The global solar container market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for modular, mobile, and rapidly deployable energy solutions. According to Grand View Research, the global containerized data center market—closely tied to energy infrastructure including solar—was valued at USD 9.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 10.8% from 2023 to 2030, with increasing adoption in remote and temporary power applications. Concurrently, Mordor Intelligence projects the solar energy market to grow at a CAGR of over 6% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by sustainability mandates, falling photovoltaic costs, and the scalability of containerized solar systems. As hybrid energy solutions gain traction across telecom, disaster relief, construction, and microgrid sectors, solar container manufacturers are emerging as pivotal enablers of decentralized power. In this evolving landscape, nine manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, reliability, and global deployment—setting the benchmark for efficiency and integration in containerized solar technology.
Top 9 Solar Container Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Canadian Solar
Domain Est. 2001
Website: canadiansolar.com
Key Highlights: Active buying customers in more than 160 countries. Subsidiaries in 23 countries & regions on 6 continents. Over 20 solar & energy storage manufacturing ……
#2 PowerFilm Solar
Domain Est. 2005
Website: powerfilmsolar.com
Key Highlights: PowerFilm designs and manufactures custom solar cells, panels, and power solutions for energy harvesting, portable, and remote power applications….
#3 Products, portable solar
Domain Est. 2016
Website: ecosuninnovations.com
Key Highlights: Fix-Watt® stationary solar container … The stationary solar solution for projects from 10 to 25 years. Degree of mobility. Ease of deployment….
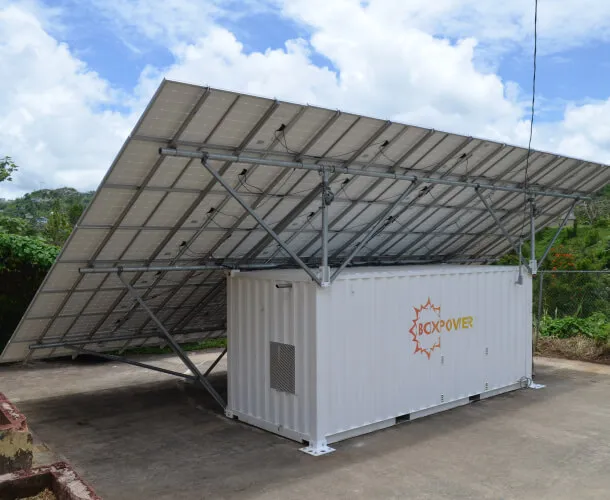
#4 BoxPower
Domain Est. 2017
Website: boxpower.io
Key Highlights: BoxPower offers turnkey solar microgrid solutions for off-grid and grid-tied applications. We specialize in project development, system design and engineering….
#5 About us
Domain Est. 2019
Website: solar-containers.com
Key Highlights: The container that supplies solar energy is a recycled container, transformed in France, at ERM Energies. Depending on the progress of the project, ……
#6 That’s us
Domain Est. 2023
Website: solarcontainer.one
Key Highlights: The foundation of the Joint venture SolarCont GmbH is sealed and the solar container matures into a marketable product….
#7 Mobile Solar Container: Green Energy Anywhere
Domain Est. 2023
Website: zn-meox.com
Key Highlights: MEOX Mobile solar container is CE-certified, IP65-rated, resistant to dust, water, Level 8 wind, and magnitude 8 earthquakes. Designed for 15+ years of service ……
#8 Solar Mobile Construction Container
Website: beloenergy.eu
Key Highlights: The BELO mobile construction container with photovoltaics is an excellent helper for both small and large construction sites. It offers an output starting ……
#9 Sesame Solar: Energy Resilient Off
Website: sesame.solar
Key Highlights: Sesame Solar is revolutionizing dual-use, self-generating off-grid power for defense and commercial applications. Powered by solar + hydrogen + battery storage….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Container

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Solar Containers
The global solar container market is poised for significant transformation and expansion by 2026, driven by the convergence of technological innovation, rising demand for mobile and off-grid energy solutions, and supportive government policies aimed at decarbonization. Solar containers—modular, transportable units integrating photovoltaic panels, battery storage, inverters, and control systems—offer scalable, plug-and-play renewable energy solutions across diverse sectors. The following trends are expected to shape the solar container market in 2026:
-
Accelerated Adoption in Off-Grid and Remote Applications
By 2026, solar containers are projected to see increased deployment in remote industrial sites, disaster relief operations, military installations, and rural electrification projects. Their portability and rapid deployment capability make them ideal for locations with limited or no grid infrastructure. Emerging economies in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America are expected to be key growth regions, supported by donor-funded energy access initiatives. -
Integration with Hybrid and Microgrid Systems
Solar containers are increasingly being combined with diesel generators, wind turbines, and hydrogen fuel cells to form hybrid energy systems. By 2026, intelligent energy management systems will allow seamless integration into microgrids, optimizing energy use and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This trend is particularly prominent in mining, construction, and telecom sectors requiring reliable off-grid power. -
Advancements in Battery Technology and Energy Density
The adoption of next-generation battery technologies—such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and emerging solid-state batteries—will enhance the efficiency, safety, and lifespan of solar containers. By 2026, improved energy density will allow for more compact designs with higher power output, reducing transportation costs and expanding deployment versatility. -
Growth in Temporary and Event-Based Power Solutions
The event management, film production, and emergency response sectors are increasingly utilizing solar containers as clean, quiet, and mobile power sources. By 2026, demand is expected to rise due to stricter emissions regulations in urban areas and heightened environmental awareness among event organizers. -
Standardization and Modular Scalability
The market will see greater standardization in design and component interoperability, enabling plug-and-play functionality and easier scaling. Companies are expected to offer modular systems that allow users to stack multiple containers for higher capacity, improving cost-efficiency and customization. -
Supportive Regulatory and Incentive Frameworks
National clean energy targets and carbon reduction mandates—such as the EU Green Deal and U.S. Inflation Reduction Act—are expected to drive public and private investment in mobile solar solutions. Tax credits, grants, and subsidies will lower the total cost of ownership, accelerating market penetration. -
Increased Focus on Digitalization and Remote Monitoring
By 2026, most solar containers will come equipped with IoT-enabled monitoring platforms, allowing real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and remote control via cloud-based dashboards. This digital integration improves operational efficiency and reduces downtime. -
Rise of Leasing and Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS) Models
To lower entry barriers, providers are expected to expand leasing and pay-per-use business models. EaaS offerings will allow customers to access solar container solutions without upfront capital expenditure, particularly appealing to SMEs and short-term projects. -
Sustainability and Circular Economy Considerations
Manufacturers will place greater emphasis on recyclability, sustainable materials, and end-of-life management. By 2026, certifications for low-carbon and circular design could become key differentiators in procurement decisions. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The market is expected to witness increased competition, with traditional solar companies, container manufacturers, and energy tech startups entering the space. Strategic partnerships and mergers may lead to consolidation, with a few dominant players offering integrated turnkey solutions.
In summary, by 2026, the solar container market will evolve into a mature, dynamic segment of the distributed energy ecosystem, characterized by technological sophistication, regulatory support, and expanding application diversity. The combination of mobility, scalability, and sustainability positions solar containers as a critical enabler of the global energy transition.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solar Containers (Quality, IP)
Sourcing solar containers—pre-fabricated, containerized solar power systems—offers convenience and rapid deployment, but it comes with significant risks if due diligence is not performed. Two major areas of concern are quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these can lead to project delays, safety hazards, financial losses, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Component Specifications
Many suppliers cut costs by using substandard solar panels, inverters, batteries, or racking systems. These components may have lower efficiency, shorter lifespans, or fail under extreme conditions. Buyers must verify that all components meet international standards (e.g., IEC, UL) and are from reputable manufacturers.
2. Poor Container Build and Integration
The container itself must be engineered to protect sensitive equipment from temperature extremes, moisture, dust, and corrosion. Common issues include insufficient insulation, poor ventilation, inadequate sealing, or improper mounting of internal components. This can lead to system failures and increased maintenance costs.
3. Lack of Third-Party Testing and Certification
Some vendors claim compliance without proper third-party validation. Always request test reports for thermal performance, structural integrity, and electrical safety (e.g., IP65 rating for dust and water resistance, CE, or UL certification). Absence of verifiable documentation is a red flag.
4. Inconsistent Manufacturing and Quality Control
Especially with offshore manufacturers, batch-to-batch inconsistencies can occur. Without on-site audits or consistent QC processes, delivered units may differ from prototypes or samples, potentially compromising performance and safety.
5. Insufficient Thermal and Climate Management
Solar containers generate heat and must operate in diverse climates. Poor thermal design—such as inadequate cooling or heating systems—can degrade battery life and electronics. Ensure the system includes active HVAC or passive cooling solutions suited to the deployment environment.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Components
Some suppliers integrate counterfeit or cloned inverters, controllers, or software to reduce costs. These may infringe on IP rights, leading to legal liability for the buyer. They also often lack support, firmware updates, and warranty coverage.
2. Proprietary Software and Locked Systems
Certain vendors use proprietary control software that restricts access, monitoring, or integration with third-party SCADA or energy management systems. This creates vendor lock-in and limits operational flexibility. Ensure contracts include rights to data access, API availability, and software licensing terms.
3. Unclear Ownership of Design and Customization
When customizing a solar container, the buyer may assume they own the design improvements. However, unless explicitly stated in the contract, the supplier may retain IP rights. This can prevent replication, resale, or modification of the design.
4. Risk of IP Infringement in Overall System Design
The integration of components and system architecture may inadvertently infringe on existing patents (e.g., in modular power conversion or thermal management). Buyers should require indemnification clauses in supply agreements to protect against IP litigation.
5. Lack of Documentation and Source Code Access
For maintenance and troubleshooting, access to technical drawings, wiring schematics, and source code (if applicable) is essential. Suppliers may withhold these under IP claims. Ensure contracts mandate full documentation delivery upon purchase.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct factory audits and request component datasheets.
- Require third-party certification reports.
- Include IP indemnification and documentation clauses in contracts.
- Use escrow agreements for critical software or firmware.
- Partner with reputable suppliers with verifiable track records.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough technical vetting and strong contractual safeguards to ensure both quality and IP integrity in solar container projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Containers
Overview of Solar Containers
Solar containers are repurposed shipping containers equipped with integrated solar power systems, designed for off-grid or mobile energy solutions. They typically include solar panels, battery storage, inverters, and control systems, all housed within a standard 20ft or 40ft container. Due to their modular nature, solar containers are used in remote power generation, disaster relief, construction sites, and temporary events. Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are critical to ensure safe transportation, installation, and operation.
Transportation & Handling
Solar containers must be transported in accordance with international shipping standards for heavy and specialized cargo. They are typically moved via flatbed trucks, rail, or maritime containerships. Securement during transit is essential to prevent shifting, damage to components, or safety hazards. Pre-shipment inspections should verify that all internal equipment is properly braced and that the container meets structural integrity standards. Use certified lifting points for crane operations, and avoid tilting beyond manufacturer-specified angles.
Weight & Dimension Considerations
Standard solar containers conform to ISO container dimensions (e.g., 20ft: 6.1m x 2.4m x 2.6m; 40ft: 12.2m x 2.4m x 2.6m), but their operational weight can exceed standard dry containers due to added equipment. Fully loaded solar containers may weigh 25,000–30,000 kg, requiring verification against road and port weight limits. Over-dimensional or overweight permits may be required for overland transport. Always confirm axle load distribution and center of gravity with the manufacturer.
International Shipping Requirements
For cross-border or overseas shipments, solar containers must comply with International Maritime Organization (IMO) and International Convention for Safe Containers (CSC) standards. The container must bear a valid CSC safety approval plate and be structurally certified for stacking and handling. Documentation should include a cargo manifest, bill of lading, and detailed equipment list. Hazardous materials, such as lithium-ion batteries, are subject to IMDG (International Maritime Dangerous Goods) Code regulations and may require special labeling, packaging, and declarations.
Electrical & Safety Compliance
Solar containers must meet regional electrical safety standards at the destination. In the U.S., compliance with National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 690 for solar installations is mandatory. In the EU, adherence to IEC 62109 and Low Voltage Directive (LVD) is required. All electrical systems should be installed and certified by licensed professionals. Grounding, arc fault protection, and emergency disconnects must be in place. Pre-shipment electrical inspections and certification (e.g., UL, CE, TÜV) are strongly recommended.
Import & Customs Regulations
Importing solar containers may trigger customs duties, value-added tax (VAT), or import restrictions depending on the destination country. Required documentation typically includes a commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and technical specifications. Some countries offer reduced tariffs for renewable energy equipment—verify eligibility under local green energy programs. Lithium-ion batteries may be subject to additional customs scrutiny or require special import permits.
Environmental & Site Compliance
Upon deployment, solar containers must comply with local environmental and zoning regulations. Noise levels, electromagnetic emissions, and visual impact may be regulated, especially in residential or protected areas. Stormwater runoff and potential chemical leaks (e.g., from batteries) must be managed per environmental protection standards. Obtain necessary permits for grid connection or fuel backup systems if applicable. Decommissioning plans should address responsible recycling of batteries and electronic components.
Operational & Maintenance Standards
Regular maintenance is essential for system longevity and safety. Follow manufacturer guidelines for inspecting solar panels, battery health, cooling systems, and structural integrity. Maintain accessible service logs and ensure on-site personnel are trained in emergency shutdown procedures. Remote monitoring systems should be implemented where possible to detect faults early. Update compliance documentation annually or after major system modifications.
Conclusion
Successfully deploying solar containers requires careful coordination across logistics, regulatory, and technical domains. Proactive planning for transportation, compliance, and site-specific requirements minimizes delays and ensures safe, efficient operation. Partnering with experienced solar integrators, freight forwarders, and local regulatory consultants is recommended to navigate complex international and environmental standards.
Conclusion for Sourcing Solar Containers
Sourcing solar containers presents a strategic and sustainable solution for scalable, mobile, and rapidly deployable energy systems. These integrated units combine solar power generation, energy storage, and control systems within a robust, transportable structure—making them ideal for remote operations, emergency response, off-grid communities, and temporary power needs.
The key advantages of sourcing solar containers include reduced installation time, enhanced durability, modular scalability, and lower long-term operational costs. Additionally, they support environmental sustainability goals by providing clean, renewable energy with minimal carbon footprint.
However, successful sourcing requires careful vendor evaluation, attention to specifications (such as power capacity, battery technology, and climate resilience), compliance with international standards, and consideration of after-sales support and maintenance. Partnering with experienced and certified suppliers ensures reliability, performance, and long-term return on investment.
In conclusion, solar containers are a forward-thinking energy solution that combines innovation, efficiency, and flexibility. With the right sourcing strategy, organizations can harness renewable energy effectively, improve energy access, and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.