engine of industrial and economic transformation worldwide.
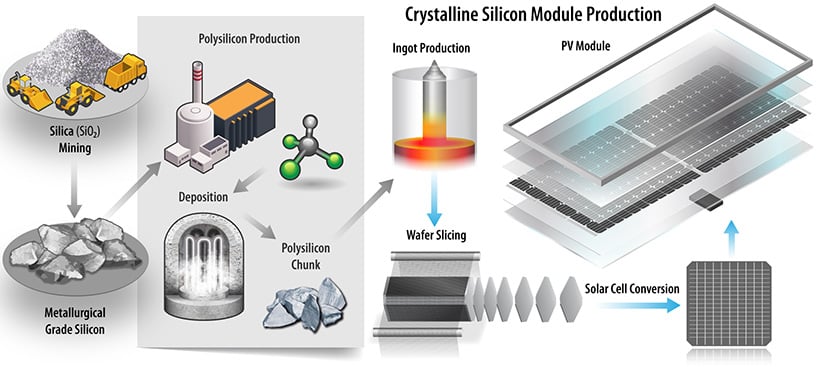
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Solar Modules: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing solar modules involves more than just securing a competitive price. Buyers often encounter significant challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks, which can undermine project performance, increase long-term costs, and expose companies to legal liabilities. Understanding these pitfalls is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Performance and Degradation Rates
One of the most common quality issues is receiving modules that underperform relative to their specified power output or degrade faster than stated. Some manufacturers may provide inaccurate or overly optimistic performance data, particularly in real-world conditions. Modules with higher-than-advertised degradation rates can significantly reduce energy yield over time, impacting project ROI.
2. Substandard Materials and Manufacturing Defects
Low-cost suppliers may cut corners by using inferior materials—such as low-grade encapsulants, subpar backsheets, or weak frame alloys—that compromise module durability. This can lead to premature failures like delamination, corrosion, hotspots, or junction box issues. Poor manufacturing processes, including inconsistent lamination or soldering, increase the risk of early field failures.
3. Inadequate or Misleading Certifications
While certifications like IEC 61215 (performance), IEC 61730 (safety), and UL listings are critical, some suppliers present outdated, fraudulent, or region-specific certifications as globally valid. Buyers may inadvertently source modules that lack proper third-party testing or that have been certified under less stringent standards.
4. Lack of Traceability and Batch Consistency
Without robust quality control systems, manufacturers may produce inconsistent batches, making it difficult to trace defects or ensure uniform performance across a project. This is particularly problematic in large-scale deployments where mismatched modules can reduce system efficiency.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Use of Counterfeit or Copycat Technology
Some suppliers, especially in less-regulated markets, produce modules that infringe on patented cell technologies (e.g., PERC, TOPCon, HJT) or design elements. Purchasing such modules exposes buyers to legal risks, potential shipment seizures, and reputational damage if involved in IP litigation.
2. Lack of IP Transparency from Suppliers
Many solar module manufacturers do not disclose the origin of their cell technology or whether licenses are held for proprietary designs. This opacity makes it difficult for buyers to verify if the modules they are sourcing are legally compliant, especially when importing into regions with strict IP enforcement like the U.S. or EU.
3. Exposure to Trade Sanctions and Forced Labor Allegations
Sourcing from manufacturers that use polysilicon or components from regions associated with forced labor (e.g., Xinjiang, China) can trigger customs detention under regulations like the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA) in the U.S. These supply chain risks are closely tied to IP and ethical sourcing, as companies may unknowingly support illegal or unethical practices.
4. Voided Warranties Due to IP Conflicts
If a module is found to violate IP rights, manufacturers may cease operations or retract warranties, leaving buyers without recourse for performance issues. Additionally, financiers and insurers may refuse to back projects involving high-risk IP exposure, undermining project viability.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough technical due diligence, including independent lab testing of sample modules.
– Require full traceability of components and verification of third-party certifications.
– Engage legal counsel to assess IP compliance and supply chain transparency.
– Prioritize suppliers with strong reputations, transparent manufacturing practices, and auditable supply chains.
– Include stringent quality clauses and IP indemnification in procurement contracts.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure reliable performance, regulatory compliance, and long-term success of their solar energy projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Modules
Overview
Solar modules, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are critical components in renewable energy systems. Due to their size, fragility, value, and international trade implications, proper logistics planning and compliance adherence are essential for efficient and legal transportation and deployment. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, compliant, and cost-effective movement of solar modules from manufacturer to end-user.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Solar modules are sensitive to mechanical stress, moisture, and temperature extremes. Proper packaging and handling are critical to prevent damage during transit.
– Standard Packaging: Modules should be packed in robust wooden or recyclable composite pallets with edge protection, anti-slip layers, and weather-resistant wrapping (e.g., plastic film or moisture barrier).
– Orientation: Always transport modules vertically (standing upright) unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer. Horizontal stacking increases breakage risk.
– Handling Instructions: Use forklifts or pallet jacks with care. Never lift modules by the frame alone. Follow manufacturer labels: “This Side Up,” “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack.”
– Environmental Protection: Protect from rain, snow, and prolonged exposure to UV light during storage and transit.
Transportation Modes & Best Practices
The choice of transportation depends on distance, volume, destination, and infrastructure.
– Road Freight (Truck): Most common for regional or domestic shipments. Secure loads with straps and corner protectors. Use enclosed trailers when possible to avoid weather exposure.
– Rail: Cost-effective and eco-friendly for long-distance land transport. Ensure compatibility with loading gauges and secure bracing.
– Sea Freight (Containerized): Standard for international shipments. Use dry van or flat rack containers. Avoid container condensation with desiccants or moisture barriers.
– Air Freight: Rare due to high cost and size constraints; used only for urgent, small-volume deliveries. Verify aircraft compatibility and weight limits.
International Trade Compliance
Solar modules are subject to various international regulations and trade policies.
– HS Code Classification: Use the correct Harmonized System (HS) code—typically 8541.40 for solar cells/modules. Accurate classification affects tariffs and customs clearance.
– Country-Specific Tariffs & Duties: Be aware of anti-dumping or countervailing duties (e.g., U.S. Section 201 tariffs, EU trade measures on Chinese modules). Verify origin rules and preferential trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP).
– Certificates of Origin: Required for duty exemptions under free trade agreements. Ensure proper documentation from the manufacturer.
– Customs Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/airway bill, and any required permits or licenses.
Regulatory & Safety Standards
Compliance with safety and performance standards is mandatory in most markets.
– IEC 61215 & IEC 61730: International standards for PV module design qualification and safety. Required for CE marking and many import approvals.
– UL 61730 & UL 1703 (North America): Safety certification by Underwriters Laboratories for U.S. and Canadian markets.
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Restriction of hazardous substances and chemical compliance. Ensure modules are lead-free or appropriately documented.
– WEEE Compliance: Producers may be responsible for end-of-life recycling. Check local producer responsibility schemes.
Import/Export Controls & Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation ensures smooth customs clearance.
– Export Declarations: Required in the country of origin. Include technical specifications, value, and end-use.
– Import Licenses: Some countries require specific permits for renewable energy equipment (e.g., India, Brazil).
– Product Registration: Markets like Australia (Clean Energy Council), Germany (VDE), and Japan (JET) may require pre-approval or listing.
– Labeling Requirements: Modules must bear permanent labels with manufacturer, model, electrical ratings, certification marks, and serial numbers.
Insurance & Risk Management
Solar modules are high-value cargo vulnerable to damage and theft.
– Marine Cargo Insurance: Covers loss or damage during transit (e.g., Institute Cargo Clauses A).
– All-Risk Coverage: Recommended for comprehensive protection, including handling and temporary storage.
– Proper Documentation: Maintain proof of condition at origin (pre-shipment inspection reports) to support claims.
Environmental & Sustainability Considerations
- Carbon Footprint Tracking: Measure and report emissions from transport (Scope 3) for ESG reporting.
- Sustainable Packaging: Use recyclable or reusable materials to reduce environmental impact.
- End-of-Life Planning: Design logistics for future module collection and recycling; comply with local take-back regulations.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for solar modules ensures timely delivery, reduces costs, and avoids legal or regulatory setbacks. By adhering to packaging best practices, understanding international trade rules, and maintaining certification standards, stakeholders can support the global expansion of solar energy in a responsible and efficient manner. Always consult local regulations and work with experienced freight forwarders and compliance experts familiar with the solar industry.
Conclusion: Sourcing Solar Module Suppliers
In conclusion, selecting the right solar module suppliers is a critical step in ensuring the long-term success, efficiency, and reliability of solar energy projects. A well-structured sourcing strategy should prioritize supplier credibility, product quality, performance warranties, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with international standards such as IEC and ISO certifications. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on manufacturing capacity, financial stability, after-sales support, and sustainability practices contributes to resilient supply chain management.
Diversifying the supplier base across different geographic regions can mitigate risks related to geopolitical instability, trade tariffs, and logistics disruptions. Technological advancements, including bifacial modules and half-cut cell designs, further emphasize the need to partner with forward-thinking manufacturers committed to innovation.
Ultimately, a thorough supplier assessment—supported by due diligence, performance tracking, and ongoing relationship management—leads to improved project outcomes, enhanced return on investment, and a stronger contribution to global renewable energy goals. By aligning supplier selection with strategic project requirements and sustainability objectives, stakeholders can build a robust foundation for scalable, reliable, and cost-efficient solar deployments.