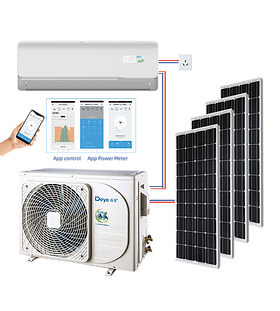
The global solar air conditioning market is gaining momentum as demand for energy-efficient and sustainable cooling solutions rises. According to Mordor Intelligence, the solar air conditioning market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 12.5% from 2024 to 2029, driven by increasing energy costs, supportive government policies, and advancements in photovoltaic (PV) and thermal solar technologies. As commercial and residential sectors prioritize decarbonization, solar-powered HVAC systems are emerging as a viable alternative to conventional cooling methods. This growth has catalyzed the expansion of a competitive supplier landscape, with leading manufacturers innovating in efficiency, integration, and scalability. Based on market presence, product performance, and technological advancement, the following nine companies stand out as top solar air conditioning supply manufacturers shaping the future of sustainable cooling.
Top 9 Solar Air Conditioning Supply Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Wholesale HVAC Equipment
Domain Est. 2014
Website: myiaire.com
Key Highlights: iAIRE, Inc. is a leading designer and manufacturer of HVAC, solar energy, and air purification products for commercial, industrial, and residential applications ……
#2 Solar Air Conditioner
Domain Est. 2019
Website: solar-air-conditioner.com
Key Highlights: SUPERGREEN TECH CO., LTD is a professional manufacturer of solar-powered home appliances including solar air conditioner,solar fan,solar freezers,solar fridge , ……
#3 Solarcraft Inc.
Domain Est. 1998
Website: solarcraft.net
Key Highlights: At Solarcraft, we design and build high-quality engineered systems and enclosures for powering, sheltering, and operating essential field-based automation….
#4 SUNRAIN: China Solar Water Heater
Domain Est. 2002
Website: en.sunrain.com
Key Highlights: SUNRAIN is a professional leader China solar water heater, heat pump, solar collector manufacturer with high quality and reasonable price….
#5 Solar Air Conditioner Heat Pump Manufacturer & Supplier
Domain Est. 2020
Website: solarker.com
Key Highlights: Solarker new energy is one of the Chinese main designer and manufacture of solar air conditioner and solar heat pump products.We focus on the research and ……
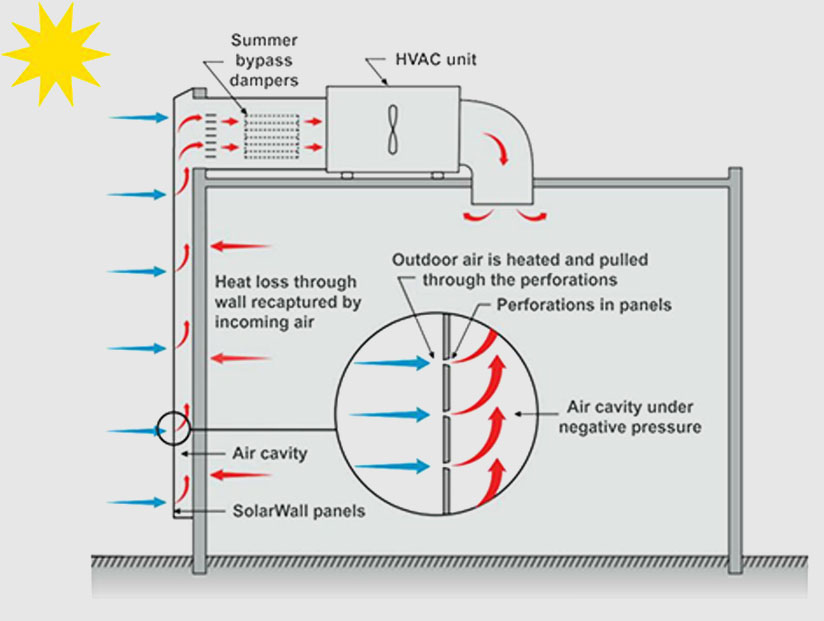
#6 SolarWall
Domain Est. 1997
Website: solarwall.com
Key Highlights: SolarWall® systems use solar energy to heat ventilation air, save money, and provide clean carbon-free heating to beautiful & energy-savvy buildings around ……
#7 Southwes Solar
Domain Est. 2002
Website: southwest-solar.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to Southwest Solar which is an innovative, 30 year old North American company specializing in solar powered ultra low energy evaporative cooling. We ……
#8 Solar Supply
Domain Est. 2003
Website: solarsupply.us
Key Highlights: Residential & Commercial HVAC ; locations. Located in Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas ; Products. Products for all your HVAC needs ……
#9 All Products
Domain Est. 2010
Expert Sourcing Insights for Solar Air Conditioning Supply
2026 Market Trends for Solar Air Conditioning Supply
The global solar air conditioning supply market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, supportive government policies, rising energy costs, and increasing environmental awareness. This analysis explores key trends shaping the supply landscape of solar air conditioning systems in the coming years.
Rising Global Demand for Energy-Efficient Cooling
As global temperatures rise and urbanization accelerates—particularly in hot and sunny regions—demand for cooling is growing rapidly. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), space cooling already accounts for nearly 20% of electricity use in buildings worldwide. By 2026, solar air conditioning is expected to capture a larger share of this demand, especially in emerging markets across Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Latin America. The integration of solar power into HVAC systems offers a sustainable solution to meet cooling needs without increasing carbon emissions.
Technological Advancements and Cost Reductions
By 2026, significant progress in photovoltaic (PV) efficiency and thermal solar technologies will enhance the performance and affordability of solar air conditioning systems. Innovations such as hybrid solar PV-thermal collectors, advanced inverters, and smart energy management systems will streamline integration with existing grid and off-grid infrastructure. Additionally, economies of scale in solar panel manufacturing and declining battery storage costs will make solar-powered AC systems more accessible, reducing reliance on traditional electricity and lowering lifecycle costs.
Supportive Government Policies and Incentives
Government initiatives are expected to play a pivotal role in expanding the solar air conditioning supply chain by 2026. Countries are increasingly adopting net-zero targets and renewable energy mandates, with specific incentives for solar HVAC installations. Examples include tax credits, rebates, feed-in tariffs, and net metering policies. In markets like India, the U.S., and the European Union, green building codes and energy efficiency standards will further boost demand for solar cooling solutions, encouraging manufacturers and suppliers to scale production.
Growth in Residential and Commercial Applications
The residential sector will remain a key driver of solar air conditioning adoption, particularly in regions with high cooling loads and abundant sunlight. Meanwhile, commercial applications—including offices, retail spaces, and hospitality—will increasingly incorporate solar AC systems to reduce operational costs and demonstrate environmental responsibility. By 2026, modular and scalable solar HVAC units tailored for different building types will become more prevalent, improving installation flexibility and market penetration.
Expansion of Supply Chain and Manufacturing Capacity
To meet rising demand, solar air conditioning suppliers are expected to expand manufacturing and distribution networks by 2026. Regions with strong solar industries—such as China, the U.S., and Germany—will lead in component production, while localized assembly hubs will emerge in high-growth markets. Strategic partnerships between solar panel manufacturers, HVAC companies, and energy storage providers will strengthen the supply ecosystem, enabling faster deployment and after-sales service.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite positive momentum, challenges remain. Intermittency of solar power, high upfront costs (despite long-term savings), and lack of consumer awareness may hinder adoption in some areas. However, these challenges present opportunities for innovation—such as better energy storage integration, leasing models, and public awareness campaigns. By 2026, digital platforms and IoT-enabled monitoring will further enhance system performance and user engagement.
Conclusion
By 2026, the solar air conditioning supply market will be shaped by strong demand, technological progress, and policy support. Suppliers who invest in innovation, scalability, and customer education will be best positioned to capitalize on this growing sector. As the world moves toward sustainable cooling solutions, solar air conditioning is set to become a mainstream component of the global energy transition.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Solar Air Conditioning Supply: Quality & Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing solar air conditioning systems presents unique challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to performance failures, financial losses, and legal complications. Below are the most common pitfalls in these two critical areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Component Performance
Many suppliers integrate solar photovoltaic (PV) panels with conventional air conditioning units without proper system-level optimization. Buyers often assume plug-and-play efficiency, but mismatched components—such as underperforming inverters or incorrectly sized compressors—can drastically reduce overall system efficiency and lifespan.
2. Lack of Certification and Testing Standards
A significant number of solar AC units, especially from emerging markets, lack third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, CE, UL, or local energy efficiency labels). Without verified testing under real-world conditions, systems may fail to deliver promised cooling capacity or solar utilization rates.
3. Poor Thermal and Electrical Integration
Solar air conditioners require seamless integration between solar energy capture and thermal cooling processes. Substandard designs may lack effective battery storage, charge controllers, or DC-optimized compressors, resulting in intermittent operation and reduced reliability during low-sunlight periods.
4. Use of Low-Grade Materials
To cut costs, some manufacturers use inferior materials in key components like copper tubing, refrigerant lines, and solar panel frames. This increases susceptibility to corrosion, leaks, and mechanical failure, especially in harsh climates.
5. Inadequate After-Sales Support and Warranty Enforcement
Even high-quality systems become liabilities if the supplier offers limited technical support or ambiguous warranty terms. Buyers may struggle to obtain replacement parts or qualified service technicians, particularly when sourcing from overseas vendors.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
1. Infringement of Patented Technologies
Solar air conditioning involves complex innovations in photovoltaic integration, DC-driven compressors, and smart energy management. Sourcing from manufacturers that use patented technologies without licensing exposes buyers to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement (e.g., the EU or U.S.).
2. Counterfeit or Clone Products
Some suppliers offer units that closely mimic branded, high-performance models but lack original engineering. These clones often copy design features protected by design patents or utility models, posing legal risks and typically delivering subpar performance and safety.
3. Ambiguous Ownership of Custom Solutions
When working with OEMs to develop customized solar AC systems, buyers may assume they own the resulting design or software. However, without clear contractual agreements, the manufacturer may retain IP rights, limiting the buyer’s ability to replicate, modify, or resell the product.
4. Exposure to Trade Secret Violations
Collaborating with suppliers may require sharing technical specifications or performance data. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and secure data handling protocols, there’s a risk of sensitive information being used by the supplier for competitive gain or leaked to third parties.
5. Import Restrictions Due to IP Disputes
Customs authorities in various countries can seize shipments suspected of IP infringement. Even if unintentional, sourcing a product that violates existing patents can lead to shipment delays, fines, or destruction of goods—particularly at major ports with active IP enforcement programs.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including site audits and reference checks.
– Require valid certifications and performance test reports under standardized conditions.
– Verify IP clearance through patent searches and legal consultations.
– Establish clear contracts defining IP ownership, warranty terms, and compliance obligations.
– Partner with reputable third-party inspection agencies for quality control during production.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns ensures reliable performance, legal safety, and long-term value in solar air conditioning investments.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Solar Air Conditioning Supply
Overview
This guide outlines the key logistics and compliance considerations for the supply, distribution, and installation of solar air conditioning systems. Proper planning in these areas ensures timely delivery, regulatory adherence, and customer satisfaction.
Product Classification & International Trade Regulations
Solar air conditioning units combine refrigeration, electrical, and photovoltaic technologies, requiring classification under multiple international codes. Use Harmonized System (HS) codes such as 8415 (air conditioning units), 8541 (solar panels), and 8504 (power inverters) for accurate customs declaration. Verify country-specific import regulations, including energy efficiency standards, environmental compliance, and certification requirements (e.g., CE, UKCA, or DOE ratings).
Shipping & Transportation Logistics
Solar air conditioning components are often heavy, bulky, and sensitive to environmental conditions. Use climate-controlled transport where necessary, especially for inverters and electronic controllers. Secure photovoltaic panels with edge protection to prevent micro-cracks. Coordinate multimodal shipping (road, sea, air) based on destination and urgency. Label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Protect from Moisture”) and provide detailed packing lists.
Storage & Inventory Management
Store components in dry, temperature-stable environments to prevent condensation and degradation. Keep solar panels horizontally stacked with protective spacers; avoid leaning. Refrigerant-containing units must be stored upright to prevent oil migration. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practices to minimize exposure to environmental stress and ensure warranty validity.
Regulatory Compliance & Certification
Ensure all products meet local and international standards:
– Electrical Safety: IEC 62109 (PV power converters), IEC 60335 (household HVAC safety)
– Energy Efficiency: ENERGY STAR (U.S.), MEPS (Australia), Ecodesign Directive (EU)
– Environmental: F-Gas Regulation (EU), Section 608 EPA certification (U.S. for refrigerant handling)
– Solar-Specific: UL 1703 (PV modules), IEC 61215 (crystalline silicon performance)
Provide documentation—including certificates of conformity, test reports, and installation manuals—with every shipment.
Installation & On-Site Compliance
Installation must comply with national electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the U.S., IEC 60364 internationally) and building regulations. Technicians must be certified in HVAC, electrical work, and solar PV installation. Refrigerant handling requires licensed personnel under local environmental laws. Submit post-installation documentation to authorities where required, such as grid interconnection approvals or building permits.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for traceability and compliance audits:
– Bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list
– Certificates of origin and conformity
– Warranty and service logs
– Proof of technician certifications
– Customs clearance documentation
Digital record systems with secure cloud backup are recommended.
Returns, Warranty & End-of-Life Management
Establish clear return authorization (RMA) procedures for defective or damaged goods. Track warranty claims and manage repairs or replacements efficiently. Comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives or equivalent for end-of-life product recycling. Partner with certified e-waste handlers for responsible disposal of solar panels, batteries, and HVAC units.
Risk Management & Insurance
Insure shipments against loss, damage, and delays. Coverage should include all transport legs and storage periods. Assess risks related to geopolitical issues, port congestion, and extreme weather. Develop contingency plans for supply chain disruptions, including alternative suppliers and routing options.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and strict compliance are critical for the successful supply of solar air conditioning systems. By adhering to international standards, maintaining accurate documentation, and training qualified personnel, suppliers can ensure safe, legal, and efficient delivery and installation worldwide.
In conclusion, sourcing solar air conditioning systems presents a strategic opportunity to achieve energy efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and lower long-term operational costs. By carefully evaluating suppliers based on product quality, system compatibility, certifications, technical support, and after-sales service, organizations can ensure reliable and sustainable cooling solutions. The integration of solar-powered HVAC systems not only supports corporate sustainability goals but also aligns with global efforts to transition toward renewable energy. As technology advances and economies of scale drive down costs, investing in solar air conditioning becomes increasingly viable across residential, commercial, and industrial applications. A well-structured sourcing strategy—emphasizing due diligence, lifecycle cost analysis, and partnerships with reputable manufacturers—will be key to maximizing performance, reliability, and return on investment in solar cooling solutions.