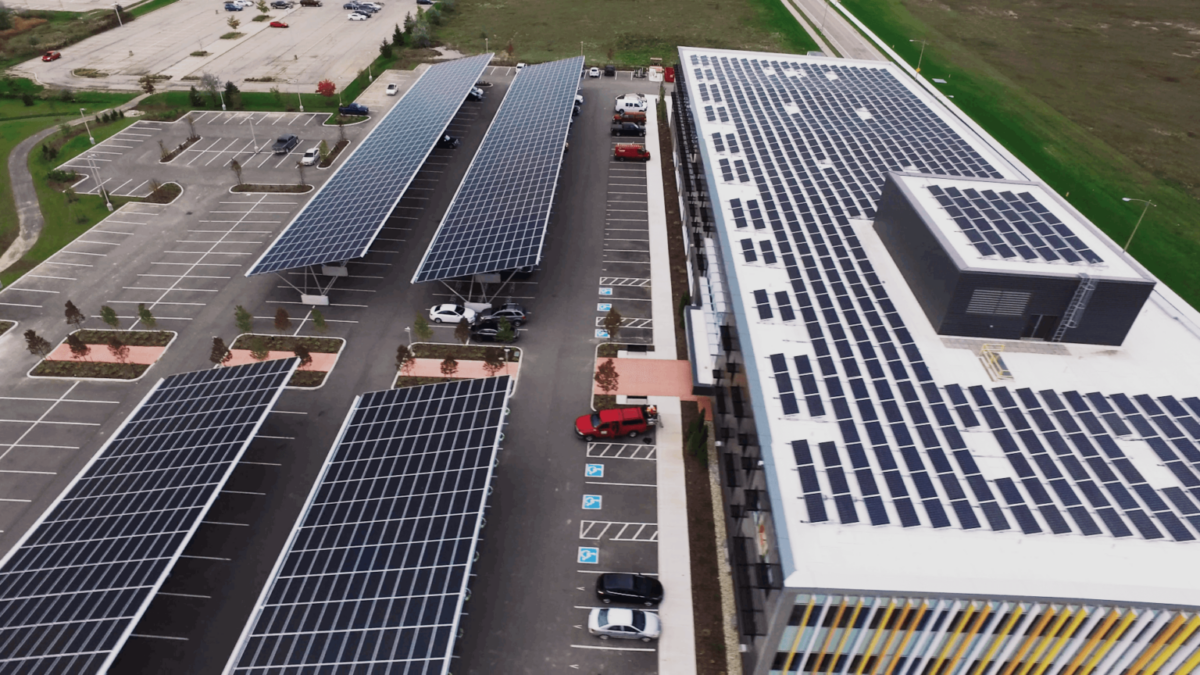
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) module market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by declining costs, supportive government policies, and increasing demand for clean energy. According to Mordor Intelligence, the solar module market was valued at USD 67.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6.5% from 2024 to 2029. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates the market size at USD 70.2 billion in 2023, with a CAGR of 6.7% during the same forecast period. This sustained growth is fueled by rising utility-scale installations, advancements in cell efficiency, and aggressive renewable energy targets across key regions such as Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe. As demand surges, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as market leaders, leveraging scale, innovation, and vertical integration to dominate global supply. The following analysis identifies the top 10 solar module manufacturers based on shipment volumes, technological capabilities, and market reach, offering a comprehensive view of the industry’s current leaders shaping the future of solar energy.
Top 10 Solar Module Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Boviet Solar
Domain Est. 2017
Website: bovietsolar.com
Key Highlights: Boviet Solar is a solar energy technology company specializing in manufacturing top-performing solar PV modules for solar projects….
#2 Solar panel manufacturer, trusted since 1996
Domain Est. 2004
Website: recgroup.com
Key Highlights: REC Group is a solar panel manufacturer, trusted for almost three decades. Since its founding in 1996, REC has been a true pioneer in the solar industry….
#3 Suniva
Domain Est. 2005 | Founded: 2007
Website: suniva.com
Key Highlights: Suniva is America’s oldest and largest monocrystalline solar cell manufacturer in North America. Suniva was founded in 2007….
#4 SEG Solar
Domain Est. 2012
Website: segsolar.com
Key Highlights: We are a Leading US Solar Module Manufacturer with A Fully Integrated Supply Chain. About us. 1GW+. Global Cumulative Module Shipments. 1GW. Global PV Module ……
#5 Illuminate USA
Domain Est. 2019
Website: illuminateusa.com
Key Highlights: Illuminate USA is the largest single-site solar panel manufacturer in North America, using advanced manufacturing to supply the American solar market….
#6 First Solar
Domain Est. 1999
#7 Solar Manufacturing Map
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: The US Solar Photovoltaic Manufacturing Map shows only active manufacturing sites that contribute to the solar photovoltaic supply chain….
#8 PowerFilm Solar
Domain Est. 2005
Website: powerfilmsolar.com
Key Highlights: PowerFilm designs and manufactures custom solar cells, panels, and power solutions for energy harvesting, portable, and remote power applications….
#9 Heliene
Domain Est. 2009
Website: heliene.com
Key Highlights: We manufacture high quality solar photovoltaic modules in our American facilities. The supply chains are short, and our modules are never held up in port or ……
#10 ENF List of Solar Companies and Products
Domain Est. 2009
Website: enfsolar.com
Key Highlights: “Welcome to ENF Solar. Our site features a company directory profiling 65,059 solar manufacturers, sellers and solar panel installers; and a product ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Module

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Solar Modules
The solar module market in 2026 is poised for transformative growth, driven by technological innovation, policy support, supply chain evolution, and increasing global demand for clean energy. As the world accelerates its transition toward net-zero emissions, solar photovoltaics (PV) remain at the forefront of renewable energy deployment. Below is an in-depth analysis of key trends shaping the solar module market in 2026:
1. Dominance of High-Efficiency Cell Technologies
By 2026, PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) technology, while still widely deployed, is being overtaken by next-generation cell architectures. TOPCon (Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact) and HJT (Heterojunction) modules are gaining significant market share due to their higher efficiency (24–26%) and better temperature coefficients. Additionally, IBC (Interdigitated Back Contact) and tandem cells—particularly perovskite-silicon tandem modules—are emerging in niche premium markets, with pilot production scaling up.
The shift toward high-efficiency modules is being accelerated by balance-of-system (BOS) cost savings and land-use optimization, especially in space-constrained or high-installation-cost regions.
2. Increased Adoption of Larger Wafer Formats
The industry standard has consolidated around 182mm (M10) and 210mm (G12) wafers. By 2026, the 210mm format is gaining dominance in utility-scale projects due to lower LCOE (Levelized Cost of Electricity), higher power output per module (exceeding 700W), and improved logistics efficiency. However, M10 remains strong in residential and commercial segments due to handling and racking compatibility.
Module manufacturers are increasingly standardizing on these larger formats, pushing older 166mm and smaller wafers into obsolescence.
3. Vertical Integration and Supply Chain Resilience
Leading manufacturers—especially in China—are deepening vertical integration, controlling polysilicon, ingot, wafer, cell, and module production. This trend enhances cost control and supply stability. However, geopolitical tensions and trade policies (e.g., U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act, EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) are pushing non-Chinese markets to build localized supply chains.
Countries like the U.S., India, and members of the EU are investing heavily in domestic solar manufacturing under initiatives such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and India’s Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. By 2026, these efforts are beginning to yield meaningful capacity, though China still accounts for over 80% of global module supply.
4. Sustainability and Transparency in Manufacturing
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are becoming critical in solar procurement. Buyers, especially in Europe and North America, are demanding low-carbon solar modules produced with renewable energy and transparent supply chains. Certification schemes like ECM (Environmental Certificate for Modules) and IEC 64086 are gaining traction.
Polysilicon production is shifting toward hydro-powered facilities in regions like Yunnan and Sichuan (China) or new green polysilicon plants in the Middle East and the U.S., reducing the carbon footprint of modules.
5. Bifacial Modules Gain Mainstream Adoption
Bifacial solar modules, which capture light from both sides, are now standard in utility-scale installations. With improved albedo modeling, racking solutions, and bankability, bifacial gains are now reliably factored into energy yield predictions. By 2026, over 60% of utility projects globally deploy bifacial modules, offering 5–15% energy gain depending on installation conditions.
6. Smart Modules and Digital Integration
The integration of module-level power electronics (MLPEs) such as DC optimizers and microinverters is rising, particularly in residential markets. Smart modules with embedded monitoring enhance performance tracking, fault detection, and safety (e.g., rapid shutdown compliance). IoT-enabled modules and AI-driven analytics are enabling predictive maintenance and improved O&M efficiency.
7. Global Demand Expansion and Regional Shifts
Global solar installations are projected to exceed 400 GW annually by 2026, with strong growth across multiple regions:
– China remains the largest market, driven by “dual carbon” goals and massive desert solar bases.
– United States sees sustained growth due to IRA incentives, with demand shifting toward domestically manufactured or assembled modules.
– India accelerates deployment under its 500 GW non-fossil target by 2030, with strong government tender activity.
– Europe continues steady growth, supported by REPowerEU and rooftop solar mandates.
– Emerging markets in Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Africa are scaling up with support from development banks and falling module prices.
8. Price Volatility and Market Consolidation
After the extreme price fluctuations in 2022–2023 due to supply chain bottlenecks and overcapacity, 2026 sees a more stabilized, albeit competitive, pricing environment. Average module prices hover around $0.10–0.13/W, driven by manufacturing overcapacity in China and aggressive pricing from Tier-1 suppliers.
This pressure is leading to industry consolidation, with weaker players exiting or being acquired. Innovation and cost efficiency are now key differentiators.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the solar module market is characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability demands, and global supply chain diversification. While China remains the manufacturing powerhouse, policy-driven localization efforts are reshaping trade flows. The convergence of higher efficiency, digitalization, and ESG compliance is redefining the value proposition of solar modules, positioning them as a cornerstone of the global clean energy transition.
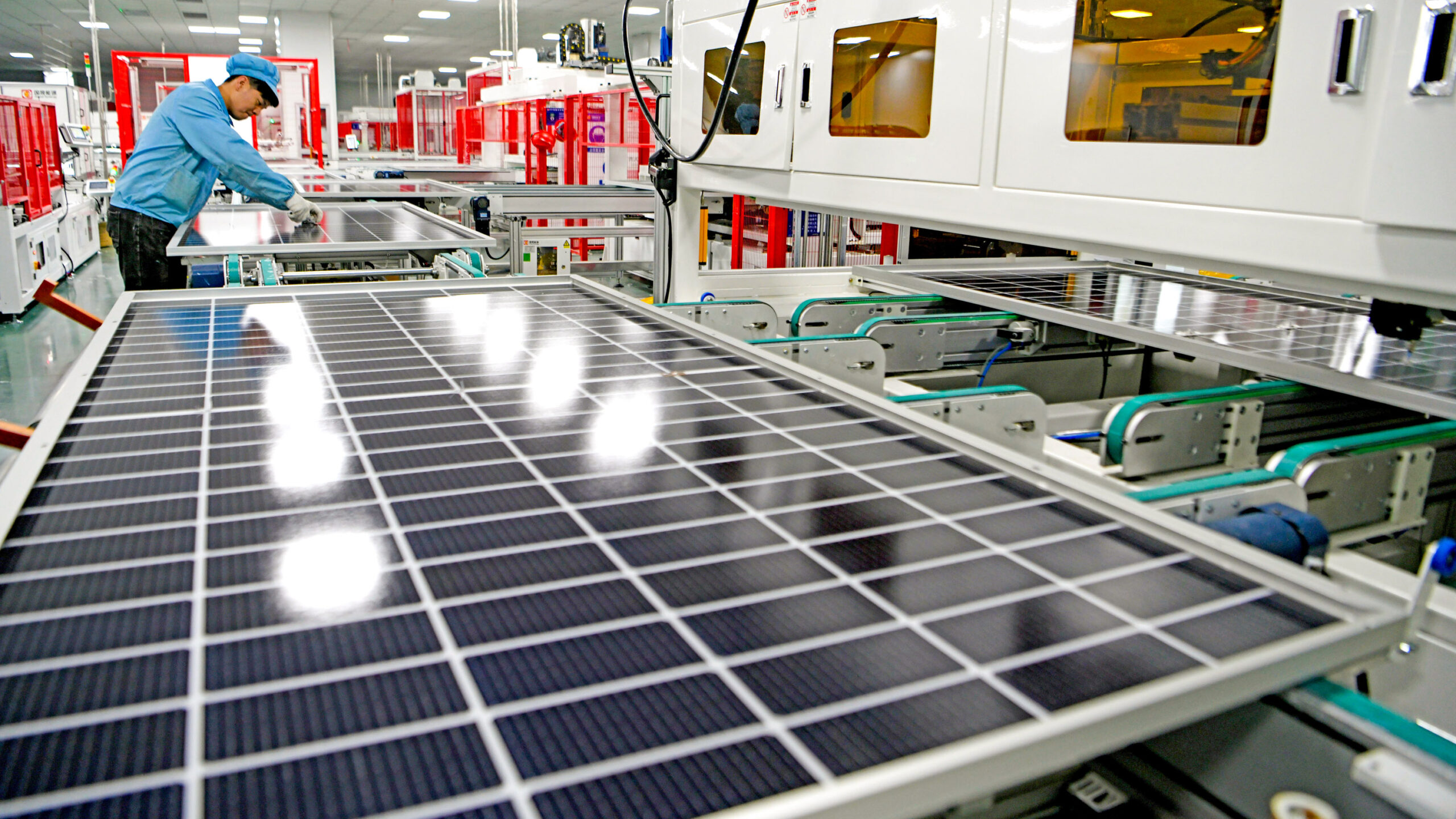

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solar Modules: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing solar modules involves critical considerations beyond price and availability. Overlooking quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to long-term financial losses, project delays, and reputational damage. Here are key pitfalls to avoid:
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Supplier Vetting
Relying solely on datasheets or certifications without verifying a manufacturer’s track record can lead to substandard products. Be cautious of suppliers with no proven history of bankable projects or inconsistent quality control processes. Always conduct on-site audits or third-party inspections before committing to large orders.
2. Counterfeit or Recycled Modules
Some suppliers may offer “brand-name” modules at suspiciously low prices, which could be counterfeit, recycled, or re-labeled. These modules often fail early and lack proper warranty support. Insist on original manufacturer documentation, batch traceability, and use anti-counterfeiting verification tools where possible.
3. Overreliance on Certifications Without Verification
While IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 certifications are essential, fraudulent or expired certificates exist. Verify certification status directly with the issuing body and request test reports from independent labs, especially for new or lesser-known manufacturers.
4. Insufficient Performance and Degradation Guarantees
Not all performance warranties are equal. Watch out for vague language or overly optimistic degradation rates (e.g., claiming less than 0.25% annual degradation without supporting data). Ensure the warranty is backed by a financially stable manufacturer and includes clear terms for claims and replacement.
5. Poor Workmanship and Hidden Defects
Microcracks, delamination, and poor soldering may not be visible during initial inspection but can cause early failure. Require extended stress testing (e.g., PID, thermal cycling) and consider engaging third-party quality assurance services during production.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Sourcing from Manufacturers with Dubious IP Practices
Some module producers use patented cell technologies (e.g., PERC, TOPCon, HJT) without proper licensing. Purchasing such modules exposes buyers to legal risk, including customs seizures or project shutdowns if IP infringement is discovered. Always verify that the supplier holds legitimate licenses for advanced technologies.
2. Lack of Transparency in Technology Origins
Suppliers may not disclose whether their modules use licensed or proprietary technology. Request documentation on technology partnerships and licensing agreements, especially when sourcing high-efficiency modules.
3. Warranty Voidance Due to IP Infringement
If a module is found to violate IP rights, the original technology owner may invalidate warranties or block replacement parts. This can leave project owners without support, even if the modules were purchased in good faith.
4. Supply Chain Contamination Risk
Modules incorporating IP-infringing components (e.g., cells or coatings) can taint the entire project. Conduct due diligence on the full supply chain, particularly for vertically integrated manufacturers, to ensure all components are legally sourced.
Mitigation Strategies
– Partner with reputable, bankable suppliers with transparent manufacturing and IP practices.
– Include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
– Perform technical and legal due diligence before finalizing suppliers.
– Use trusted procurement agents or consultants with industry expertise.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, solar developers and buyers can protect their investments, ensure long-term project performance, and avoid costly legal and operational complications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Modules
Overview
Solar modules are specialized, fragile, and internationally traded goods that require careful handling, precise documentation, and adherence to various regulations throughout the supply chain. This guide outlines key logistics and compliance considerations for the safe and legal transport of solar modules from manufacturer to end-user.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Solar modules must be packaged to withstand vibration, moisture, and impact during transit. Standard practices include:
– Use of robust wooden pallets or frames with corner protectors
– Waterproof wrapping (e.g., stretch film or moisture barrier bags)
– Secure strapping to prevent shifting
– Orientation labels (“This Side Up”) and fragile markings
– Protection against scratches and breakage with foam or cardboard interlayers
Handle modules vertically whenever possible and avoid stacking beyond recommended limits. Lift only by the pallet—never by the module frame alone.
Transportation Modes & Considerations
Choose transportation based on volume, distance, cost, and delivery timeline:
– Ocean Freight: Most common for international shipments; requires compliance with IMDG Code for hazardous components (e.g., lithium batteries in some storage-integrated modules)
– Air Freight: Faster but expensive; subject to IATA regulations if batteries are included
– Road & Rail: Ideal for regional distribution; ensure vehicles have adequate suspension and secure loading systems
Temperature and humidity controls may be necessary during extended transit to prevent condensation and degradation.
Import & Export Compliance
Ensure full compliance with national and international trade regulations:
– Obtain and verify accurate HS Codes (e.g., 8541.40 for photovoltaic modules)
– Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin
– Comply with Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) or equivalent security programs where applicable
– Confirm adherence to anti-dumping and countervailing duties, especially for modules from certain countries (e.g., China, Southeast Asia)
Check destination country requirements for solar imports, including trade remedy measures and local content rules.
Regulatory & Safety Standards
Solar modules must meet technical and safety standards in the target market:
– IEC 61215 (crystalline silicon performance), IEC 61646 (thin-film), and IEC 61730 (safety) are internationally recognized
– UL 61730 and UL 1703 required in the United States
– CE Marking required in the European Union under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) and Low Voltage Directive
– UKCA Marking for the UK market post-Brexit
Ensure test reports and certifications are current and issued by accredited bodies.
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
Many jurisdictions require compliance with environmental directives:
– RoHS (EU) and China RoHS: Restrict hazardous substances like lead, cadmium, and mercury
– REACH (EU): Requires declaration of substances of very high concern (SVHC)
– WEEE Directive (EU): Mandates end-of-life take-back and recycling programs
– Carbon footprint declarations may be required under green public procurement policies
Maintain documentation proving compliance and support product lifecycle responsibility.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain a complete and auditable trail:
– Module serial numbers and batch traceability
– Certificates of Conformity (CoC) and test reports
– Warranty and performance data sheets
– Bill of Materials (BOM) for regulatory audits
Digital tracking platforms (e.g., blockchain or ERP systems) enhance transparency and support compliance verification.
Risk Mitigation & Insurance
Solar modules are high-value and susceptible to damage. Mitigate risks by:
– Procuring all-risk cargo insurance covering breakage, water damage, and theft
– Conducting pre-shipment inspections
– Using logistics partners experienced in handling solar equipment
– Monitoring shipments via GPS and environmental sensors where feasible
Conclusion
Successful logistics and compliance for solar modules require coordination across technical, regulatory, and operational domains. By adhering to international standards, maintaining accurate documentation, and partnering with certified suppliers and carriers, stakeholders can ensure efficient, legal, and safe delivery of solar products worldwide.
Conclusion: Sourcing Solar Module Manufacturers
Sourcing solar module manufacturers is a strategic process that requires careful evaluation of multiple factors including product quality, technological efficiency, manufacturing capacity, financial stability, certifications, and geographic proximity. As the global demand for renewable energy continues to rise, selecting the right manufacturer is critical to ensuring reliable supply, long-term performance, and cost-effectiveness.
The ideal supplier should demonstrate compliance with international standards (such as IEC, UL, and ISO), possess strong R&D capabilities, and offer transparent supply chain practices. Additionally, considerations such as warranty terms, after-sales support, and sustainability practices are increasingly important in aligning with corporate social responsibility goals.
By conducting thorough due diligence, leveraging third-party audits, and building long-term partnerships, organizations can mitigate risks associated with quality inconsistencies, delays, and geopolitical uncertainties. Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy not only enhances project performance and ROI but also contributes to the scalability and sustainability of solar energy initiatives worldwide.
In conclusion, successful sourcing of solar module manufacturers goes beyond price comparison—it involves a holistic assessment of technical, operational, and ethical factors to ensure a resilient and future-ready solar supply chain.